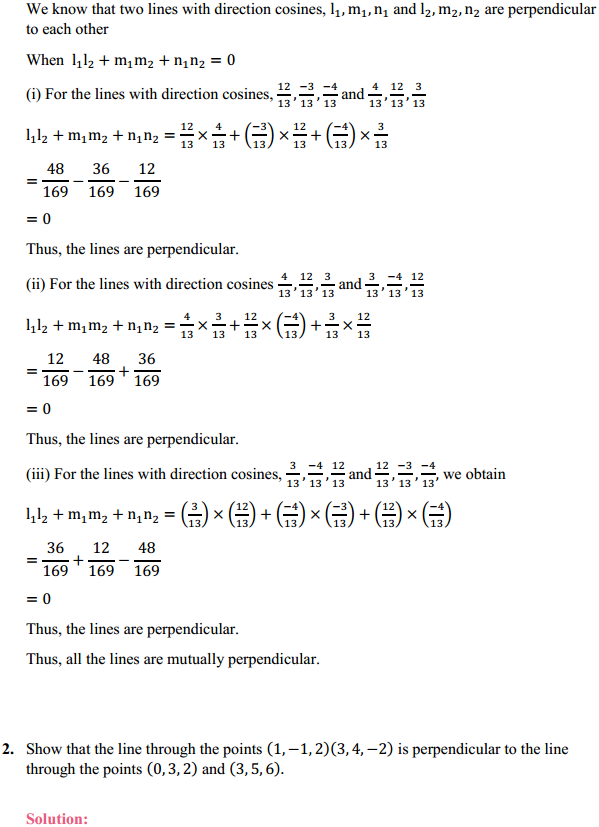
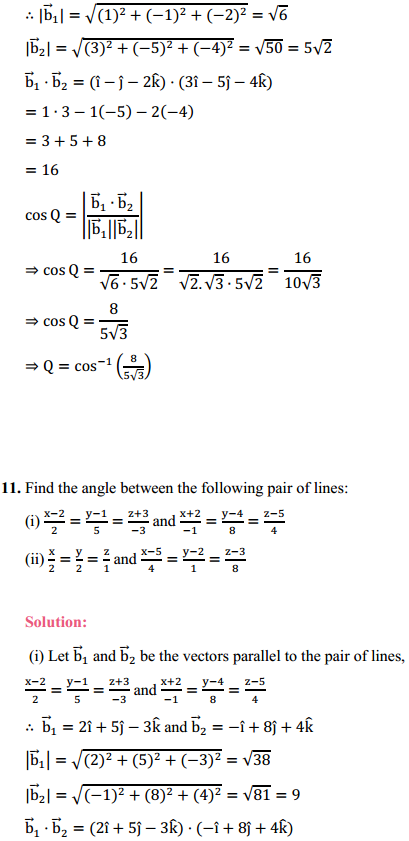
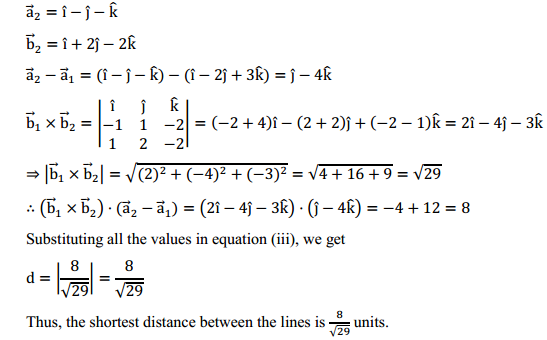
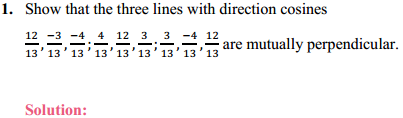NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 7 New Questions and Ideas are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 7 New Questions and Ideas.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Social Science History |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 |
| Chapter Name | New Questions and Ideas |
| Number of Questions Solved | 8 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 7 New Questions and Ideas
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES (Pages 73-74)
LET’S RECALL
Question 1.
Describe the ways in which the Buddha tried to spread his message to the people.
Answer:
Buddha tried to spread his message to the people in tire following ways:
- Buddhataughtinthelanguageofthepeople, Prakrit, so that everyone could understand his message.
- He spent his life traveling on foot, going from place to place, teaching people, till he passed away at Kumara.
- He’s also encouraged people to think for themselves, rather than to simply accept what he sends.
Question 2.
Write whether true or false:
- The Buddha encouraged animal sacrifices.
- Sarnath is important because it was the place where the Buddha taught for the first time.
- The Buddha taught that karma has no effect on our lives.
- The Buddha attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya.
- Upanishadic thinkers believed that the atman and brahman were ultimately one.
Answer:
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True.
Question 3.
What were the questions that Upanishadic thinkers wanted to answer?
Answer:
The questions which Upanishadic thinkers wanted to answer were:
- They wanted to know about life after death.
- They wanted to know why sacrifices should be performed.
- They believed that there was something permanent in the universe that would last even after death. They described this as ‘atman’ or individual soul.
- They believed that ultimately both the atman and the brahman were one.
Question 4.
What were the main teachings of the Mahavira? (Most Imp.)
Answer:
Mahavira taught a simple doctrine: men and women who wish to know the truth must leave their homes. Mahavira told them to follow ‘ahimsa’—not hurting any living being.
LET’S DISCUSS
Question 5.
Why do you think Anagha’s mother wanted her to know the story of the Buddha?
Answer:
Anagha’s mother wanted her to know about the story of Buddha because she was going on a school trip to Varanasi. Varanasi has many places like -Samath, -which are closely related to the life of Buddha. It would have enriched her knowledge about one of the greatest teachers and preachers of ancient times.
Question 6.
Do you think it would have been easy for slaves to join the sangha Give reasons for your answer?
Answer:
Slaves were allowed to join ‘sanghas’. Those who followed Buddhism did not believe in dividing the society and Buddha taught that all humans are equal.
LET’S DO
Question 7.
Make a list of at least five ideas and questions mentioned in this lesson. Choose three from the list and discuss why you think they are important even today.
Answer:
The five ideas are:
- Life is full of suffering.
- People should be kind to others and respect them all their lives.
- People were taught in their own language.
- Some people wanted to know about life after death.
- People should lead simple lives
Question 8.
Find out more about men and women who renounce the world today. Where do they live, what kinds of clothes do they wear, what do they eat? Why do they renounce the world?
Answer:
Mother Teresa was one such lady who gave up worldly pleasures and decided to serve humanity. She had become a nun at a very early age. The sufferings of the people, especially the people affected by leprosy, made her serve humanity. She started many homes, where the sick, old, and infants were looked after. She wore simple-clothes, a white cotton saree with a blue border, and ate the same food as others.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 7 New Questions and Ideas, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science History Chapter 7 New Questions and Ideas, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.