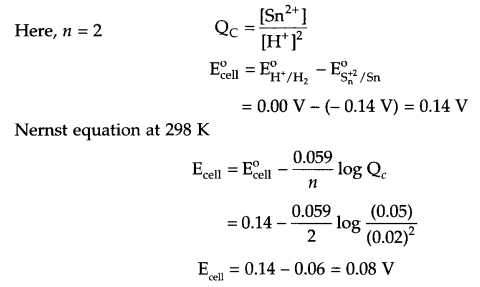
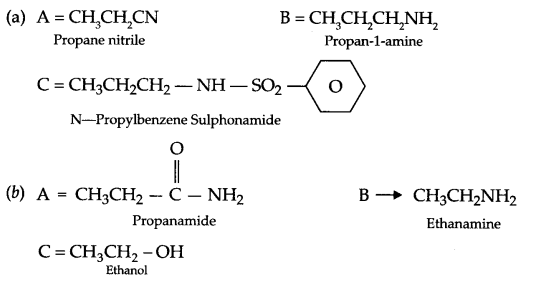
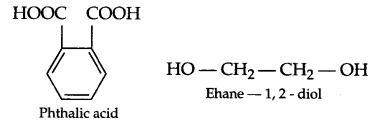
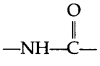These Sample papers are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Paper 4
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Paper 4
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Geography |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 4 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 4 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Geography is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- There are 22 questions in all.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question numbers 1-7 are very short answer questions carrying 1 mark each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 40 words.
- Question numbers 8-13 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Out of which one question is a value based question. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 80-100 words.
- Question numbers 14-20 are long answer questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 150 words.
- Question numbers 21 and 22 are related to identification or locating and labelling of geographical features on maps carrying 5 marks each.
- Outline maps of the World and India provided to you must be attached within your answer book.
- Use of templates or stencils for drawing outline maps is allowed.
Questions
Question 1.
Name the area which has now become the rust bowl of the U.S.A.
Question 2.
Give the meaning of ‘ports of call’ with suitable example.
Question 3.
Explain the term bilateral trade.
Question 4.
Define the term poverty.
Question 5.
Name the two broad categories of reasons responsible for migration in India.
Question 6.
Name the sea port which was developed as satellite port to relieve the pressure at the Mumbai Port.
Question 7.
State any two sources of air pollution.
Question 8.
Explain any three characteristics of extensive commercial grain cultivation in the world.
Question 9.
Mention any three characteristics of retail trading services.
Question 10.
“Slavery was a curse.” Justify the statement.
Question 11.
Explain the economic significance of river Rhine in three points.
Question 12.
Cultural activities such as pilgrimage, religious fairs, tourism cause water pollution. By which human values such activities may be minimised/controlled.
Question 13.
Describe any three characteristics of hamlet rural settlement in India.
Question 14.
Describe any five features of plantation agriculture in the world.
Question 15.
Road transport plays a vital role in the promotion of trade and tourism in the world. Support this statement with the suitable arguments
Question 16.
Name the first city of a million population in the world. Describe any two characteristics of administrative and cultural towns.
Question 17.
Define the term ‘growth of population’. Explain any four causes for the steady growth of population in India in the decades 1921-1951.
Question 18.
Explain the important factors which influenced the location of Rourkela Steel Plant.
Question 19.
“Maize is a food as well as fodder crop”. Discuss.
Question 20.
Explain the advantages of satellite communication with reference to India.
Question 21.
Identify the five geographical features shown on the given political outline map of the world as A, B, C, D and E and write their correct names on the lines marked near them with the help of the following information.
(A) A large country of the size of continent in term of area
(B) A mega city
(C) A major area of nomadic herding
(D) A sea port
(E) An International airport.
Question 22.
Locate and label the following five features with appropriate symbols on the given political outline map of India.
(i) A state having highest gender ratio.
(ii) A leading producer state of Rice.
(iii) An oil refinery situated in Gujarat
(iv) An international airport of Assam.
(v) A software technology park situated in Jammu & Kashmir.
Answers
Answer 1.
North Aplacian (Pittsburg)
Answer 2.
These are the ports which originally developed as calling points on main sea routes where
ships used to anchor for refuelling, watering and taking food items. Aden and Singapore are good examples.
Answer 3.
Bilateral trade is done by two countries with each other and enter into agreement to trade specified commodities amongst them.
Answer 4.
Poverty is a state of deprivation. In absolute terms it reflects the inability of an individual to satisfy certain basic needs for a sustained, healthy and reasonably productive living.
Answer 5.
(i) Push factors
(ii) Pull factors
Answer 6.
Jawaharlal Nehru Port
Answer 7.
(i) Combustion of fossil fuels.
(ii) Mining and Industries.
Answer 8.
(i) It is practised in the interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid latitudes.
(ii) Wheat is the principal crop though other crops like com, barley, oats and rye are also grown.
(iii) The size of the farm is very large. Entire operations of cultivation from ploughing to harvesting are mechanised. There is low yield per acre but high yield per person.
Answer 9.
(i) This is the business activity concerned with the sale of goods directly to the consumers.
(ii) Most of the retail trading takes place in fixed establishments or stores solely devoted to selling.
(iii) Street peddling, handcarts, trucks, door-to-door, mail order, telephone, automatic vending machines and Internet are examples of non-star retail trading.
Answer 10.
(i) 15th century onwards the European colonialism began and along with trade of exotic commodities, a new form of trade emerged known as slave trade.
(ii) The Portuguese, Dutch, Spaniards and British captured African natives and forcefully transported them to the newly discovered America for their labour in plantation.
(iii) Slave trade was a lucrative business for more than two hundred years till it was abolished.
Answer 11.
(i) It flows through a rich coal field and the whole basin has become a prosperous manufacturing area.
(ii) Huge tonnage moves along the stretch south of the Ruhr.
(iii) It connects the industrial areas of Switzerland, Germany, France, Belgium and the Netherlands with the North Atlantic Sea route.
Answer 12.
(i) Eco-friendly
(ii) Awakening
(iii) Cooperation
Answer 13.
(i) These settlement are fragmented into several units physically separated from each other bearing common name.
(ii) These units are locally called panna, para, palli, nagla, dhani etc.
(iii) This segmentation of a village is often motivated by social and ethnic factors.
Answer 14.
(i) This type of farming are large estates or plantation; large capital investment; managerial and technical support.
(ii) Single crop specialisation, cheap labour, and a good system of transportation which links the states to the factories and markets for the export of the products.
(iii) Important plantation on crops are tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber, cotton, oil palm, sugarcane, bananas and pineapples.
(iv) Plantation agriculture as mentioned above was introduced by the Europeans in colonies situated in the tropics.
(v) Now, ownership of the majority of plantations has passed into the hands of the government.
Answer 15.
(i) Road transport is the most economical for short distances compared to railways. It also provides door-to-door service.
(ii) Road transport is most suitable for tourists and they could observe the natural sites through them easily.
(iii) The quality of the roads varies greatly between developed and developing countries as road construction and maintenance require heavy expenditure.
(iv) Roads are universal and provide long distance links. Inter-state highways are used for speedy movement.
(v) Lorries of increasing size and power to carry heavy loads are common in increasing the trade as well as tourism.
Answer 16.
(a) London
(b) (i) National capitals, which house the administrative offices of central governments—
New Delhi, Washington are called administrative towns.
(ii) Provincial towns can also have administrative functions as Victoria, Mumbai, Bangalore (Bangluru).
(c) (i) All over the world many places (towns) are known as pilgrimage, where people visit for religious and other cultural activities. Varanasi, Mecca are the best example.
(ii) Some towns are known for their cultural activities (Movies, Drama, Literature, festivals etc). Jaipur, Panaji, Miami are the main centres.
Answer 17.
(a) Growth of population is the change in the number of people living in a particular area between two points of time.
(b) (i) An overall improvement in health and sanitation, brought down the mortality rate
(ii) Better transport and communication system improved distribution system.
(iii) The crude birth rate remained high in this period leading to higher growth rate..
(iv) Life expectancy increased.
Answer 18.
(i) It was set up in 1959. The plant was located on the basis of proximity to materials to minise the cost of transporting weight-losing material.
(ii) This plant has a unique locational advantage.
(iiii) It receives coal from Jharia and Iron ore from Sundargarh and Kandujhar.
(iv) The Hirakund project supplies power for the electric furnaces.
(v) Water is being obtained from Koel and Sankh rivers.
Answer 19.
(i) Maize is a food as well as fodder crop grown under semi arid climate condition and in the
inferior soils.
(ii) This crop occupies only about 3.6% of total cropped area. Its cultivation is not concentrated in any specific region.
(iii) It is sown all over India except eastern and north-eastern regions.
(iv) The leading producers of maize are the states of Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
(v) Yield level of maize is higher than other coarse cereals. It is high in southern states and declines towards central parts.
Answer 20.
(i) Satellites are mode of communication in themselves as well as they regulate the use of other means of communication.
(ii) The use of satellite in getting a continuous and synoptic view of larger area has made If satellite communication very vital for the country due to the economic and strategic reasons.
(iii) Satellite images can be used for the weather forecast, monitoring of natural calamities surveillance of border areas.
(iv) Satellites collect data in several spectral bonds and transmit them to the ground stations for various uses.
(v) The National Remote Sensing Agency at Hyderabad provides facilities for acquisition of data and its processing. These are very useful in the management of natural resources.
Answer 21.

Answer 22.

We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Paper 4 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Paper 4, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.