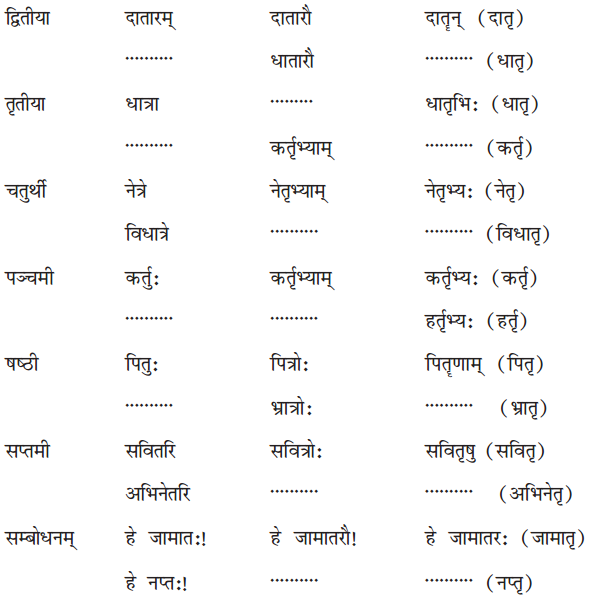
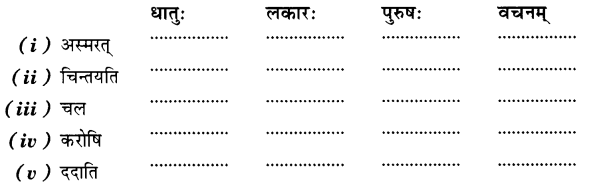
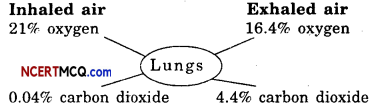
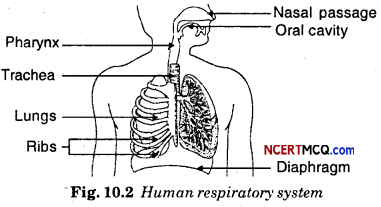
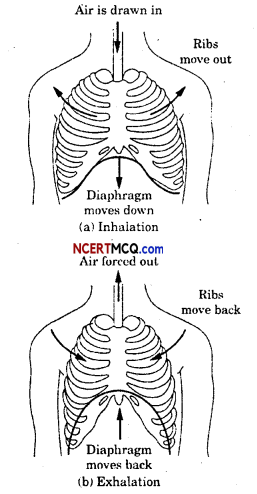
By going through these Online Education CBSE Class 7 Sanskrit Notes Chapter 9 अहमपि विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि Summary, Notes, word meanings, translation in Hindi, students can recall all the concepts quickly.
Online Education for Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 9 अहमपि विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि Summary Notes
अहमपि विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि पाठ का परिचय
प्रस्तुत पाठ के माध्यम से बाल मजदूरी के विरोध में जन जागरूकता उत्पन्न करने का प्रयास किया गया है। साथ-साथ इसे गैर कानूनी बताते हुए शिक्षा के अधिकार से विद्यार्थियों को अवगत कराया गया है।
अहमपि विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि Summary
प्रस्तुत नाटक के माध्यम से बालशोषण का विरोध दर्शाकर उनके शिक्षा के मौलिक अधिकार का ज्ञान कराया गया है। एक अल्पवयस्का बालिका से गृहकार्य करवाना अनुचित है। अतः मालिनी दर्शना को कहती है कि यह समय तो उसकी अल्पवयस्का पुत्री के पढ़ने और खेलने का है तो दर्शना कहती है कि उसकी पुत्री एक परिवार का समस्त गृहकार्य करती थी। धनाभाव के कारण उन्हें यह सब करना पड़ता हैं क्योंकि उसका बीमार पति कुछ भी काम नहीं करता।

तो मालिनी दर्शना को समझाती है कि शिक्षा बच्चों का मौलिक अधिकार है। बच्चों की शिक्षा के लिए सरकारी विद्यालयों में निःशुल्क शिक्षा, निःशुल्क परिधान, पुस्तकें, स्कूलबैग, जूते, दोपहर का भोजन और छात्रवृत्ति आदि दी जाती है। यह सुनकर दर्शना की पुत्री खुशी से ताली बजाकर नाचती है और कहती है कि मैं भी विद्यालय जाऊँगी और मालिनी के प्रति कृतज्ञता प्रकट करती है।

अहमपि विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि Word Meanings Translation in Hindi
(क) मालिनि – (प्रतिवेशिनी प्रति) गिरिजे! मम पुत्रः मातुलगृहं प्रति प्रस्थितः काचिद्
अन्यां कामपि महिला कार्यार्थं जानासि तर्हि प्रेषय।
गिरिजा – आम् सखि! अद्य प्रातः एव मम सहायिका स्वसुतायाः कृते कर्मार्थं पृच्छति स्म।
श्वः प्रातः एव तया सह वार्ता करिष्यामि।
(अग्रिमदिने प्रातः काले षट्वादने एव मालिन्याः गृहघण्टिका आगन्तारं कमपि सूययति मालिनी
द्वारमुदघाटयति पश्यति यत् गिरिजायाः सेविकया दर्शनया सह एका अष्टवर्षदेशीय, बालिका तिष्ठति)
सरलार्थः
मालिनी – (पड़ोसिनी से) हे गिरिजा! मेरा पुत्र मामा के घर गया है, किसी दूसरी महिला (औरत)
को काम के लिए जानती हो तो भेजो।।
गिरिजा – हाँ सखी! आज सुबह ही मेरी नौकरानी (सहायिका) अपनी बेटी के लिए काम हेतु पूछ
रही थी। कल सुबह ही उसके साथ बात करूँगी। (अगले दिन सुबह छह बजे ही मालिनी के घर की घंटी किसी आने वाले की सूचना देती है, मालिनी दरवाजा खोलती है कि गिरिजा की नौकरानी दर्शना के साथ एक आठ वर्ष की, लड़की खड़ी है)
English Translation :
Malini – (To her neighbour) Hey, Girijja! My son has gone to the house of maternal uncle. If you know the other woman for domestic work, send her.
Girijja – Yes, friend. Today in the morning my maid was asking for work for her daughter. I shall talk to her tomorrow in the morning only. (Next day at 6 : 00 AM only, the bell filled at the house of Malini rings to inform the arrival of someone. Malini opens the door and finds that a girl of eight years is standing with Darshana who is the maid of Girijja)
शब्दार्थाः (Word Meanings) :
प्रतिवोशिनीम्-पड़ोसिनी (neighbour)। मातुलगृहम्-मामा के घर (house of maternal uncle)। प्रति-की ओर (towards)। प्रस्थितः-चला गया है (went away)। काचिद्-कोई (any)। अन्याम्-दूसरी (another)। कार्यार्थम्-काम के लिए (for work)। तर्हि-तो (then)। प्रेषय-भेजो (send)। कमपि-किसी को भी (anyone)। सूचयति-सूचना देती है (informs)| द्वारम् उद्घाटयति-दरवाज़ा खोलती है (opens the door)। प्रातः-सुबह (morning)। सहायिका-नौकरानी (maid)। स्वसुतायाः कृते-अपनी बेटी के लिए (for one’s daughter)। कर्मार्थम्-काम के लिए (for work)। पृच्छति स्म-पूछ रही थी (was asking)। श्व:-कल (आने वाला) (tomarrow)। तया सह-उसके साथ (with him/her)। अग्रिमदिने-अगले दिन (next day)। षट्वादने-छह बजे (at 6 o’ clock)। गृहघण्टिका-घट की घंटी (bell of the house)। आगन्तारम्-आने वाले को (visitor)। अष्टवर्षदेशीया-आठ वर्ष वाली (eight years of age)।
सन्धिविच्छेदः
कमपि – काम् + अपि, कार्यार्थम् – कार्य + अर्थम्
कर्मार्थम् – कर्म + अर्थम्, द्वारमुद्घाटयति – द्वारम् + उद्घाटयति।
(ख) दर्शना – महोदये! भवती कार्यार्थं गिरिजामहोदयां पृच्छति स्म कृपया मम सुतायै अवसरं प्रदाय अनुगृह्णातु भवती।
मालिनी – परमेषा तु अल्पवयस्का प्रतीयते। किं कार्यं करिष्यत्येषा? अयं तु अस्याः अध्ययनस्य क्रीडनस्य च कालः।
दर्शना – एषा एकस्य गृहस्य संपूर्ण कार्यं करोति स्म। सः परिवारः अधुना विदेशं प्रति प्रस्थितः।
कार्याभावे अहमेतस्यै कार्यमेवान्वेषयामि स्म येन भवत्सदृशानां कार्य प्रचलेत् अस्मद्सदृशाना गृहसञ्चालनाय च धनस्य व्यवस्था भवेत्।
शब्दार्थाः (Word Meanings) :
भवती-आप (you)। कार्यार्थम्-काम के लिए (for work)। पृच्छति स्म-पूछ रही थीं (was asking)। कृपया-कृपा करके (kindly)। मम-मेरी (my)। सुतायै-बेटी के लिए (को) (for daughter)। अवसरम्-मौका (opportunity)। प्रदाय-देकर (by giving)| अनुगृह्णातु-कृपा करें (kindly)| अल्पवयस्का -कम उम्र वाली (minor)। प्रतीयते-दिख रही है (appears)। एषा-यह (this)। अध्ययनस्य-पढ़ाई का (of study)। काल:-समय (period)। एकस्य-एक (का) (one)। सम्पूर्णम्-सारा (whole)। करोति स्म-करती थी (used to do)। अधुना-इस समय (अब) (at this time)। प्रस्थित:-चला गया है (went away)। कार्याभावे-काम के न होने पर (on joblessness)। एतस्यै-इसके लिए (for this)। अन्वेषयामि स्म-ढूँढ रही थी (was searching)। येन-जिससे (so that)। भवत्सदृशानाम्-आप जैसों का (के) (people like you)। प्रचलेत्-चले (let us go)। अस्मद्सदृशाना-हमारे जैसों का (के) (people like us)। गृहसञ्चालनाय-घर को चलाने के लिए (to run our family)। व्यवस्था-व्यवस्था (इन्तज़ाम) (arrangement)। भवेत्-हो जाए। (may be managed)।
सरलार्थः
दर्शना – महोदया (मैडम)! आप काम के लिए गिरिजा जी (देवी) से पूछ रही थीं कृपया मेरी बेटी को मौका देकर आप उपकार करें।
मालिनी – परंतु यह तो कम उम्र की दिखाई देती है। क्या काम करेगी यह? यह तो इसके पढ़ने और खेलने का समय है।
दर्शना – यह एक घर का सारा काम करती थी। वह परिवार इस समय विदेश चला गया है। काम की कमी के कारण मैं इसके लिए काम ढूँढ रही थी जिससे आप जैसों का काम चले और हमारे जैसों के घर को चलाने के लिए धन की व्यवस्था हो जाए।
English Translation:
Darshana – (Madam)! you are asking Girijja Jee (Devi) for work. Kindly, give the opportunity to my daughter and oblige. Malini – But she appears to be a minor. What work can she do? This is the time for her study and play.
Darshana – She could complete the whole work of a house. At present that family has gone to some foreign country. On account of the scarcity of jobs. I was searching jobs for her, that may serve your purpose, and for people like us, money may be arranged to run our family.
सन्धिविच्छेदः-
करिष्यत्येषा – करिष्यति + एषा, कार्याभावे – कार्य + अभावे
अहमेतस्यै – अहम् + एतस्यै, कार्यमेवान्वेषयामि – कार्यम् + एव +
अन्वेषयामि, अस्मद्सदृशानाम् – अस्मत् + सदृशानाम्
(ग) मालिनी – परमेतत्तु सर्वथाऽनुचितम्। किं न जानासि यत् शिक्षा तु सर्वेषां बालकानां सर्वासां बालिकानां च मौलिकः अधिकारः।
दर्शना – महोदये! अस्मद् सदृशानां तु मौलिकाः अधिकाराः केवलं स्वोदरपूत्तिरेवास्ति। एतस्य व्यवस्थायै एव अहं सर्वस्मिन् दिने पञ्च-षड्गृहाणां कार्यं करोमि। मम रुग्णः पतिः तु किञ्चिदपि कार्यं न करोति। अतः अहं मम पुत्री च मिलित्वा परिवारस्य भरण-पोषणं कुर्वः। अस्मिन् महार्घताकाले मूलभूतावश्यकतानां कृते एव धनं पर्याप्तं न भवति तर्हि कथं विद्यालयशुल्कं, गणवेषं पुस्तकान्यादीनि क्रेतुं धनामानेष्यामि।
शब्दार्थाः (Word Meanings) :
परम्-परन्तु (but)। सर्वथा-पूरी तरह से (completely)। अनुचितम्-ठीक नहीं है (not proper)। मौलिकः-जन्मजात (मूलभूत) (natural)| अधि कार:-अधिकार (right)। अस्मद् सदृशानाम्-हमारे जैसों का (people like us)। स्वोदरपूर्तिः-अपना पेट भरना (to fill our stomac)। व्यवस्थायै-व्यवस्था के लिए (for arranging)। सर्वस्मिन्-सारा (whole)। दिने-दिन में (day)। पञ्च-षड्गृताणाम्-पाँच-छह घरों का (of five to six houses)। रुग्णः-बीमार (ill)। किञ्चित्-अपि-कुछ भी (nothing)। मिलित्वा-मिलकर के (मिल् + क्त्वा) (together with)। अस्मिन्-इस (this)। महार्घतावाले-मँहगाई के समय में (time of dearness)। मूलभूत-आवश्यकतानाम् कृते-मूलभूत (ज़रूरी) ज़रूरतों के लिए (for basic needs)। पर्याप्तम्-काफ़ी (sufficient)। तर्हि-तो (then)। विद्यालयशुल्कम्-स्कूल की फ़ीस (school fees)। गणवेषम्-युनिफ़ार्म (uniform)। आदीनि-आदि को (etc)। क्रेतुम्-खरीदने के लिए (क्री+तुमुन्) (for purchasing)। आनेष्यामि-लाऊँगी, (shall bring)। कथम्-कैसे (how)।
सरलार्थः
मालिनी – परन्तु यह तो पूरी तरह से अनुचित (ठीक नहीं) है। क्या तुम नहीं जानती हो कि शिक्षा तो सभी लड़कों और सभी लड़कियों का मूलभूत (स्वाभाविक) अधिकार है।
दर्शना – देवी (मैडम)! हमारे जैसों का तो मूलभूत अधिकार केवल अपना पेट भरना ही है। इसकी व्यवस्था के लिए ही मैं सब दिन (पूरे दिन) में पाँच-छह घरों का काम करती हूँ। मेरे बीमार पति तो कुछ भी काम नहीं करते हैं। इसलिए मैं और मेरी बेटी मिलकर परिवार का भरण-पोषण (का काम) करते हैं। इस मँहगाई के समय में मूलभूत जरूरतों के लिए ही धन काफी नहीं होता है तो कैसे विद्यालय की फ़ीस, वेशभूषा (Uniform), पुस्तकें आदि को खरीदने के लिए धन लाएँगे।
English Translation:
Malini – But it is absolutely unfair (unreasonable). Do you have knowledge that education is the fundamental (natural) right of all boys and girls.
Darshana – Devi (Madam)! For people like us our fundamental is stomach only. For this helplessness only, I work for five to six houses the whale day. My ill husband does not do any work. Therefore my daughter and I maintain our family. In the age of this dearness, if money is not sufficient for basic needs, from where shall I get money for school fees, buying uniforms, books, etc?
सन्धिविच्छेदः –
सर्वथाऽनुचितम् – सर्वथा + अनुचितम्
स्वोदरपूर्तिरेवास्ति – स्व + उदरपूर्तिः + एव + अस्ति
षड्गृहाणाम् – षट् + गृहाणाम्
किञ्चिदपि – किम् + चित् + अपि
मूलभूतावश्यकतानाम् – मूलभूत + आवश्यकतानाम्
पुस्तकान्यादीनि – पुस्तकानि + आदीनि
धनमानेष्यामि – धनम् + आनेष्यामि।
(घ) मालिनी – अहो! अज्ञानं भवत्याः। किं न जानासि यत् नवोत्तर-द्वि-सहस्र (2009) तमे वर्षे सर्वकारेण सर्वेषां बालकानां, सर्वासां बालानां कृते शिक्षायाः मौलिकाधिकारस्य घोषणा कृता। यदनुसारं षड्वर्षेभ्यः आरभ्य चतुदर्शवर्षपर्यन्तं सर्वे बालाः समीपस्थं सर्वकारीयं विद्यालयं प्राप्य न केवलं नि:शुल्कं शिक्षामेव प्राप्स्यन्ति अपितु निःशुल्कं गणवेषं पुस्तकानि, पुस्तकस्यूतम्, पादत्राणाम्, माध्याह्नभोजनम्, छात्रवृत्तिम् इत्यादिकं सर्वमेव प्राप्स्यन्ति।
शब्दार्थाः (Word Meanings) :
अहो-अरे (hei!)। अज्ञानम्-अज्ञानता (foolishness)। भवत्याः -आपकी (your)। सर्वकारेण-सरकार के द्वारा (by government)। वर्षे-साल में (during years)। बालानां कृते-बच्चों के लिए (for children)। शिक्षायाः-शिक्षा के (for education)। मौलिकाधिकारस्य-मूल अधिकार की (of fundamental right)। यदनुसार-जिसके आधार पर (on which ground)। षड्वर्षेभ्यः-छह वर्षों से (from six years)। आरभ्य-शुरू होकर (beginning from)। चतुर्दशवर्षपर्चन्तम्-चौदह वर्षों तक के (till fourteen years)। समीपस्थम्-पास में स्थित (in the locality)। सर्वकारीयम्-सरकारी (government)। प्राप्य-पहुँचकर (जाकर) (on reaching)। निशुल्कम्-बिना फीस के (without fees)। प्राप्स्यन्ति-प्राप्त करेंगे (will get)। अपितु-बल्कि (but)। गणवेषम्-वर्दी (uniforms)। पुस्तकस्यूतम्-बस्ते को (for bags)। पादत्राणम्-जूते को (for shoes)। छात्रवृत्तिम्-वजीफे को (scholorship)। मध्याह्न भोजनम्-दोपहर के भोजन को (mid-day meal)। इत्यादिकम्-आदि
को (etc)। प्राप्स्यन्ति-पाएँगे (will get)।
सन्धिविच्छेदः –
नवोत्तर – नव + उत्तर
मौलिकाधिकारस्य – मौलिक + अधिकारस्य
यदनुसारम् – यत् + अनुसारम्
षडवर्षेभ्यः – षट् + वर्षेभ्यः
इत्यादिकम् – इति + अदिकम्
सरलार्थः
मालिनी अरे यह आपकी मूर्खता (नासमझी) है। क्या नहीं जानती हो कि सन् 2001 ई० वर्ष में सरकार ने सब बच्चों, सभी बच्चियों के लिए शिक्षा के मौलिक (स्वाभाविक) अधिकार की घोषणा की है। जिसके अनुसार छह वर्षों से लेकर चौदह वर्ष तक के सारे बच्चे पास के (पास स्थित) सरकारी स्कूल में जाकर न सिर्फ निशुल्क (without fee) पढ़ाई ही करेंगे बल्कि बिना फीस वर्दी (Uniform), पुस्तकें, बस्ते (Bags), जूते, दोपहर का भोजन और वज़ीफा (Scholar ship) आदि सभी कुछ पाएँगे।
English Translation :
Malini- Hei! it is you foolishness. Do you know that in 2001 the government declared education as fundamental right for all boys and girls. Accordingly, all the children above six to fourteen years of age will not only study free of cost in government school in their surrounding, but also get free uniforms, books, bags, shoes, mid-day meal and scholarship.
(ङ) दर्शना – अप्येवम् (आश्चर्येण मालिनी पश्यति)
मालिनी – आम्। वस्तुतः एवमेव।
दर्शना – (कृतार्थतां प्रकटयन्ती) अनुगृहीताऽस्मि महोदये! एतद् बोधनाय। अहम् अद्यैवास्याः
प्रवेशं समीपस्थे विद्यालये कारयिष्यामि। दर्शनायाःपुत्री- (उल्लासेन सह) अहं विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि! अहमपि पठिष्यामि! (इत्युक्त्वा
करतलवादनसहितं नृत्यति मालिनी प्रति च कृतज्ञतां ज्ञापयति)
शब्दार्थाः (Word Meanings) :
अप्येवम्-ऐसा भी है (it is so)। आश्चर्येण-आश्चर्य से (with surprise)। वस्तुतः-वास्तव में (really)। एवमेव-यही है (it is this)। कृतार्थताम्-आभार को (of obligation)। प्रकटयन्ती-प्रकट करती हुई (showing)। अनुगृहीता-आभारी (obliged)। बोधनाय-बताने के लिए (for explanation)। प्रवेशम्-प्रवेश को (for admission)। अद्य एव-आज ही (today only)। अस्याः -इसका (its/(her)। समीपस्थे-पास में स्थित (in the locality)। कारयिष्यामि-कराऊँगी (shall get)। उल्लासेन-खुशी से (के) (with joy)। सह-साथ (together with)। पठिष्यामि-पलूंगी (shall read)। इति-इस प्रकार (therefore)। उक्त्वा -कहकर (by saying)। करतलवादनसहितम्-तालियाँ बजाने के साथ (with clapping hands)। कृतज्ञताम्-आभार को (for gratefulness)। ज्ञापयति-प्रकट करती है (expresses)।
सन्धिविच्छेदः
अप्येवम् – अपि + एवम्
अनुगृहीताऽस्मि – अनुगृहीता + अस्मि
अद्यैवास्याः – अद्य + एव + अस्याः
इत्युक्त्वा – इति + उक्त्वा
मालिनीप्रति – मालिनीम् + प्रति
अहं विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि – अहम् + विद्यालयम् + गमिष्यामि
सरलार्थः
दर्शना – ऐसा भी है (आश्चर्य से मालिनी को देखती है)
मालिनी – हाँ! वास्तव में यही है।
दर्शना – (कृतार्थता) (धन्यवाद) को प्रकट करती हुई) मैडम! मैं आभारी हूँ। यह बताने के लिए। मैं आज ही इसका प्रवेश पास (निकट) स्थित विद्यालय में कराऊँगी।
दर्शना की बेटी – (खुशी के साथ) मैं विद्यालय जाऊँगी। मैं भी पढंगी! (ऐसा कहकर ताली बजाकर नाचती है और मालिनी के लिए आभार व्यक्त करती है)
English Translation :
Darshna – It is so! (looking at Malini with surprise)
Malini – Yes! In reality, it is so.
Darshna – (Expressing gratefulness and thanks) Madam! I am obliged for telling this fact. Today I shall get her admitted to the school in the locality.
Darshna’s daughter – (Happily) I shall go to school. I shall also study (by telling this, she dances with clapping hands and expresses gratefulness to Malini)