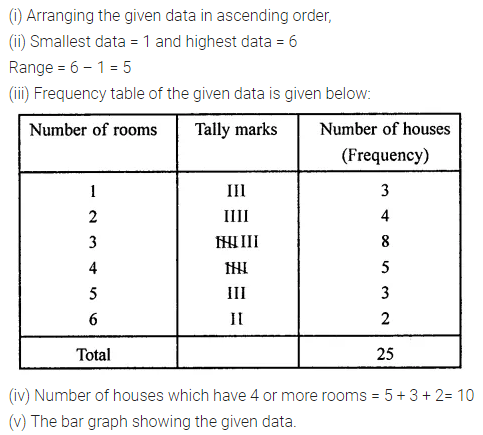
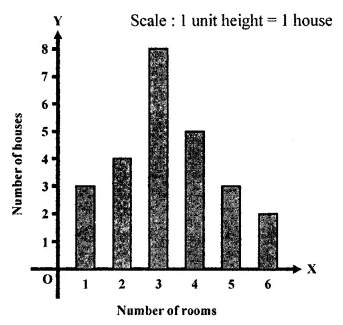
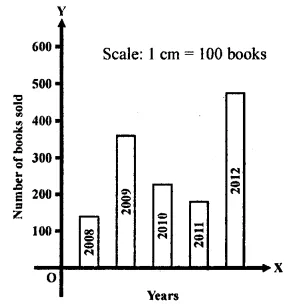
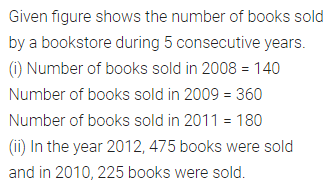
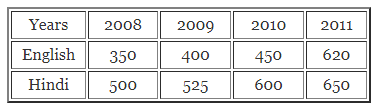
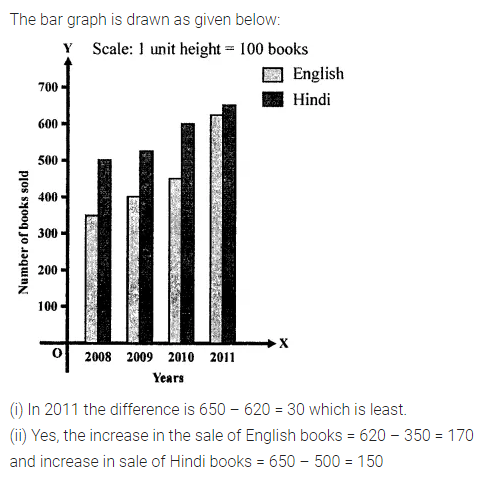
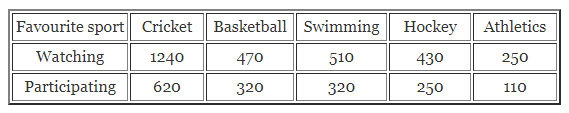
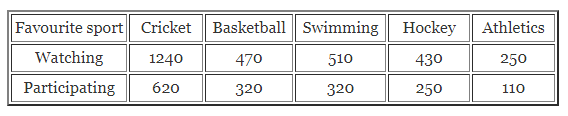
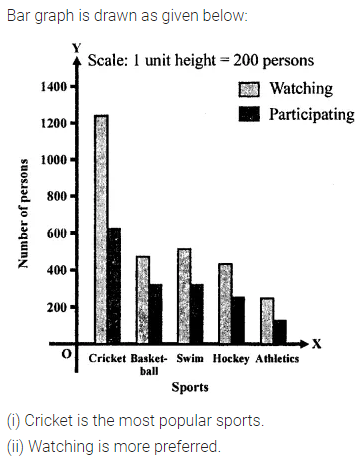
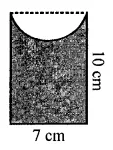
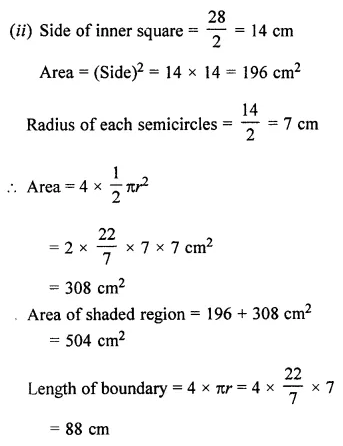
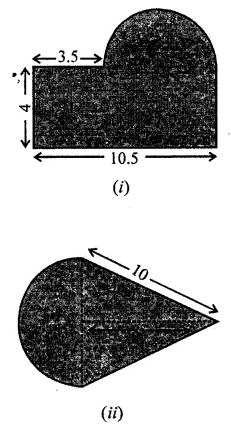
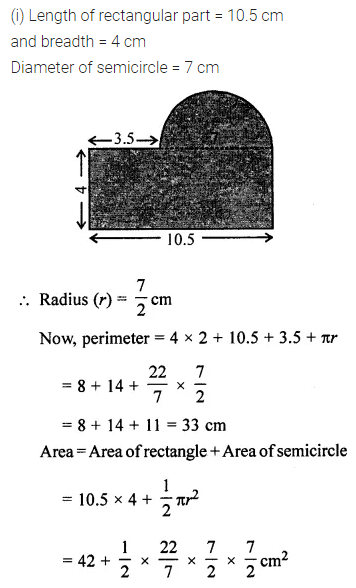
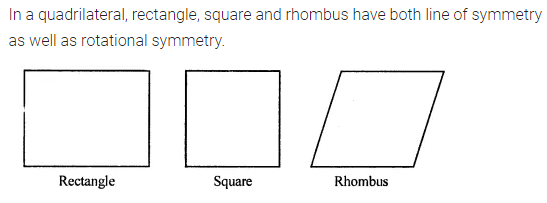
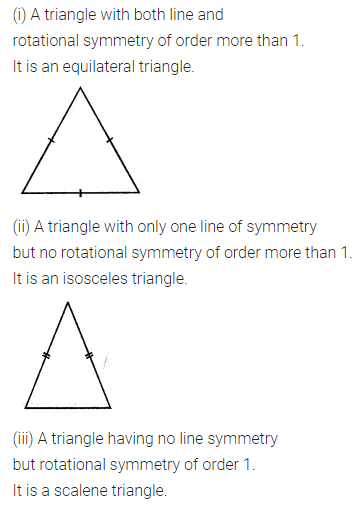
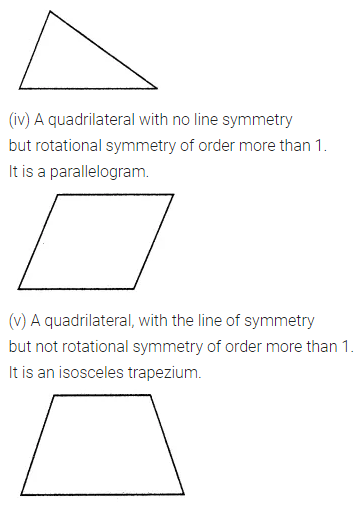
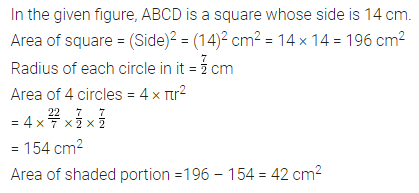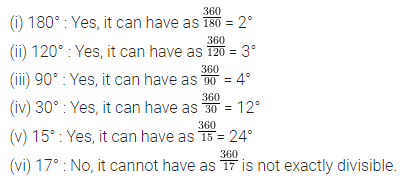ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions Chapter 17 Data Handling Ex 17.4 for ICSE Understanding Mathematics acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 17 Data Handling Ex 17.4
Question 1.
Tell whether the following is certain to happen, impossible to happen, can happen but not certain:
(i) You are older today than yesterday.
(ii) Two hundred people can sit in a Maruti car.
(iii) A tossed coin will land heads up.
(iv) A die when tossed shall land up with 8 on top.
(v) India will win the next test series.
(vi) Tomorrow will be a cloudy day.
(vii) The next traffic light seen will be green.
Solution:

Question 2.
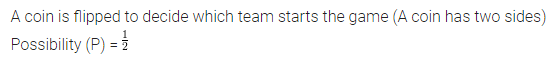
A coin is flipped to decide which team starts the game. What is the probability that your team will start the game?
Solution:
Question 3.
There are 6 marbles in a box with numbers 1 to 6 marked on them.
(i) What is the probability of drawing a marble with number 5?
(ii) What is the probability of drawing a marble with number 2?
Solution:

Question 4.
A die is tossed once. Find the probability of getting
(i) a number less than 3
(ii) a prime number
(iii) a number greater than 2
Solution:

Question 5.
A box contains 3 defective mangoes and 21 good mangoes. One mango is drawn from the box at random. Find the probability of getting
(i) a defective mango
(ii) a good mango
Solution:

Question 6.
A card is drawn from a well-shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability of getting
(i) a red card
(ii) a king
(iii) a card of spades
Solution: