Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Motion and Measurement of Distances Class 6 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Class 6 Science Chapter 10 MCQ With Answers
Science Class 6 Chapter 10 MCQs On Motion and Measurement of Distances
Choose the correct option in the following questions:
Class 6 Science Chapter 10 MCQ Question 1.
Which is a standard unit of measurement?
(a) Angul (finger)
(b) Mutthi (fist)
(c) Step
(d) Inch
Answer
Answer: (d) Inch
Explanation:
All other units vary from person to person
Motion And Measurement Of Distances Class 6 MCQs Question 2.
What is the SI unit of length?
(a) Metre
(b) Centimetre
(c) Kilometre
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Metre
Explanation:
All other are multiples of metre.
MCQ Questions For Class 6 Science Chapter 10 Question 3.
4 kilometres are equal to
(a) 4,00,000 metre
(b) 40,000 metre
(c) 4,00p metre
(d) 400 metre
Answer
Answer: (c) 4,00p metre
Explanation:
1 km = 1000 m, 4 km = 4000 m
Motion And Measurement Class 6 MCQ Question 4.
15 cm are equal to
(a) 150 mm
(b) 15 mm
(c) 1.5 mm
(d) 0.15 mm
Answer
Answer: (a) 150 mm
Explanation:
1 cm = 10 mm, 15 cm = 150 mm
Measurement And Motion Class 6 MCQ Question 5.
Which is a correct relationship?
(a) 1 m = 100 cm
(b) 1 cm = 100 mm
(c) 1 km = 100 m
(d) all of these
Answer
Answer: (d) all of these
Explanation: 1 m = 100 cm.
MCQ On Motion And Measurement Of Distances Class 6 Question 6.
In the following figure, the proper way of reading scale is
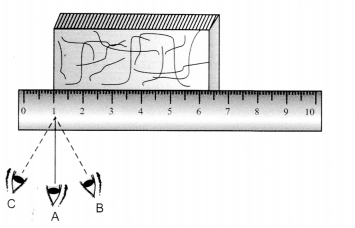
(a) C
(b) B
(c) A
(d) Any way can be choosen
Answer
Answer: (c) A
Explanation:
B and C are incorrect positions.
Motion And Measurement Of Distances Class 6 MCQ With Answers Question 7.
An example of rectilinear motion is
(a) apple falling from a tree
(b) motion of a car on road
(c) a spinning top
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer
Answer: (d) both (a) and (b)
Explanation:
Apple falling from a tree and motion of a car on road are the examples of rectilinear motion.
Ncert Class 6 Science Chapter 10 MCQ Question 8.
Which is an example of a periodic motion?
(a) Oscillation of a pendulum
(b) Motion of a bus on road
(c) A spinning top
(d) A stone dropped from a certain height
Answer
Answer: (a) Oscillation of a pendulum
Explanation:
Oscillation of a pendulum is an example of periodic motion.
Class 6 Science Ch 10 MCQ Question 9.
What kind of motion is executed by a pendulum of a wall clock?
(a) Oscillatory motion
(b) Vibratory motion
(c) Circular motion
(d) Linear motion
Answer
Answer: (a) Oscillatory motion
Explanation:
The to-and-fro motion of a body along the same path is called oscillatory motion.
Motion And Measurement Of Distances Class 6 MCQ Question 10.
One metre is equal to ………….. millimetre.
(a) 10
(b) 1000
(c) 100
(d) 10000
Answer
Answer: (b) 1000
Explanation:
1 metre = 1000 millimetre.
Match the following items given in Column A with that in Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Metre | (i) Unit used to measure very small distances. |
| (b) Yard | (ii) Unit used to measure large distances. |
| (c) Hand span | (iii) SI unit of length. |
| (d) LeaSt count | (iv) Non-standard unit of length. |
| (e) Millimetre | (v) Standard unit of length. |
| (f) Kilometre | (vi) Apple falling from a tree. |
| (g) Rest | (vii) Motion of the tip of the blade of a fan. |
| (h) Motion | (viii) Motion of a pendulum. |
| (i) Circular motion | (ix)Motion of a top. |
| (j) Rectilinear motion | (x) State of moving objects. |
| (k) Rotational motion | (xi) State of stationary objects. |
| (l) Periodic motion | (xii) Minimum amount that can be measured by a device. |
Answer
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Metre | (iii) SI unit of length. |
| (b) Yard | (v) Standard unit of length. |
| (c) Hand span | (iv) Non-standard unit of length. |
| (d) LeaSt count | (xii) Minimum amount that can be measured by a device. |
| (e) Millimetre | (i) Unit used to measure very small distances. |
| (f) Kilometre | (ii) Unit used to measure large distances. |
| (g) Rest | (xi) State of stationary objects. |
| (h) Motion | (x) State of moving objects. |
| (i) Circular motion | (vii) Motion of the tip of the blade of a fan. |
| (j) Rectilinear motion | (vi) Apple falling from a tree. |
| (k) Rotational motion | (ix)Motion of a top. |
| (l)Periodic motion | (viii) Motion of a pendulum. |
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
1. Striker in the game of carroms moves in a …………. .
Answer
Answer: straight line
2. Powerful shot by a batsman makes the ball move in ………….. motion.
Answer
Answer: rectilinear
3. Moving ceiling fan is an example of …………… motion.
Answer
Answer: circular
4. Rotational motion is known as ………….. motion also.
Answer
Answer: periodic
5. …………….. motion is also a periodic motion.
Answer
Answer: Oscillatory
6. Invention of…………. made great change in modes of transport.
Answer
Answer: wheel
7. Measurement means the comparison of an ………………….. quantity with some ……….. quantity of the same kind.
Answer
Answer: unknown, known
8. It was the …………………. who developed the ‘foot’ as their unit of length.
Answer
Answer: Greeks
9. In 1790, the French created a standard unit of measurement called the ……….. system.
Answer
Answer: metric
10. System of units now used is known as ……………… system.
Answer
Answer: S.I.
11. Each metre is decided into 100 equal divisions, called ……………. .
Answer
Answer: centimetre
12. Each centimetre has ………………. equal divisions called millimetre.
Answer
Answer: ten
13. Motion is the change in …………….. of an object.
Answer
Answer: position
14. Motion of a branch of tree is …………….. motion.
Answer
Answer: periodic
15. A ball rolling on ground executes a rectilinear motion as well as ……………. motion.
Answer
Answer: rotational
State whether the statements given below are True or False:
1. Swinging of our arms or legs are periodic motions.
Answer
Answer: False
2. Beating of our heart is non-periodic motion.
Answer
Answer: True
3. Periodic motion helps us to measure time.
Answer
Answer: True
4. In a circular motion; the objects or any of their parts move in a circular path.
Answer
Answer: True
5. Motion of second’s hand of a clock is rectilinear.
Answer
Answer: False
6. SI unit of length is ‘Foot’.
Answer
Answer: False
7. For measuring large distances metre is not a convenient unit.
Answer
Answer: True
8. Motion of a vehicle on a straight road is a rectilinear motion.
Answer
Answer: True
9. Marchpast of soldiers in a parade is a periodic motion.
Answer
Answer: False
10. Motion of second’s hand in a clock is a circular motion.
Answer
Answer: True
11. In rotational motion whole body moves about an axis.
Answer
Answer: True
12. The result of a measurement is expressed in two parts.
Answer
Answer: True
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Motion and Measurement of Distances CBSE Class 6 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 6 Science MCQ:
- Food Where Does It Come From Class 6 MCQ
- Components of Food Class 6 MCQ
- Fibre to Fabric Class 6 MCQ
- Sorting Materials Into Groups Class 6 MCQ
- Separation of Substances Class 6 MCQ
- Changes Around Us Class 6 MCQ
- Getting to Know Plants Class 6 MCQ
- Body Movements Class 6 MCQ
- The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings Class 6 MCQ
- Motion and Measurement of Distances Class 6 MCQ
- Light Shadows and Reflection Class 6 MCQ
- Electricity and Circuits Class 6 MCQ
- Fun with Magnets Class 6 MCQ
- Water Class 6 MCQ
- Air Around Us Class 6 MCQ
- Garbage In Garbage Out Class 6 MCQ
