Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks. This consists of 1 mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions and previous year questions from Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter.
Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 2
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Give the names and formulae of two
(i) strong monobasic acids
(ii) two weak dibasic acids.
Answer:
(i) hydrochloric acid (HCl), nitric acid (HNO3)
(ii) carbonic acid (H2CO3), oxalic acid (C2H2O4).
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
Question 2.
How will you show that acetic acid is a monobasic acid ?
Answer:
When acetic acid is reacted with sodium hydroxide solution, only one H atom of the acid gets replaced and the product is sodium acetate and water. This shows that acetic acid is a monobasic acid.
![]()
Question 3.
Why alkalies like sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide should not be left exposed to air ?
Answer:
Because they are hygroscopic in nature and absorb moisture from atmosphere in which they ultimately dissolve.
Question 4.
The pH of an aqueous solution decreases from 3 to 2. What will happen to the nature of the solution ?
Answer:
The acidic character of the solution will further increase.
Question 5.
What happens to the crystals of washing soda when exposed to air ?
Answer:
They undergo efflorescence. As a result, washing soda (Na2CO3.10H2O) changes to washing powder (Na2CO3.H2O).
Question 6.
State whether an aqueous solution of washing soda is acidic or alkaline.
Answer:
An aqueous solution of washing soda is alkaline (turns red litmus blue). On dissolving in water, it forms NaOH (strong base) and carbonic acid (weak acid).
![]()
Therefore, resulting solution is alkaline or basic in nature.
Question 7.
What is the chemical name and chemical formula of baking soda ?
Answer:
The chemical name of baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate or sodium bicarbonate. Its chemical formula is NaHCO3.
Question 8.
When a few drops of phenolphthalein indicator were added to the solution of some compound A’, the solution became pink. What does it indicate ?
Answer:
This shows that the solution of compound A’ is of basic nature since phenolphthalein becomes pink in basic medium.
Question 9.
Which is a stronger acid ? A solution with pH 5 and a solution with pH 2 ?
Answer:
A solution with pH 2 is a stronger acid. In general, lesser the pH, more will be the acidic nature of the solution.
Question 10.
What is the nature of NaHCO3 salt ?
Answer:
It is an acidic salt since it has still one replaceable hydrogen atom present.
Question 11.
Give two examples of the salts belonging to the chloride family.
Answer:
Sodium chloride (NaCl) and potassium chloride (KCl).
Question 12.
What will be the colour acquired by a basic solution if a few drops of indicator methyl orange are added to it ?
Answer:
The solution will acquire a yellow colour.
Question 13.
Name the gas evolved when dilute HCl reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. How is it recognised ?
Answer:
The gas evolved is carbon dioxide (CO2). When the gas is bubbled through lime water, it becomes milky.
Question 14.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their pH values :
NaOH solution, blood, lemon juice
Answer:
Increasing order of pH values is : lemon juice < blood < NaOH solution
Question 15.
How does the pH change when the solution of base is diluted with water ?
Answer:
Upon diluting a solution of base with water, the number of OH’ ions in solution per unit volume decrease. The basic strength of the base decreases and pH of solution decreases.
Question 16.
Which one of these has a higher concentration of H+ ions ?
Answer:
IM HCl or IM CH3COOH.
Although both the acid solutions have the same molar concentration (lM) in aqueous solution, but HCl will release more H+ ions as compared to CH3COOH since it is a stronger acid.
Question 17.
Which bases are called alkalies ? Give an example of alkalies ?
Answer:
Water soluble bases are called alkalies. Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is an example of alkalies.
Question 18.
Name the natural source of each of the following :
(a) Citric acid
(b) Oxalic acid
(c) Lactic acid
(d) Tartaric acid. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
(a) Citrus fruits like lemons and oranges
(b) Tomatoes
(c) Milk
(d) Tamarind.
Question 19.
Write the name and chemical formula of the main product formed by heating baking soda.
Answer:
Baking soda is chemically sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). Upon heating, it forms sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) as the main product.
![]()
Question 20.
Write the names and chemical formulae of the products formed by heating gypsum at 373 K.
Answer:
Gypsum upon heating to 373 K forms Plaster of Paris and water
![]()
Question 21.
A student tested the pH of distilled water and found that the colour of pH paper changed to light green.
He found the pH again after dissolving a pinch of common salt in it. What will be colour of pH paper ?
Answer:
Distilled water is neutral with pH close to 7. An aqueous solution of common salt is also neutral. This means that there will be no change in the pH. The colour of pH paper will remain the same i.e., light green.
Question 22.
The pH of rain water collected from two cities A and B was found to be 6 and 5 respectively. The water of which city is more acidic ?
Answer:
Rain water of city B with pH 5 is more acidic.
Question 23.
Why does an aqueous solution of alcohol fail to conduct electric current ?
Answer:
An aqueous solution of alcohol fails to conduct electric current since it does not release H+ ions in solution.
Question 24.
Name the chemical substance which constitutes bees sting.
Answer:
It is methanoic acid or formic acid (HCOOH).
Question 25.
Which substance constitutes the enamel coating of our teeth ?
Answer:
Calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2 constitutes the enamel coating of our teeth.
Question 26.
What happens when a base reacts with a non-metallic oxide. What would you infer about the nature of the non-metallic oxide ?
Answer:
A base reacts with a non-metal oxide to form salt and water. The non-metal oxide is, therefore, an acidic oxide. For example.
2 NaOH (aq) CO2 (g) ———> Na2CO3 (aq) + H2O (aq) .
Question 27.
Name the acids and bases from which the following salts may be obtained.
(i) Potassium sulphate
(ii) Calcium chloride
Answer:
(i) Potassium hydroxide (KOH), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
(ii) Calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2, Plydrochioric acid (HCl)
Question 28.
What will be the pH of the following salt solutions.
(i) Salt made from strong acid and strong base.
(ii) Salt made from strong acid and weak base.
Answer:
(i) The solution will be neutral with pH close to 7 (e.g. NaCl).
(ii) The solution will be acidic with pH less than 7 (e.g. NH4Cl).
Question 29.
Give examples of two substances having water of crystallisation. Write their formulae also.
Answer:
Blue vitriol or hydrated copper sulphate : CuSO4. 5H2O.
Green vitriol or hydrated ferrous sulphate : FeSO4. 7H2O.
Question 30.
What are the pH values of distilled water and common salt solution ?
Answer:
Both are neutral and have pH close to 7.
Question 31.
Which one is a stronger acid, with = 5 or with pH = 2 ?
Answer:
The acid with pH = 2 is a stronger acid.
Question 32.
The pW of three solutions A, B and C are 4, 9 and 6 respectively. Arrange them in increasing order of acidic strength.
Answer:
The increasing order of acidic strength is : B < C < A.
Short Answer Questions
Question 33.
How will you find pH of lemon juice ?
Answer:
(a) Take about 5mL of the given sample of lemon juice in a test tube.
(b) Dip a strip of the universal pH paper in the tube.
(c) Take out the strip and note its colour. It will acquire a orange red colour.
(d) On comparison with pH paper chart, the pH of the solution falls in the range between 2 and 3.
Question 34.
A sample of bleaching powder was kept in an air tight container. After a month, it lost some of its chlorine content. How will you account for it ?
Answer:
Bleaching powder if kept even in an air tight container, will slowly decompose of its own and form calcium chlorate and calcium chloride. The reaction is called auto-oxidation. This will result in decrease in its chlorine contents.
![]()
Question 35.
An aqueous solution of sodium carbonate is basic and not acidic. Assign reason.
Answer:
Sodium carbonate reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and carbonic acid.
![]()
Since the base is strong while acid is weak, the solution is basic and not acidic.
Question 36.
An old person complained of acute pain in the stomach. Doctor gave him a small antacid tablet and he got immediate relief. What actually happened ?
Answer:
The old person was suffering from acute acidity. Antacid tablet contains sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). It reacts with the acid (HCl) formed because of acidity and neutralizes its effect. That is how the old person got relief.
Question 37.
A milkman adds very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk. What happens to its pW ?
Answer:
The pH of fresh milk is nearly 6. Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3). On adding it to fresh milk, the medium becomes alkaline and its pH therefore, increases.
Question 38.
A few drops of phenolphthalein indicator were added to an unknown solution A. It acquired pink colour. Now another unknown solution B was added to it dropwise and the solution ultimately became colourless. Predict the nature of the solutions A and B.
Answer:
The solution A is basic in nature and phenolphthalein has imparted pink colour to it. The solution B is of an acid which has ultimately made solution A colourless by neutralising its basic effect.
Question 39.
A compound which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with proper quantity of water. Identify the compound. Write chemical equation to prepare the compound. Mention one important use of the compound.
Answer:
The compound is Plaster of Paris (CaSO4.½ H2O). It is formed from Gypsum (CaSO2.2H2O) upon heating to a temperature of 373 K and also changes back to Gypsum on adding water. Plaster of Paris is used for setting fractured bones.
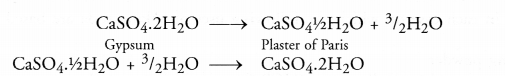
Question 40.
The oxide of a metal M was water soluble. When a blue litmus strip was dipped in this solution, it did not undergo any change in colour. Predict the nature of the oxide.
Answer:
The metal oxide (MO) is of basic in nature. It dissolves in water to form metal hydroxide as follows :
MO + H2O ———-> M(OH)2
A blue litmus does not undergo any change in colour in the basic medium.
Question 41.
Does tartaric acid help in making cake or bread fluffy ? Explain.
Answer:
No, tartaric acid with the formula CH(OH)COOHCH(OH)COOH does not evolve any carbon dioxide during baking. Its role is to react with Na2CO3 formed when NaHCO3 decomposes.
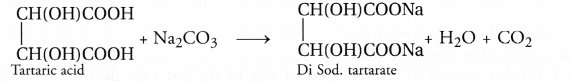
If it is not done, Na2CO3 will impart a bitter taste to the cake.
Question 42.
A doctor applied surgical bandages on the fractured bones of changes are likely to occur ?
Answer:
Surgical bandages are made from Plaster of Paris. When applied on the fractured bones after making them wet, it changes into a hard mass called Gypsum.
![]()
The hard mass keeps the bones in proper position and the gap is slowly filled because of calcification that is taking place on the broken parts. This helps in uniting broken bones and they change to a single piece again.
Question 43.
A chemical compound having smell of chlorine is used to remove yellowness of white clothes in laundries. Name the compound and write the chemical equation involved in its preparation.
Answer:
The compound is bleaching powder (CaOCl2). It removes yellowness from clothes due to its bleaching action. For chemical equation,
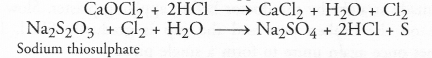
Question 44.
Explain giving reasons :
(i) Tartaric acid is a component of baking powder used in making cakes.
(ii) Gypsum, CaSO4.2H2O is used in the manufacture of cement.
Answer:
(i) Role of tartaric acid in baking powder (mixture of tartaric acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate) is to neutralise sodium carbonate formed upon heating sodium hydrogen carbonate.
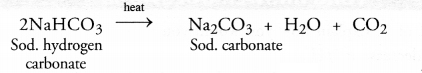
In case it is not done, cake will be bitter and sodium carbonate will also have injurious side effects.
(ii) The role of gypsum (CaSO4.2H2O) in the manufacture of cement is to slow down the process of setting of cement.
Question 45.
What happens when crystals of washing soda are exposed to air ?
Answer:
Washing soda undergoes efflorescence and as a result loses nine molecules of water to form white powder.
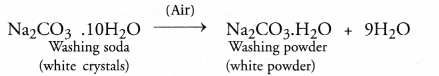
Question 46.
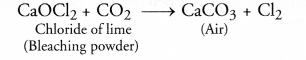
How is chloride of lime chemically different from calcium chloride ? Why does chloride of lime gradually lose its chlorine when kept exposed to air ?
Answer:
Chloride of lime is calcium oxy chloride [(Ca(OCl)Cl] also known as bleaching powder. Calcium chloride is CaCl2. Bleaching powder loses its chlorine on exposure to air because CO2 present in air reacts with it to evolve chlorine as follows :
Question 47.
State the chemical property in each case on which the following uses of baking soda are based :
(i) as an antacid.
(ii) as a constituent of baking powder.
Answer:
(i) It is weakly alkaline in nature and neutralizes acid (HCl) formed in the stomach.
NaHCO3 + HCl ———-> NaCl + H2O + CO2
(ii) It evolves CO2 in the form of bubbles when cake is made by baking. As a result, the cake becomes porous as well as fluffy.
![]()
Question 48.
Crystals of copper sulphate are heated in a test tube for some time.
(a) What is the colour of copper sulphate crystals (i) before heating (ii) after heating ?
(b) What is the source of liquid droplets seen on the inner upper side of the test tube during the heating process ?
Answer:
(a) Colour of crystals before heating : blue.
Colour of crystals after heating : white.
(b) The liquid droplets formed in the inner upper side of the test tube during the heating process are of water. It is released from the crystals of copper sulphate during heating.
![]()
Question 49.
A knife, which is used to cut a fruit, was immediately dipped into water containing drops of blue litmus solution.
If the colour of the solution is changed to red, what inference can be drawn about the nature of the fruit and why ?
Answer:
Since the colour of the blue litmus has changed to red, this means that the fruit juice is acidic in nature.
Question 50.
A person is suffering from indigestion due to the intake of hot spicy food. What remedy you will prescribe to the patient ?
Answer:
Give the name of a chemical that can give relief to him.
The spicy food has resulted in acidity in the stomach. An antacid is needed to cure it. Magnesium hydroxide Mg(OH)2 acts as an antacid.
Question 51.
(a) Give the chemical names of acids present in :
- ants
- lemon
- milk
- tomato.
(b) Write the chemical names of two salts belonging to sodium family.
Answer:
(a)
- Methanoic acid (Formic acid)
- Citric acid
- Lactic acid
- Oxalic acid.
(b) Sodium chloride (NaCl) and Sodium nitrate (NaNO3).
Long Answer Questions
Question 52.
(a) A solution has a pH of 7. Explain how you would you :
(i) increase its pH
(ii) decrease its pH
(b) If a solution changes the colour of the litmus from red to blue, what can you say about its pH ?
(c) What can you say about the pH of a solution that liberates carbon dioxide from sodium carbonate ?
Answer:
(a) The solution with pH 7 is neutral. Its pH can be increased by adding a small amount of base like sodium hydroxide. Basic solutions have pH more than 7. Similarly, pH can be decreased by adding small amount of acid like hydrochloric acid. Acidic solutions have pH less than 7.
(b) The change in colour of litmus from red to blue indicates that the solution is of basic nature with pH more than 7.
(c) Carbon dioxide can be liberated by reacting sodium carbonate solution with acid like dilute hydrochloric acid. This shows that the solution is of acidic nature with pH less than 7.
Question 53.
Explain why :
(i) Common salt becomes sticky during the rainy season
(ii) Blue vitriol changes to white upon heating
(iii) If bottle full of concentrated sulphuric acid is left open in the atmosphere by accident, the acid starts flowing out of the bottle of its own.
Answer:
(i) Common salt contains the impurity of magnesium chloride (MgCl2) which is of deliquescent nature. When exposed to atmosphere, it becomes moist. Therefore, common salt becomes sticky during the rainy reason.
(ii) Blue vitriol (CUSO4.5H2O) upon heating changes to anhydrous copper sulphate (CUSO4) which is white in colour.
(iii) Concentrated sulphuric acid is highly hygroscopic. It absorbs moisture from air and gets diluted. Since the volume increases, the acid starts flowing out of the bottle.
Question 54.
(a) Name the raw materials used in the manufacture of sodium carbonate by Solvay process.
(b) How is sodium hydrogen carbonate formed during Solvay process separated from a mixture of NH4Cl and NaHCO3 ?
(c) How is sodium carbonate obtained from sodium hydrogen carbonate ?
Answer:
(a) The raw materials used are : NaCl, lime stone or CaCO3 and NH3.
(b) Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) is sparingly soluble or less soluble in water and gets separated as a preciptate while NH4Cl remains in solution. The precipitate is removed by filtration.
(c) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is converted to sodium carbonate upon heating.
![]()
Question 55.
(a) What is the action of red litmus on
- dry ammonia gas
- solution of ammonia gas in water ?
(b) State the observations you would make on adding ammonium hydroxide to aqueous solution of
- ferrous sulphate
- aluminium chloride.
Answer:
(a)
- Red litmus has no action on dry ammonia gas because it does not release any hydroxyl ions (OH)–
- When passed through water, ammonia (NH3) is converted to ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH). It dissociates to give hydroxyl ions (OH)– and the solution is basic in nature. Red litmus acquires a blue colour.
(b)
- A green precipitate of ferrous hydroxide would be formed by double displacement reaction.
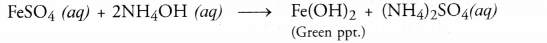
- A white precipitate of aluminium hydroxide will be formed by double displacement reaction.

Question 56.
(a) Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity ?
(b) How does the concentration of hydrogen ions [H3O]+ change when the solution of an acid is diluted with water ?
(c) Which has a higher pH value ; a concentrated or dilute solution of hydrochloric acid ?
(d) What would you observe on adding dilute hydrochloric acid to
- sodium bicarbonate placed in a test tube ?
- zinc metal in a test tube ?
Answer:
(a) An aqueous solution of an acid conducts electricity because in water, an acid (e.g. HCl) dissociates to give ions. Since the current is carried by the movement of ions, an aqueous solution of acid conducts electricity.
(b) Upon dilution, more of acid dissociates into ions. Therefore, concentration of [H3O]+ ions increases upon dilution.
(c) Although more [H3O]+ ions are formed upon dilution, but the number of ions per unit volume decrease. Therefore, pH will increase upon dilution.
(d)
- Carbon dioxide gas would evolve accompanied by brisk effervescene.
NaHCO3 (s) + HCl (aq) ———–> NaCl(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(aq) - Hydrogen gas would evolve accompanied by brisk effervescene.
Zn(s) + 2HCl (aq) ———–> ZnCl2(ag) + H2(g)
Question 57.
(a) A gas is produced when cone. H2SO4 is added to solid sodium chloride taken in a test tube and the tube is heated. The gas coming out through the delivery tube is passed over a dry litmus paper and then over a moist litmus paper. What would you observe ? Explain your answer,
(b) Fresh milk has pH of 6. When it changes to curd (yogurt), will its pH value increase or decrease ? Why ?
(c) What will be the colour of blue litmus in a solution of sodium carbonate ?
Answer:
(a) Upon heating sodium chloride with cone. H2SO4, hydrogen chloride gas evolves.
NaCl(s) + H2SO4(aq) ———> NaHSO4 (aq) + HCl (g)
In the gaseous state, the acidic character is not shown because HCl does not release any H+ ions. In the presence of moisture (moist litmus paper), the gas changes to hydrochloric acid i.e., HCl(aq). The acid releases H+ ions and thus, shows acidic character. Therefore, moist blue litmus paper becomes red.
(b) When fresh milk changes to curd, the pH of the solution is likely to decrease. Actually, lactose present in milk gets converted to lactic acid when curd or yogurt is formed from milk. Therefore, the medium becomes more acidic and its pH decreases.
(c) The solution of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is of basic nature. Actually, the salt dissolves in water to produce NaOH (strong base) and H2CO3(weak acid). The blue litmus will not undergo any change in the basic medium. It will remain blue.
![]()
Question 58.
When electricity is passed through a common salt solution, sodium hydroxide is produced along with the liberation two gases ‘X’ and ‘Y’. The gas ‘X’ burns with a pop sound whereas ‘Y’ is used for disinfecting drinking water.
(i) Identify X and Y.
(ii) Give the chemical equation for the reaction stated above.
(iii) State the reaction of Y with dry slaked lime.
Answer:
(i) The gas ‘X’ is H2 and gas ‘Y’ is Cl2
(ii) The chemical equation for the reaction is :

(iii) Cl2 reacts with slaked lime to form bleaching powder.
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 ———–> CaOCl2 + H2O.
Question 59.
(i) What are strong acids and weak acids ? Give an example for each.
(ii) A dry pellet of a common base ‘B’ when kept in open absorbs moisture and turns sticky. The compound is also formed by Chloralkali process. Identify B. What type of reaction occurs when B is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid ? Write the chemical equation.
Answer:
(i) The strength of an acid is expressed in terms of its H+ ions releasing tendency in aqueous solution or in terms of its degree of dissociation
(α). Strong acids have large value of α (close to one) while weak acids have comparatively less value. For example, hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a strong acid while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is a weak acid.
(ii) The available information suggests that the base ‘B’ present in the pellet is sodium hydroxide (NaOH). It is of deliquescent nature. It absorbs moisture from atmosphere and becomes sticky. The base reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form salt and water. This reaction is known as neutralisation reaction.
NaOH (aq) + HCl(aq) ———–> NaCl (aq) + H2O(l)
Question 60.
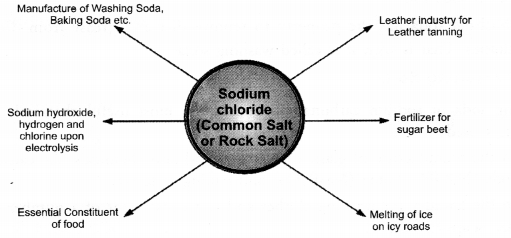
Write the chemical name and formula of common salt. List two main sources of common salt in nature. Write any three uses of common salt. How is it connected to our freedom struggle ?
Answer:
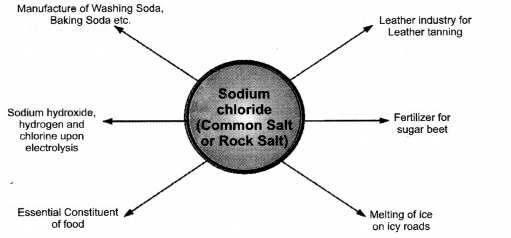
Sodium chloride (NaCl) also called common salt or table salt is the most essential part of our diet. Chemically it is formed by the reaction between solutions of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. Sea water is the major source of sodium chloride where it is present in the dissolved form alongwith other soluble salts such as chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium. It is separated by some suitable method. Deposits of the salt are found in different parts of the world and is known as rock salt. The formation of rock salt is due to the slow evaporation of sea water which takes ages. When pure, it is a white crystalline solid. However, it is often brown due to the presence of impurities.
• Sodium Chloride — Essential for Life
Sodium chloride is quite essential for life. Biologically, it has a number of functions to perform such as in muscle contraction, in conduction of nerve impulses in the nervous system and is also converted into hydrochloric acid in the stomach which helps in the digestion of food. When we sweat, there is loss of sodium chloride and some. Other salts alongwith water. This leads to muscle cramps. The loss has to be compensated suitably by giving certain salt preparations to the patients. These are called electrolytes Electral powder is a very popular electrolyte.
• Chemicals from Common Salt
Sodium chloride is also a very useful raw material for different chemicals. A few out of these are : hydrochloric acid (HCl), washing soda (Na2CO3-10H2O), baking soda (NaHCO3) etc. Upon electrolysis, a strong solution of the salt (brine), sodium hydroxide, chlorine and hydrogen are obtained.
Apart from these, it is used in leather industry for the leather tanning. In severe cold, rock salt is spread on icy roads to melt ice. It is also, a fertilizer for sugar beet.
Question 62.
State what happens when a concentrated solution of sodium chloride (brine) is electrolysed ? Name the process. Write the equation of the reaction involved. Write the names of the products obtained. Mention one use of each product.
Answer:
Sodium chloride (NaCl) also called common salt or table salt is the most essential part of our diet. Chemically it is formed by the reaction between solutions of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid. Sea water is the major source of sodium chloride where it is present in the dissolved form alongwith other soluble salts such as chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium. It is separated by some suitable method. Deposits of the salt are found in different parts of the world and is known as rock salt. The formation of rock salt is due to the slow evaporation of sea water which takes ages. When pure, it is a white crystalline solid. However, it is often brown due to the presence of impurities.
• Sodium Chloride — Essential for Life
Sodium chloride is quite essential for life. Biologically, it has a number of functions to perform such as in muscle contraction, in conduction of nerve impulses in the nervous system and is also converted into hydrochloric acid in the stomach which helps in the digestion of food. When we sweat, there is loss of sodium chloride and some. Other salts alongwith water. This leads to muscle cramps. The loss has to be compensated suitably by giving certain salt preparations to the patients. These are called electrolytes Electral powder is a very popular electrolyte.
• Chemicals from Common Salt
Sodium chloride is also a very useful raw material for different chemicals. A few out of these are : hydrochloric acid (HCl), washing soda (Na2CO3-10H2O), baking soda (NaHCO3) etc. Upon electrolysis, a strong solution of the salt (brine), sodium hydroxide, chlorine and hydrogen are obtained.
Apart from these, it is used in leather industry for the leather tanning. In severe cold, rock salt is spread on icy roads to melt ice. It is also, a fertilizer for sugar beet.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.