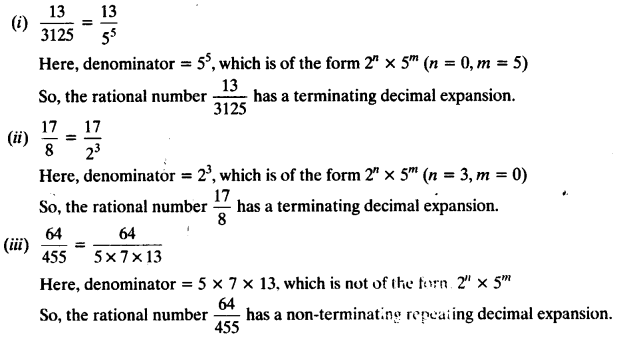
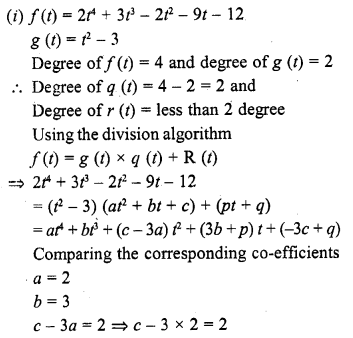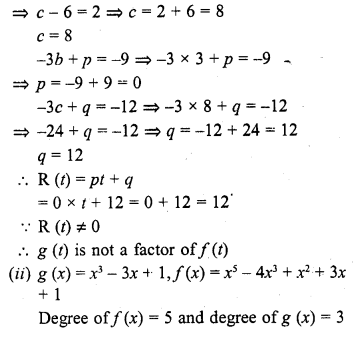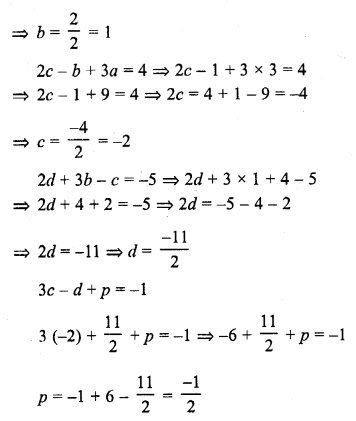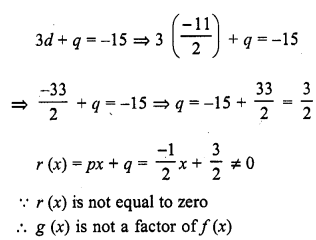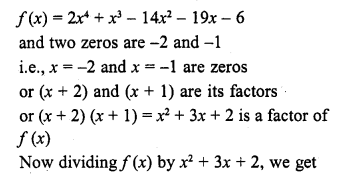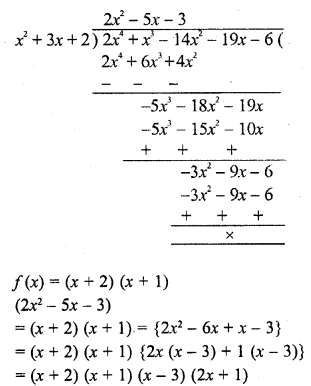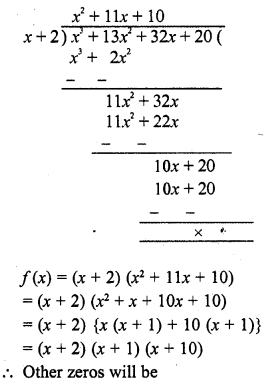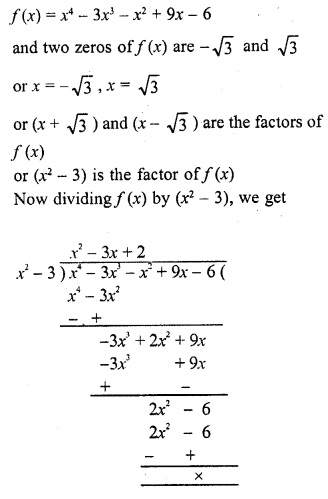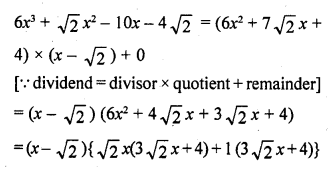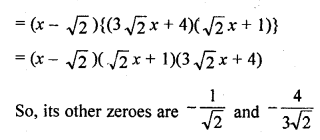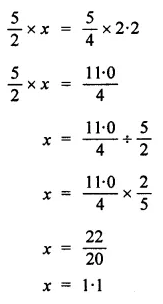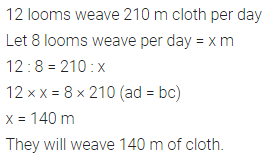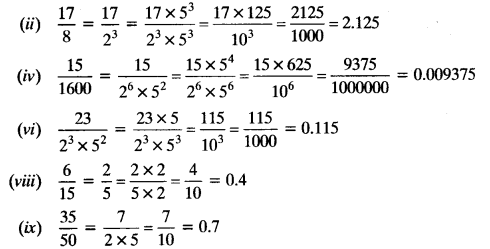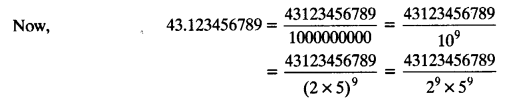Chapter 6 Life Processes Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks. This consists of 1 mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions and previous year questions from Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter.
Life Processes Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 6
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name the term for transport of food from leaves to other parts of plants.
Answer:
Translocation of food.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
Question 2.
What process in plants is known as transpiration ?
Answer:
It is loss of water in the vapour form from the exposed parts of a plant.
Question 3.
Name the tissue which transports soluble products of photosynthesis in a plant.
Answer:
Phloem.
Question 4.
Name the tissue which transports water and minerals in a plant.
Answer:
Xylem.
Question 5.
How do autotrophs obtain CO2 and N2 to make their food ?
Answer:
Autotrophs obtain CO2 from air and N2 as nitrate or ammonium ion from soil.
Question 6.
Which pancreatic enzyme is effective in digesting protein ?
Answer:
Trypsin.
Question 7.
Which enzyme present in saliva breaks down starch ?
Answer:
Ptyalin or salivary amylase.
Question 8.
What is the role of acid in our stomach ?
Answer:
HCl of gastric juice disinfects the food and acidifies it for proper functioning of proteolytic enzyme pepsin.
Question 9.
What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food ? (CBSE Delhi 2008, CCE 2014, 2016)
Answer:
Saliva moistens the ingested food with mucus, sterilises it with lysozyme and partially digests starch part of food into sugar with the help of salivary amylase or ptyalin.
Question 10.
State the function of digestive enzymes. (CBSE A.I. 2008 C)
Answer:
Digestive enzymes are hydrolytic enzymes which cause breakdown of complex and insoluble components of food into simple, soluble and absorbable substances.
Question 11.
Name the two ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms.
(CBSE A.I. 2008 C)
Answer:
- Aerobic respiration in which glucose is completely oxidised to carbon dioxide and water with the help of oxygen releasing 686 kcal of energy per mole.
- Anaerobic respiration in which glucose is incompletely broken down in the absence of oxygen to form generally either lactic acid or ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide releasing about 50 kcal of energy.
Question 12.
Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis ? (CBSE A.I. 2008 C, CCE 2015)
Answer:
- Carbon
- Water and Mineral Salts. From soil in terrestrial plants and liquid medium in aquatic habitat.
- Energy. Solar radiations.
Question 13.
Where does digestion of fat take place in our body ? (CBSE A.I. 2009)
Answer:
Digestion of fat occurs in first part (duodenum and jejunum) of small intestine with the help of enzyme lipase that acts on emulsified fat to form fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 14.
Mention how organisms like Bread Mould and Mushroom obtain their food. (CBSE Foreign 2010)
Answer:
They obtain their food saprophytically from external organic matter by dissolving the same with the help of digestive enzymes.
Question 15.
Name the component of blood that helps in the formation of blood clot in the event of a cut.
(CBSE Foreign 2010)
Answer:
Blood platelets which release thromboplastin on rupturing.
Question 16.
State one difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
(CBSE A.I. 2010, CCE 2012)
Answer:
In autotrophic nutrition, the food is self manufactured while it is obtained ready-made from outside in heterotrophic nutrition.
Question 17.
Name the process in plants where water is lost as water vapour. (CBSE A.I. 2010)
Answer:
Transpiration.
Question 18.
What is translocation in plants ? (CBSE A.I. 2010)
Answer:
Translocation is passage of food materials in solution form in plants from the region of their supply or manufacture to the region of their use or storage.
Question 19.
State basic difference in the processes of respiration and photosynthesis. (CBSE Foreign 2010)
Answer:
Respiration is a catabolic process in which glucose is broken down to release energy while photosynthesis is an anabolic process in which glucose and other organic substances are manufactured from raw materials with help of solar radiations.
Question 20.
Name the intermediate and the end products of glucose breakdown in aerobic respiration.
(CBSE Foreign 2010)
Answer:
Intermediate: Pyruvic acid (+ Energy)
End Products: CO2 + H2O (+ Energy)
Question 21.
What is the purpose of sending blood to the kidney for filtration ?
Answer:
For removal of nitrogenous wastes, excess salts and some toxins.
Question 22.
Name the stored food of animals. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Glycogen and fat.
Question 23.
How does transport of water occur at night in the absence of transpiration ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Due to root pressure and partly to meet daytime water deficit of aerial parts.
Question 24.
Name the component of food not digested in stomach. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Starch and other carbohydrates.
Question 25.
State the purpose of making urine. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Extract the soluble waste products from the blood for expulsion out of the body.
Question 26.
Mention the site of complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in humans. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Small intestine.
Question 27.
Ventricles have thicker muscular walls than atria. ,Give reason. (CCE 2014, 2016)
Answer:
Ventricles have to pump blood forcefully so as to reach even distant capillaries, right ventricle into lungs and left ventricle to all the remaining body parts, while atria are to pump blood into adjacent ventricles.
Question 28.
How do plant cells change their shape ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Due to osmotic entry or exit of water and differential thickening, eg., guard cells.
Question 29.
Name two enzymes present in pancreatic juice. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Trypsin, pancreatic amylase, pancreatic lipase.
Question 30.
State the function of alveoli in the lungs. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Exchange of gases (CO2 and O2) between blood and air.
Question 31.
Name the form in which energy derived from food is stored in humans. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Glycogen (and fat).
Question 32.
When we breathe out, the air passage does not collapse. Why ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Due to the presence of rings (c-shaped) of cartilage.
Question 33.
Name the process used by single celled organism for taking in food, exchange of gases or removal of wastes.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
Diffusion.
Question 34.
Identify the category in which organisms using carbon dioxide and water as food are placed. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Autotrophs/photoautotrophs.
Question 35.
Even when we are not doing any apparent activity, we need energy. Justify giving reason. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
A lot of metabolic activity is continuously occurring even when we are not doing any work, e.g., heart beat, breathing, digestion, absorption, blood circulation, etc. All of them require energy.
Question 36.
Name the components of blood which transport
- Food, carbon dioxide and nitrogenous wastes
- Oxygen. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
- Blood Plasma. Food, CO2 and nitrogenous wastes.
- Erythrocytes (Haemoglobin). Oxygen.
Question 37.
Rings of cartilage are present in trachea. Why ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
To prevent the collapse of air passage after expiration.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
(a) Name two different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms.
(b) Write any two differences between the two ways of oxidation of glucose in organisms.
(CBSE A.I. 2008, CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Aerobic and anaerobic.
(b) Differences
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| 1. Oxygen. There is complete breakdown of respiratory substrate with the help of oxygen, the products being CO2 and H2O.
2. Energy. It forms 38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. |
There is incomplete breakdown of respiratory substrate due to non-use of oxygen with atleast one product being organic.
It forms only two ATP molecules per glucose molecule. |
Question 2.
What is the function of trachea ? Why do the walls not collapse even when there is less air in it ?
(CCE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
Trachea is a tube that connects pharynx with lungs for carrying air to and from lungs. Trachea is lined by ciliated mucus secreting pseudostratified epithelium for trapping dust particles and microbes.
Trachea does not collapse in reduced air pressure due to support of C-shaped cartilaginous rings.
Question 3.
Name any two digestive enzymes secreted in the human digestive system and write their function.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
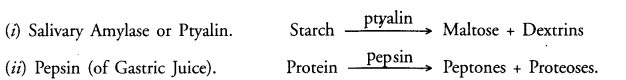
Question 4.
How do they take up carbon dioxide and perform photosynthesis ? (CCE 2010, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is absorbed during night when stomata are open. It is fixed in malic acid from which the same is released during day time for performing Calvin cycle in light.
Question 5.
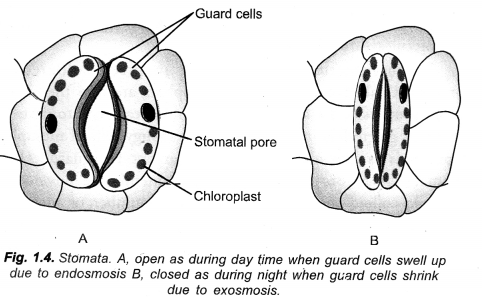
(a) What will happen to guard cells and the stomatal pore when water flows into guard cells.
(b) How do plants transmit information from cell to cell ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Guard cells swell up and a stomatal pore is created in between them.
(b) Information is transmitted from one plant cell to another through plasmodesmata and hormones.
Question 6.
What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms ?
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
(i) Aerobic. C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy
(it) Anaerobic,
(a) C6H12O6 —> 2 Ethanol + 2 CO2 + Energy.
(b) C6H12O6 —> 2 Lactic acid + Energy
Question 7.
What is excretion ? How do unicellular organisms remove their wastes ? (CCE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
Excretion is the biological process of removal of harmful metabolic waste products from the body.
In unicellular organisms, excretion occurs through simple diffusion from the surface.
Question 8.
What is internal energy reserve in plants ? Do the animals have the same energy reserve ? Justify your answer.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
The major internal energy reserve in plants is starch (a complex carbohydrate). Animals do not have the same energy reserve. Instead, they possess glycogen (and fat).
Question 9.
Explain the significance of peristaltic movement that occurs all along the gut during digestion.
(CCE. 2010, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Peristaltic movement or peristalsis is a wave of alternate contraction and expansion that passes through the gut from oesophagus to large intestine. It moves the food forward in a regulated manner along the digestive tract for processing in each part properly.
Question 10.
Major amount of water is selectively reabsorbed by the tubular part of nephron in humans. What are the factors on which the amount of water reabsorbed depends ? (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- Amount of excess water present.
- Amount of dissolved wastes to be excreted.
Question 11.
Name two digestive glands associated with digestive system in humans. Name their secretions. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
1. Salivary glands — saliva.
2. Pancreas — pancreatic juice.
Question 12.
Which mechanism plays an important role in transportation of water in plants
(a) During daytime
(b) At night ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Transpiration pull
(b) Water deficit of daytime and afterwards root pressure.
Question 13.
Give reasons for the following :
(a) Why is diffusion not sufficient to meet oxygen requirement of all the cells in multicellular organisms ?
(b) How desert plants perform photosynthesis if their stomata remain closed during the day ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) All living cells are not in direct contact with environment. Diffusion is a slow process and it will take very long time, days and months, to reach every living cell inside the body of a multicellular organisms.
(b) Carbon dioxide is absorbed during night when stomata are open. It is fixed in malic acid from which the same is released during day time for performing Calvin cycle in light.
Question 14.
What is translocation ? How does it take place in plants ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Translocation is the transport of nutrients/food in solution form inside phloem from the region of photosynthesis (or storage) to the area of consumption. For translocation, food molecules or nutrients enter phloem actively, develop an osmotic pressure and pass to the area of utilisation in a mass flow where active withdrawal occurs.
Question 15.
State two differences between arteries and veins. (CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
| Artery | Vein |
| 1. Direction of Flow. It carries blood from heart to an organ. | It brings blood from an organ towards the heart. |
| 2. Speed. Blood flow is rapid in artery. | Blood flow is slow in vein. |
| 3. Jerks. Blood flows with jerks. | Blood flows smoothly. |
| 4. Pressure. Blood flows under pressure | There is little pressure. |
| 5. Internal Valves. They are absent. | Internal valves are present to prevent back flow. |
| 6. Wall. It is thick and elastic. | It is comparatively thinner and little elastic. |
| 7. Lumen. Narrow. | Wide. |
| 8. Type of Blood. Artery carries oxygenated blood except pulmonary arteries. | Vein carries deoxygenated blood except pulmonary veins. |
| 9. Occurrence. It is deep seated. | It is superficial. |
| 10. Collapsibility. Artery is not collapsible. | Vein is collapsible. |
| 11. Blood After Death. It does not contain blood after death. | Vein is full of blood even after death. |
Question 16.
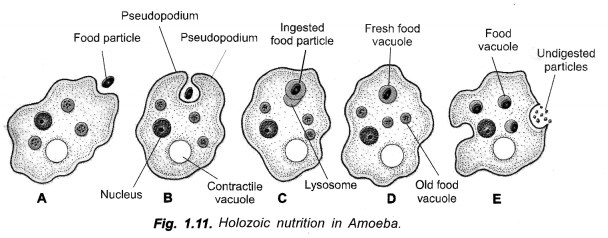
Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Amoeba ingests food particles with the help of its pseudopodia. The ingested food particle or phagosome fuses with lysosome to form food vacuole. The digested food passes out of the vacuole into cytoplasm. The undigested matter is thrown out. Fig. 1.11 B and E, if possible.
Question 17.
Explain parasitic mode of nutrition with two examples. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Parasitic mode of nutrition is a mode of nutrition where one living being (parasite) obtains food from another living being (host) of different species.
Examples. Ascaris (in human intestine), Cuscuta (on other plants).
Question 18.
Leakage of blood from vessels reduces the efficiency of pumping system. How is leakage prevented ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Blood contains blood platelets. In the region of leakage, the platelets burst and release thromboplastin. It helps in coagulation of blood and seal the place of leakage or injury.
Question 19.
Draw a labelled diagram to show nutrition in Amoeba. Give one more example of unicellular organism.
(CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Fig. 1.11 B and E.
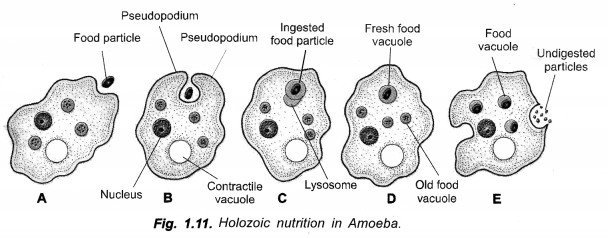
Other Example. Paramoecium.
Question 20.
Leaves of a healthy potted plant were coated with vaseline. Will this plant remain healthy for long ? Give reasons for your answer. (CCE 2011, 2015)
Answer:
The plant will not remain healthy for long. Vaseline covers the cuticle and blocks the stomata.
As a result
- It is unable to obtain oxygen from air for respiration,
- It is unable to perform photosynthesis as no carbon dioxide diffuses from air.
- In the absence of transpiration, the leaves get heated up and injured.
Question 21.
How is the process of transpiration useful to plant ? (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- It helps in upward transport of sap (water and minerals)
- Transpiration cools down the sun-exposed leaves and concentrates the minerals present in the rising water.
Question 22.
Mention the two main components of the transport system in plants.
State one function of each one of these components. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Transport system of plants consists of two main components, xylem and phloem. Xylem (through vessels and tracheids) takes part in conduction of sap mostly in the upward direction. Phloem (through sieve tubes) transports food marterials both in upward and downward directions.
Question 23.
State the function of guard cells. What will happen to guard cells and stomatal pore when water flows to guard cells. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Function of Guard cells : Opening, closing and regulating the stomata or stomatal pores.
Flow of Water : Passage of water into guard cells will make them turgid. The turgid guard cells bend is such a way as to open the stomatal pore.
Question 24.
Give reason :
(i) Fine hair and mucus are present in the nasal passage.
(ii) Rings of cartilage are present in the throat. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(i) They trap fine dust particles and microbes from inhaled air.
(ii) They prevent collapsing of trachea when air pressure is low.
Question 25.
Tooth enamel is the hardest substance in our body. Name the compound of which it is made up of. At what pH of the mouth it gets corroded ? State the role of bacteria present in the mouth. Suggest a method to prevent tooth decay. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Enamel is chemically hydroxyapetite (= calcium phosphate, 95%) alongwith proteins emamelins (5%). It gets corroded in acidic pH. The acid is produced by bacterium Streptococcus mutans that forms plaques over teeth if the teeth are not regularly cleaned as after meals.
Question 26.
Mention the site of complete digestion in our body. Name the end products formed on complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Site: Small intestine.
End Products:
Carbohydrates. Glucose.
Proteins. Amino acids.
Fats. Fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 27.
(i) Write the balanced chemical equation for the process of photosynthesis.
(ii) When do desert plants take up CO2 and perform photosynthesis ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
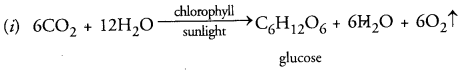
(ii) Carbon dioxide is absorbed during night when stomata are open. It is fixed in malic acid from which the same is released during day time for performing Calvin cycle in light.
Question 28.
(i) Why are cramps caused in our muscles during sudden activity ?
(ii) Name the type of respiration that takes place in Yeast during fermentation. (CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
(i) Cramps develop in muscles during excessive activity due to formation and accumulation of lactic acid as a result of lesser oxygen availability than required by muscles.
(ii) Anaerobic respiration.
Question 29.
In an experiment to prepare temporary mount of leaf peel, staining of leaf peel is done before putting a drop of glycerine. Explain why ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Staining is required for clearer observation as it brings about differentiation of cells and cellular components.
As extra stain has to be removed, staining is carried out before mounting.
Question 30.
In the experiment to prepare temporary mount of leaf peel, which stain is preferred and how is extra stain on the slide removed. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Stain Preferred . Safranin. Removal of Extra Stain. By blotting/filter paper.
Question 31.
Explain why only turgid leaf is selected for the preparation of temporary mount of a leaf peel. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- The peel can be removed easily,
- Peel can be spread easily.
- The cells are of normal shape and structure.
Question 32.
In an experiment to prepare temporary stained mount of a leaf epidermal peel, how can extra stain be removed ? What possible outcome would be observed if it is removed with cotton wool ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Extra stain is removed with the help of blotting paper. Cotton wool is not used as it has a tendency to spread the stain.
Question 33.
David observed temporary mount of leaf peel under the high power of microscope. He found two types of nucleated cells. Name the cells observed by him. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Epidermal cells, guard cells (of stomata).
Question 34.
You have been provided with a freshly plucked leaf of Rhoeo or Lilly. What will you do to obtain a transparent leaf peel? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Twist and tear the leaf obliquely with a jerk. A small transparent peel will be observed. The same is cut and placed in a drop of water or watch glass having water. In Rhoeo, it is the lower side which gives a good peel. Q. 35. In an experiment to prepare temporary mount of a leaf peel to show its stomata Ram was provided with a monocot leaf whereas Shyam, a dicot leaf.
Question 35.
Mention the ideal location where you would expect them to obtain the leaf peel for the experiment. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Middle of the leaf. It is twisted and torn with a jerk. In dicot leaf, stomata occur mostly on the lower surface while in monocot leaf both the surfaces possess stomata.
Question 36.
Mention the shape of guard cells and write its constituents. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
In dicots the guard cells are bean-shaped in outline. They are two in number and joined at the ends with thick walls towards each other and thin walls towards outside. Each guard cell contains a single nucleus and a number of chlroplasts.
Question 37.
State any two functions of the cells that surround the stomata. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Functions of Guard Cells :
- Opening and closing of stomata.
- Allowing exchange of gases and transpiration.
Question 38.
Explain why leaf is preferred for preparation of temporary mount to show stomata. State two functions of stomata. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Leaf is the plant organ where maximum number of stomata are present.
Functions :
- Absorption of CO2
- Release of O2 during day time.
- Seat of maximum transpiration.
Question 39.
Mention the materials required to prepare a temporary mount of leaf peel to show stomata. (CCE 2015)
Answer:”
Apparatus: A small potted plant, a small pot of the same size and same amount of soil as that of potted plant, a stick of the height of the plant, plastic sheets.
Observation: The internal surface of the plastic sheet belonging to the set having potted plant becomes wet. There is no such change in the second set.
Question 40.
Suresh prepared a list of materials required to prepare a temporary mount of leaf peel to show stomata but his list is not complete. Name any four materials which are not included in his list.
Leaf, petridish, coverslip, needle, forceps, brush, watch glass, safranin, microscope. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Water, blotting paper, dilute glycerine, slide.
Question 41.
Name the observed parts of a temporary mount of a leaf peel when it is focussed under :
(a) Low power
(b) High power of a compound microscope. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Low Power : Leaf epidermal cells and a few stomata, each with two minute greenish guard cells.
(b) High Power : A stomate surrounded by colourless epidermal cells. The stomate has two bean-shaped guard cells with thicker inner walls, a number of chloroplasts and one nucleus in each.
Question 42.
Draw a labelled diagram of cross-section of a leaf. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
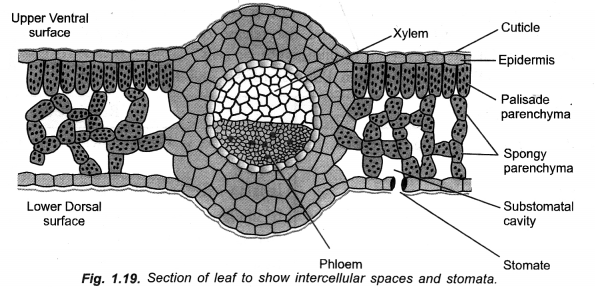
Question 43.
(i) Name any two substances that are selectively reabsorbed as the urine flows along the tube.
(ii) Name the part of the excretory system in which urine is stored for some time. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(i) Glucose, amino acids.
(ii) Urinary bladder.
Question 44.
Name two enzymes secreted by pancreas. Write the function performed by these two. (CCE 2015)
Answer:

Question 45.
Give reason –
(i) The two ventricles have thicker muscular walls than the two atria in human heart.
(ii) The capillaries have walls which are one-celled thick. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(i) Atria are to receive blood from veins and pump the same into adjacent ventricles only. They have, therefore, thin walls. Ventricles are to pump blood into arteries forcefully as it is to be sent to lungs (right ventricle) and all parts of the body (left ventricle). Therefore, walls of ventricles are thick and muscular with those of left ventricle being thicker.
(ii) Capillaries take part in exchange of materials (nutrients, wastes, gases) between blood and tissue fluid.
Question 46.
Name the cells that control the opening and closing of stomatal pore. Flow do they perform this function ?
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
Guard cells: Opening and closing of stomata is regulated by gain or loss of turgidity of their guard cells. During opening of stomata, guard cells withdraw K+ ions from surrounding epidermal cells, followed by absorption of water from them. As a result, guard cells swell up and become turgid. Their outer thin and elastic walls bend outwardly followed by outward movement of thicker inner walls. The latter creates a pore in between the two guard cells.
During closure movement of stomata, guard cells send out K+ ions. Water also passes out. Guard cells become flaccid. Their inner thick walls come to touch each other. The stomatal pore gets closed.
Question 47.
(i) Name two organisms that obtain food through parasitic nutritive strategy,
(ii) How do fungi obtain their food ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(i) Parasitic Nutrition. Cuscuta (a plant), Plasmodium (Malarial Parasite).
(ii) Most of the fungi are saprotrophs. They obtain their nourishment from organic matter.
Question 48.
Saprotrophs pour digestive enzymes over the organic matter in order to dissolve it. The dissolved ingredients are absorbed. David observed a temporary mount of a leaf under high power of microscope. He found two types of nucle¬ated cells. Name the cells observed by him. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Epidermal cells, pairs of guard cells forming stomata.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
Question 1.
When is blood clotting useful ? In a flow chart illustrate the four major events involved in blood clotting.
(CBSE Delhi 2006)
Answer:
Usefulness of Blood Clotting.
(i) “Plugging the place of injury.
(ii) Stoppage of blood flow from the region of injured blood vessel.
Events in Blood Clotting:
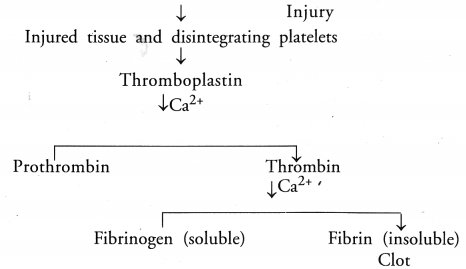
Question 2.
Give reasons for the following :
(i) Glottis is covered by epiglottis
(ii) Lung alveoli are covered with blood capillaries
(iii) The wall of trachea is supported by cartilage rings. (CBSE A.I. 2006, CCE 2012)
Answer:
(i) Epiglottis. To prevent entry of food and water during swallowing.
(ii) Lung Alveoli. Lung alveoli constitute the respiratory surface of the lungs. Their walls have rich supply of blood for gaseous exchange, i.e. passage of oxygen from alveolar air to blood and passage of carbon dioxide from blood to alveolar air.
(iii) Tracheal Rings (C-shaped). For providing support, preventing collapse of trachea and allowing for uninterrupted flow of air.
Question 3.
(a) What do you mean by double circulation of blood ? (CBSE A.I. 2007, Delhi 2008 C,CCE 2011, 2012)
(b) Why is it necessary ? (CBSE Delhi 2008 C)
Answer:
(a) Double circulation is the passage of same blood twice through heart, first from right side to lungs and back to left side for passage to rest of the body to be returned to right side. It consists of two components, pulmonary circulation (from heart to lungs and back) and systemic circulation (from heart to different parts of body and back). In pulmonary circulation deoxygenated blood is converted into oxygenated blood. In systemic circulation oxygenated blood is supplied to all parts of the body. It gets changed into deoxygenated form.
(b) Importance. Double circulation ensures supply of oxygenated blood to all body parts for efficient release of energy to ensure higher physical activity and thermoregulation of body. It also provides for direct passage of all deoxygenated blood to lungs for oxygenation.
Question 4.
What are stomata ? Draw labelled diagram of stomata. Write any two functions of stomata.
(CBSE Foreign 2008, CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Stomata. They are pores regualted by two chloroplast containing guard cells that occur in the epidermis of leaves and young stems for exchange of gases and transpiration.
(b) Diagram.
(c) Functions of Stomata,
- Exchange of gases,
- Transpiration.
Question 5.
(a) Name the process by which autotrophs prepare their own food.
(b) List three events which occur during this process. (CCE 2012)
(c) State two sources from which plants obtain nitrogen for synthesis of proteins and other compounds.
(CBSE Foreign 2008)
Answer:
(a) Process. Photosynthesis.
(b) Events,
- Photolysis of water.
- Production of assimitory power as ATP and NADPH2.
- Reduction of CO2.
(c) Sources of Nitrogen,
- Nitrate from soil,
- Ammonium ion from soil.
Question 6.
What are final products produced after digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats ? (CCE 2010, 2011, 2013) \
Answer:
Carbohydrates. Glucose.
Proteins. Amino acids.
Fats. Fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 7.
When a sportsman runs, he gets muscle cramps. Why ?
Or
Lack of oxygen in muscles often leads to cramps among cricketers. Explain. Why ? (CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
Cramp is an involuntary contraction of an already contracted muscle. It occurs due to accumulation of lactic acid during anaerobic breakdown of glucose when oxygen supply is unable to match the requirement. Lactic acid acts on neuromuscular junction producing fatigue and cramps.
Question 8.
The pH of the mouth of a person is lower than 5.5. What changes will occur in his mouth ? How can these changes be controlled ? Write any two measures. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) pH of the mouth becomes lower than 5.5, despite regular secretion of near neutral saliva, due to presence » of decaying food and bacteria present therein.
(b) Enamel of teeth being made of hydroxyapedte (calcium phosphate) undergoes corrosion in acidic medium. This starts tooth decay.
(c)
- Routinely cleaning the mouth after meals,
- Brushing the teeth with tooth paste which is generally alkaline.
Question 9.
(a) “Breathing cycle is rhythmic whereas exchange of gases is a continuous process”. Justify this statement.
(b) What happens if conducting tubes of circulatory system develops a leak ? State in brief how could this be avoided ?
(c) How opening and closing of stomata take place ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Even after forceful exhalation, a large quantity’of air called residual volume is left in the lungs. It is helpful in continuous exchange of gases.
(b) Leakage will result in loss of blood from circulatory system, loss of efficiency of pumping system and non-supply of fresh blood to many organs. It results in death. To avoid it, blood platelets release thromboplastin in the region of leakage. It helps in sealing the place of injury through clotting of blood.
(c) Opening and closing of stomata take place by gain and loss of turgidity in the guard cells.
Question 10.
Assume you are a veterinary doctor and you had removed a good length of small intestine of a bear that was suffering from an intestinal tumour. Now, would you suggest a plant based or a meat based diet for the bear after its recovery ? Give reason for your suggestion.
Answer:
Meat based. A nonvegetarian diet requires a shorter alimentary canal while a vegetarian diet requires a longer alimentary canal for complete digestion.
Question 11.
In the human alimentary canal, name the site of complete digestion of various components of food. Explain the process of digestion. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Site of Complete Digestion. Small intestine.
Digestion. It is the conversion of complex insoluble food ingredients into simple absorbable form. Digestion is essential as complex components of food cannot pass into body cells for nourishment. Digestion occurs with the help of digestive enzymes. In simple holozoic animals, it is intracellular. In higher animals digestion is performed in a digestive tract and is, therefore, intercellular or extracellular. The digested materials are absorbed, transported and picked up by individual cells of the body for assimilation.
Question 12.
List three kinds of blood vessels of human circulatory system and write their functions in a tabular form.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Capillaries, arteries and veins.
- Capillaries,
- Exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid,
- Filtering out tissue fluid and diapedesis
- Arteries,
- Quick passage of blood from heart to different parts of body,
- Supply of oxygenated blood to all body parts except lungs
- Passage of deoxygenated blood to lungs for oxygenation.
- Collection and transport of deoxygenated from all body parts and passage to heart.
- Transport of oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium.
Question 13.
Name three different glands associated with the digestive system in humans. Also name their secretion.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Salivary Glands: They are three pairs, a pair each of parotid, submaxillary and sublingual. Secretion is called saliva. It contains antimicrobial lysozyme and digestive enzyme ptyalin or salivary amylase.
- Liver: It secretion is called bile. Bile takes part in alkalisation of food and emulsification of fat.
- Pancreas: It secretion is called pancreatic juice. It contains proteolytic enzyme trypsin (secreted as trypsinogen), pancreatic lipase (steapsin) and pancreatic amylase (amylopsin).
Question 14.
List in tubular form three differences between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
(CCE 2012, 2014)
Answer:
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| 1.Oxygen: There is complete breakdown of respiratory substrate with the help of oxygen, the products being CO2 and H2O.
2. Energy: It forms 38 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. |
There is incomplete breakdown of respiratory substrate due to non-use of oxygen with atleast one product being organic.
It forms only two ATP molecules per glucose molecule. |
Question 15.
With the help of a schematic flow chart, show the breakdown of glucose in a cell to provide energy :
- In the presence of oxygen
- In the absence of oxygen
- When there is lack of oxygen. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
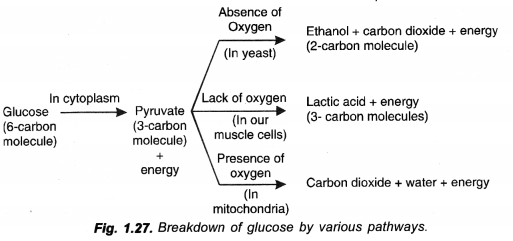
Question 16.
(a) Name the respiratory pigment in human beings and state the cell in which it is present.
(b) A product is formed is our muscles due to breakdown of glucose when there is lack of oxygen. Name the product and also mention the effect of build up of this product.
(c) Differentiate between fermentation in Yeast and aerobic respiration on the basis of end products formed.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
- Respiratory Pigment. Haemoglobin
- Cell. Red blood corpuscles or erythrocytes.
(b)
- Product. Lactic acid
- Effect. Fatigue and cramps.
(c) In yeast, fermentation produces alcohol and CO2 while aerobic respiration forms only CO2 and water.
Question 17.
Mention the role of following in digestion : (CCE 2012, 2013, 2015)
- Pepsin
- Saliva
- Villi
- Bile Juice.
Answer:
- Pepsin: Breakdown of proteins into pepteoses and proteoses in acidic medium.
- Saliva: Moistening of food, partial breakdown of starch and glycogen to form maltose by means of enzyme ptyalin (salivary amylase).
- Villi: Their bases bear intestinal glands that secrete intestinal juice for completion of digestion. Villi take part in absorption of digested food.
- Bile Juice – Juice released by liver is bile.
Functions
- Neutralising acidity of chyme,
- Making food alkaline for action of pancreatic enzymes,
- Emulsification of fat.
Question 18.
List the role of each of the following in our digestive system :
(a) Muscles of stomach wall
(b) Hydrochloric acid
(c) Mucus. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Muscles of Stomach. They bring about churning movement that breaks food into small particles and mixes it with gastric juice.
(b) Hydrochloric Acid. It is gastric secretion which softens, sterilises and acidifies the food for action of enzyme pepsin.
(c) Mucus. It lubricates the food passing through alimentary canal and protects the wall of digestive tract from digestive enzymes.
Question 19.
(a) Why is transpiration important for plants ?
(b) Why plants generally wilt in the afternoon and regain their freshness in the next morning ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Importance
- Cooling: Evaporation of water from the aerial parts results in lowering of their temperature which will otherwise rise due to exposure to sun.
- Concentration of Mineral:. Transpiration helps in increasing concentration of minerals present in rising water.
- Transport: It creates a pull that helps in transport of water and minerals.
(b) Excessive transpiration and comparatively less water absorption from soil during hotter parts of day creates a water deficit in the leaf cells resulting in their loss of turgidity. As a result plants show wilting. There is little transpiration during evening and night while absorption and ascent of sap continue. As a result leaf cells become turgid and the plant regains its freshness in the morning.
Question 20.
(a) In which form, nitrogen is taken by plants ?
(b) What type of nutrition is present in Bread Mould ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Nitrate, nitrite, ammonium ions and some organic compounds elaborated by bacteria.
(b) Bread Mould (Rhizopus) is a fungus that undertakes saprophytic type of heterotrophic nutrition. Its rhizoidal hyphae are fixed in medium having organic food/organic remains. They secrete digestive enzymes into the medium. The enzymes cause breakdown of complex compounds into simple and soluble substances. The fungus absorbs the same.
Question 21.
(a) Match the key words with their definition :
(i) Excretion
(ii) Elimination
(A) Is the removal of faeces (B) Applies to metabolic waste products that cross a plasma membrane.
(b) Name various excretory organs in vertebrates. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a)
(i) — B,
(ii) — A.
(b) Kidneys. Some accessory excretory organs of vertetrates are skin, lungs, liver and large intestine.
Question 22.
(a) Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of large multicellular organisms like humans ?
(b) What type of arrangement exists in the bodies of large animals to meet their oxygen requirement adequately ?
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Every living cell requires oxygen for performing cellular respiration. In unicellular organisms (e.g., Amoeba), the single cell is in direct contact with environment. Oxygen passes into it through diffusion. In simple multicellular organisms (e.g., Hydra), every cell may also get oxygen through diffusion from environment. This is not possible in complex multicellular organisms like humans. The body is covered by dead cells. The living cells are not in contact with external environment. Air containing intercellular spaces are absent. Therefore, quick diffusion cannot occur. Cell to cell diffusion is a very slow process. Passage of oxygen from lungs to toes through cell to cell diffusion will take about three years. Therefore, diffusion cannot meet the oxygen requirement of multicellular organisms like humans.
(b) Large animals have a respiratory system for meeting their oxygen requirement,
- There is a large moist permeable membrane over a respiratory area for quick exchange of gases,
- The respiratory surface has abundant blood supply for bringing in CO2 and taking away O2.
- There is a mechanism for quick movement of fresh air over the respiratory surface and rapid disposal of foul air.
Question 23.
(a) Mohan’s friend was seriously injured and lost a lot of blood. He was advised blood transfusion immediately. But because of the rare blood group, it was not available. Immediately Mohan and his friends made efforts for the announcement to be made on TV and Radio. Soon they got many people to help them and a life was saved,
(a) What is the composition of blood ?
(b) How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in our body ?
(c) What values are being displayed by Mohan and his friends ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Composition of Blood,
- Plasma (55% of blood, 92% water, 8% solutes),
- Red blood corpuscles (erythrocytes),
- White blood corpuscles (leucocytes),
- Blood platelets.
(b) Transport of O2 and CO2 – The two are transported by blood. Oxygen is picked up by blood from respiratory surface (97% as oxyhaemoglobin and 3% dissolved in plasma). In body tissues, oxygen separates from blood and passes into cells through tissue fluid. In return, blood picks up CO2 from cells (70% as bicarbonates, 7% as carbonic acid and 23% as carbaminohaemoglobin) for disposal over the respiratory surface.
(c) Values Shown by Mohan and His Friends,
- Comradeship
- Social awakening and social service
- Management skills.
Question 24.
(a) List the functions of juice released by the liver.
(b) Pancreas acts both as endocrine and exocrine gland. Justify giving reasons. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Juice released by liver is bile.
Functions
- Neutralising acidity of chyme,
- Making food alkaline for action of pancreatic enzymes,
- Emulsification of fat.
(b) Pancreas is heterocrine gland having both exocrine and endocrine regions. Exocrine regions produce pancreatic juice while endocrine regions secrete hormones like insulin and glucagon.
Question 25.
“About 180 litre of filtrate is produced each day but only 1.5 litre of urine is excreted out.” Justify this statement. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Glomerular filtrate contains a lot of water and useful substances while the blood passing into efferent arteriole contains a good quantity of wastes. Therefore, a long passage and hence lot of filtrate is required to correct the situation. It involves reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, ions and water in PCT and secretion of urea and other wastes from blood capillaries into urine in DCT. Urine concentration occurs in PCT, loops of Henle, DCT, collecting tubules and ducts.
Question 26.
(a) Name the site of complete digestion in human,
(b) Small intestine receives the secretions of which two organs ?
(c) Which organ secretes trypsin ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Small intestine
(b) Pancreas and liver
(c) Pancreas as trypsinogen.
Question 27.
List three characteristics of lungs which make them an efficient respiratory surface. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
- Large surface area of about 80 m² for exchange of respiratory gases in the form of several million alveoli.
- Rich supply of blood capillaries over alveoli for quick exchange of gases,
- Non-collapsible respriatory passage supported of chitinous rings in early part and surfactant in delicate part,
- Closure in thorax where a small drop of pressure causes inhalation and a small rise in pressure produces exhalation.
Question 28.
(a) With the help of neat labelled diagram show how Amoeba captures its food ?
(b) What is the mode of nutrition in Amoeba ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) As soon as Amoeba comes in contact with a food particle, it put out pseudopodia around it, engulfs the same and forms a vesicle called phagosome. A lysosome fuses with phagosome to produce a food vacuole. Digestion occurs. The digested nutrients pass out into cytoplasm for assimilation. The food vacuole with indigestible material passes to the surface and throws out the undigested matter.Fig., 1-11 B and E.
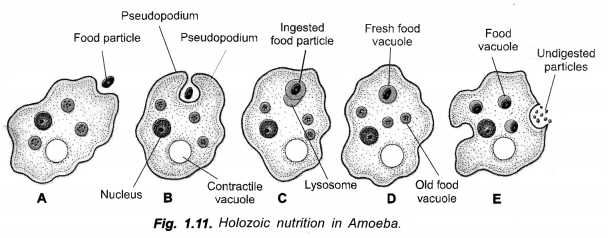
(b) Holozoic.
Question 29.
(a) What is translocation ? Why is it essential for plants ?
(b) Where are the substances translocated by phloem delivered ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Translocation is passage of food materials in solution form in plants from the region of their supply or manufacture to the region of their use or storage.
In plants the region of manufacture of food is only foliage while food is required by the whole plant including deep root tips and top buds and flowers. Similarly regions of storage are also away. Therefore, a translocation is always required.
(b) Delivery of Translocated Substances. The major areas where translocated substances are delivered are storage regions, growing regions, ripening fruits, etc. Of course, every living cell requires the translocates.
Question 30.
(a) Why does a piece of bread taste sweet when chewed for some time ?
(b) Cellulose acts as a roughage in man but serves as a source of nutrient in cow. Justify the statement.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Bread contains starch which is acted upon by ptyalin (salivary amylase) to form sweet sugar maltose.
(b) Human beings have no enzymes and symbiotic bacteria for digestion of cellulose. Therefore, cellulose functions only as roughage in human beings. In cow the stomach contains cellulose digesting (fermenting) bacteria and protozoa that convert it into soluble and absorbable components including glucose.
Question 31.
Explain why is the transportation of materials necessary in animals ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Animals are complex multicellular organisms where there is specialisation for almost all functions like intake of food, exchange of gases and elimination of body wastes. However, every cell of the body requires nutrients and oxygen. It also eliminates CCfy and wastes. Therefore, each and every cell has to be connected to a transportation system for receiving and giving out materials. The transportation system is blood circulatory system in vertebrates. It picks up nutrients from digestive tract, oxygen from respiratory system and hormones from endocrine glands. The same are supplied to cells. Similarly, it takes carbon dioxide to respiratory surface and excretory products to kidneys for removal from’ the body.
Question 32.
Write one function each of the following components of the transport system in human beings :
(a) Blood vessels
(b) Lymph
(c) Heart. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Blood Vessels. Transport of blood to different parts of the body and exchange of materials in the region of capillaries.
(b) Lymph. To collect extra tissue fluid and materials which cannot directly enter the blood, pouring the same into blood.
(c) Heart. Pumping of bood, deoxygenated to lungs and oxygenated to all the remaining parts of the body.
Question 33.
Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label on it
(i) Diaphragm and (ii) Larynx. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
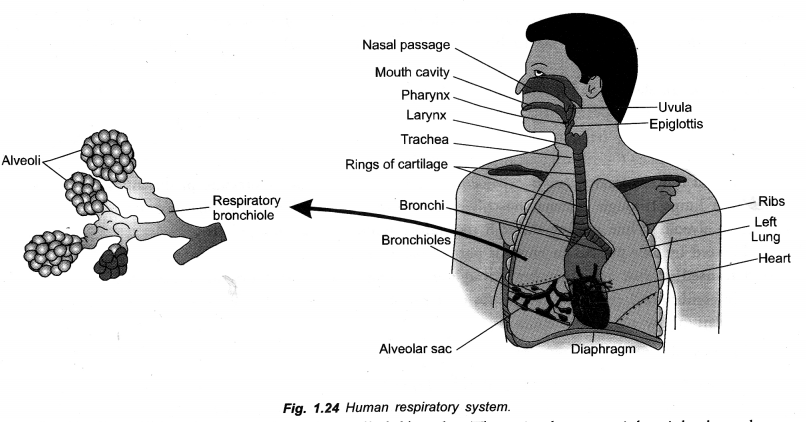
Question 34.
Three Kinds of Blood Cells. Red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles and blood platelets.
Answer:
- Red Blood Corpucles (RBCs, Erythrocytes). Transport of oxygen and smaller quantity of CO2.
- White Blood Corpuscles (WBCs, Leucocytes). Phagocytosis (of microbes and broken body cells) and immune response.
- Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes). Blood clotting and plugging place of injury.
Question 35.
Draw a diagram of human excretory system and label kidneys/left kidney, ureters/urinary bladder on it.
(CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
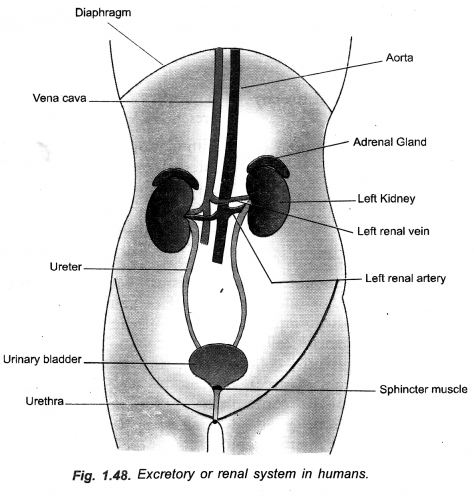
Question 36.
Draw a neat diagram of sectional view of human heart and label on it
(i) Pulmonary artery
(ii) Pulmonary vein. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Question 37.
In single celled organisms, diffusion is sufficient to meet all their requirements of food, exchange of gases or removal of wastes but it is not in case of multicellular organisms. Explain the reason for this difference.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
Single celled organisms are in direct contact with the environment so that diffusion is helpful to them in exchange of gases, removal of wastes and even meeting their requirement of food. However, in most * multicellular organisms, the body is covered by dead cells. Cell to cell diffusion is unable to meet the requirement of all body cells. For example, in humans cell to cell diffusion will take three .years to send oxygen from lungs to toes. Multicellular organisms have developed specialised structures for performing different functions, e.g., digestive tract, respiratory surface, excretory organs. These structures are connected to all body cells through a transport system, e.g., circulatory system in animals, xylem and phloem in plants. The transport system is quite fast to bring materials to and from the cells.
Question 38.
(a) State the reason for the following :
- Rings of cartilage are present in the trachea
- Plants look green in colour.
(b) Write other names of the following :
- Alveolar sac
- Voice box.
Answer:
(a)
- For providing support, prevent collapse under low pressure and allowing uninterrupted flow of air.
- Presence of photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll.
(b)
- Alveolar Sac. Sacculus alveolares, air sac.
- Voice Box. Larynx.
Question 39.
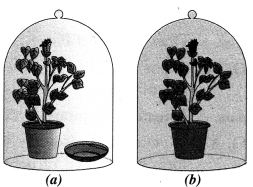
In the experimental set up to establish that one of the atmospheric gases is essential for photosynthesis in plants
(i) Name the atmospheric gas which is essential for photosynthesis.
(ii) What is kept in watch glass in figure a and why ?
(iii) State the difference between the plants in the pots a and b after a few days. (CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
(i) CO2
(ii) KOH in order to deprive the plant in a of CO2.
(iii) After a few days the plant in pot a will turn yellow and may wither due to absence of nourishment. The plant of pot b will, however, remain healthy and green.
Question 40.
Explain how water and minerals are transported in plants. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Water and minerals absorbed by the plant roots are passed into xylem as sap. Sap present in xylem is under tension or negative pressure as mesophyll and other cells of aerials parts lose water to the outside through transpiration.
Development of Negative Pressure. Loss of water by mesophyll and other cells of aerial parts in transpiration increases their suction pressure. They withdraw water from xylem channels. As there are billions of transpiring mesophyll cells withdrawing water from xylem channels, water present in xylem comes under negative pressure of 10-20 atmospheres. However, water column does not break due to
(a) Cohesive force amongst water molecules and
(b) Adhesion force between walls of xylem channels and water moecules.
Rise of Sap (Water and Minerals). Tension or negative pressure of water column results in upward pull just as cold-drink is sucked with the help of straw pipe. Since it develops due to transpiration, it is called transpiration pull. The mechanism of this ascent of sap was put forth by Dixon and Joly in 1894.
Question 41.
Explain why respiration through mouth is harmful. Mention the special features of nasal respiration that makes it a safer process. (CCE 2015, 2016)
Answer:
Breathing through mouth is harmful. Processing of incoming air is not carried out. Particles present in the incoming air cause irritation. Microbes present in it cause infection. Dry hot or cold air produces irritation of mucous lining.
Nasal Breathing. It has a mechanism to filter, clean, sterilise, moisten and condition the inspired air. Chances of infection, desiccation and irritation of respiratory tract are minimized. Nasal breathing is, therefore, safer.
Question 42.
Explain an activity with diagram to show that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.(CCE 2015, 2016)
Answer:
Apparatus: A destarched potted plant of Croton, Pothos (Money Plant) or Coleus having variegated leaves (with green and non-green parts), Rice paper, Soft pencil, Beakers, Petridishes, Tripod stand, Wire gauze, Water bath, Blotting paper, Dropper, Box of matches, Burner or spirit lamp, spirit (or 70% alcohol), iodine solution, water, forceps.
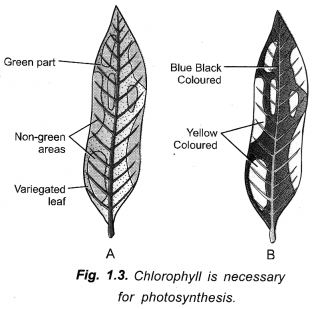
Procedure: Destarch a potted plant of Croton or Pothos (Money Plant) having variegated leaves by keeping it in complete darkness for 2-3 days. Expose the destarched potted plant to sunlight for 2-6 hours. Pluck a variegated leaf. Place a rice paper over it. Draw the outline of green and non-green areas. The green areas contain chlorophyll. The non-green areas are pale in colour and devoid of chlorophyll. Place the leaf in boiling water for 5-10 minutes. Boiling kills the leaf. Dip the leaf in spirit or alcohol kept at 50°-60° C with the help of a water bath. After 30-45 minutes, the leaf will be decolourised completely. Take out the decolourised leaf, dip in hot water for softening the same. Spread the leaf in a petri dish. Pour dilute iodine solution over the leaf. After 4-5 minutes, rinse off excess iodine and observe.
Question 43.
Define excretion. Write two vital functions of kidney. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Excretion. It is the elimination of metabolic waste products from the body.
Vital Functions of Kidney,
- Elimination of metabolic waste products.
- Maintenance of water balance or osmoregulation of body.
Question 44.
Compare alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
| Alveoli | Nephrons |
| 1. Shape. They are rounded or polyhedral. | They are elongated tubules. |
| 2. Components. Alveoli are single entities. | Each nephron has two components-Malpighian capsule and renal tubule. Renal tubule has three parts – PCT, loop of Henle and DCT. |
| 3. Blood Capillaries. They are of one type and lie all over the alveoli. | Blood capillaries form two patches—glomerulus and peritubular capillaries. |
| 4. Materials. They deal with respiratory gases. | They deal with body fluids. |
| 5. Function. Alveoli perform exchange of gases between blood and inhaled air. | Nephrons bring about separation of waste products from blood. |
| 6. Processes. Gaseous exchange occurs through diffusion. | Urine formation occurs through ultrafiltration, reabsorption, secretion and osmosis. |
Question 45.
Explain the structure of bronchi with the help of neat diagram and label on it (CCE 2015)
(i) Trachea
(ii) Bronchiole.
Answer:
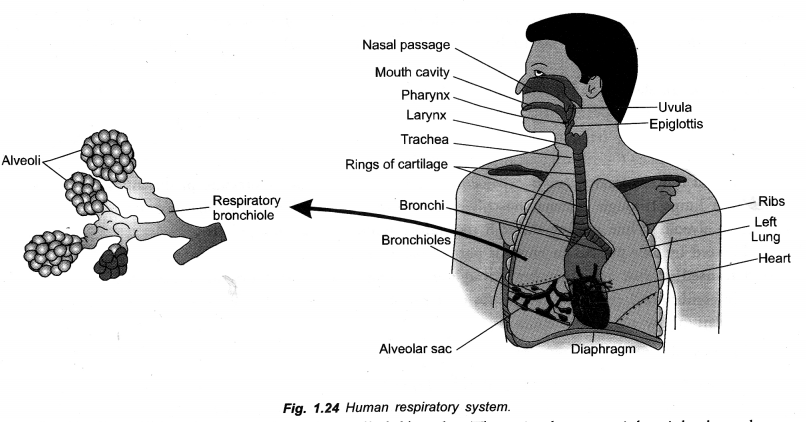
Bronchi: Trachea divides into two branches called bronchi. There is short, straight right bronchus and a slightly longer oblique left bronchus. Each bronchus enters the lung of its side, branches and rebranches. Bronchi and their branches bear incomplete or C-shaped cartilaginous rings for support. They are also lined internally by ciliated and mucus secreting epithelium. Branches of bronchi ultimately produce very fine tubes called bronchioles. Bronchioles do not possess supporting cartilaginous rings. Finer bronchioles give rise to alveoli or alveolar sacs. Epithelial lining of alveoli and fine bronchioles do not possess cilia and mucus glands. They possess cells which secrete a surfactant (dipalmityl lecithin-protein complex) for preventing their collapse during exhalation. Alveoli are polyhedral to rounded sacs having extremely thin single layered wall invested closely with blood capillaries. Alveoli are actual sites of gaseous exchange.
Question 46.
Name three life processes which are essential for maintaining life and briefly explain the functioning of any one of them. (CCE 2015, 2016)
Answer:
Nutrition, respiration, exchange of materials.
Nutrition: It is the process by which living beings procure food for obtaining energy and body building materials. Body building materials are usually carbon-based. The food sources are also carbon based. They are, of course, varied. Plants manufacture their own food in the process of photosynthesis. Animals obtain food from outside. Food obtained from outside is first broken down through digestion into simpler soluble substances for absorption. Inside the cells, the simple substances are converted into various complex biochemicals to form components of protoplasm. Some biochemicals function as respiratory substfates.
Question 47.
Explain the process by which the energy requirements of the autotrophic organisms are fulfilled. In which form the unused carbohydrates get stored ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Photosynthesis. It occurs in the following steps :
- Photolysis: With the help of light energy, oxygen evolving Z-complex splits up water into its components — protons (H+), electrons (e–) and oxygen.
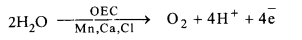
- Absorption of Light Energy: Chlorophyll absorbs light energy.
- Primary Reaction: Chlorophyll converts the absorbed light energy into chemical energy. It is called primary reaction of photosynthesis. It builds up ATP with the help of excited electrons.
- Formation of Reducing Power: Coenzyme NADP+ is changed to reduced form of NADPH.
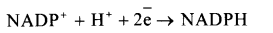
- Reduction of CO2: Carbon dioxide is reduced enzymatically with the help of NADPH and ATP to form carbohydrates.
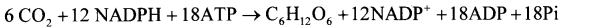
Storage: Starch.
Question 48.
Explain why digestion of food is essential for all living beings. Mention the form in which energy derived from the food we eat is stored. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Food consists of complex components which cannot pass into body cells directly for nourishment. They are broken down into simpler absorbable form through the process of digestion. Digestion is intracellular in simple animals. It is intercellular inside a digestive tract in higher animals including humans. The digested materials are absorbed and transported by blood to all parts for picking up by individual cells for assimilation. The latter is then used for both release of energy and building of cellular components.
(b) Energy derived from food is stored as glycogen and fat.
Question 49.
Explain an activity with diagram to show that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis. (CCE 2015)
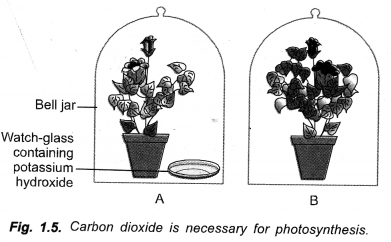
Answer:
Apparatus: Two destarched potted plants, Two glass slabs, Two bell jars, Vaseline, Watch glass, Potassium hydroxide solution, Apparatus for starch test (water, alcohol, beakers, petri dishes, iodine solution, tripod stand, wire gauze, spirit lamp, water bath, dropper, forceps, box of matches).
Procedure: Take two potted plants which have been destarched by keeping them in dark for 2-3 days. Place them on glass slabs.
Keep a watch glass having potassium hydroxide solution on one slab. Invert bell jar over each potted plant. Seal the edges of bell jars by vaseline. Place the two sets in the sunlight. After two hours pluck one leaf from each pot and test the same for starch.
Observation: The leaf of the set B which was without potassium hydroxide solution turns blue-black while the leaf of the other set A with potassium hydroxide solution remains pale coloured.
Inference: Leaf of set B which turns blue-black has synthesised starch with the help of photosynthesis. Its bell jar contains carbon dioxide as there is no potassium hydroxide. Leaf of set A has not synthesised starch. Photosynthesis did not occur. The bell jar of this set does not contain carbon dioxide as the same is absorbed by potassium hydroxide solution. Therefore, carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.
Question 50.
Explain giving any three reasons the significance of transpiration in plants. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
- Cooling: Evaporation of water from the aerial parts results in lowering of their temperature which will otherwise rise due to exposure to sun.
- Concentration of Minerals: Transpiration helps in increasing concentration of minerals present in rising water.
- Transport: It creates a pull that helps in transport of water and minerals.
Question 51.
Explain why there is need for transportation system with special tissues or organs in plants and animals ?
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
Transportation is the passage of nutrients, wastes, water and other materials from the region of their availability to the region of their use, storage or elimination. Food has to be sent to all parts of the body from the area of digestion in animal and the area of synthesis in plants. It has to be stored in special organs for supply during periods of deficiency. Plants have vascular strand for translocation while animals have blood vascular system. Animals have a pumping organ or heart for circulation of blood. Plants have distinct channels of xylem and phloem for passage of sap and nutrients.
Question 52.
Name one nitrogenous waste present in urine. What is basic unit kidney called ? How is the amount of urine produced regulated ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Nitrogenous Waste. Urea.
Unit. Nephron or uriniferous tubule.
Regulation. Vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone regulates the amount of urine produced. It is secreted by pituitary in amount requied to concentrate urine through bringing about reabsorption of water from the primary urine.
Question 53.
State three common features of respiratory organs of animals. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Large surface area, thin permeable membrane, abundant blood supply.
- Large Surface Area: There is a large respiratory surface that is either in contact with environment directly or receives air or water from outside,
- Thin Permeable Membrane: The respiratory surface has thin permeable wall for quick diffusion and exchange of gases,
- Abundant Blood Supply: Except in tracheal system, the respiratory surface has abundant blood supply due to presence of a network of blood capillaries.
Question 54.
Describe the structure and function of nephron with the help of diagram only. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
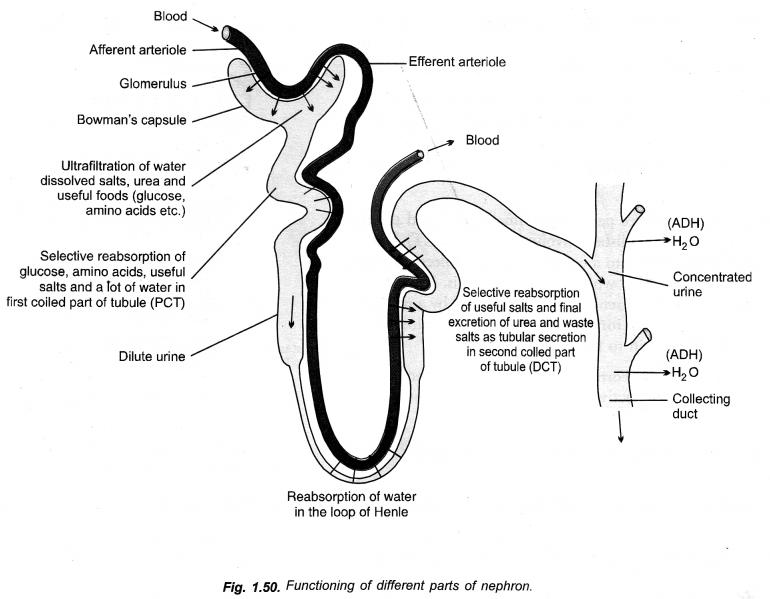
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks Each)
Question 1.
(a) List two differences between ‘holozoic nutrition’ and ‘saprophytic nutrition. Give two examples each of these two types of nutrition.
(b) State the roles of liver and pancreas.
(c) Name the organ which performs the following functions in humans :
- Absorption of digested food
- Absorption of water.
(d) Explain the statement, “Bile does not contain any enzyme but it is essential for digestion.”
(CBSE A.I. 2005, Delhi 2007, 2009)
Answer:
(a) Differences between Holozoic Nutrition and Saprophytic Nutrition
| Holozoic Nutrition | Saprophytic Nutrition |
| 1. Type. It is ingestive type where solid food is taken in.
2. Digestion. It is internal. Examples. Tiger, Cattle. |
It is absorptive type of nutrition where simple soluble substances are taken in.
Digestion is external. Examples. Rhizopus, Mushroom. |
(b)
- Role of Liver: Decomposition of haemoglobin, formation and secretion of bile for emulsification of fat. Formation of urea, heparin fibrinogen and prothrombin. Detoxification of chemicals and elimination of pathogens.
- Role of Pancreas: Secretion of pancreatic juice having lipase, trypsin and amylase; secretion of hormones, insulin and glucagon.
(c)
- Absorption of Digested Food. Ileum part of small intestine.
- Absorption of Water. Large intestine.
(d) Role of Bile in Digestion.
- Breaking of fat into fine globules or emulsification,
- Neutralisation of acidity and making food alkaline for action of pancreatic and other enzymes.
Question 2.
(a) Draw a diagram to show the human alimentary canal and label on it the following : Gall bladder,
Stomach. Name the longest part of the alimentary canal. (CCE 2013)
(b) Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds ?
(CBSE A.I. 2009 C, CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
(a)
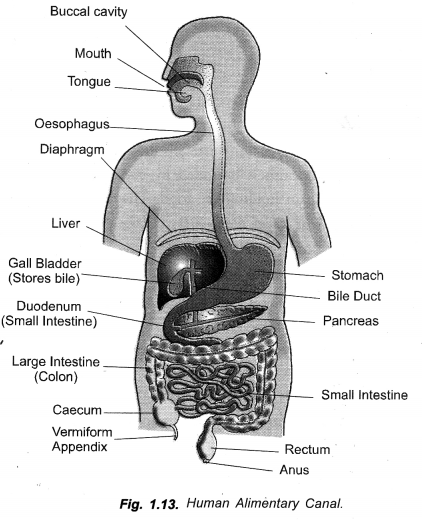
Longest Part. Small intestine (about 6 metres).
(b) Separation of Oxygenated and Deoxygenated Bloods in Birds and Mammals.
Energy needs of birds and mammals are higher due to thermoregulation of body and increased activity. They require regular and quicker supply of oxygenated blood for all body parts. This is possible only when there is complete separation of oxygenated blood and quicker oxygenation of deoxygenated blood.
Question 3.
(a) List three events that occur during the process of photosynthesis. State in brief the role of stomata in this process.
(b) Describe an experiment to show that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.
(CBSE Delhi 2010, CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a)
- Three Events of Photosynthesis: Information is transmitted from one plant cell to another through plasmodesmata and hormones.
- Role of Stomata in Photosynthesis. Inward diffusion of carbon dioxide and outword diffusion of oxygen.
(b) Sunlight is Essential for Photosynthesis: It is the source of energy for photosynthesis. Light is visible part of the electromagnetic radiations. It has a wavelength of 390-760 nm. Photosynthetically active radiations or PAR are 400-700 nm. Natural source of light is sun but artificial light can also provide energy to plants for their photosynthesis. Plants absorb light mostly in violet-blue and red parts of visible light. Violet-blue light carries more energy as compared to red light. Plants growing under shade of others receive mostly green and some violet light. They have lower rates of photosynthesis.
Light has two functions, photolysis of water and excitation of chlorophyll to emit electrons. Photolysis of water produces oxygen, protons and electrons. Electrons and protons (Hydrogen ions) help in producing ATP and NADPH2, popularly called assimilatory power.
Question 4.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of alimentary canal and label the following parts :
- The largest gland,
- The gland that secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones,
- The part where digested food is absorbed.
(b) What are villi ? Mention their functions. (CCE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
(a)
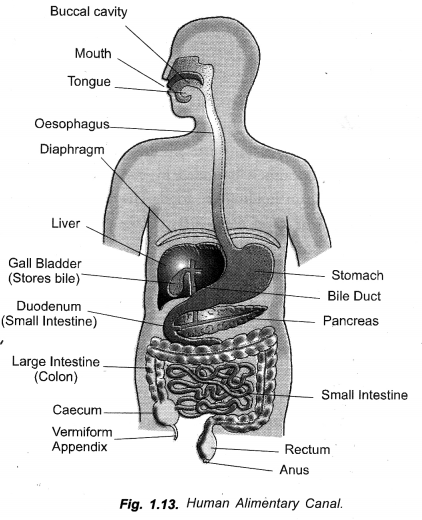
- The largest gland —Liver
- The gland that secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones — Pancreas
- The part where digested food is absorbed — Small Intestine.
(b) Villi: They are transverse folds of intestine wall that not only increase surface area but also reach deep into the lumen of intestine for absorption of digested food. Villi possess blood capillaries and lacteals (lymph vessels) for quick transport of absorbed food,
Question 5.
(a) Draw the cross section of the leaf and label the following parts :
- Upper epidermis
- Chloroplast
- Vascular bundle
- Xylem
- Phloem.
(b) Define photosynthesis.
(c) List three events which occur during this process
(d) Write the chemical equation involved in photosynthesis.
(e) How is unused energy stored in plants ?
(f) What is the site for photosynthesis ?
Answer:
(a)
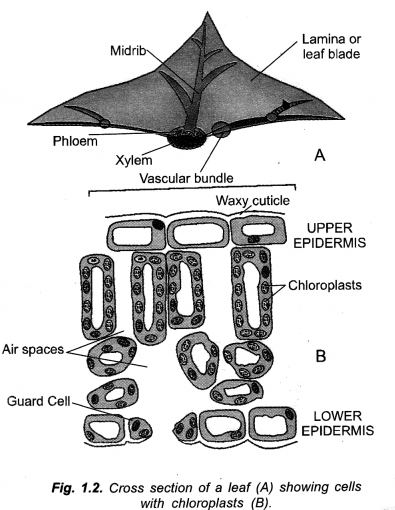
(b) Photosynthesis: It is synthesis of organic food from inorganic raw materials with the help of light energy inside chlorophyll containing cells.
(c) Events: Information is transmitted from one plant cell to another through plasmodesmata and hormones.![]()
(e) Starch, organic substances.
(f) Chloroplasts.
Question 6.
(a) Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal and label on it
- Gall bladder
- Liver
- Pancreas
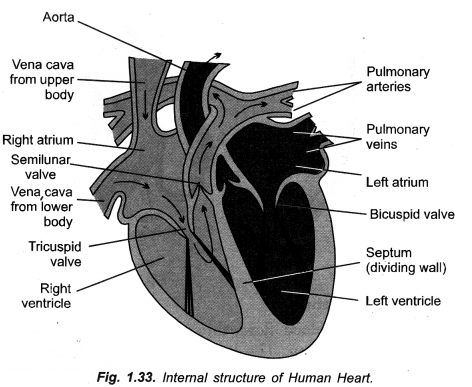
- Small intestine
- Buccal cavity
- Large intestine.
(b) What is emulsification of fat ? Why is it necessary ?
(c) On which type of food does salivary amylase act in buccal cavity and write the name of initial product due to action of amylase.
(d) Where do carbohydrates, proteins and fats get digested in human beings ? (CCE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
(a)
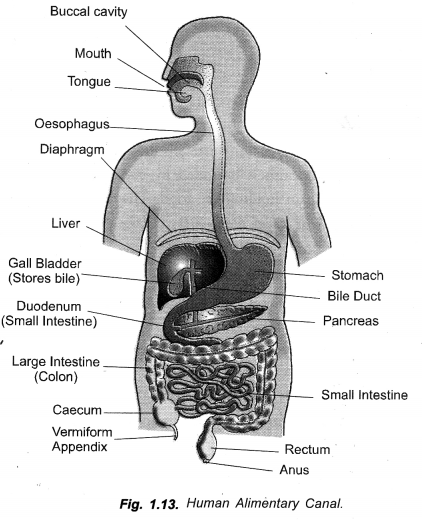
(b) Emulsification of fat is the conversion of large fat pieces into very fine fat globules which can be efficiently acted upon by lipase.
(c) Salivary amylase or ptyalin acts on starch. It produces maltose and dextrins.
(d) In small intestine. Digestion of course, begins in buccal cavity (carbohydrates), stomach (proteins) and duodenum (fats).
Question 7.
(a) Draw sectional view of human heart and label
- Pulmonary artery
- Aorta
- Septum
- Ventricles.
(b) Arteries have thick walls while veins have valves. Explain.
(c) Why are valves needed in the heart ?
(d) Leakage of blood from vessels reduces the efficiency of pumping system. How is the leakage prevented ?
(CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a)
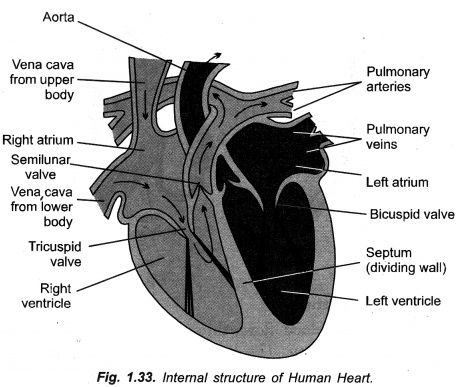
(b) In arteries, blood flows under pressure so that their walls are thick and elastic. In veins the blood is Therefore, their walls are thin. Rather, they possess semilunar valves to check back flow of blood.
(c) Valves are needed in the heart to direct the flow of blood in a particular direction.
(d) Leakage of blood from injured blood vessels is prevented by first clotting of blood at the site of injury. This seals the place of injury. Later on, the area of leakage is healed up.
Question 8.
(a) Draw human excretory system and label
- Left kidney
- Ureter
- Urinary bladder
- Vena cava.
(b) What is the main toxic waste kidney filters from blood ?
(c) Name any two substances which are selectively reabsorbed from the tubules of a nephron.(CCE 2010, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a)
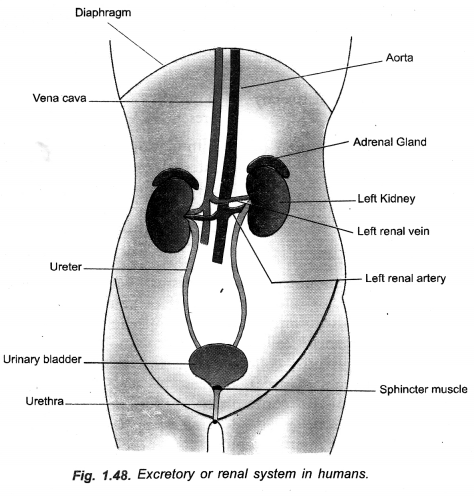
(b) Main Toxic Waste. Urea. Selective Reabsorption, Glucose, Amino acids.
Question 9.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of human respiratory system. Label
- Bronchioles
- Rings of cartilage
- Pharynx
- Trachea
- Larynx
- Diaphragm.
(b) What are the factors needed for maintaining direction of diffusion in plants ?
(c) Why do aquatic animals breathe faster than terrestrial animals ? (CCE 2012, 2013)
(d) How are lungs designed in human beings to maximise the area of exchange of gases ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a)
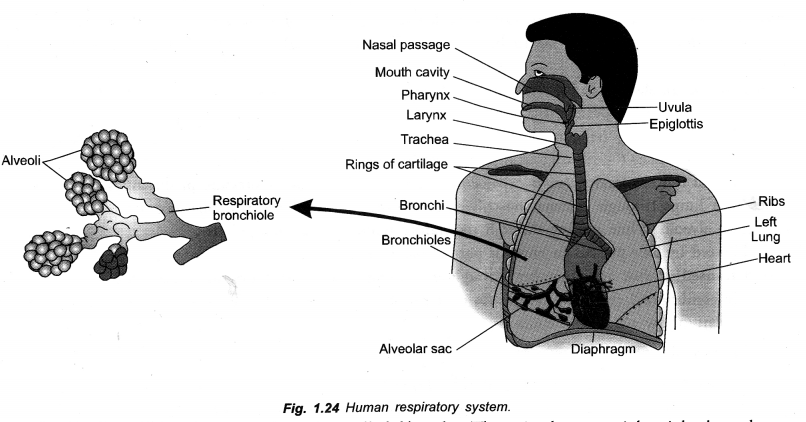
(b) Direction of Diffusion :
- Maintenance of higher concentration in the region from which diffusion occurs,
- Maintenance of low concentration in the region to which diffusion is to occur
- Path of diffusion.
(c) Aquatic Animals Breathe Faster. Water contains less than 1% oxygen dissolved in it while air has 21% oxygen. Therefore, aquatic animals have to breathe faster for withdrawing higher amount of oxygen from water.
(d) Each lung has a highly branched respiratory tract called respiratory tree. A primary bronchus divides into secondary bronchi, secondary into segmental bronchi, segmental bronchus into bronchioles which divide into terminal bronchioles, respiratory bronchioles, alveolar sacs and alveoli. Alveoli are small rounded or polyhedral pouches which are extremely thin walled and possess a network of capillaries over their surface. They function as respiratory surfaces. The total area of all the alveoli is more than 80 m2. It is several times more than the surface area of the whole human body.
Question 10.
Draw a neat diagram of internal structure of human heart and label the parts which do the following functions :
(a) Chamber where oxygenated blood from lungs in collected,
(b) Largest blood vessel in our body,
(c) Muscular wall separating right and left chambers.
(d) Blood vessel that carries blood from heart to lungs. (CCE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
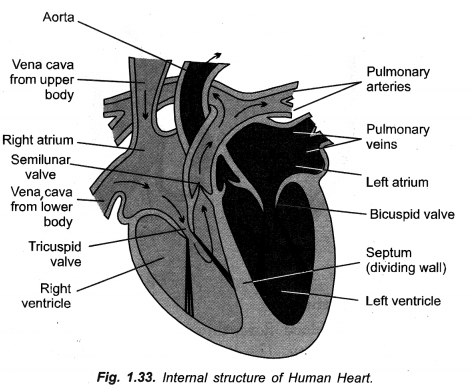
Label
(a) Left auricle
(b) Aorta ( = systemic aorta)
(c) Septum
(d) Pulmonary artery ( = Pulmonary aorta).
Question 11.
How do the guard cells regulate opening and closing of stomatal pores ? Explain with the help of diagram. Also indicate what happens to the rate of photosynthesis if stomata get blocked due to dust. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Regulation of Stomatal Pore:
Opening and closing of stomata is regulated by gain or loss of turgidity of their guard cells. During opening of stomata, guard cells withdraw K+ ions from surrounding epidermal cells, followed by absorption of water from them. As a result, guard cells swell up and become turgid. Their outer thin and elastic walls bend outwardly followed by outward movement of thicker inner walls. The latter creates a pore in between the two guard cells.
During closure movement of stomata, guard cells send out K+ ions. Water also passes out. Guard cells become flaccid. Their inner thick walls come to touch each other. The stomatal pore gets closed.
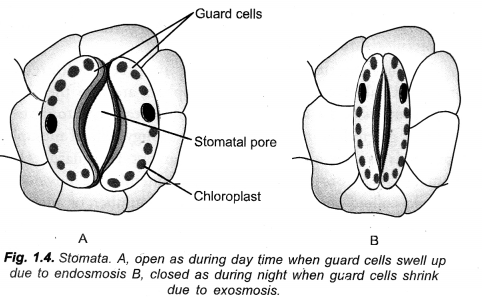
Blocking of Stomata:
- Photosynthesis will be reduced,
- There will be no gaseous exchange and transpiration. As a result leaves will burn up in hot summer sun.
Question 12.
(a) Name the enzyme present in saliva. Why is it important ?
(b) What is emulsification ?
(c) Name the substance that is oxidised in the body during respiration.
(d) Why are lungs divided into very small sac-like structures ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Enzyme. Ptyalin or salivary amylase. It breaks down starch to form maltose sugar.
(b) Emulsification: Emulsification of fat is the conversion of large fat pieces into very fine fat globules which can be efficiently acted upon by lipase.
(c) Glucose
(d) To increase surface area for exchange of gases.
Question 13.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of human excretory system and label the part that
- produces urine
- releases urine to the outside
(b) What are the end products of digestion of fat and protein in human beings ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
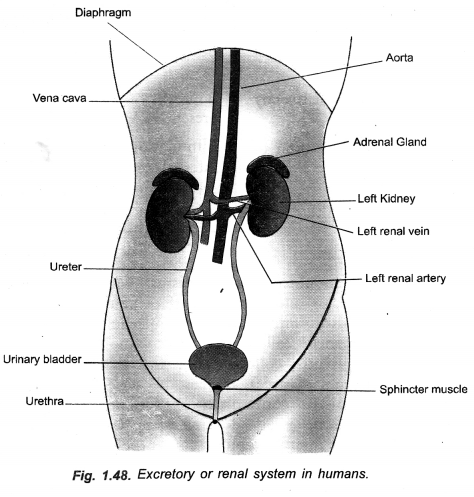
kidney (produces urine) and urethra (releases urine to the outside).
(b)
- Fat—fatty acids and glycerol.
- Protein—amino acids.
Question 14.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of excretory system of human beings and label the following : (t) Kidney (it) Ureter (iit) Urinary bladder (iv) Urethra.
(b) How is urine produced ?
(c) Name two excretory products other than 02 and C02 in plants. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
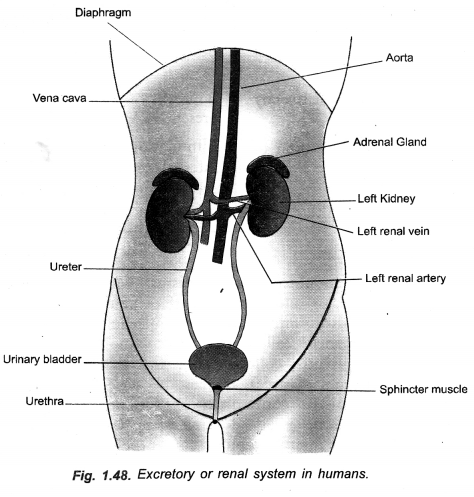
(b) A kidney has very large number of nephrons which function as filtration units. Useful substances (water, glucose, amino acids, salts) are selectively reabsorbed from primary urine. It gives rise to urine having waste products (e.g. urea, uric acid, creatine, oxalate, some salts, water soluble vitamins).
(c) Resin, Gum, Tannin.
Question 15.
(a) Draw diagram to show nutrition in Amoeba and label the part used for this purpose. Mention a purpose served by this part other than nutrition.
(b) Name the glands associated with digestion of starch in human digestive tract and mention their role.
(c) How is required pH maintained in the stomach and small intestine ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
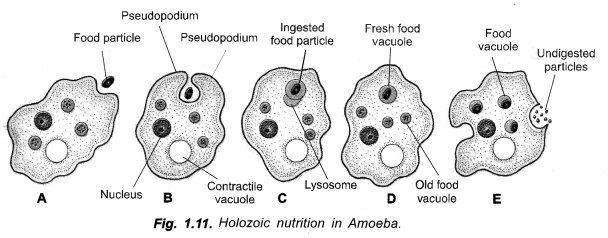
pseudopodia in part B. The other function of pseudopodia is locomotion.
(b)
- Salivary glands—salivary amylase—starch to maltose sugar
- Pancreas—pancreatic amylase—starch to maltose sugar
- Intestine—disaccharidases—disaccharides to glucose.
(c) Stomach—acidic pH, due to secretion of HC1 by gastric glands.
Small Intestine—alkaline pH, due to bicarbonates and other bases present in bile and pancreatic juice.
Question 16.
Draw a labelled diagram of human heart. Write the function of any two chambers of human heart.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
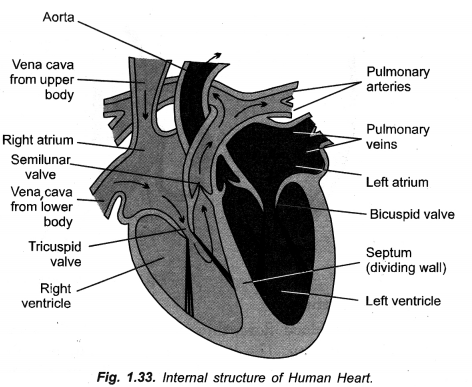
Functions:
Left Atrium – Receiving oxygenated blood from lungs.
Right Atrium – Receiving deoxygenated blood from the body as well as walls of the heart.
Question 17.
(a) Draw a diagram of an excretory unit of human kidney and label the following : Bowman’s capsule,
Glomerulus, collecting duct, Renal artery. ‘
(b) Write the important function of structural and functional unit of kidney.
(c) Write any one function of an artificial kidney. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
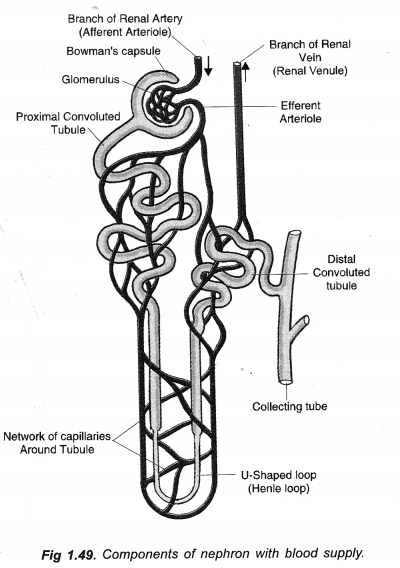
(b) Nephron. It takes part in filtration, reabsorption and selective secretion to form urine.
(c) Artificial kidney. It helps in removal of toxins, relieve uraemia, and remove wastes in patients with damaged kidneys.
Question 18.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of human respiratory system and label : Rings of cartilage, Lung, Bronchii, Alveolar sac.
(b) Name any two parasitic plants and two parasitic animals. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
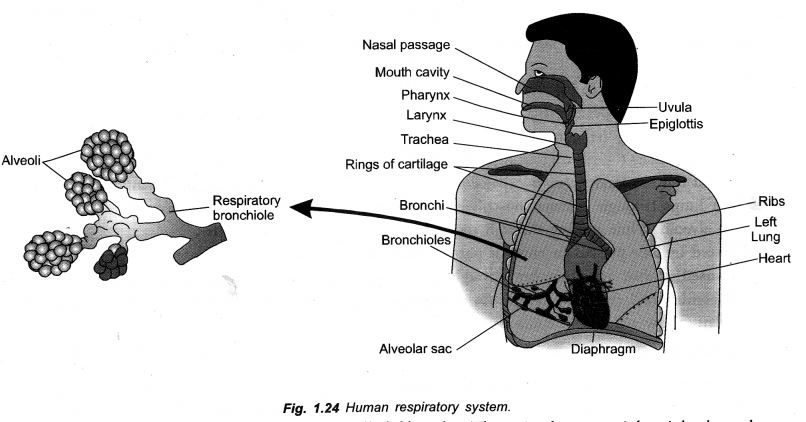
(b)
- Parasitic Plants. Cuscuta, Mistletoe
- Parasitic Animals. Ascaris, Plasmodium.
Question 19.
“Sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis.” Explain an experiment to prove it.
Answer:
Light is Necessary for Photosynthesis. ,
Apparatus: Destarched potted plant, Ganong’s light screen or Black paper, Scissors and Cellotape or Clip, Water, Denatured spirit, Dropper, Forceps, Beakers, Petri dishes, Tripod stand, Wire gauze, Spirit lamp, Water bath, Iodine solution, Blotting paper, Box of matches.
Ganong’s light screen is a small metallic box with a spring handle, ventilating holes and a lid having a design cut in the centre. Alternately take a strip of black paper.
Procedure: Fix a strip of black paper in the middle on the upper surface of a leaf of destarched potted plant by means of cellotape or clips. Alternately attach a Ganong’s light screen or a black paper with a central cut design over it. Expose the plant to sunlight for 2-3 hours. Remove the black paper or Ganong’s light screen. Pluck the leaf. Test it for starch by first boiling in water for 5-10 minutes, drying in folds of blotting paper, dipping in warm denatured spirit for 30-45 minutes, washing with hot water and pouring iodine over it.
Observation: Covered part of leaf remains yellow while parts of leaf which received light turn bluish black. Bluish black colour indicates the presence of starch or photosynthesis.
Inference: Only that leaf part shows photosynthesis or positive starch test which is exposed to light. The covered part which does not receive sunlight also does not perform photosynthesis as is evident from the absence of starch. Therefore, light is necessary for photosynthesis.
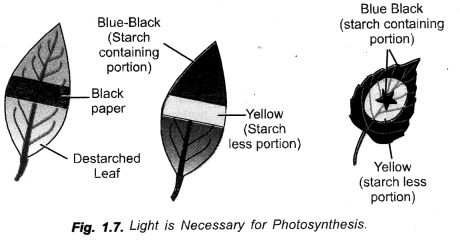
Question 20.
(a) What happens to glucose, amino acids, salts and water that enter the nephron alongwith filtrate.
(b) Draw a neat labelled diagram of stomata. Write two functions of stomata.
(c) What are the basic materials used during photosynthesis ? Write chemical equation for photosyntheis.
(CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) They are reabsorbed by the living cells of nephrons and then passed on to capillary blood.
(b)
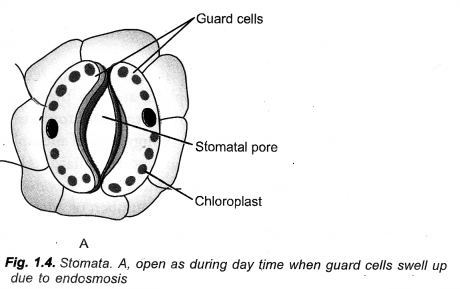
Functions,
- Exchange of gases,
- Transpiration.
(c) Raw Materials. CO2 and H2O in the presence of solar energy and chlorophyll.
![]()
Question 21.
List and describe in brief in tabular form any five functions of blood.
Answer:
| 1. Transport of Respiratory Gases. | Blood transports O2 from respiratory surface to tissues and CO2 from tissues to respiratory surface. . |
| 2. Transport of Nutrients. | Blood picks up nutrients from digestive tract and passes the same to all parts of body for assimilation (and storage). |
| 3. Transport of Waste Products | It transports waste products to kidneys for separation and elimination. |
| 4. Regulation of Body Temperature | Blood distributes heat to all parts of body and dissipates the excess heat from the surface. |
| 5. Body Defence | It contains phagocytes and immunocytes for defence against germs. |
Question 22.
(a) Draw the diagram of human heart and label the following parts which
- Receives deoxygenated blood from vena cava
- Sends deoxygenated blood to lung through pulmonary artery
- Receives oxygenated blood from lungs and
- Sends oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through aorta.
(b) What does the blood consist of ?
(c) Name the respiratory pigment in human beings and discuss its role. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
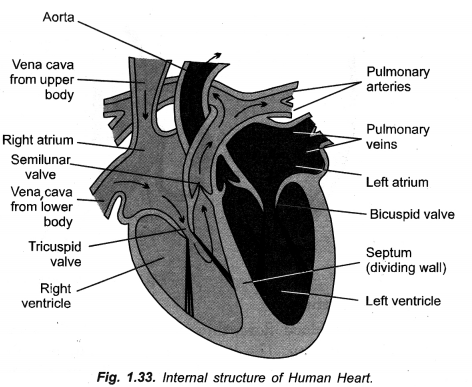
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle.
(b) Blood consists of blood plasma, red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles and blood platelets.
(c) Haemoglobin: It transports oxygen as oxyhaemoglobin and a part of CO2 as carbaminohaemoglobin.
Question 23.
Draw diagram of human alimentary canal and label the following (CCE 2011)
- Part in which starch digestion starts
- Part in which bile is stored
- Part in which nutrients are absorbed
- Part in which water is absorbed.
(b) Mention the role of hydrochloric acid in stomach,
(c) What function is served by
- Gastric sphincter
- Anal sphincter.
Answer:
(a)
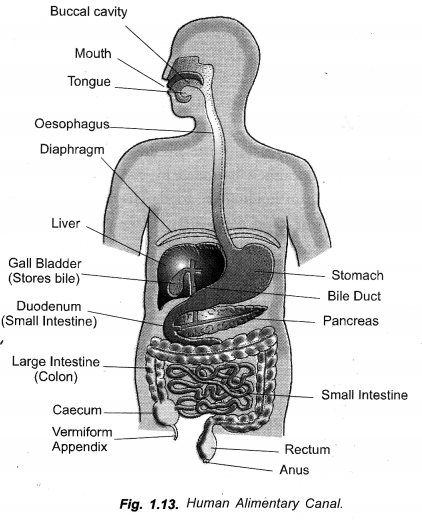
- Buccal cavity
- Gall bladder
- Small intestine
- Large intestine (colon):
(b) Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is component of gastric juice. It has five functions,
- Softening of food,
- Conversion of pepsinogen and prorennin into active forms of pepsin and rennin
- Acidify the food for proper action of pepsin,
- Killing of microorganisms present in food,
- Stoppage of action of salivary amylase.
(c)
- Controls release of food from stomach to duçdenum.
- Controls release of faeces through anus.
Question 24.
(a) Draw diagram of respiratory system and label the following :
- Part through which air is taken in
- Part which protects the lungs
- Part which carries air into the lungs.
(b) What are alveoli ? Mention their role in respiration. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
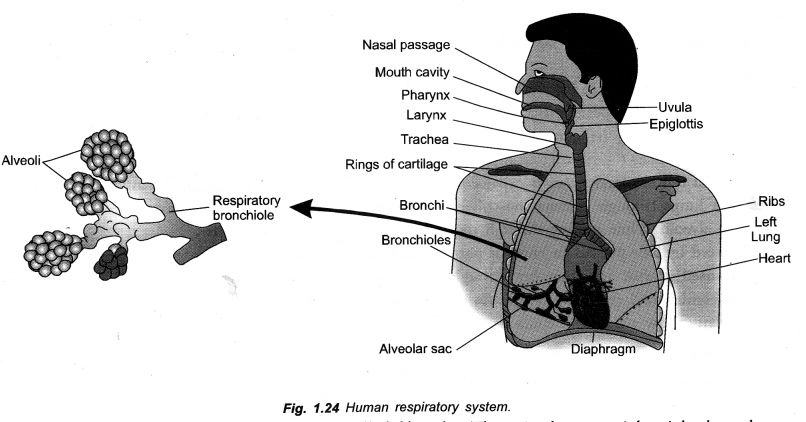
- Nasal passage
- Ribs
- Trachea and bronchi.
(b) Lung Alveoli: Lung alveoli constitute the respiratory surface of the lungs. Their walls have rich supply of blood for gaseous exchange, i.e. passage of oxygen from alveolar air to blood and passage of carbon dioxide from blood to alveolar air.
Question 25.
Draw a schematic representation of transport and exchange of 02 and C02 in human body.
(b) Draw a schematic representation of movement of water in plants during transpiration and explain it.
(c) Explain transport of food and other substances in plants.
(d) Diffusion will not be sufficient to provide raw materials in leaves and energy in roots of plants. Therefore, a proper system of transportation is essential. Explain. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a)
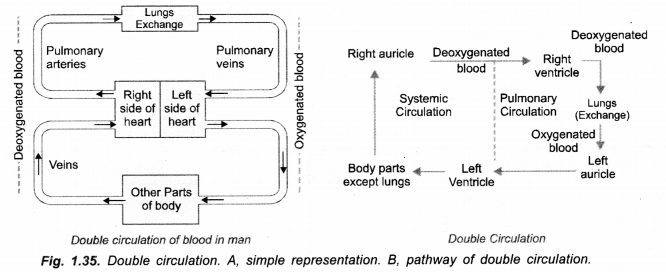
(b)
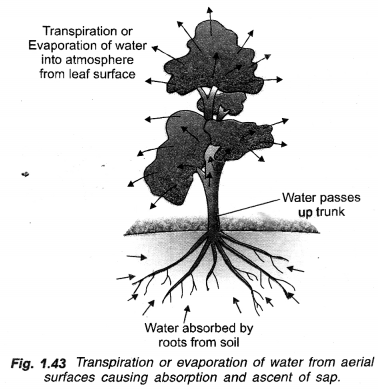
Transpiration creates a tension or negative pressure in the water column of the plant. It causes an upward transpiration pull of water and minerals (sap) which is replenished by absorption of same from the soil through the roots.
(c) Food and other nutrients pass into sieve tubes of phloem through an active process in the region of manufacture or source. An increased osmotic pressure creates a turgor gradient towards sink or region of utilisation in a mass flow. Nutrients and other organic substances are then withdrawn from the sieve tubes actively.
(d) Diffusion is a very slow process (0-05 mm/hr) while the distances are comparatively very large in plants. Therefore, raw materials absorbed by roots will take several days to reach leaves if they are to diffuse only. Similar is the case of food materials that are to travel from leaves to roots. Therefore, a proper system of rapid transportation is required.
Question 26.
(a) How many times the blood goes through the heart during one cycle in fish and why ?
(b) List the respiratory pigment present in our body. Where is it pressent ?
(c) Why are valves present in heart and viens ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Fish has single circulation, that is, blood passes once through the heart in one cycle. It goes from heart to gills, from gills to body and back to heart.
(b) Haemoglobin. It occurs inside red blood corpuscles.
(c) Valves occur in heart and veins to prevent back flow of blood.
Question 27.
(a) Explain in brief the mechanism of circulation of blood in the human body.
(b) “Lymph is another type of fluid involved in transportation”. Justify the statement by explaining the process.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Deoxygenated blood is collected by superior vena cava from upper part of the body, by inferior vena cava from middle and lower parts of the body and coronary sinus from the walls of heart. All the three pour their blood into right auricle. Oxygenated blood is brought by pulmonary veins from the lungs. It is poured into left auricle. On being filled, the two auricles contract simultaneously and pass their bloods into ventricles, deoxygenated in right ventricle and oxygenated in left ventricle. The distended ventricles now undergo contraction or systole forcefully. Right ventricle passes blood to pulmonary arch which divides to form pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary arteries take the deoxygenated blood to lungs. Left ventricle passes blood to systemic aorta that supplies oxygenated blood to all parts of the body.
(b) Lymph is a fluid that is specialised to collect those materials from the tissues which cannot pass directly into blood, e.g., proteins, hormones, fats (from intestine). Lymph collects the same and pass them to blood in the region of subclavian veins. For passage of lymph, the lymphatic system has lymph capillaries, lymph vessels and lymph nodes.
Question 28.
(a) Explain the excretory system in human beings. (CCE 2011)
(b) List four strategies used by plants for excretion. (CCE 2011, 2016)
Answer:
(a) In human beings, the excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and a urethra.
Kidneys are a pair of reddish brown bean-shaped structures that lie dorsally in the abdominal cavity. A renal artery and a renal vein occur on the concave hilus region of each kidney. About a million structural and functional units called nephrons occur in each kidney. Blood is filtered in the glomerular region of a nephron. Useful substances (e.g. glucose, amino acids, salts, water) are reabsorbed and urine passes into collecting ducts. Ureters are pulsatile drainage tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder is a pear-shaped distensible sac that stores urine till its volume becomes 300-800 ml. Urethra is a fine tube that carries urine from urinary bladder to the outside.
(b) Excretion Strategies in Plants,
- Excess water is passed out through transpiration,
- Excess O2 formed during the day diffuses out of the leaves.
- Alkaloids, organic acids and tannins are the common secondary metabolites. Some of these are stored in the cell vacuoles of leaves which when old fall down,
- Resins and gums alongwith other wastes are also deposited in old non-functional xylem.
Question 29.
(a) Some finger-like projections are present in the inner wall of small intestine. Write their name. Why are they important ?
(b) What is the use of residual volume of air in lungs ? (CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Villi :
- They increase surface area for absorption of digested food
- Pass deep into lumen of intestine for increased availability of digested food.
- Possess capillaries and lacteals for quick transport of absorbed food
- Their epithelial cells possess microvilli for enlarging absorptive surface area.
(b) Residual volume of air is the volume of air that h left in the lungs even after maximum exhalation. The air is useful as exchange of gases continues with the blood in between exhalation and fresh inhalation.
Question 30.
Draw a diagram of sectional view of human heart and on it name and label the following parts :
(a) The chamber of heart that pumps out deoxygenated blood,
(b) The blood vessel that carries away oxygenated blood from heart
(c) The blood vessel that receives deoxygenated blood from lower part of our body. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
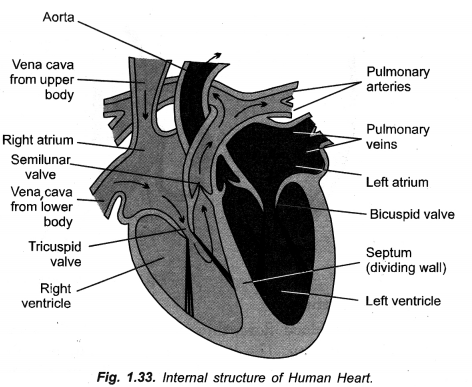
(a) Right ventricle (pumps deoxygenated blood)
(b) Aorta (carries away oxygenated blood from heart)
(c) Inferior vena cava.
Question 31.
(a) Draw human respiratory system and label the following — lung, bronchi, alveoli
(b) During breathing cycle what is the advantage of residual volume of air in lungs ? Explain. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
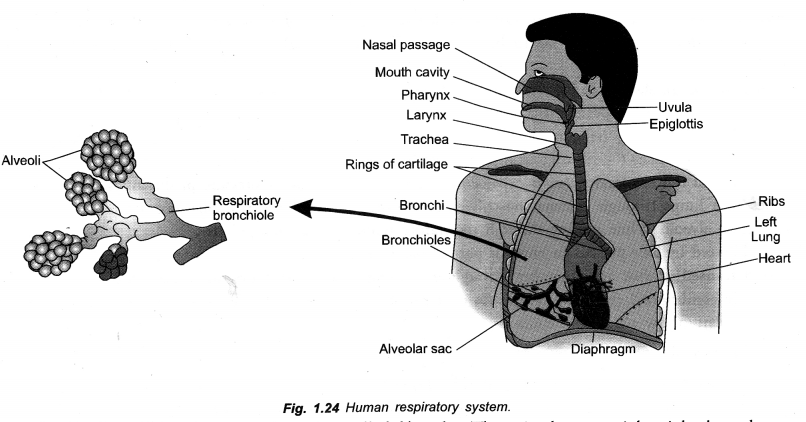
(b) Residual volume of air is the air left in the lungs after an exhalation or expiration. It is useful for continuous exchange of gases between blood and alveolar air.
Question 32.
(a) Draw a sectional view of human heart and label on it
- Pulmonary artery
- Right auricle
- Vena cava
- Pulmonary vein,
(b) Explain why ventricles have thick muscular walls than the atria ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
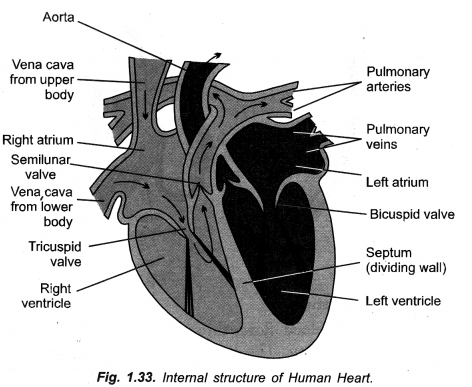
(b) Atria are to receive blood from veins and pump the same into adjacent ventricles only. They have, therefore, thin walls. Ventricles are to pump blood into arteries forcefully as it is to be sent to lungs (right ventricle) and all parts of the body (left ventricle). Therefore, walls of ventricles are thick and muscular with those of left ventricle being thicker.
Question 33.
Draw a neat diagram of a section of human heart. Name and label the following on the diagram
(a) Structure/ part that divides the heart into right and left halves and prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
(b) Part which prevents backflow of blood
(c) Chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body
(d) Chamber from where oxygenated blood is pumped out to various parts of the body.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
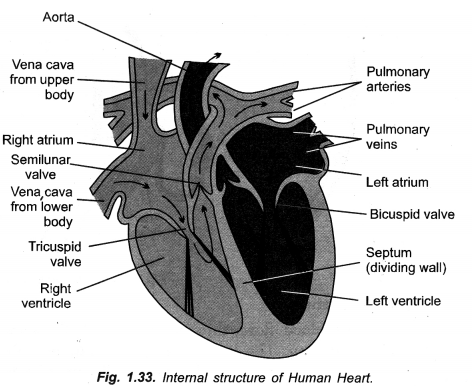
(a) Septum
(b) Valves
(c) Right auricle
(d) Left ventricle.
Question 34.
(a) Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label
- Part where air is filtered by fine hair and mucus
- Part which terminates in balloon-like structures
- Balloon-like structures where exchange of gases takes place
- Part which separates chest cavity from abdominal cavity.
(b) Draw a diagram of human excretory system and label the following
- Part in which urine is produced
- Part which stores the Purpose. To collect excretory products for expulsion from body.
Answer:
(a)
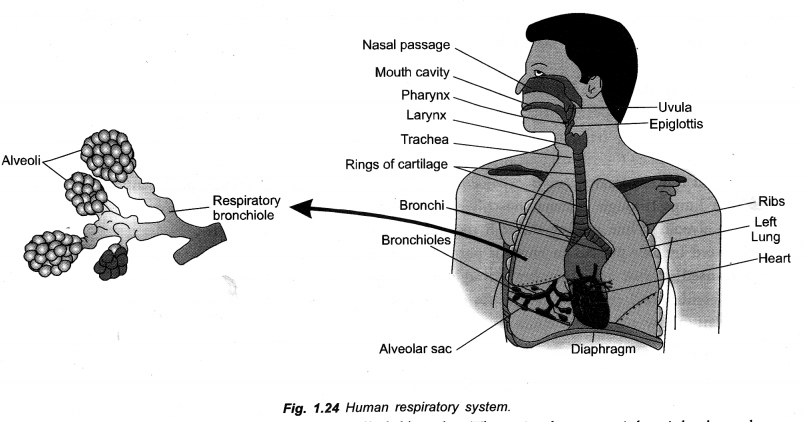
label
- Nasal chamber
- Trachea
- Alveoli
- Diaphragm.
(b)
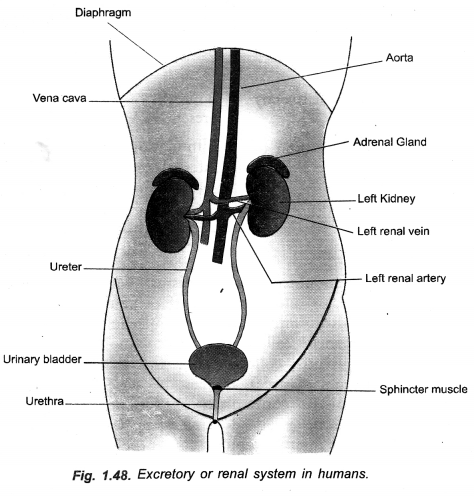
label
- Kidney
- Urinary bladder
- Ureter
- Urethra.
Question 35.
(a) Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba with the help of diagram. (CCE 2013, 2016)
(b) Explain how does Paramoecium obtain its food ? (CCE 2012)
(c) Name the form in which the following are stored :
- Unused carbohydrates in plants
- The energy derived from food in humans.
Answer:
(a) As soon as Amoeba comes in contact with a food particle, it put out pseudopodia around it, engulfs the same and forms a vesicle called phagosome. A lysosome fuses with phagosome to produce a food vacuole. Digestion occurs. The digested nutrients pass out into cytoplasm for assimilation. The food vacuole with indigestible material passes to the surface and throws out the undigested matter. Fig., 1-11 B and E.
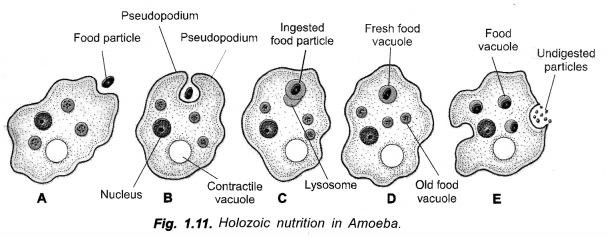
(b) Paramoecium creates a current in water with the help of cilia. The food particle passes into cytostome or cell mouth for engulfment and formation of food vacuole. The indigestible material passes out through a temporary opening called cytopyge.
(c)
- Starch
- ATP.
Question 36.
(a) What is the mode of nutrition in
- Fungi
- Amarbel (Cuscuta)
(b) Name the part of alimentary canal where
- Food is completely digested
- Secrete juice that has trypsin
- Secrete bile
- Absorbs water from unabsorbed food
(c) Mention the names of any two secretions by the gastric glands and state one role played by each in our body. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)
- Fungi. Heterotrophic, commonly saprophytic
- Amarbel (Cuscuta). Pleterotrophic, parasitic,
(b)
- Small intestine
- Pancreas
- Liver
- Large intestine,
(c)
- Pepsin — breakdown of proteins into peptones and proteoses,
- HCl — makes food soft, sterilised and acidified for pepsin to act upon it.
Question 37.
(a) List the major steps involved in formation of urine and state in brief their functions.
(b) State how is the process of breathing brought about in our body. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
(a) Major Steps in Urine Formation,
- Glomerular Filtration,
- Ultrafiltration of blood passing through urine
- Part which connects (i) and (ii).
- Part from which urine is passed out glomerule produces a dilute filtrate having most of the small volume solutes of plasma. It passes into Bowman’s capsule and then renal tubule,
- Formation of Urine. Useful solutes and a major part of water are reabsorbed while some waste products left in the blood are secreted into filtrate to form urine.
(b) Breathing In (Inhalation). Thoracic cavity enlarges due to
- Straightening of diaphragm by contraction of phrenic muscles
- Upward and outward expansion of ribcage due to contraction of external intercostal muscles. Enlargement of thoracic cavity causes expansion of lungs and decrease in air pressure in them. Outside air rushes into lungs to equalise pressure.
Question 38.
(a) List in tubular form two ways in which transpiration is different from translocation,
(b) Why do plants have a slow transport system ?
(c) What are stomata ? What function do they perform ? With the help of diagram explain opening and closing of stomata. (CEE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Differences
| Transpiration | Translocation |
| 1. Activity. It is loss of water in the vapour form from aerial parts of the plant.
2. Function. It helps in cooling the sun heated aerial parts as well as create a negative pressure for ascent of sap. |
1. It is transport of materials inside the plant from one part to another.
2. It passes nutrients from source to sink region. |
(b) Plants Have Slow Transport System. Plants are fixed. Most of their body is made of dead cells. Energy requirement is less. Therefore, plants have slow transport system.
(c) Stomata: Carbon dioxide is absorbed during night when stomata are open. It is fixed in malic acid from which the same is released during day time for performing Calvin cycle in light and draw Fig. 1.4.
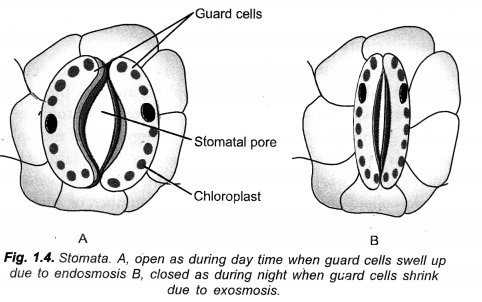
Question 39.
Draw a neat diagram of human excretory system and label
(a) Renal artery and
(b) Urethra on it. State the function of renal artery, kidney, ureter and urinary bladder. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
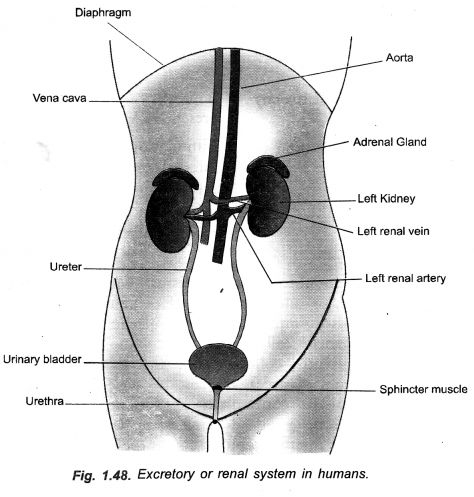
Functions:
Renal Artery: Bringing oxygenated blood laden with waste products.
Kidney: Excretion of nitrogenous and other waste products, regulation of salt content, blood pressure and water balance.
Ureter: Taking urine from kidney to urinary bladder.
Urinary Bladder: Storage of urine.
Question 40.
What is lymph ? How is composition of lymph different from blood plasma ? What is the direction of its flow ?
List two functions of lymphatic system. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Lymph: It is a colourless or slightly yellowish viscous fluid which is derived from tissue fluid and is present inside special tubes called lymph vessels.
Difference Between Lymph and Blood Plasma
| Lymph | Blood Plasma |
| 1. Water. It is 94%
2. Protein. Protein content is 3.0-4.5% 3. Fibrinogen. It is low. 4. Albumin/Globulin Ratio. It is 1.5 5. Food and Waste Materials. Lymph is rich in them. |
1. It is 92%.
2. Protein content is 6-8%. 3. Fibrinogen content is high. 4. It is unity. 5. The content is comparatively lower. |
Direction of Flow: Lymph flows from tissues to subclavian veins—It is unidrectional.
Functions of Lymphatic System:
- Lymph functions as a middleman that exchanges materials between blood and tissue fluid.
- Maintenance of Blood Volume. Blood volume continues to decrease due to filtration of blood plasma from blood capillaries. Lymph collects the same and puts it back into blood.
- They mature inside the lymph nodes and released into lymph passing through the same.
- Tissue Secretions. Hormones, macromolecules, plasrha proteins and other secretions of the tissues are first poured into lymph for passage into blood.
- Lymph picks up digested fat from alimentary canal for pouring into blood.
- Wastes from tissues are first passed into lymph before they are poured into blood for separation in kidneys.
- Lymph capillaries are specialised to attract and localise germs. The germs are taken to lymph nodes for destruction.
Question 41.
Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label
- Organ that is surrounded by cartilaginous rings
- Structure where exchange of gases takes place
- Voice box
- Muscular structure which flattens during inhalation. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
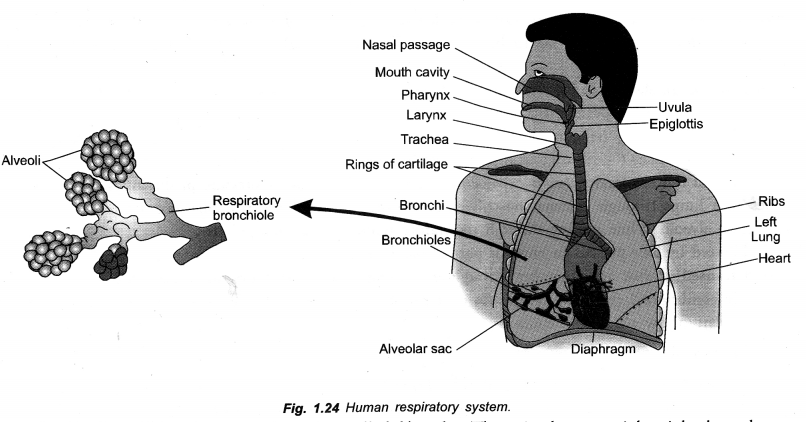
- Trachea
- Alveoli
- Larynx
- Diaphragm.
Question 42.
(a) Bile does not contain any digestive enzyme, yet it is important for digestion of food
(b) Name the products formed after complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats in small intestine. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Role of Bile in Digestion.
- Breaking of fat into fine globules or emulsification,
- Neutralisation of acidity and making food alkaline for action of pancreatic and other enzymes.
(b) Carbohydrates: Glucose.
Proteins: Amino acids.
Fats: Fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 43.
(a) Draw a diagram of human respiratory system and label Trachea, Bronchi, Diaphragm.
(b) Give reasons
- Lungs always contain residual volume,
- Nostrils are lined with mucus. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a)
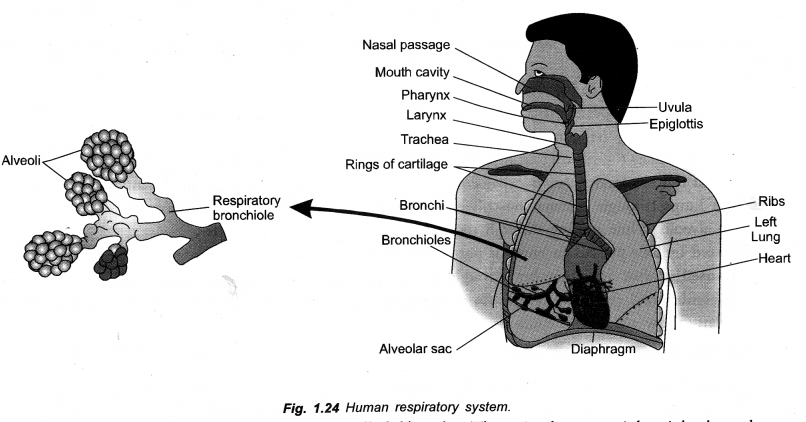
(b)
- Lungs always contain residual volume due to presence of cartilaginous rings and surfactant in its components,
- To trap dust particles and microbes.
Question 44.
(a) Draw a well labelled diagram of heart showing major arteries and veins
(b) What is selective reabsorption and how does it take place ?
Answer:
(a)
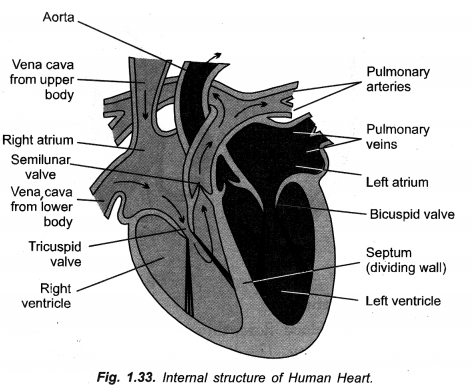
(b) Selective Reabsorption. It is reabsorption of useful substances (e.g., glucose, amino acids, vitamin C, Ca, K) from glomerular or nephric filtrate by walls of nephrons and peritubular capillaries. Selective reabsorption occurs by both active and passive processes.
Question 45.
(a) Draw a well labelled diagram of nephron
(b) Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a)
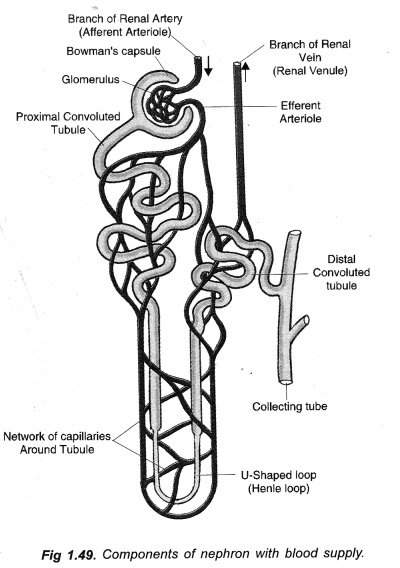
(b)
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| 1. Method: It is the common method of respiration. | It occurs permanently only in a few organisms. In others it may occur as a temporary measure to overcome shortage of oxygen. |
| 2. Steps: It is completed in 3 steps—glycolysis, Krebs cycle and terminal oxidation. | There are two steps— glycolysis and anaerobic breakdown of pyruvic acid. |
| 3. Oxygen: It requires oxygen. | Oxygen is not required. |
Question 46.
(a) Explain the process of digestion of proteins in the stomach and small intestine.
(b) How is small intestine designated to absorb digested food. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a)
- In Stomach. Pepsin of gastric juice acts on proteins in acidic medium. It converts proteins into peptones and proteoses.
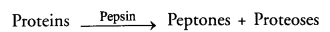
- In Intestine. Trypsin of pancreatic juice acts on proteins, peptones and proteoses in alkaline medium to form peptides.
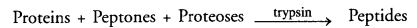
Erepsin or peptidases of intestinal juice acts on peptides of form amino acids. The latter are absorbed.
(b) Small intestine is lined by epithelium which is specialised to absorb. It has mechanisation to increase its absorbing surface area several times,
- Villi: They are transverse folds of intestine wall that not only increase surface area but also reach deep into the lumen of intestine for absorption of digested food. Villi possess blood capillaries and lacteals (lymph vessels) for quick transport of absorbed food,
- Microvilli: The columnar cells of the intestinal epithelium have fine microscopic outgrowths called microvilli. Microvilli increase the surface area of epithelial cells.
Question 47.
(a) What are stomata ? What function do they perform ?
(b) With the help of diagram explain opening and closing of stomata. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Stomata:
Stomata are minute pore complexes found on the surface of leaves and other soft aerial parts. Each stomate has two small specialised chloroplast containing epidermal cells called guard cells. All other epidermal cells are large and without chloroplasts. The structure of guard cells is such (kidney shaped, dumb-bell shaped) that their swelling creates a pore in between them while their contraction closes the pore. The pore is called stoma or stomatal aperture.
Function. By developing pores, stomata perform
- Gaseous exchange
- Transpiration.
(b) Opening and Closing:
Opening and closing of stomata is regulated by gain or loss of turgidity of their guard cells. During opening of stomata, guard cells withdraw K+ ions from surrounding epidermal cells, followed by absorption of water from them. As a result, guard cells swell up and become turgid. Their outer thin and elastic walls bend outwardly followed by outward movement of thicker inner walls. The latter creates a pore in between the two guard cells.
During closure movement of stomata, guard cells send out K+ ions. Water also passes out. Guard cells become flaccid. Their inner thick walls come to touch each other. The stomatal pore gets closed.
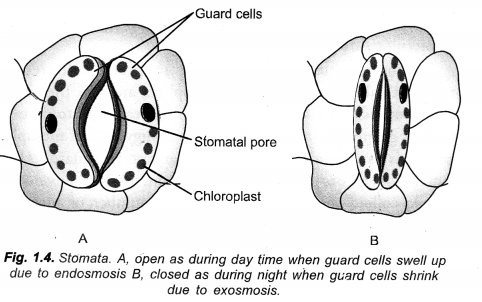
Question 48.
- Draw a neat sectional diagram of human heart and label — right ventricle, septum.
- Name the artery which carries deoxygenated blood.
- Name the chamber of heart which receives oxygenated blood.
- Why are walls of the ventricles thicker than the auricles ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
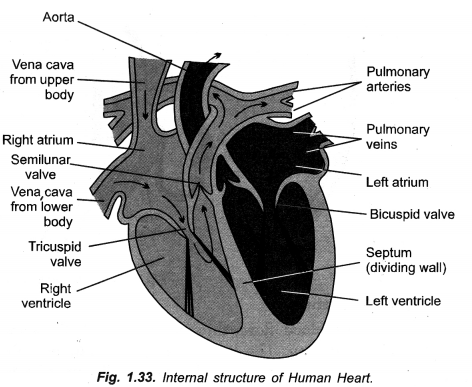
- Pulmonary artery
- Left atrium
- Atria are to receive blood from veins and pump the same into adjacent ventricles only. They have, therefore, thin walls. Ventricles are to pump blood into arteries forcefully as it is to be sent to lungs (right ventricle) and all parts of the body (left ventricle). Therefore, walls of ventricles are thick and muscular with those of left ventricle being thicker.
Question 49.
Mention the location of four major glands associated with digestive system of humans and explain function of each. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
- Salivary Glands. Three pairs — Parotid below ears, submaxillary (at the angles of lower jaw) and sublingual (below tongue). Secrete saliva which moistens the food, disinfects food by lysozyme and digests starch/glycogen partially.
- Gastric Glands. Inside stomach. Secrete HCI (for acidification and disinfection of food) and pepsin (for partial digestion of proteins to form peptones and proteoses).
- Liver. Right upper side of abdomen below the diaphragm. Secretes bile, which neutralises the acidity of chyme and emulsifies fat.
- Pancreas. Lies in the loop of duodenum below the stomach. Secretes three types of digestive enzymes— proteolytic trypsin, amylolytic amylase (amylopsin) and lipolytic lipase (steapsin). All of them function in alkaline medium.
Question 50.
(a) Draw a sectional view of human heart and label the following parts on it : Pulmonary artery, right atrium, left ventricle, septum.
(b) What do the following transport :
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Pulmonary vein
- Vena cava. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a)
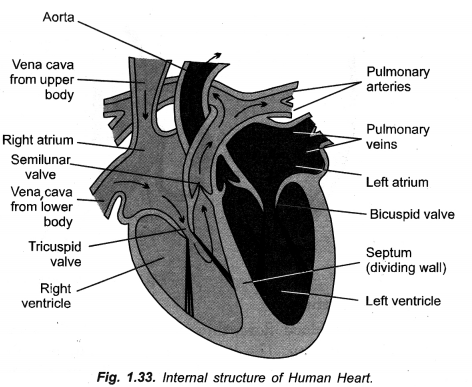
(b)
- Xylem. Sap (Water + mineral salts)
- Phloem. Organic food or nutrients.
- Pulmonary Vein. Oxygenated blood.
- Vena Cava. Deoxygenated blood.
Question 51.
(a) Draw a diagram of human excretory system and label the following parts on it :
- Aorta
- Vena cava
- Urinary bladder
- Left kidney
(b) List two vital functions of kidney.
Answer:
(a)
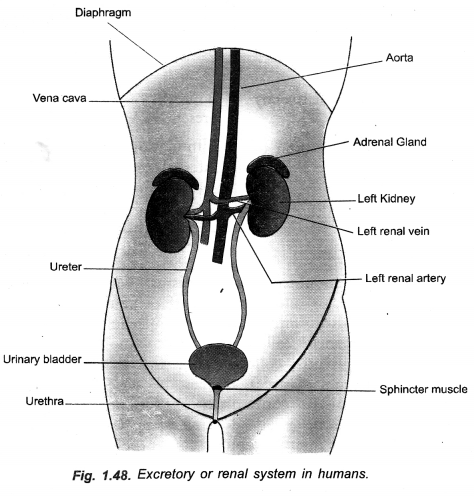
(b) Vital function of kidney:
- Elimination of metabolic waste products.
- Maintenance of water balance or osmoregulation of body.
Question 52.
(a) In the given representation of transport and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in human heart label the parts marked as a, b, c, d, e, and f.
(b) Write two points of difference between pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a)
- (a)—Pulmonary artery
- (b)—Lung capillaries
- (c) —Pulmonary vein
- (d)—Aorta
- (e) —Capillaries in body organs
- (f) —Vena cava.
(b)
| Pulmonary artery | Pulmonary vein |
| 1. Distance. It operates through short distance.
2. Flow. It is from heart to lungs and back. 3. Pumping. Blood is pumped by right ventricle and received by left auricle. „ 4. Oxygenation-Deoxygenation. Deoxygenated blood is pumped into lungs. Oxygenated blood is received from lungs. |
It operates through long distance.
It is from heart to body parts (other than lungs) and back. Blood is pumped by left ventricle and received by right auricle. Oxygenated blood is pumped into different body parts (other than lungs). Deoxygenated blood is received from body organs. |
Question 53.
(a) It was found that the leaves of a plant started getting wilted. Name the tissue which might have been blocked. State the role of this tissue in plants.
(b) Explain opening and closing of stomata with the help of labelled diagrams.
(c) Name the physical phenomenon by which exchange of gases occurs between plant body and atmosphere.
(CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Xylem. Role-
- Conduction of sap through its tracheary elements,
- Mechanical strength.
(b) Opening and closing of stomata is regulated by gain or loss of turgidity of their guard cells. During opening of stomata, guard cells withdraw K+ ions from surrounding epidermal cells, followed by absorption of water from them. As a result, guard cells swell up and become turgid. Their outer thin and elastic walls bend outwardly followed by outward movement of thicker inner walls. The latter creates a pore in between the two guard cells.
During closure movement of stomata, guard cells send out K+ ions. Water also passes out. Guard cells become flaccid. Their inner thick walls come to touch each other. The stomatal pore gets closed.
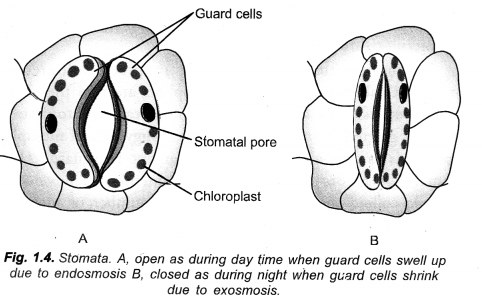
(c) Diffusion.
Question 54.
(a) Draw sectional view of the human heart and label the following parts on it :
Pulmonary artery, right artium, left artium, septum.
(b) What do the following transport
- Xylem
- Phloem
- Pulmonary vein
- Vena cava ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a)
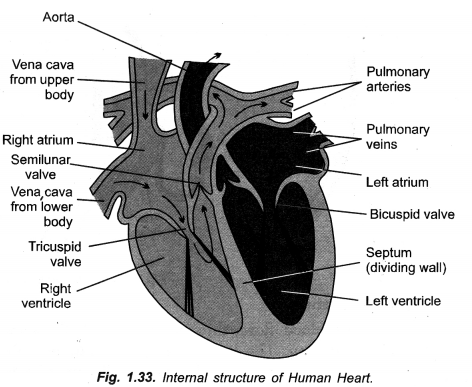
(b)
- Xylem: Transport of sap (water + minerals),
- Phloem: Translocation of nutrients.
- Pulmonary Vein: Oxygenated blood from lungs to heart,
- Vena Cava: Deoxygenated blood from all parts of body to heart.
Question 55.
(a) Explain how does the exchange of gases occur in plants across the surface of stem, roots and leaves.
(b) How are water and minerals transported in plants ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a)
- Old stem and old root. By diffusion through lenticels which possess intercellular spaces amongst complementary cells for exchange of gases between atmosphere and stem interior.
- Young root. By diffusion between root interior and soil interspaces through the epiblema root hair
complex in young roots. - Young stem and leaves. Diffusion across stomata between atmosphere and intercellular spaces.
(b) Transport of water and minerals.
Water and minerals absorbed by the plant roots are passed into xylem as sap. Sap present in xylem is under tension or negative pressure as mesophyll and other cells of aerials parts lose water to the outside through transpiration.
Development of Negative Pressure. Loss of water by mesophyll and other cells of aerial parts in transpiration increases their suction pressure. They withdraw water from xylem channels. As there are billions of transpiring mesophyll cells withdrawing water from xylem channels, water present in xylem comes under negative pressure of 10-20 atmospheres. However, water column does not break due to
- Cohesive force amongst water molecules and
- Adhesion force between walls of xylem channels and water moecules.
Rise of Sap (Water and Minerals): Tension or negative pressure of water column results in upward pull just as cold-drink is sucked with the help of straw pipe. Since it develops due to transpiration, it is called transpiration pull. The mechanism of this ascent of sap was put forth by Dixon and Joly in 1894.
Question 56.
(a) The upward movement of water normally requires a pump in our houses, but in tall trees water rises up without any external support. Explain the mechanism.
(b) State three points of difference between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem tissues.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) Water and minerals absorbed by the plant roots are passed into xylem as sap. Sap present in xylem is under tension or negative pressure as mesophyll and other cells of aerials parts lose water to the outside through transpiration.
Development of Negative Pressure. Loss of water by mesophyll and other cells of aerial parts in transpiration increases their suction pressure. They withdraw water from xylem channels. As there are billions of transpiring mesophyll cells withdrawing water from xylem channels, water present in xylem comes under negative pressure of 10-20 atmospheres. However, water column does not break due to
- Cohesive force amongst water molecules and
- Adhesion force between walls of xylem channels and water moecules.
Rise of Sap (Water and Minerals). Tension or negative pressure of water column results in upward pull just as cold-drink is sucked with the help of straw pipe. Since it develops due to transpiration, it is called transpiration pull. The mechanism of this ascent of sap was put forth by Dixon and Joly in 1894.
(b)
| Xylem |
Phloem |
| 1. Direction. In xylem transport is unidirectional, mostly in the upward direction.
2. Tension. Transport occurs due to negative pressure or tension. 3. Cells. Nonliving cells, vessels and tracheids, take part in transport. |
1. In Phloem transport occurs both in upward and downward directions.
2. Transport occurs due to positive pressure. 3. Living cells, sieve tube cells, take part in transport. |
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.