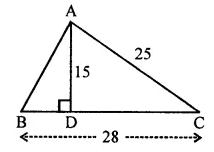
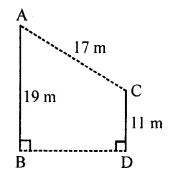
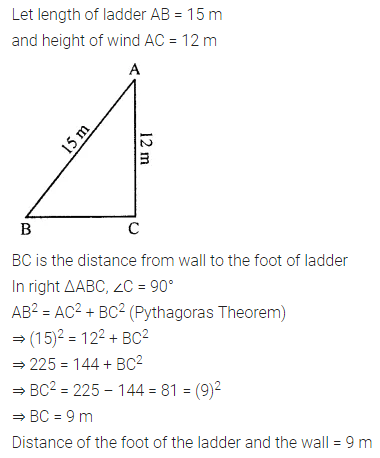
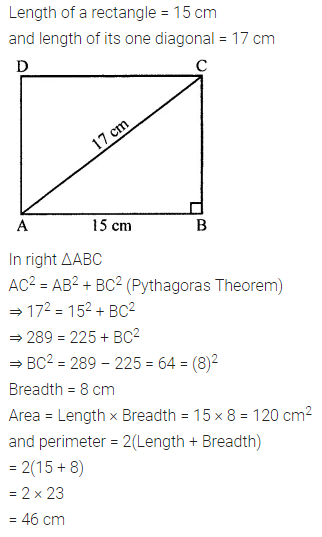
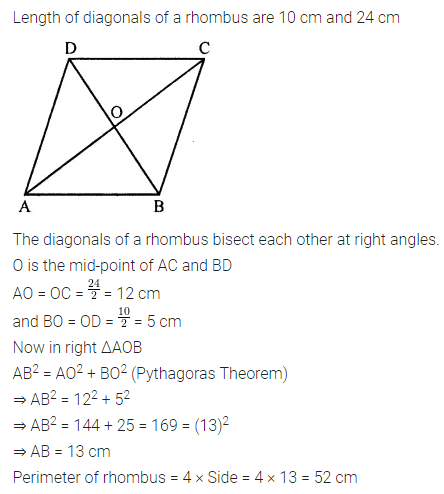
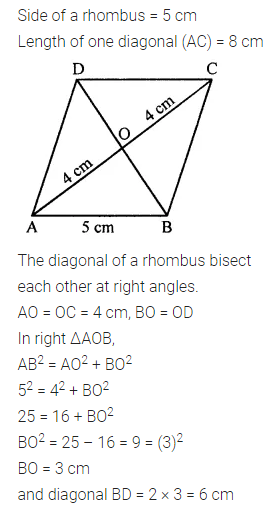
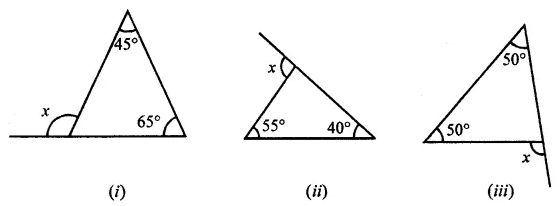
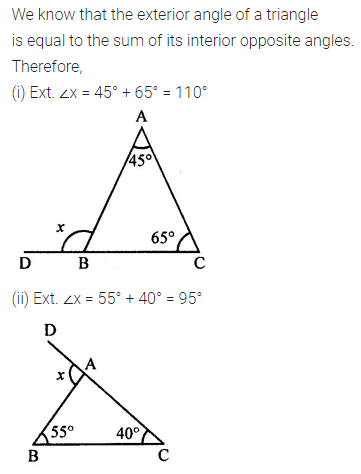
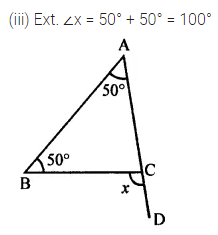
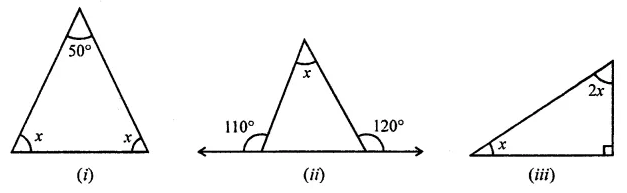
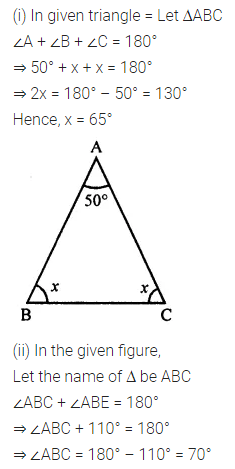
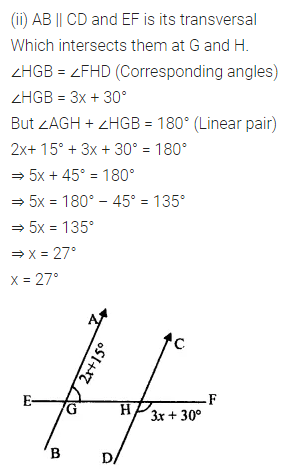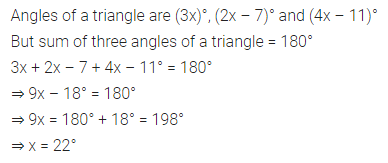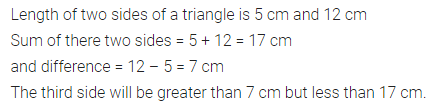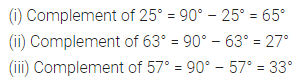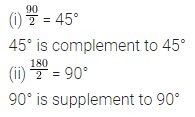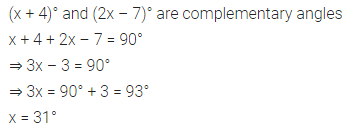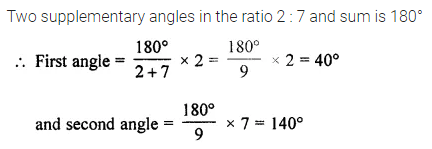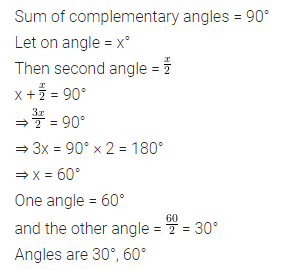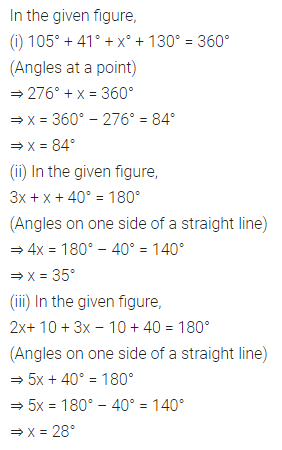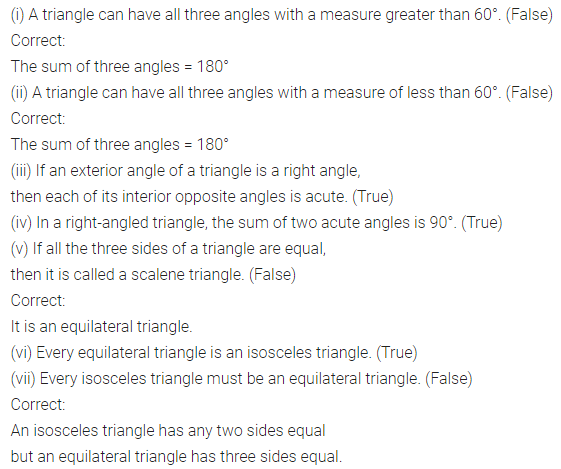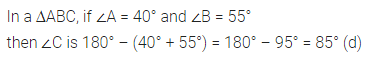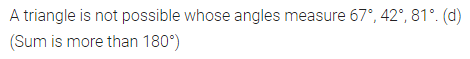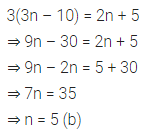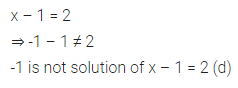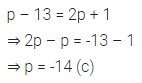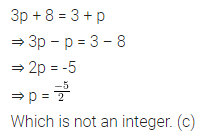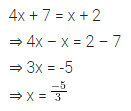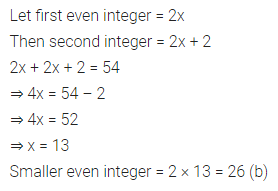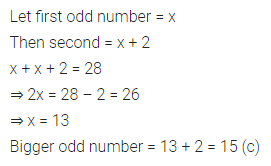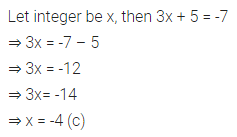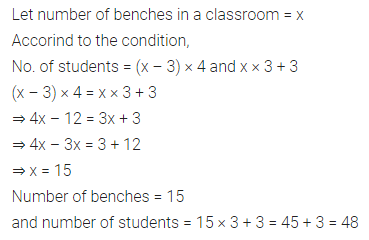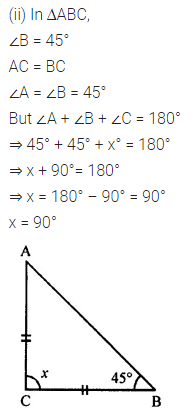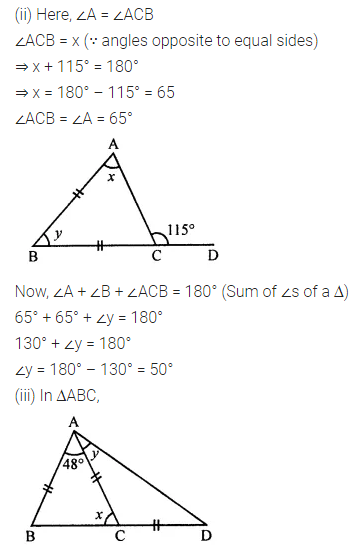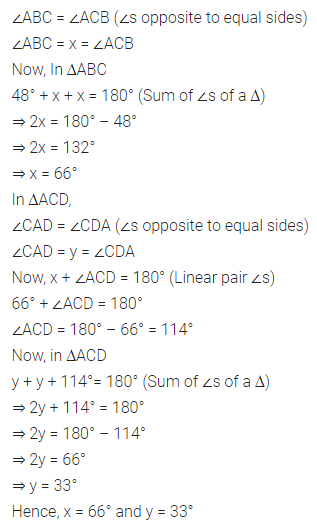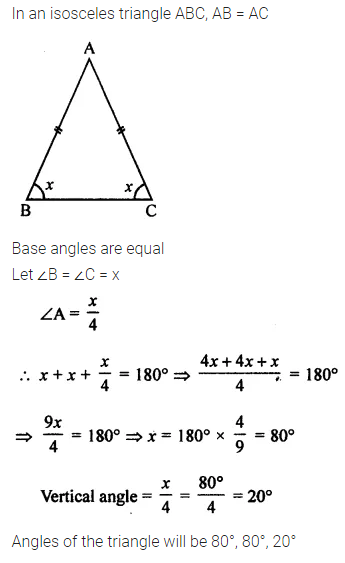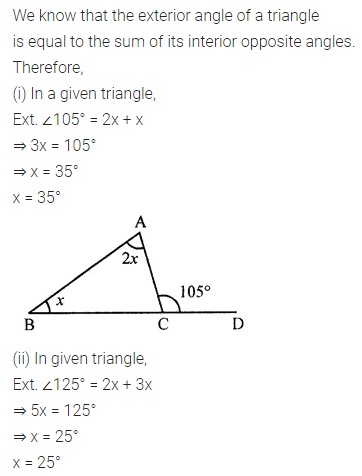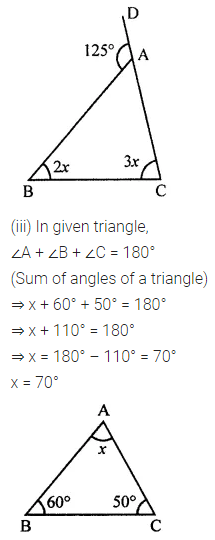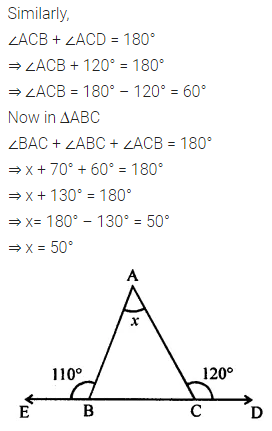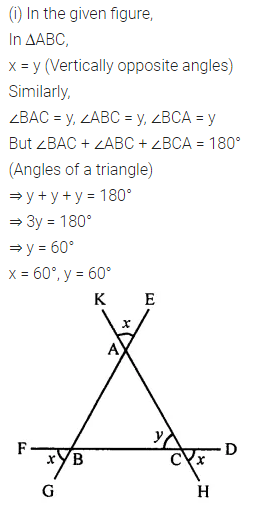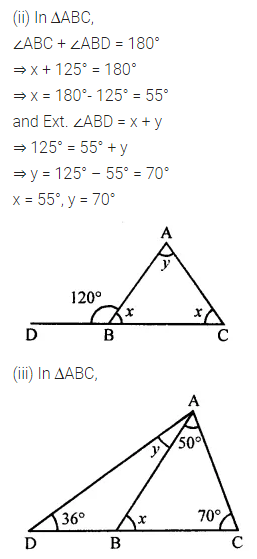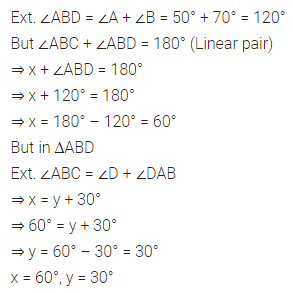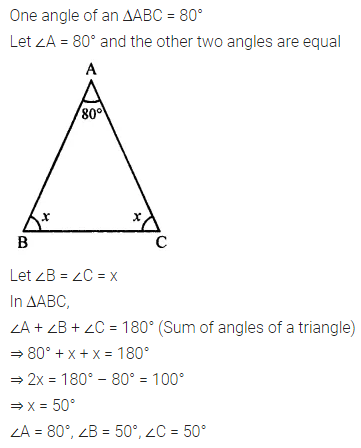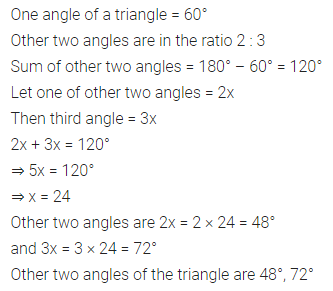ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions Chapter 10 Lines and Angles Objective Type Questions for ICSE Understanding Mathematics acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 10 Lines and Angles Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
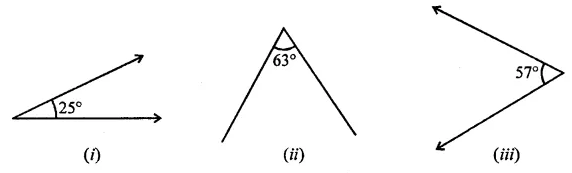
(i) If two angles are complementary, then the sum of their measures is ………..
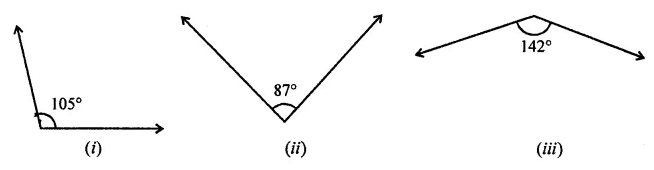
(ii) If two angles are supplementary, then the sum of their measures is …………
(iii) Supplement of an obtuse angle is ……….
(iv) Two angles forming a linear pair are ……….
(v) If two adjacent angles are supplementary, then they form a ………..
(vi) Angles of a linear pair are as well as ………..
(vii) Adjacent angles have a common vertex, a common ……….. and no common ………
(viii)Angles formed by two intersecting lines having no common arms are called ………..
(ix) If two lines intersect and if one pair of vertically opposite angles are acute angles, then the other pair of vertically opposite angles are ……..
(x) Two lines in a plane which never meet are called ……….
(xi) Alternate interior angles have one common …………
(xii) Corresponding angles are on the ……….. side of the transversal.
(xiii) Alternate interior angles are on the ………… side of the transversal.
(xiv) If two lines are cut by a transversal such that a pair of corresponding angles are not equal, then the lines are ………..
Solution:

Question 2.
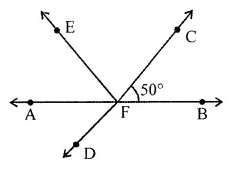
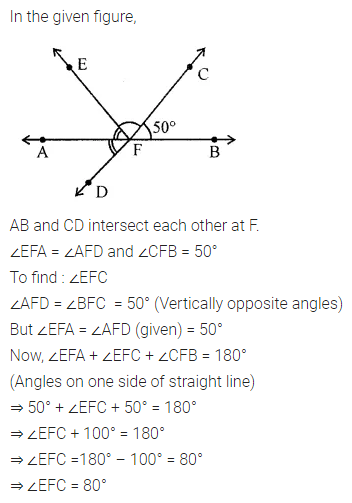
In the given figure, AB is a straight line and OD ⊥ AB. Observe the figure and fill in the following blanks:
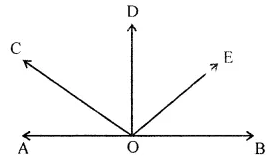
(i) ∠AOC and ∠COE form a pair of ……….. angles.
(ii) ∠AOC and ∠COB are ……….. angles.
(iii) ∠AOC is ………… of ∠COD.
(iv) ∠BOE is …………. of ∠EOA.
Solution:

Question 3.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) Two obtuse angles can be supplementary.
(ii) Two acute angles can form a linear pair.
(iii) Two obtuse angles can form a linear pair.
(iv) Two adjacent angles always form a linear pair.
(v) Pair of vertically opposite angles are always supplementary.
(vi) 30° is one-half of its complement.
(vii) If two lines are cut by a transversal,
then each pair of corresponding angles are equal.
(viii) If two lines are cut by a transversal,
then each pair of alternate interior angles are equal.
Solution:


Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (4 to 14):
Question 4.
A pair of complementary angles is
(a) 130°, 50°
(b) 35°, 55°
(c) 25°, 75°
(d) 27°, 53°
Solution:

Question 5.
A pair of supplementary angles is
(a) 55°, 115°
(b) 65°, 125°
(b) 47°, 133°
(d) 40°, 50°
Solution:

Question 6.
If an angle is one-third of its supplement, then the measure of the angle is
(a) 45°
(b) 30°
(c) 135°
(d) 150°
Solution:
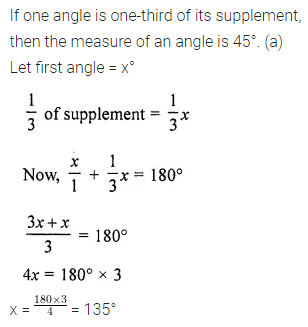
Question 7.
If an angle measures 10° more than its complement, then the measure of the angle is
(a) 40°
(b) 55°
(c) 35°
(d) 50°
Solution:
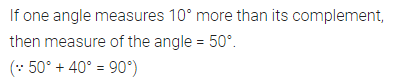
Question 8.
If one angle of a linear pair is acute, then the other angle is
(a) acute
(b) obtuse
(c) right
(d) straight
Solution:

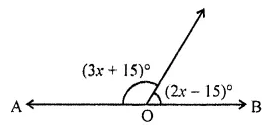
Question 9.
In the given figure, the value of x that will make AOB a straight line is
(a) x = 40
(b) x = 35
(c) x = 30
(d) x = 25
Solution:
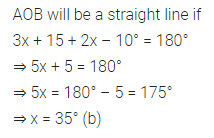
Question 10.
If two lines are intersected by a transversal, then the number of pairs of interior angles on the same side of transversal is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Solution:

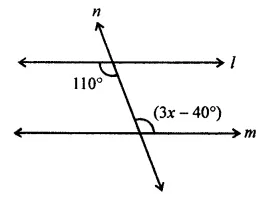
Question 11.
In the given figure, if l || m then the value of x is
(a) x = 50
(b) x = 60
(c) x = 70
(d) x = 45
Solution:
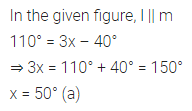
Question 12.
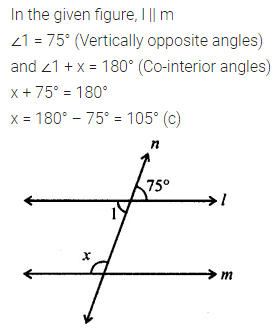
In the gitsen figure, if l || m then the value of x is
(a) x = 75°
(b) x = 95°
(c) x = 105°
(d) x = 115°
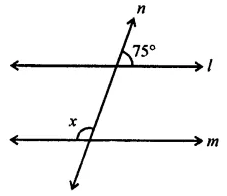
Solution:
Question 13.
In the given figure, AB || CD. If ∠APQ = 50° and ∠PRD = 130°, then ∠QPR is
(a) 30°
(b) 50°
(c) 80°
(d) 130°
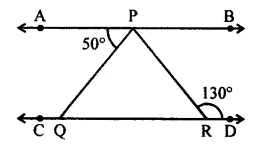
Solution:

Question 14.
In the given figure, PA || BC || DQ and AB || DC. Then the values of x and y are respectively:
(a) 50°, 120°
(b) 50°, 130°
(c) 60°, 120°
(d) 60°, 130°
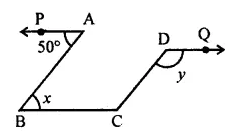
Solution:

Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
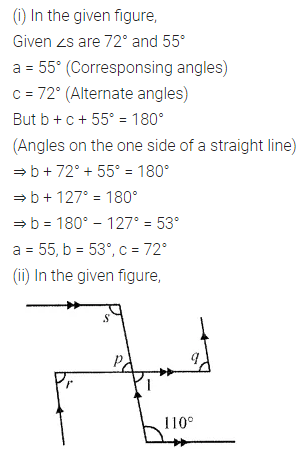
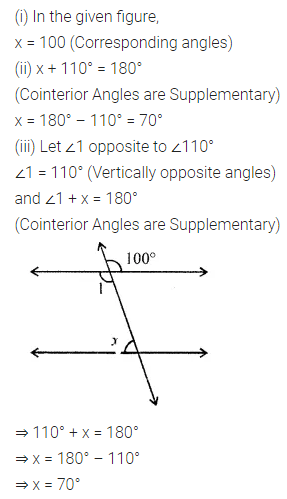
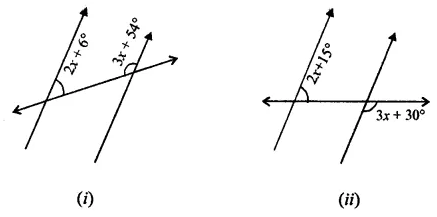
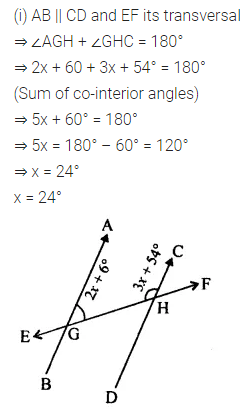
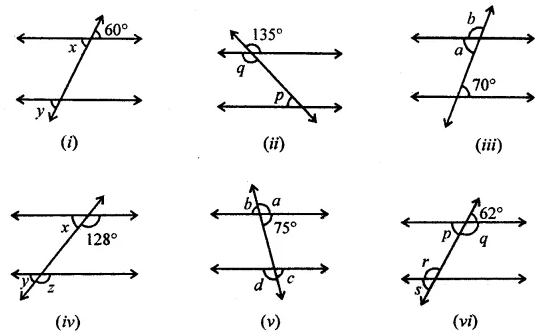
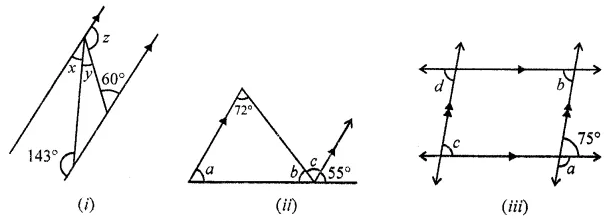
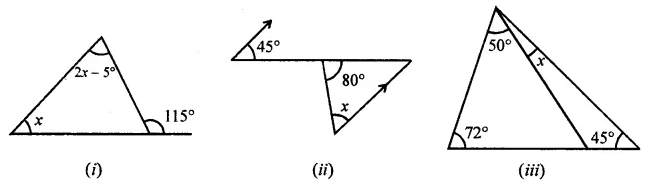
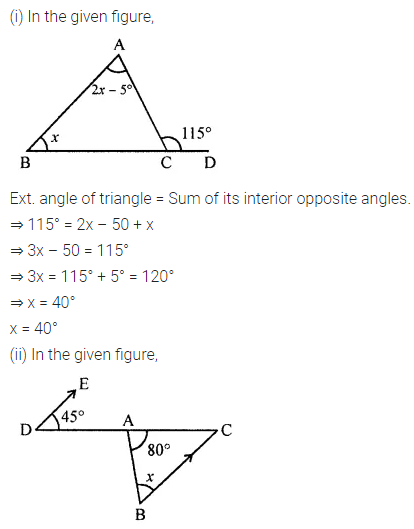
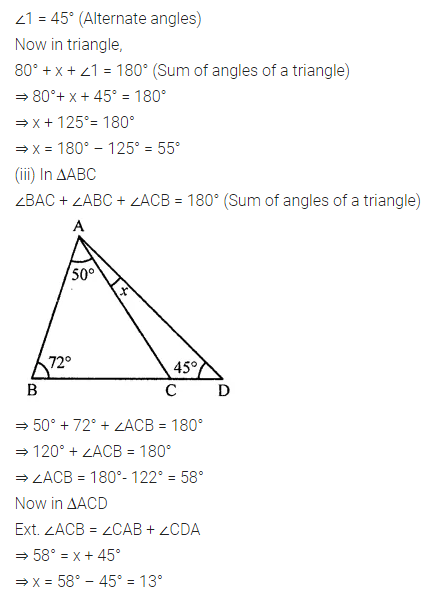
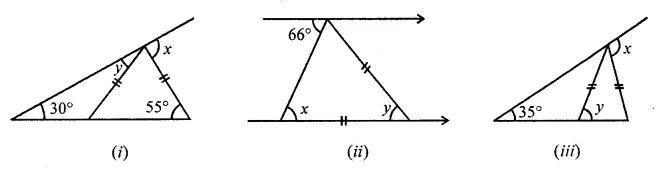
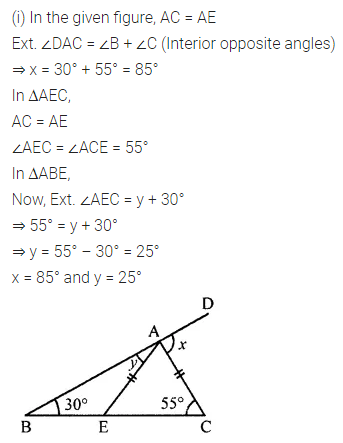
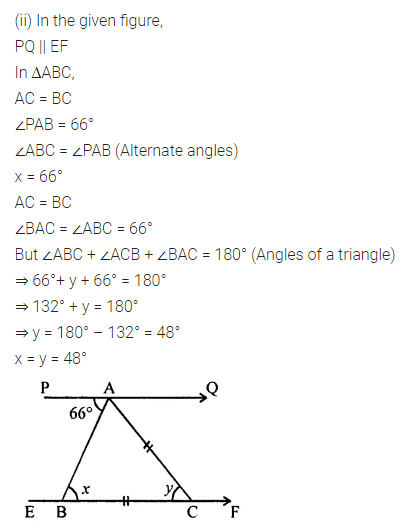
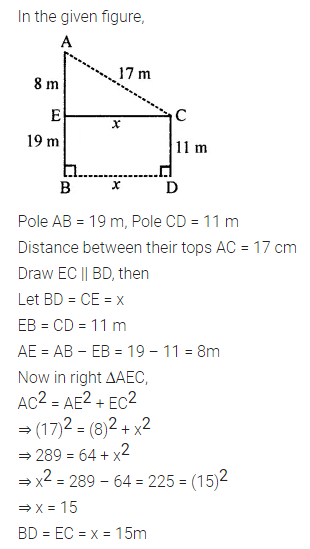
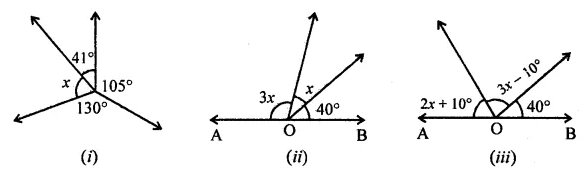
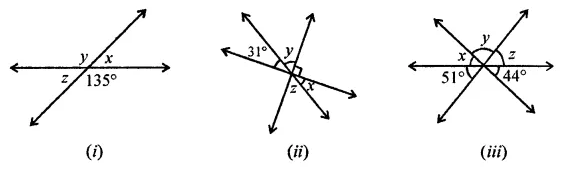
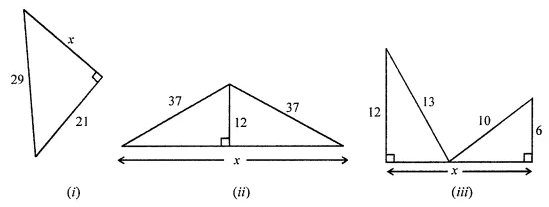
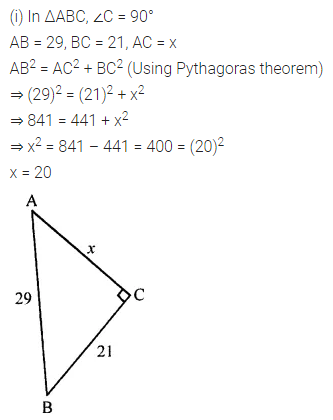
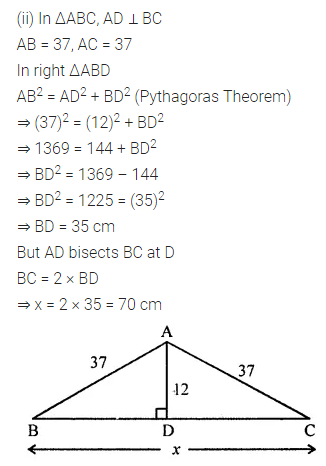
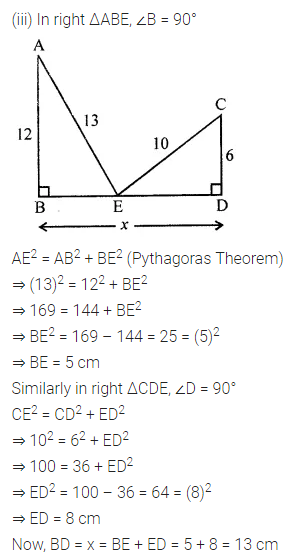
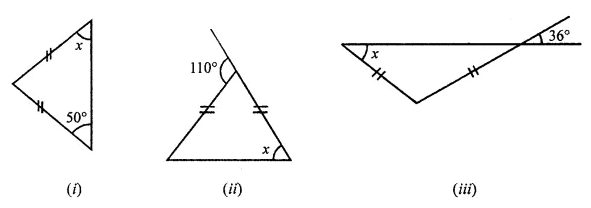
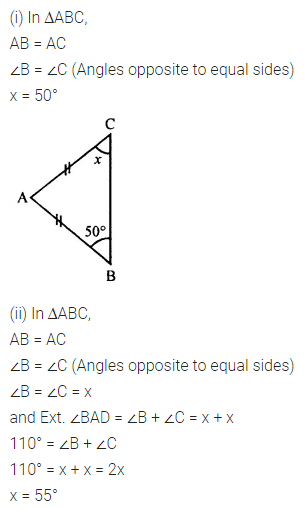
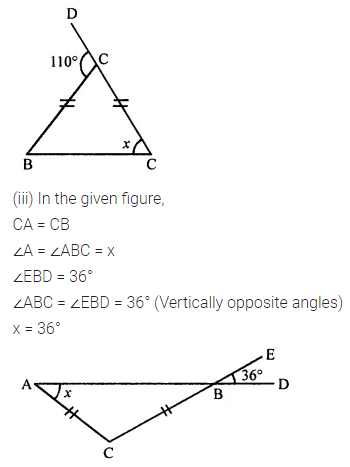
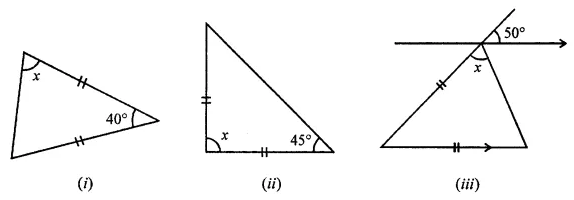
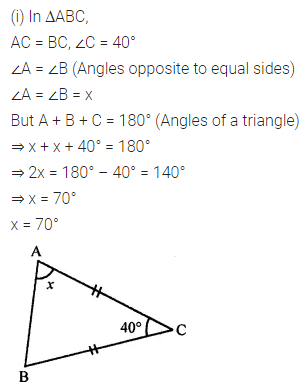
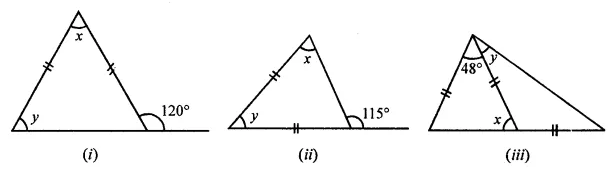
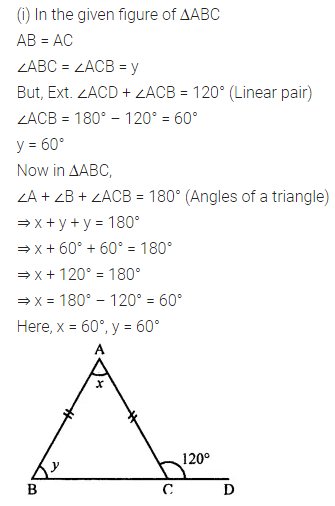
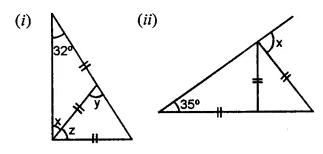
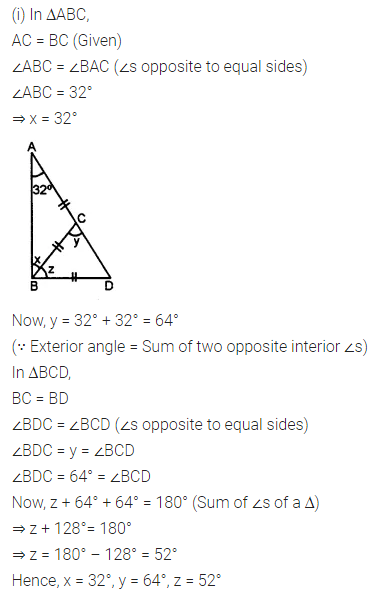
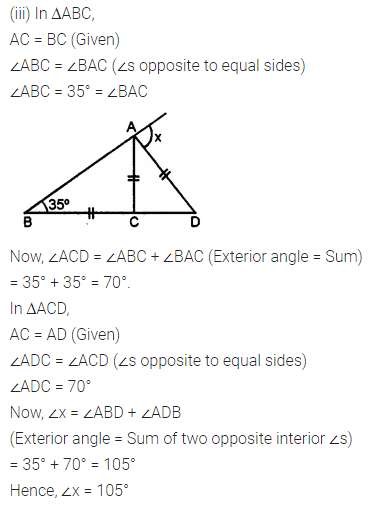
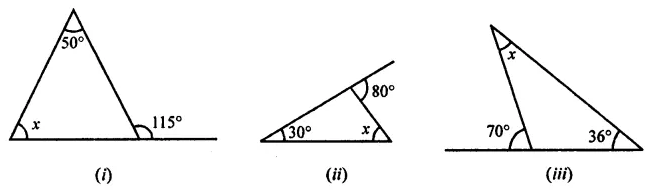
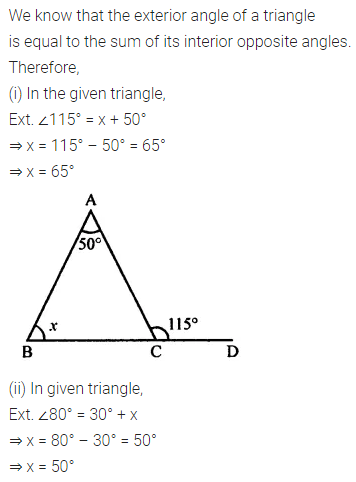
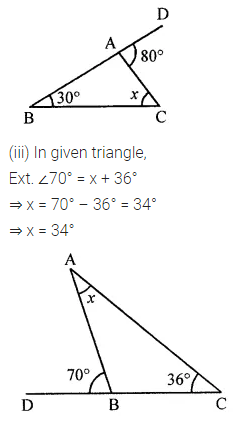
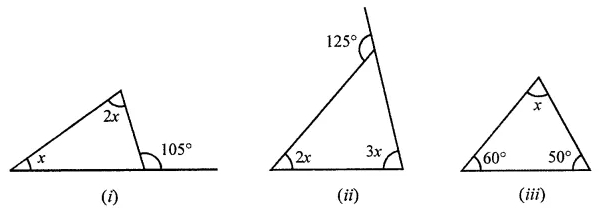
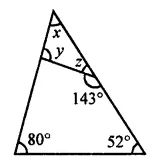
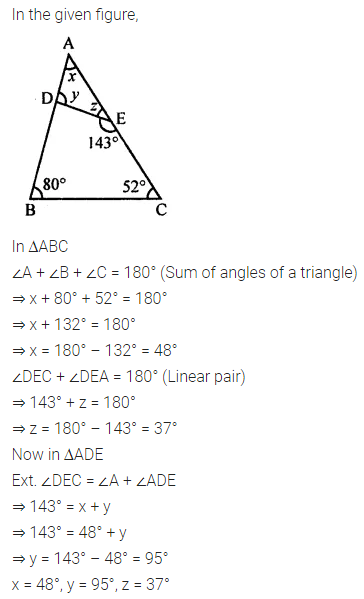
Question 1.
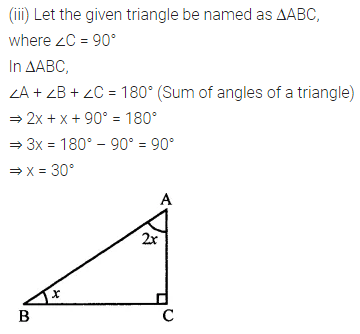
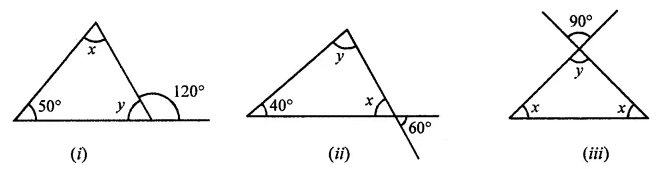
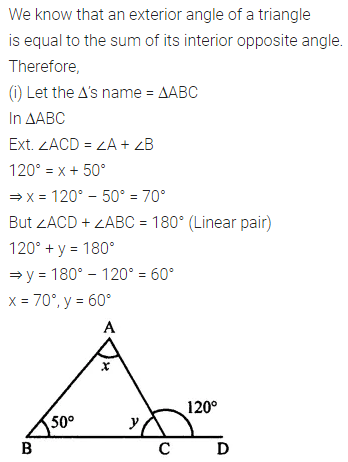
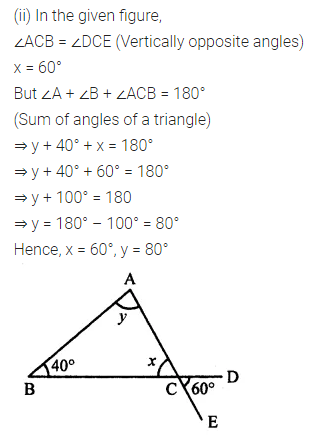
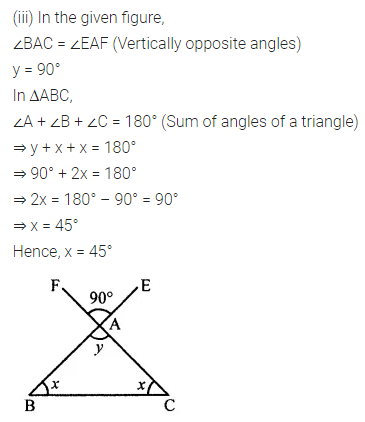
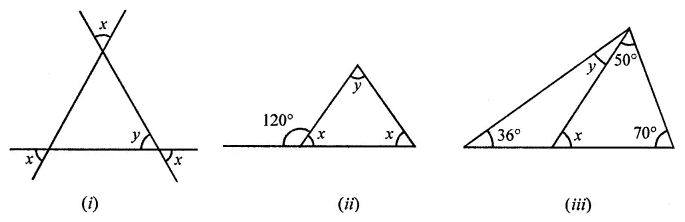
Calculate the measure of each lettered angle in the following figures (parallel line segments / rays are denoted by thick matching arrows):
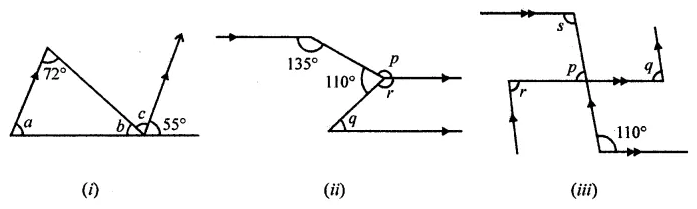
Solution: