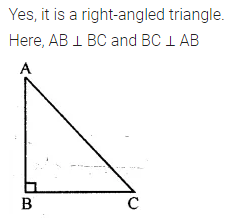
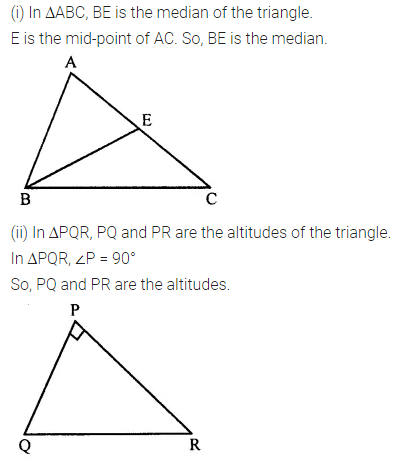
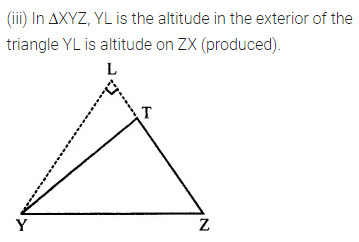
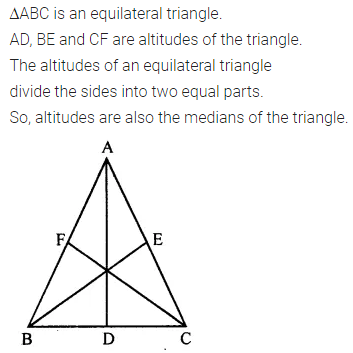
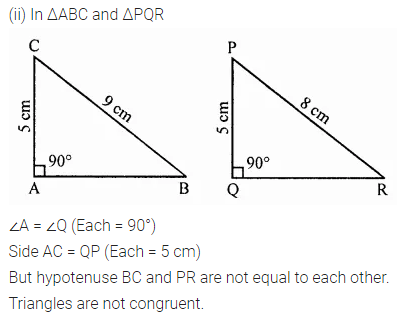
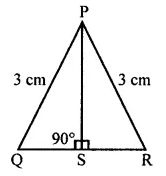
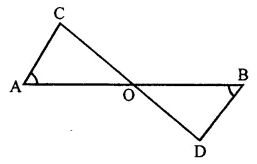
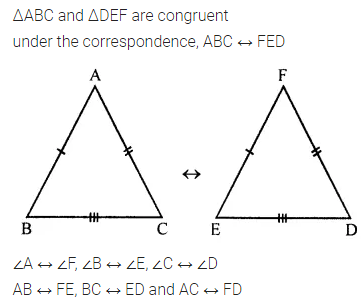
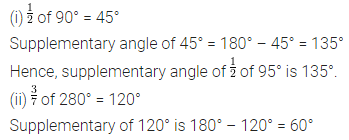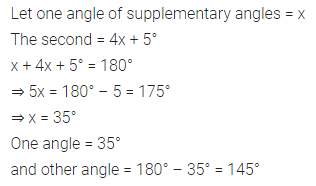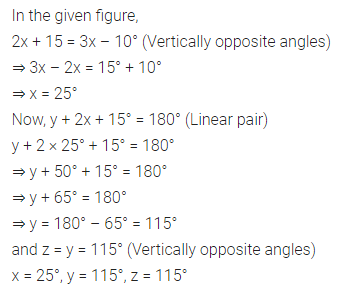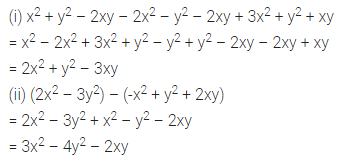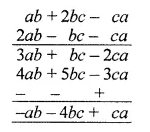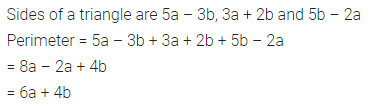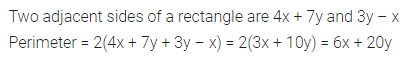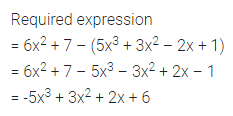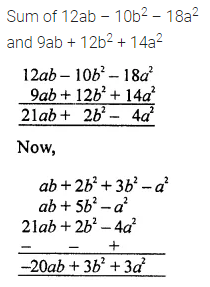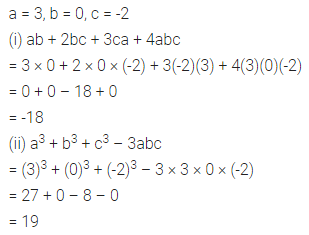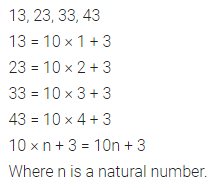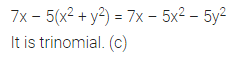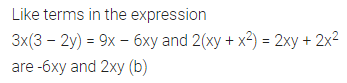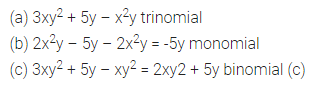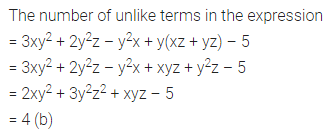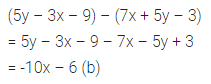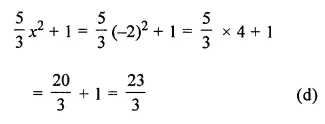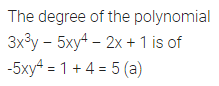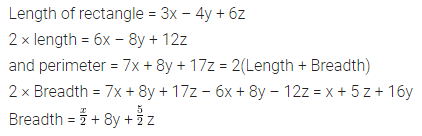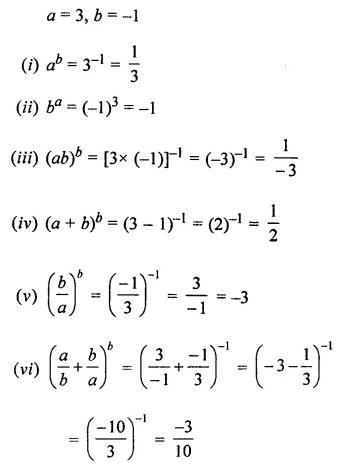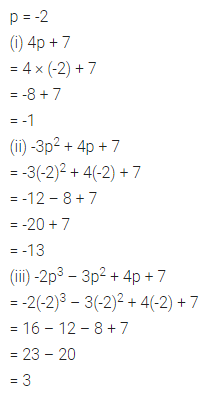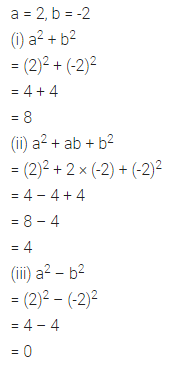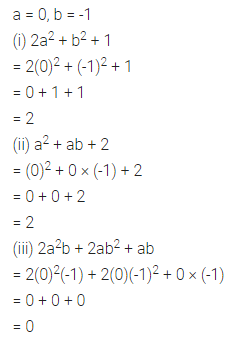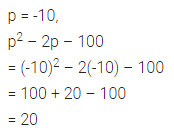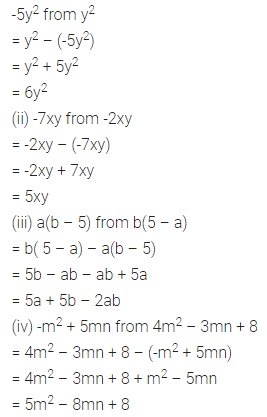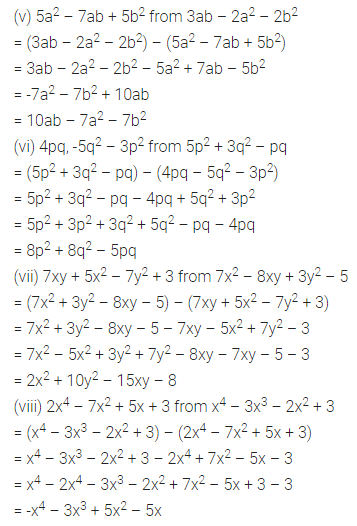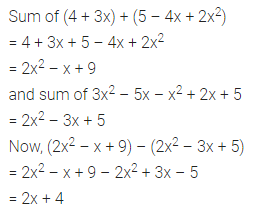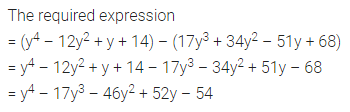ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions Chapter 16 Perimeter and Area Ex 16.2 for ICSE Understanding Mathematics acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 16 Perimeter and Area Ex 16.2
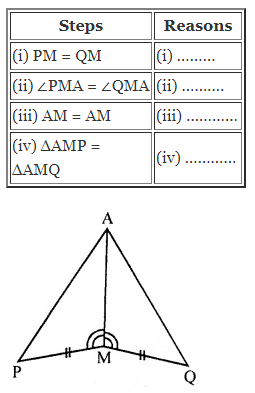
Question 1.
Find the area of each of the following parallelogram:
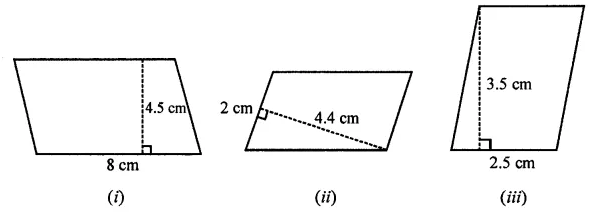
Solution:

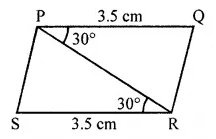
Question 2.
Find the area of each of the following triangles:
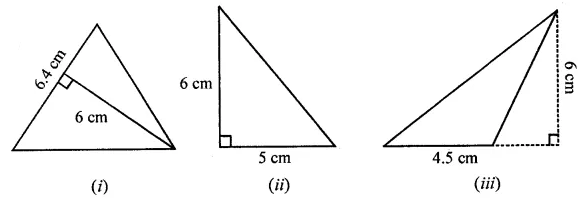
Solution:

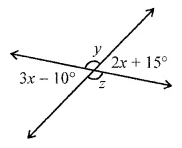
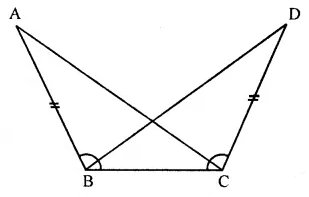
Question 3.
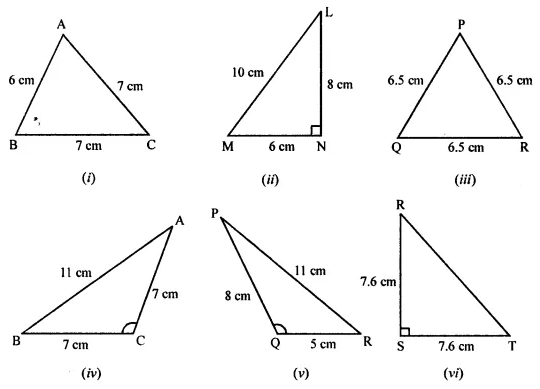
Find the missing values:
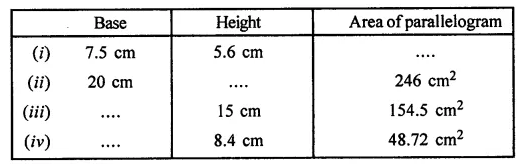
Solution:
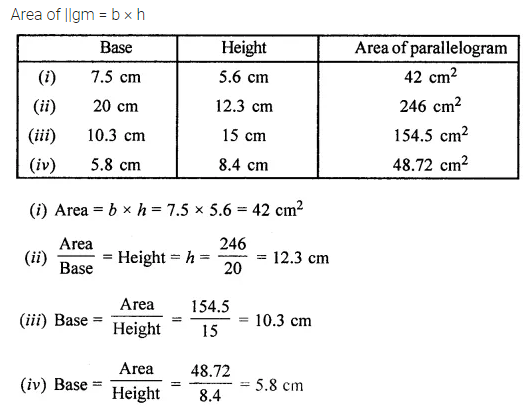
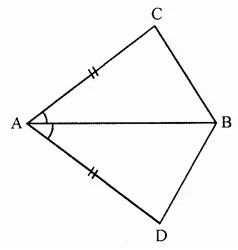
Question 4.
Find the missing values:
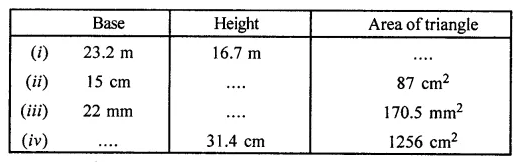
Solution:

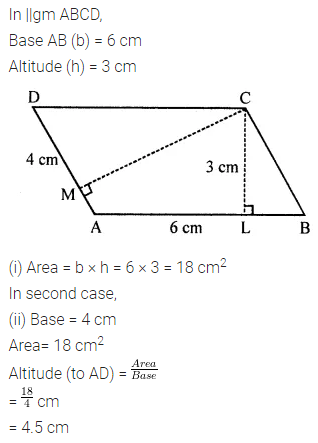
Question 5.
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram whose two adjacent sides are 6 cm and 4 cm. If the height corresponding to the base AB is 3 cm, find:
(i) the area of parallelogram ABCD
(ii) the height corresponding to the base AD.
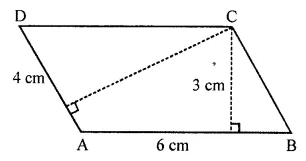
Solution:
Question 6.
In the given figure, ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC = 7.5 cm and BC = 9 cm. If the height AD from A to BC is 6 cm, find:
(i) the area of ∆ABC
(ii) the height CE from C to AB.
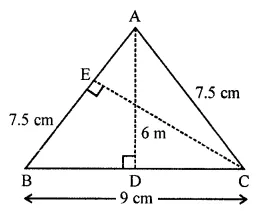
Solution:

Question 7.
If the base of a right-angled triangle is 8 cm and the hypotenuse is 17 cm, find its area.
Solution:

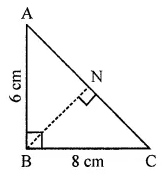
Question 8.
In the given figure, ∆ABC is right-angled at B. Its legs are 8 cm and 6 cm. Find the length of perpendicular BN on the side AC.
Solution:

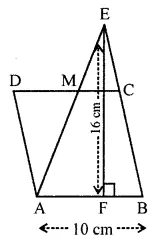
Question 9.
In the given figure, the area of ∆ABE is equal to the area of parallelogram ABCD. If altitude EF is 16 cm long, find the length of the altitude of the parallelogram to the base AB of length 10 cm. What is the area of ∆AMD, where M is mid-point of side DC?
Solution:

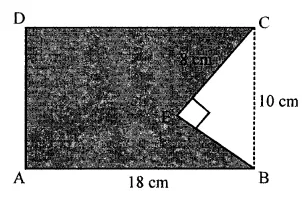
Question 10.
In the given figure, ABCD is a rectangle of size 18 cm by 10 cm. In ABEC, ∠E = 90° and EC = 8 cm. Find the area of the shaded region.
Solution:

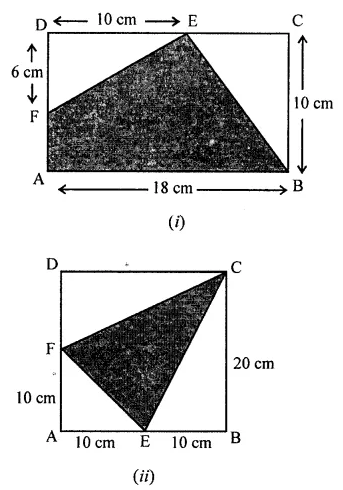
Question 11.
In the following figures, find the area of the shaded regions:
Solution: