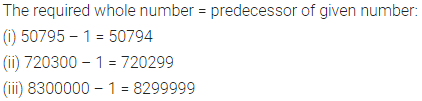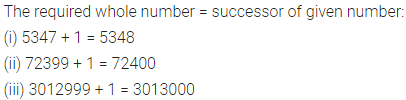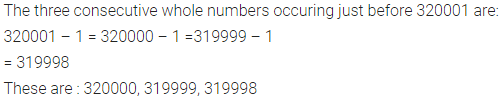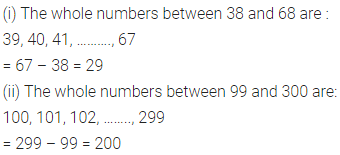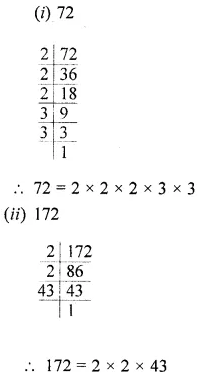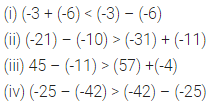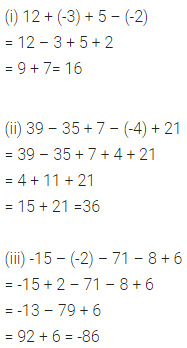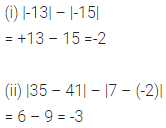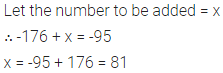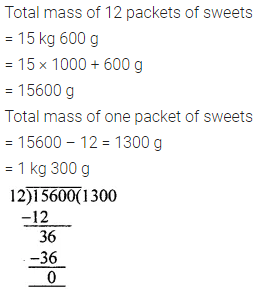ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions for ICSE Maths Model Question Paper 1 acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 7 ICSE Maths Model Question Paper 1
(Based on Chapters 1 to 3)
Time allowed: 1 Hour
Maximum Marks: 25
Instructions
- Questions 1-2 carry 1 mark each
- Questions 3-5 carry 2 marks each
- Questions 6-8 carry 3 marks each
- Questions 9-10 carry 4 marks each.
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (1-2):
Question 1.
(-10) × 2 + 0 ÷ (-2) is equal to
(a) -20
(b) 20
(c) -22
(d) 22
Solution:
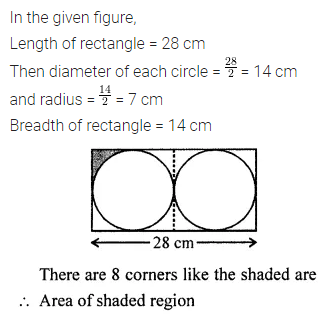
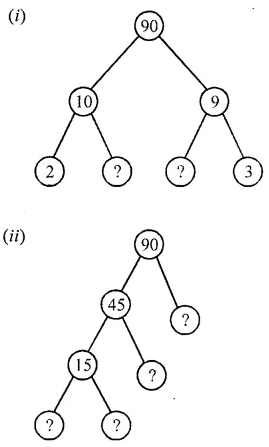
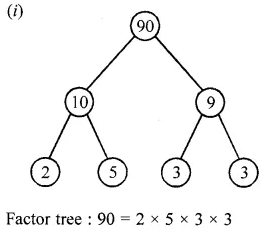
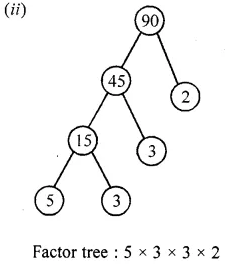
![]()
Question 2.
The sum of a rational number \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\) and its multiplicative inverse is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -2\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(d) -2
Solution:

Question 3.
Evaluate: (-36) ÷ ((-14) + 2).
Solution:
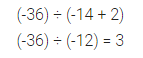
Question 4.
If the length of a rectangle is 8.26 cm and its breadth is 5.5 cm, then find the area of the rectangle.
Solution:

Question 5.
Reduce the rational number \(\frac { 105 }{ -168 }\) standard form.
Solution:
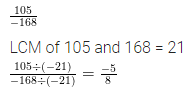
Question 6.
In a competition, the question paper consists of 20 questions. 5 marks are awarded for every correct answer and 2 marks are deducted for every incorrect answer and 0 marks for every question not attempted. Vishal attempted 17 questions and got 11 correct answers. What is his score?
Solution:

Question 7.
Barkha bought 20\(\frac { 3 }{ 8 }\) kg rice at the rate of ₹ 17\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) per kg and sent it to an orphanage. Find the amount spent by Barkha. What value is being promoted?
Solution:

Question 8.
Which rational number is greater -5\(\frac { 5 }{ 9 }\) or -5\(\frac { 7 }{ 12 }\) ?
Solution:
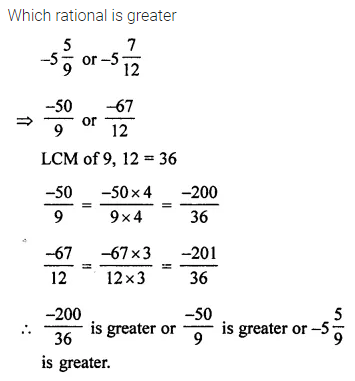
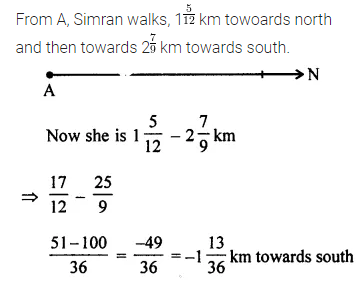
Question 9.
Simran walks 1\(\frac { 5 }{ 12 }\) km from a place A towards north and then from there she walks 2\(\frac { 7 }{ 9 }\) km towards south. Where will be she now from place A?
Solution:
Question 10.
If the product of two decimal numbers is 17.55 and one of them is 2.7, then find the other.
Solution: