Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks in your exams.
The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 5
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Which organelles are called
- Power house
- Suicide bags of the cell ? (CCE 2010, 2011, 2013)
Answer.
- Power house of Cell-Mitochondria.
- Suicide Bags of Cell-Lysosomes.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 9
- HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science
Question 2.
State two important functions of the nucleus of a cell.
(CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
- Genetic Information: Nucleus contains genetic information not only for the cell but also for the whole organism.
- Control Centre: Nucleus functions as control centre for cell metabolism and cell activities.
Question 3.
Name two cell organelles that have their own genetic material/DNA and ribosomes. (CCE 2010, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Mitochondria, Plastids.
Question 4.
Name the plastid which stores starch, oils and protein granules. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Leucoplasts – amyloplast for starch, elaioplast for oil and aleuroplast for protein.
Question 5.
Name the cell organelle which is able to destroy a damaged old/ and worn out cell. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Lysosome.
Question 6.
Who discovered cells in organisms ? Give an example of unicellular organism. (CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
Robert Hooke (1665). Example. Amoeba, Paramoecium
Question 7.
Name the process in which diffusion takes places place through a selectively permeable membrane. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Osmosis: It is diffusion ofwater from the side of its higher
concentration (dilute solution) to the side of its lower concentration (concentrated solution) through a semipermeable membrane.
Question 8.
Name the organelle of the cell which has membrane bound sac filled with powerful digestive enzymes. Write its any one function in the cells. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Lysosome. Function. Intracellular digestion and disposal of worm out cell organelles.
Question 9.
State the full form of ATP. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Adenosine triphosphate.
Question 10.
Name the cell organelle, other than mitochondria, which has its own DNA and ribosomes. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Plastid.
Question 11.
Why do egg shells dissolve in dilute hydrochloric acid ?
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
Egg shells are made of calcium carbonate which reacts with HC1 and forms soluble calcium chloride.
Question 12.
Name the functional unit of DNA that carries genetic information. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Gene.
Question 13.
Name the site organelle where proteins are synthesized in a cell. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Ribosomes.
Question 14.
Name the cell organelle responsible for intracellular transport. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Endoplasmic reticulum.
Question 15.
Name the process through which Amoeba acquires its food from external environment. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Endocytosis.
Question 16.
Identify the cell organelle which is known as the power house of the cell. State reason. (CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Mitochondrion. It is the major seat of production of ATP used as source of energy for various cell functions.
Question 17.
In what way a prokaryotic cell is different from eukaryotic cell with respect to nuclear membrane ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
A nuclear membrane is absent in prokaryotic cell. It is present in eukaryotic cell.
Question 18.
Name the plastid involved in conversion of a green brinjal to violet. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Non-green chromoplast.
Question 19.
Name the phenomenon of losing water by a living plant cell through osmosis. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Exosmosis.
Question 20.
Name
(i) The cells which have changing shape,
(ii) The cells which have typical shape. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(i) Leucocytes
(ii) Liver cell, parenchyma.
Question 21.
Identify single-celled organisms from the following : Cockroach, Chlamydomonas, Snake, Mosquito, Bacteria. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Chlamydomonas, Bacteria.
Question 22.
Name two cell organelles having membrane envelope.(CCE 2012, 2016)
Answer:
Mitochondria (double membrane covering), lysosome (single membrane envelope).
Question 23.
Name the factor which decides the movement of water across the plasma membrane. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Difference in the concentration of water inside the cell and outside solution.
Question 24.
State the significance of membrane biogenesis. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
It replaces the membrane depleted due to exocytosis and injury.
Question 25.
List the constituents of plasma membrane. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Phospholipids, proteins and small carbohydrates.
Question 26.
State the reason for calling cell membrane as selectively permeable membrane. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Cell membrane is called selectively permeable because it
- Allows diffusion of some substances including water
- Allows active passage of some solutes but
- Remains impermeable to others.
Question 27.
Name two components of chromosomes. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
DNA and proteins.
Question 28.
Name two cell organelles having double membrane envelope. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Plastids, Mitochondria.
Question 29.
Mention the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in terms of nuclear region present in them. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Genetic material is enclosed inside the nucleus in eukaryotes while it lies coiled in the cytoplasm as nucleoid in prokaryotes.
Question 30.
Name the cell organelle that detoxifies poisons and drugs in the liver of vertebrates. (CCE 2012, 2015)
Answer:
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Question 31.
Name the kind of plastid which is important for photosyntheis in leaves of plants. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Chloroplasts (green chromoplasts).
Question 32.
Name the main constituent substance present in plant cell wall and state its function. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Cellulose. It provides mechanical strength and rigidity to the cell wall.
Question 33.
Mention the change in human red blood cells when they are placed in hypotonic salt/sugar solution. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
RBCs will continue to swell and ultimately burst.
Question 34.
When a living plant cell loses water through osmois, there is contraction of contents of the cell away from the cell wall. What is this phenomenon called ? (CCE 2012, 2015, 2016)
Answer:
Plasmolysis.
Question 35.
Identify and name the following structures
(a) The undefined nuclear region of prokaryotic cell
(b) Site of energy release inside the cell. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Nucleoid
(b) Mitochondria.
Question 36.
What would happen if an animal cell is kept in distilled water for 24 hours ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
It will swell up and burst.
Question 37.
State the function of chromosome in a cell.(CCE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
It contains genetic information in the form of genes and takes part in equitable distribution of the same at the time of cell division.
Question 38.
The raisins added to porridge swell after some time. Name the process involved. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Osmosis.
Question 39.
Name the factor which decides the movement of water across the plasma membrane. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Concentration of water.
Question 40.
What is nucleoid ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Genetic material of prokaryotes which is devoid of a nuclear envelope and consists of a single compacted DNA molecule (equal to a single chromosome) is called nucleoid.
Question 41.
Every multicellular organism has come from a single cell. Justify this statement. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Every multicellular organism develops from a single cell called zygote, which is formed by fusion of two types of gametes.
Question 42.
Identify the single celled organisms from the following :
Cockroach, Amoeba, Snake, Mosquito, Bacteria. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Amoeba, Bacteria.
Question 43.
Which part of the cell is called brain of the cell ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Nucleus, as it controls all the activities of the cell.
Question 44.
Who discovered cells in living organisms ? Give an example of a unicellular organism. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Leeuwenhoek (1674). Amoeba.
Question 45.
Name the process of building of cell membrane. (CCE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
Membrane biosynthesis.
Question 46.
Mention the commonly used name of cell membrane.
(CCE 2014)
Answer:
Plasma membrane.
Question 47.
What is the name given to the components of the cell ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Cell organelles.
Question 48.
State the role of vacuole in a plant cell. ( CCE 2015)
Answer:
Vacuole: Storage, dumping and development of osmotic concentration.
Question 49.
Pick up the odd one out of ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and give suitable reason. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Ribosomes. Ribosomes have no membrane covering while covering membranes occur in others.
Question 50.
Which process plays an important role in gaseous exchange between cells ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Diffusion.
Question 51.
Name the process by which unicellular fresh water organisms and most plant cells tend to gain water. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Osmosis.
Question 52.
Name the cell organelle which is commonly called “suicide bag” of the cell. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
Lysosome.
Question 53.
Why do chromatin fibres organise themselves into chromosomes? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
For equitable distribution of genetic material during cell division.
Question 54.
State the site of manufacture of fat molecules in a cell.
Answer:
Surface of smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
(a) What is DNA ? Where is it found ?
(b) Name the functional segment of DNA. (CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a) DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is genetic material of living beings. It occurs as part of chromatin in nucleus and as such in mitochondria and plastids.
(b) Gene.
Question 2.
Name two similarities between mitochondria and plastids.
(CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
Both of them possess
- Double membrane covering
- Their own DNA.
Question 3.
Mention any two functions of endoplasmic reticulum.
(CCE 2010, 2011, 2013)
Answer:
- Biosynthesis: Endoplasmic reticulum is engaged in synthesis of lipids (SER) and proteins (RER).
- Support: It provides support to cytoplasm.
Question 4.
Give function of the following organelles
- Chloroplast
- Nucleus
- Ribosomes. (CCE 2010, 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- Chloroplast: Photosynthesis,
- Nucleus: Control of cellular activities and inheritance
- Ribosomes: Protein synthesis.
Question 5.
State cell theory. Name the scientist who presented it. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Cell theory states that cells are the structural and functional units of bodies of all living beings. The theory was put forward by Schleiden and Schwann ( 1839).
Question 6.
What is plasmolysis ? Give one example. (CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
Plasmolysis is shrinkage of protoplasm from the cell wall due to continued exosmosis when cells are placed in hypertonic solution. A peeled carrot piece placed in salt solution will contract due to plasmolysis of its cells.
Question 7.
Write the names of two cell organelles that have their own DNA and ribosomes. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Plastids
- Mitochondria.
Question 8.
What is endocytosis ? Name an organism that feeds by this method. (CCE 2010, 2011, 2013)
Answer:
Endocytosis is the bulk transfer of materials from outside to inside of a cell with the help of special vesicles developed by plasma membrane. Organism (that feeds by endocytosis). Amoeba.
Question 9.
(a) What is plasma membrane made up of ?
(b) Name the process and also explain how food and other substances enter through plasma membrane. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Plasma membrane is made of a bilayer of lipids (or phospholipids) and proteins located inside and outside the same,
(b) Food passes through plasma membrane by endocytosis. Other bulk transports also occur through it. For soluble substances, plasma membrane shows selective permeability.
Question 10.
Two Rhoeo peels were taken. One peel was put in a petridish containing cold water and the other was put in a petridish containing hot water. After a while both were transferred to hypertonic solutions. If the peels were observed under the microscope, will there be any difference in the observation of both the peels. Yes or no. Give reason for your answer.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
Yes. There is difference. The peel placed initially in hot water does not undergo plasmolysis. Plasmolysis occurs in cells of the peel initially kept in cold water. Hot water kills the cells. Dead cells do not show osmosis.
Question 11.
Give technical term for a medium which has exactly the same concentration as the cell ? Why does the size of the cell remain the same when placed in such a solution ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Isotonic solution. A cell placed in isotonic solution neither gains water nor loses water as equal amount of water passes inwardly and outwardly in it.
Question 12.
Mention two functions of Golgi apparatus. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
- Formation of complex sugars,
- Formation of lysosomes.
- Storage, modification and packaging of various substances,
- Secretion and excretion.
Question 13.
How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of cell? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
CO2 moves into and out of cell though diffusion or passage from the area of its higher concentration to the area of its lower concentration across the cell membrane.
Water moves into and out of cell through osmosis or passage of water from the area of higher concentration (e.g., dilute solution) to the area of lower concentration (e.g., strong solution) across the cell membrane which acts as a semipermeable membrane.
Question 14.
(a) In which form does mitochondria release energy ? Write its full form.
(b) The inner membrane of mitochondria is deeply folded. What is the advantage of these folds ? (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) As ATP or adenosine triphosphate.
(b) Folding of inner membrane creates a large surface area for ATP generating reactions.
Question 15.
Where are chromosomes located in a cell ? What are they composed of ? What important information they contain ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Location: Nucleus.
Composition: DNA and proteins.
Information: They carry genetic information for structural and functional traits in the form of genes.
Question 16.
Preetha was observing live cells of Onion in biology laboratory. She observed cell wall, cytoplasm and nucleus clearly. Suddenly her friend who was doing chemistry experiment spilled a few drops of salt water on the slide. After some time Preetha observed the slide and found some changes,
(a) What would have been the change in the live cells of Onion peel after adding salt water ?
(b) Name the type of process.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) There was shrinkage of cytoplasm away from cell wall.
(b) Plasmolysis.
Question 17.
How can plant cells withstand much greater changes in the surrounding medium than the animal cells ?
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
Plant cells are covered by a rigid wall. The cell wall allows the plant cells to withstand changes in the surrounding medium better than animal cells.
Question 18.
Write two characteristics of prokaryotic cells. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(i) Genetic material is equal to a single chromosome which is not organised into a nucleus,
(ii) Membrane bound cell organelles absent.
Question 19.
What are unicellur organisms ? List two examples. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Organisms made of single cells are called unicellular organisms. Examples. Amoeba, Paramoecium.
Question 20.
Which stain is used to prepare an Onion peel slide ? Why do we need a stain to be added ? (CCE 2013)
Answer:
Safranin. The stain is added to make the cellular components clearly visible under the microscope.
Question 21.
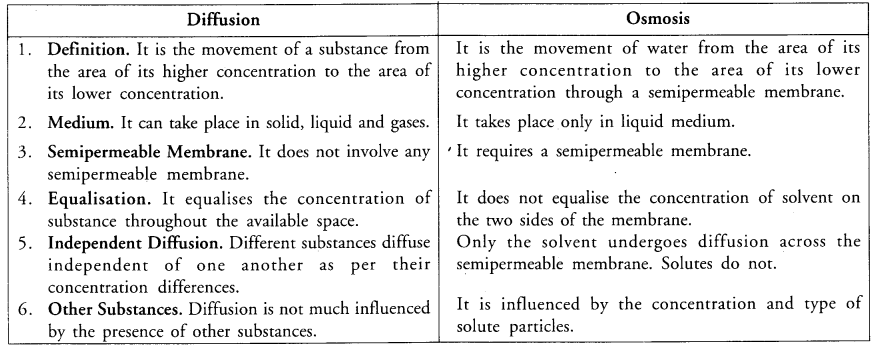
Name the process by which
(a) Oxygen moves in and out of the cell,
(b) Water moves in and out of the cell. Differentiate between the two processes. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Diffusion
(b) Osmosis.
Question 22.
What will happen if
(a) Almonds are soaked in water.
(b) Concentrated solution of fertilizer is applied to green grass lawn. Give suitable reason in support of your answer.
(CCE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Almond will swell up due to endosmosis. There is higher concentration of water around almonds than inside them.
(b) Grass will shrivel due to exosmosis. There is higher concentration of water inside grass plants than in outer concentrated fertilizer solution.
Question 23.
Give one function each of RER and SER. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
Function of RER. Synthesis of protein for export to Golgi apparatus.
Function of SER. Synthesis of lipids.
Question 24.
Name a cell organelle which lacks membrane. Where is it prepared ? (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(i) Ribosome,
(ii) It is synthesised in the form of subunits in nucleolus part of nucleus.
Question 25.
Differentiate between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, based on the size and number of chromosomes. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
The genetic material of a prokaryotic cell is equal to a small histone free chromosome and is often called prochromosome. A eukaryotic cell has two to several histone supported larger chromosomes.
Question 26.
What is the importance of osmosis in :
(a) Unicellular organisms
(b) Plants ? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Osmosis in Unicellular Organisms. Absorption of water, osmoregulation.
Osmosis in Plants. Absorption of water from soil, cell to cell movement of water.
Question 27.
Which cell organelle is known as “suicide bags” of the cell ? Why? (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes against all types of organic materials. If their covering membrane breaks as it happens during injury to cell, the digestive enzymes will spill over the cell contents and digest the same. As lysosomes are organelles which on bursting can kill the cells possessing them, they are called suicide bags.
Question 28.
Describe the structure of mitochondria with reference to its membrane covering. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
Structure: Mitochondria are rod or sausage shaped colourless organelles of aerobic eukaryotes that have a double membrane covering. The outer membrane is porous. The inner membrane is folded. The folds are called cristae. They bear ATP generating elementary particles. The matrix contains enzymes of Krebs cycle,
Question 29.
(a) Name the cell organelle which helps in packaging and
dispatching the material synthesised over the endoplasmic reticulum to various targets inside and outside the cell.
(b) Name and write function of cell organelle formed by the above cell organelle. ( CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a) Golgi apparatus,
(b) Lysosome: Lysosomes possess digestive enzymes which help in intracellular digestion and removal of scenescent cellular structures.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
Question 1.
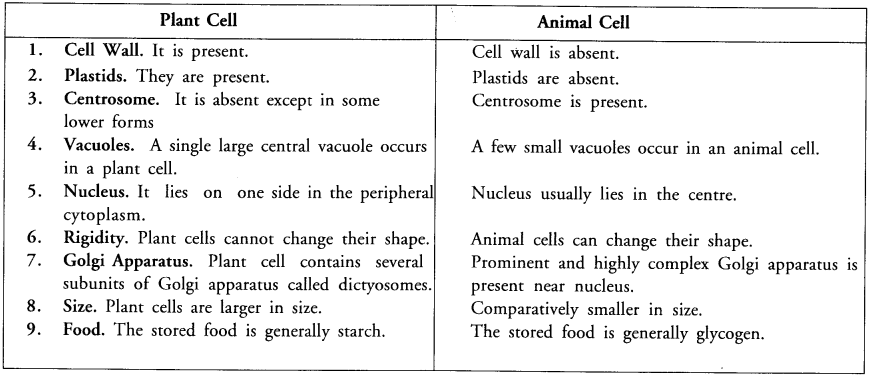
Write in a tabular form three differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. (CCE 2010, 2011, 2012)
Answer:
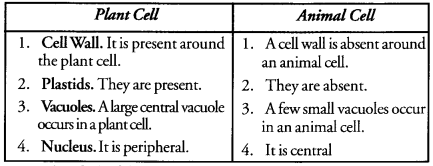
Question 2.
Classify the following as osmosis or diffusion :
(a) Aquatic animals using oxygen dissolved in water during respiration.
(b) Swelling up of raisins on keeping in water.
(c) Spreading of virus on sneezing. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Diffusion
(b) Osmosis (endosmosis)
(c) Diffusion.
Question 3.
(a) Which cell organelles are called power houses of the cell and why ? (CCE 2010, 2012)
(b) Why is ATP called energy currency of the cell ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Mitochondrion is known as power house of the cell because it produces most of the molecules of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which are required for providing energy for synthesis of new chemicals, mechanical and other cellular functions.
(b) ATP or adenosine triphosphate is called energy currency of the cell as it is built up when energy is available as from an * exothermic reaction and broken down to release the energy whernsver required for performing an activity or an endothermic reaction.
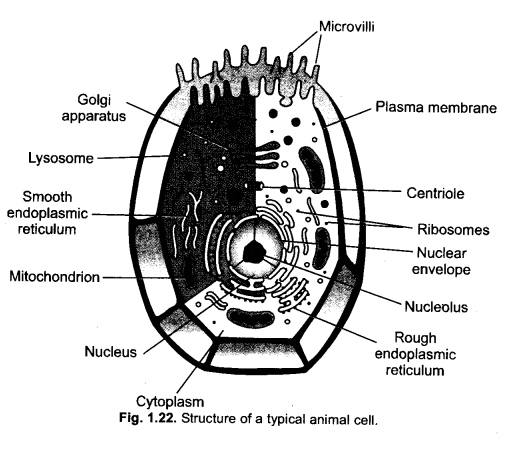
Question 4.
Draw a neat diagram of an animal cell and label on it the following :
Plasma membrane. Nucleus, Lysosome/RER, centriole, Lysosome. (CCE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
Question 5.
List any three functions performed by endoplasmic reticulum.
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Biosynthesis: Endoplasmic reticulum is engaged in synthesis of lipids (SER) and proteins (RER).
- Support: It provides support to cytoplasm.
- Transport: It helps in intracellular as well as intercellular transport of substances.
Question 6.
- State two types of plastids
- Write one function of each. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
- Chloroplasts and chromoplasts.
- Chloroplasts. Photosynthesis. Chromoplasts. Providing colouration to flowers and fruits for attracting animals to perform pollination and dispersal respectively.
Question 7.
What are chromosomes ? List their two functions. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
Chromosomes are rod-like DNA containing stainable condensed chromatin units which become visible at the time of cell division.
Functions:
- They carry genetic information in the form of genes arranged in a linear sequence.
- By their replication just before cell division and equitable distribution during cell division, chromosomes maintain the hereditary content of the cells.
Question 8.
List three differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (CCE 2010, 2011, 2012)
Answer:

Question 9.
Describe the role played by lysosomes. Why are these termed as suicide bags ? How do they perform their function ?
(CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
Role: Lysosomes take part in
- Destruction of foreign particles.
- Intracellular digestion of food
- Digestion and removal of worn out cell organelles.
Suicide Bags: Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes against all types of organic materials. If their covering membrane breaks as it happens during injury to cell, the digestive enzymes will spill over the cell contents and digest the same. As lysosomes are organelles which on bursting can kill the cells possessing them, they are called suicide bags.
Working: Lysosomes are full of digestive enzymes. They fuse with foreign and worn out cell structures. Lysosomal enzymes bring about their digestion. The digested substances diffuse out into cell while the undigested materials are thrown out of the cell.
Question 10.
Explain your observation in the following with reason involved in the process : (a) Salt is applied to raw mango pieces (b) Dried raisins are kept in water for a few hours.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Salt applied over raw mango pieces will kill the surface cells and prevent growth of microbes over them due to exosmosis.
(b) Raisins swell up due to endosmosis or entry of water into their cells due to osmosis.
Question 11.
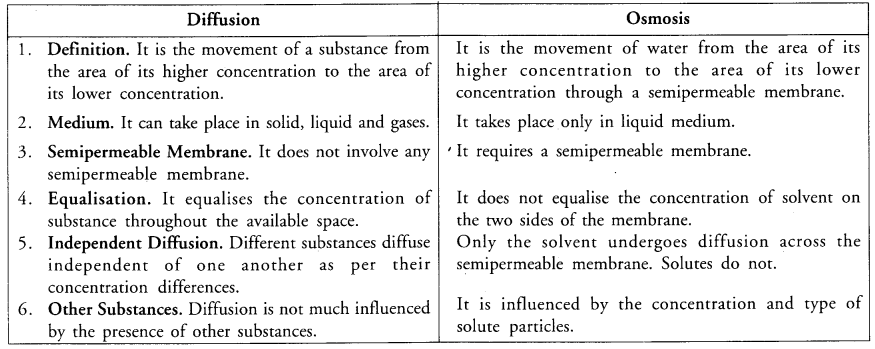
Differentiate between diffusion and osmosis. Write any two examples where a living organism uses osmosis to absorb water. (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a)
(b) Examples :
(i) Absorption of soil water by roots.
(ii) Gaining of water by guard cells during opening of stomata.
Question 12.
(a) Name the organelles which provide turgidity to the plant cell. Name any two substances which are present in it.
(b) How are they useful in unicellular organisms like Amoeba ?
(CCE 2011, 2014)
Answer:
(a) Vaculoes.
- Water,
- Dissolved storage and waste substances (Sugars, salts, amino acids, organic acids).
(b) In unicellular organisms vacuoles take part in
- Osmoregulation and excretion by contractile vacuoles,
- Digestion of food in food vacuoles.
Question 13.
Distirigush amongst hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Hypotonic solution has lower osmotic concentration and higher water concentration as compared to the cell. The cell gains water from Such external solution by osmosis. Isotonic solution is the one which has the same osmotic concentration and water concentration as that of the cell. The cell placed in such a solution will neither gain nor lose water.
Hypertonic solution has a higher osmotic concentration and lower water concentration as compared to the cell. The cell loses water to such an external solution and gets plasmolysed.
Question 14.
(a) What is osmosis ?
(b) What happens to cell when it is placed in hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic solutions respectively ?
(c) What is plasmolysis ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Osmosis is diffusion of water from the region of its higher concentration (pure water or dilute solution) to the region of its lower concentration (strong solution) through a semipermeable membrane.
(b)
- Cell in Hypotonic Solution. Swells up due to endosmosis and becomes turgid.
- Cell in Isotonic Solution. No change.
- Cell in Hypertonic Solution. Cell contents shrink due to exosmosis or outward passage of water.
(c) Plasmolysis is shrinkage of protoplasm from the cell wall due to continued exosmosis when cells are placed in hypertonic solution. A peeled carrot piece placed in salt solution will contract due to plasmolysis of its cells.
Question 15.
State main functions of the following :
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Vacuoles. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Mitochondria,
- Site of aerobic respiration.
- Liberation of energy as ATP (hence power house of cells).
(b) Golgi Apparatus.
- Formation of lysosomes.
- Complexing, packaging, secretion and excretion of substances.
(c) Vacuoles,
- Storage ofinorganic and organic substances.
- Dumping ofwastes.
- Developing osmotic concentration for absorption of water and maintenance of turgidity of cells.
Question 16.
Briefly explain the structure and function of nucleus.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
Structure: Nucleus is oval or rounded dense cellular structure having four components :
- A double membrane porous envelope (nuclear envelope),
- Nuclear sap or nucleoplasm.
- Chromatin made of threads of DNA and protein which get converted into chromesomes at the time of cell division,
- Nucleolus, a rounded naked structure attached to chromatin and seat of ribosome formation.
Functions:
- Nucleus controls cellular activities.
- It contains genetic or hereditary information over its chromosomes for expression of various traits.
- Ribosomes are formed in its nucleolus.
Question 17.
What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum ? Mention one function of each. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Types: There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Rough endoplasmic reticulum bears ribosomes on its surface. The same are absent over SER.
Function of RER: Synthesis of proteins over its ribosomes.
Function of SER: Synthesis of lipids and steroids.
Question 18.
What are chromoplasts and leucoplasts ? Give an example of chromoplasts which has green pigment. ( CCE 2011)
Answer:
Chromoplasts. The coloured plastids are called chromoplasts. Leucoplasts. The colourless plastids are known as leucoplasts. Green Chromoplasts. Chloroplasts.
Question 19.
What will happen if the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Organisation is important for performing different functions of the cell. If organisation is destroyed, the cell will not be able to perform many of its functions. This will lead to senescence and death of the cell Bursting of lysosomes will quicken death of the cell.
Question 20.
Draw the diagram to show animal cell and label the following parts :
(a) Power house of the cell,
(b) Suicidal bag
(c) Organelle which helps in protein synthesis
(d) Organelle which helps during cell division.
(CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
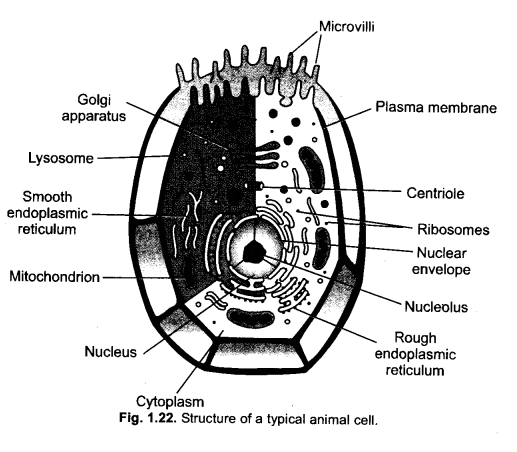
(a) Mitochondrion
(b) Lysosome
(c) Ribosome
(d) Centriole.
Question 21.
(a) State two types of plastids. Mention the function of each.
(b) How do vacuoles help in ingestion and egestion in single celled organisms ? (CCE 2011, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Leucoplasts and chromoplasts. Leucoplast. Storage of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Chromoplast. Photosynthesis by chloroplasts (green chromoplasts) and attractive colouration in flowers and fruits by non-green chromoplasts.
(b) During ingestion of food, the plasma membrane invaginates in contact with food particle and pinches off as small food containing vacuole called phagosome. Phagosome fuses with lysosome to form food vacuole. Digestion occurs. The digested materials pass out into cytoplasm. The vacuole containing undigested food pieces rises to the surface, fuses with plasma membrane to perform egestion.
Question 22.
What is the relationship between chromatin material and chromosomes ? (CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer:
Chromatin is an intertwined mass of thread-like DNA- protein complex that occurs in the nucleus. At the time of cell division, chromatin condenses and gets organised into chromosomes.
Question 23.
(a) Explain the phenomenon of plasmolysis.
(b) Explain how do cell walls permit cells of fungi to withstand very dilute external media without bursting.
(CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Plasmolysis is shrinkage of protoplasm from the cell wall due to continued exosmosis when cells are placed in hypertonic solution. A peeled carrot piece placed in salt solution will contract due to plasmolysis of its cells.
(b) Despite being present in very dilute medium, the fungal cells do not undergo unlimited swelling. Swelling stops as soon as the limit of cell wall elasticity is reached. At this time, the cell wall exerts an opposite force that prevents further entry of water.
Question 24.
List the specific functions of the following :
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosomes
- Mitochondria
- Plastids
- Vacuoles in unicellular organisms. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
- Protein synthesis,
- Golgi Apparatus.
- Formation of lysosomes.
- Complexing, packaging, secretion and excretion of substances.
- Lysosomes. Waste disposal, intracellular digestion,
- Mitochondria,
- Site of aerobic respiration.
- Liberation of energy as ATP (hence power house of cells).
- Plastids Photosynthesis (chloroplasts), storage (leucoplasts), colouration (non-green chromoplasts).
- Vacuoles in Unicellular Organisms. Osmoregulation, excretion, ingestion, digestion and egestion.
Question 25.
Describe the structure and write any two functions of Golgi apparatus. (CCE 2011)
Answer:
Golgi apparatus is a stack of curved membrane bound flat sacs called cisternae/cisterns that bear tubules and vesicles on the sides Functions.
Golgi Apparatus:
(a) Formation of lysosomes.
(b) Complexing, packaging, secretion and excretion of substances.
Question 26.
(a) Which organelles supply energy to a cell ? In what form it is stored ?
(b) Explain the structure of this organelle,
(c) Does this organelles contain DNA ? Why ? (CCE 2011)
Answer:
(a) Mitochondria. The energy is stored in the form of ATP.
(b) Structure. Mitochondria are rod or sausage shaped colourless organelles of aerobic eukaryotes that have a double membrane covering. The outer membrane is porous. The inner membrane is folded. The folds are called cristae. They bear ATP generating elementary particles. The matrix contains enzymes of Krebs cycle,
(c) Mitochondria possess DNA and ribosomes which help them in synthesis of a number of proteins for their functioning.
Question 27.
Mention the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells regarding
(i) Nuclear region
(ii) Cell organelles
(iii) Chlorophyll. (CCE2012)
Answer:
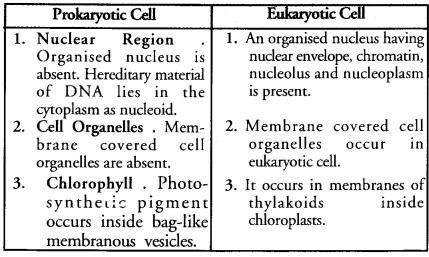
Question 28.
(a) What is membrane biogenesis ?
(b) Explain what happens when a drop of concentrated sugar solution is placed on a rheo leaf mounted on a glass slide. Name this phenomenon. Would the same happen if riieo leafwas boiled before mounting ? Give reason for your answer. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Membrane Biogenesis. It is formation, renewal and repair of biomembrane from its constituents (lipids and proteins) synthesised over smooth and rough endoplasmic membrane and their modification by Golgi apparatus.
(b)
- A concentrated sugar solution will cause exosmosis in cells of rheo peel mounted on a glass slide. The cytoplasm withdraws from cell wall. The phenomenon is called plasmolysis.
- Plamolysis does not occur in cells of rheo leaf peel if the latter has been boiled before mounting. It is because boiling kills the cells. Exosmosis can occur only in living cells.
Question 29.
(a) Which cell organelle would you associate with ATP production ? How is this organelle able to make its own protein ?
(ib) A student performed an experiment by placing a de- shelled egg in a concentrated salt solution for five minutes.
What change did he observe in the egg ? Give reason for the same. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Mitochondrion. The organelle is able to synthesise some of its proteins because it has its own DNA and ribosomes.
(b) The deshelled egg placed in salt solution contracts. The contraction is caused by exosmosis.
Question 30.
(a) Where are genes located in a cell ?
(b) Name the nucleic acids that are present in animal cell. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Genes are located in the chromatin/chromosomes inside the nucleus.
(b) Animal cell has two types of nucleic acids, DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribose nucleic acid). While RNA is mostly located in the cytoplasm, DNA is present inside nculeus (smaller quantity in mitochondria).
Question 31.
(a) State and explain the process by which Amoeba obtains its food. (CCE 2012)
(b) Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Amoeba obtains its food through endocytosis. Part of plasma membrane coming in contact with food particle
invaginâtes, engulfs the same and is pinched off into cytoplasm as phagosome. Phagosome fuses with a lysosome to produce a food vacuole. Digestion occurs in the food vacuole. The digested materials pass out into the cytoplasm. The vacuole having undigested matter rises to the surface and performs exocytosis to throw out the undigested matter.
(b) Cell membrane is semipermeable membrane for water. It permits the entry of gases through diffusion. Ions, sugar, amino acids, etc. pass through the plasma membrane by an active process. Plasma membrane is impermeable to certain other materials. Therefore, it is selectively permeable.
Question 32.
Two beakers A and B contain plain water and concentrated sugar solution respectively. Equal number of dried raisins are kept in them for a few hours and then taken out. (t) Explain the reason for the difference in the physical appearance of raisins which were taken out of the two beakers, (it) On the basis of above observation, categorise the two solutions as hypotonic and hypertonic. (CCE 2012)
Answer:
- Raisins placed in beaker A have swollen while those of beaker B remain shrivelled,
- Solution (here water) in beaker A is hypotonic (as it causes entry of water into raisins) while solution in beaker B is hypertonic as no water from this solution passes into raisins.
Question 33.
(a) How is flexible nature of plasma membrane useful to Amoeba. Name the process.
(b) Plastids are able to make their own protein. Explain.
(c) Why plant cells shrink when kept in hypertonic solution.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a)Flexible nature of plasma membrane is useful to Amoeba in
- Engulfing food particles. The process is called endocytosis.
- Formation of pseudopodia for locomotion.
(b) Plastids possess DNA and ribosomes for formation of proteins as per information present in the former.
(c) Plant cells placed in hypertonic solution shrink due to passage of a part of their contained water into outer solution due to exosmosis.
Question 34.
(a) List two roles of nucleus of a cell,
(b) Name two substances stored in the vacuoles of a plant cell.
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
(a) Roles of Nucleus,
- Control: Nucleus controls cell metabolism and cell activities,
- Hereditary Information: Nucleus contains all the hereditary information not only for the cell but also the whole organism.
(b) Substances in Vacuoles,
- Water
- Salts and some organic substances.
Question 35.
(a) Who gave the term Golgi apparatus,
(b) Name one cell organelle formed by Golgi apparatus.
(c) Write any two functions of Golgi apparatus.
Answer:
(a) Cajal (1914).
(b) Lysosome
(c)
(i) Complexing, packages, secretion and exeretion of substances,
(ii) Membrane biosynthesis.
Question 36.
Distinguish leucoplast from chromoplast based on one feature. Give an example of chromoplast present in plant cell. What is the function of chromoplast in plant cell ?
(CCE 2012)
Answer:
Leucoplast is colourless plastid while chromoplast is coloured plastid. Chromoplast present in green aerial cells of the plant is called chloroplast. It takes part in photosynthesis.
Question 37.
Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. How is endoplasmic reticulum important for membrane biosynthesis ? (CCE 2012)
Answer:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum bears ribosomes over its surfaces while the same are absent over smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The two types of endoplasmic reticulum synthesise respectively proteins and lipids that are modified and complexed by Golgi apparatus for membrane biosynthesis.
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
(a) What are lysosomes ? Why are they called “suicide bags of a cell” ?
(b) What happens to the dry raisins when we put them in plain water for some time ? State the reason for whatever is observed. What would happen if these raisins are now placed in concentrated salt solution ? (CCE2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a) Lysosomes. They are small, single membrane bound cell organelles which contain digestive enzymes for intracellular digestion and waste disposal.
Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes against all types of organic materials. If their covering membrane breaks as it happens during injury to cell, the digestive enzymes will spill over the cell contents and digest the same. As lysosomes are organelles which on bursting can kill the cells possessing them, they are called suicide bags.
(b) Dry raisins placed in water swell up due to endosmosis or osmotic entry ofwater into them. The swollen raisins placed in concentrated salt solution will shrink in size and become wrinkled due to exosmosis or osmotic expulsion of water from them.
Question 2.
(a) Distinguish between chloroplast and leucoplast with respect to their pigments and function.
(b) How would
(i) a plant cell
(ii) an animal cell behave when placed in a hypotonic solution of sodium chloride ? Explain giving reason. (CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a)
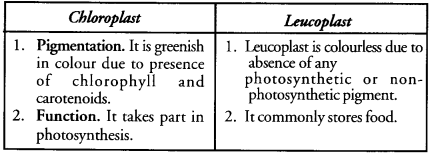
(b) Cells placed in hypotonic solution swell up due to endosmosis or osmotic entry of water into them. Swelling is limited in plant cells as they have rigid cell walls. Due to absence of a cell wall, an animal cell will continue to swell up till it bursts.
Question 3.
(a) What is endoplasmic reticulum ?
(b) Describe its structure.
(c) Name two types of endoplasmic reticulum.
(d) What crucial role does it play in the liver cells of vertebrates ?
(e) What is membrane biosynthesis ?
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Endoplasmic reticulum is a three dimensional interconnected network of membrane lined channels that run through the cytoplasm.
(b) Structure. Endoplasmic reticulum or ER has three components,
(i) Cistemae. They are interconnected flat sacs which run parallel to one another.
(ii) Tublues. They are tube-like extensions of cisternae.
(iii) Vesicles. They are oval or rounded sacs that are connected to cisternae and tubules. Membranes of endoplasmic reticulum are similar to plasma membrane but are thinner. The channels contain a fluid endoplasmic matrix.
(c) Types. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Rough endoplasmic reticulum bears ribosomes on its surface. The same are absent over SER.
(d) Detoxification. SER present in vertebrate liver detoxifies poisons and drugs.
(e) Membrane Biosynthesis. It is synthesis of cell membrane from its constituent proteins and lipids synthesised over endoplasmic reticulum and complexed by Golgi apparatus.
Question 4.
(a) Differentiate between
(i) The functions of RER and SER
(ii) Plasma membrane and cell wall.
(b) What is endocytosis ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) (i)

(ii) Differences between Plasma Membrane and Cell Wall.
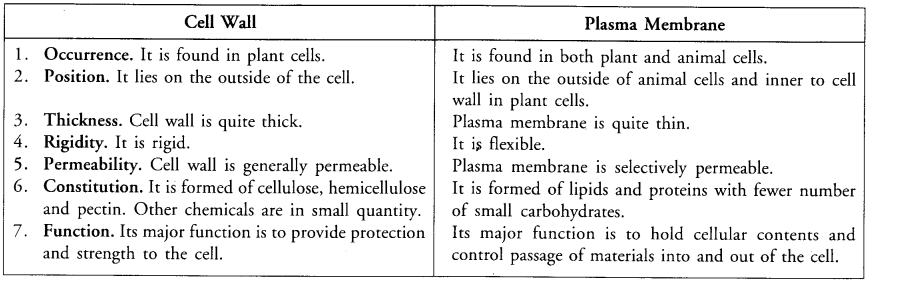
(b) Endocytosis is the bulk transfer of materials from outside to inside of a cell with the help of special vesicles developed by plasma membrane. Organism (that feeds by endocytosis). Amoeba.
Question 5.
(a) Differentiate between
(i) Nucleus and nucleoid.
(ii) Plant cell and animal cell,
(b) What is osmosis ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) (i) Differences between Nucleus and Nucleoid.

(ii) Plant Cell and Animal Cell.
(b) Osmosis: Diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane from the region of its higher concentration (dilute solution) to the region of its lower concentration (concentrated solution) is known as osmosis.
Question 6.
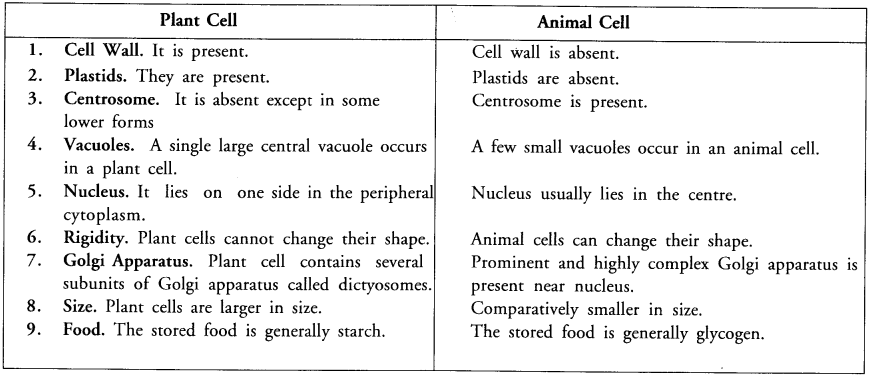
(a) In the given diagram, identify the parts marked B and C.
(b) What are the substances that organelle A stores ?
(c) Mention one function of organelles B and C.
(d) What are cisterns ? (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) B —Golgi apparatus.
C — Chloroplast.
(b) A (Central Vacuole). It stores salts, sugar, amino acids, organic acids, some proteins and waste products. Recently lysosomal enzymes have also been detected in it.
(c) Function. :
(i) B — Secretion and excretion.
(ii) C — Photosynthesis.
(d) Cisterns. They are membrane bound curved flat stacks of Golgi bodies that bear tubules and vesicles on their periphery. Similar structures also occur in endoplasmic Ans. reticulum.
Question 7.
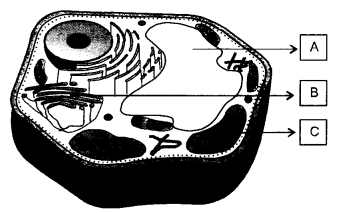
Observe the given figure and answer the questions.
(a) What has happened to cell A and B ? Explain.
(b) Identify the type of solution into which cells A and B are placed.
(c) Name and explain the process that has taken place in cells A and B. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Cell A has become turgid while cell B has become plasmolysed (flaccid).
(b) Cell A is placed in hypotonic solution while cell B is dipped in hypertonic solution.
(c) A—Endosmosis or osmotic entry of water hasoccurred. It is because cell sap has lower concentration of water while the outer solution has higher concentration of water.
Water moves from its higher concentration to lower concentration across a semipermeable membrane.
B —Exosmosis or osmotic expulsion of water has occurred. The cell sap has higher concentration of water than the external solution. Therefore, water passes from inside the cell to the outside.
Question 8.
(a) Draw a neat and labelled diagram’ of a prokaryotic cell.
(b) Why organisms like bacteria are called prokaryotes ?
(CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a)
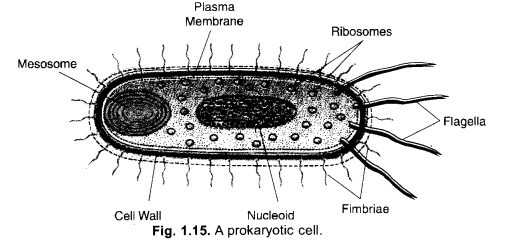
(b) Bacteria are called prokaryotes because their genetic material is not organised into a nucleus. Instead it lies directly inside cytoplasm as nucleoid.
Question 9.
(a) Categorise plastids based on their colour and function.
(b) Mention the strange similarity between plastids and mitochondria with reference to synthesis of their own materials. What do they synthesise ? (CCE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
(a) Plastids are of three types on the basis of their colour.
- Colourless Plastids or Leucoplasts. Depending upon their storage product, they are of three types — amyloplasts (storage of starch), aleuroplasts (storage of proteins), and elaioplasts (storage of oil).
- Brown-Red Plastids or Chromoplasts. They provide colouration to flowers and fruits for attracting pollinators and disseminators.
- Green Plastids or Chloroplasts. They perform photosynthesis.
(b) Similarity Between Plastids and Mitochondria. They have their own DNA and ribosomes. Ribosomes are used to synthesise a part of proteins and enzymes required by the organelles. Rest of the materials are obtained from the cytoplasm of the cell. DNA and ribosomes make the two organelles semi-autonomous.
Question 10.
(a) What is lacking in a virus which makes it dependent on a living cell to multiply ?
(b) Expand RER and SER. Differentiate between their structure and function. (CCE 2010, 2011)
Answer:
(a) Virus does not have a metabolic machinery as it lacks cytoplasm. Therefore, it is dependent upon the metabolic machinery of a living cell for multiplication.
(b) RER: Rough endoplasmic reticulum.
SER: Smooth endoplasmic reticulum.

Question 11.
Draw a labelled diagram of an animal cell and label the following organelles :
(a) The organelle that contains powerful digestive enzymes.
(b) The organelle that has its own DNA.
(c) The organelle that forms cytoplasmic framework
(d) The organelle that helps in expelling excess water in Amoeba. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
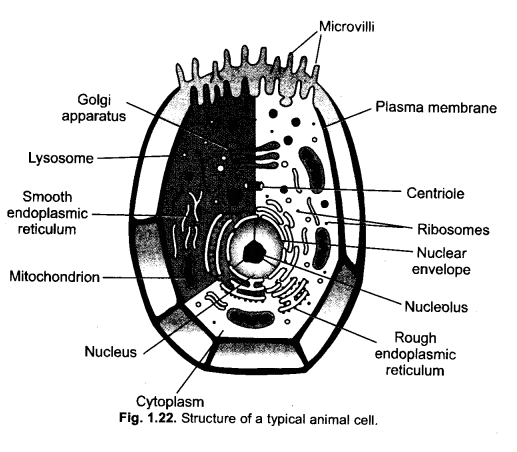
Labelling,
(a) Lysosome
(b) Mitochondrion
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Vacuole (Contractile vacuole in Amoeba).
Question 12.
(a) Why does nuclear membrane have pores ?
(b) Why do chromosomes contain DNA in the nucleus ?
(c) Give two roles of nucleus in the cell. (CCE 2010)
Answer:
(a) Pores in Nuclear Membrane. For allowing and controlling the exchange of materials between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
(b) Chromosomes Contain DNA in Nucleus, (i) In order to protect DNA from influence of cytoplasmic enzymes, (it) For separating transcription machinery from translation machinery.
(c)
- Bodies of the living beings are made up of cells and their products.
- Activities of an organism are the sum total of activities of its cells.
- Cells develop from pre-existing cells.Viruses are an exception to cell theory.
Question 13.
(i) Draw a plant cell and label the parts which
(a) Is a dead layer and is permeable
(b) Is the kitchen of the cell
(c) Packages materials coming from endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Controls and regulates all the activities of the cell.
(ii) Identify the two structures which are present only in typical plant cell. (CCE 2013)
Answer:
(i)
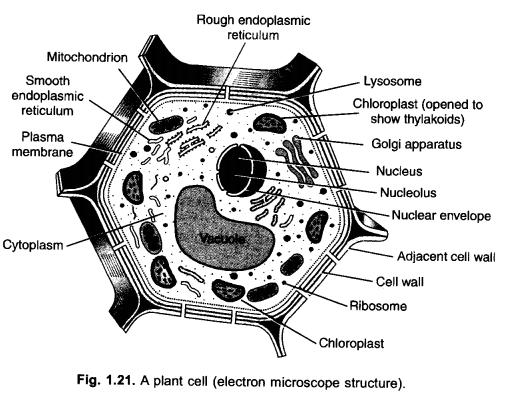
(a) Cell wall
(b) Chloroplast
(c) Golgi apparatus
(d) Nucleus.
(ii) (a) Cell wall (b) Chloroplast/plastid.
Question 14.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of an animal cell and label the parts whose functions are as follows :
- Flelps in storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles.
- Helps in keeping the cell clean by digesting worn out cell organelles,
- Helps in oxidation of glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP.
- Allows the entry and exit of some materials into and out of cells.
(b) Define nucleoid. (CCE 2014)
Answer:
(a)
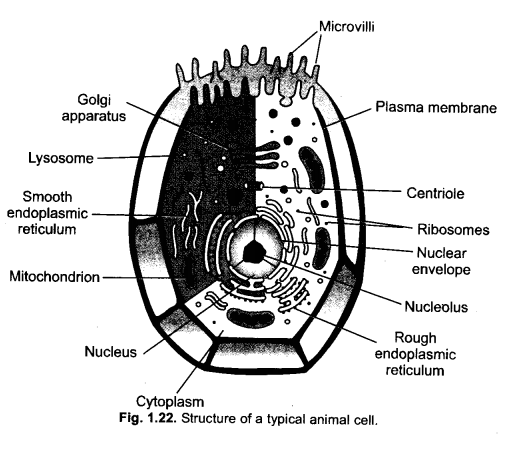
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosome
- Mitochondrion
- Plasma membrane.
(b) Nucleoid: Genetic material of prokaryotes which is devoid of a nuclear envelope and consists of a single compacted DNA molecule (equal to a single chromosome) is called nucleoid.
Question 15.
Do all cells of our body look alike in terms of shape, size and structure ? What similarities do they have ? (CCE 2015, 2016)
Illustrate by drawing diagrams of various cells present in human body. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
No. Similarities,
- Covering of plasma membrane.
- Presence of centrally placed nucleus.
- Cytoplasm and different cell organelles,
e.g., Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum. (iv) Metabolic pathways.
Cells become differentiated to perform different functions. They also come to have different shapes and sizes, e.g., nerve cell, bone cell, fat cell, ovum, sperm, blood cells, muscle fibres.
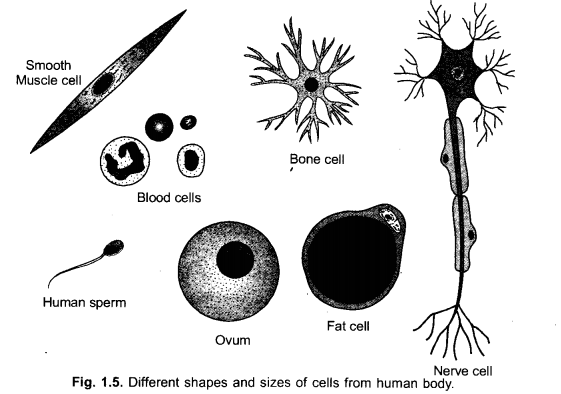
Question 16.
Draw and label a plant cell and write one main function of the following cell organelles :
(a) Chloroplast
(b) Plasma membrane
(c) Vacuole
(d) Lysosomes. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
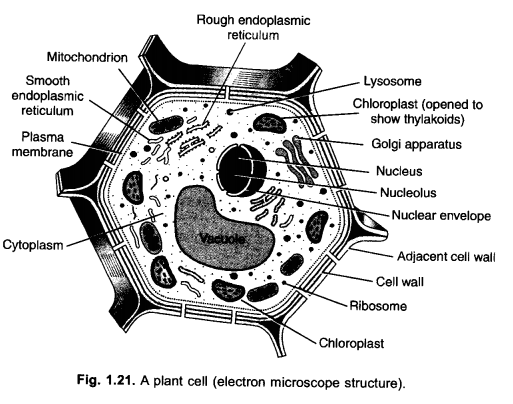
(a) Chloroplast. Photosynthesis.
(b) Plasma membrane. Holding the cell contents and selective^^” permeability.
(c) Vacuole. Storage, dumping and development of osmotic concentration.
(d) Lysosome. Scavenging, intracellular digestion and defence.
Question 17.
Write differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Draw diagram also. (CCE 2015)
Answer:

Diagrams :
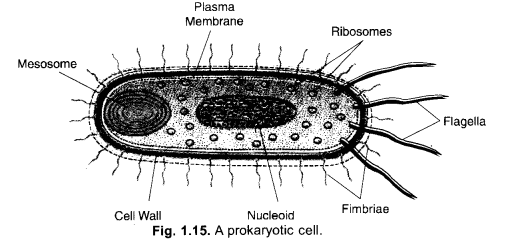
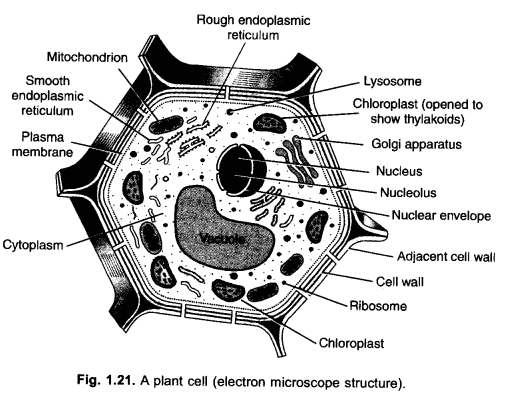
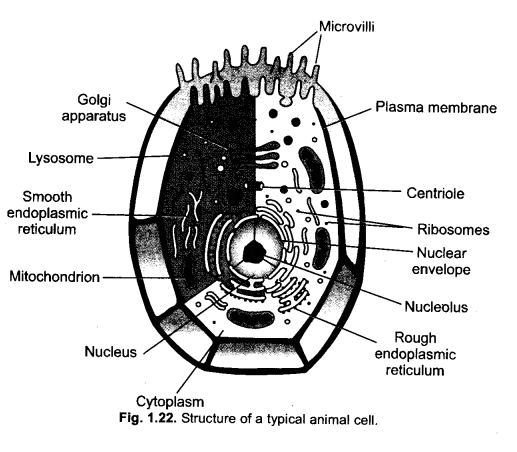
Question 18.
(a) Why is the cell called structural and functional unit of life ?
(b) Explain the concept of division of labour in multicellular organisms giving an example. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Structural Unit: A living organism is made up of one or more cells. Therefore, cell is structural unit of life. Functional Unit. All life functions of an organism reside in its cells. Cells may also become specialised to perform specific functions like contraction in muscle cell or impulse transmission in nerve cell. Therefore, cells are functional units of life.
(b) Division of labour is the taking up of different functions of the system/body by different specialised components in a coordinated fashion so that the whole is benefitted without any part put to overwork. It increases efficiency. In multicellular organisms like humans there are a number of organs, tissues and cells performing different functions, e.g. contraction and movement by muscle cells, transmission of impulses by nerve cells, transport of oxygen by RBCs, protection from germs by white blood corpuscles, gamete formation by germ cells, pumping of blood by heart, extraction of wastes by kidneys, etc.
Question 19.
On the basis of number of cells living organisms are classified as unicellular and multicellular,
(a) Name two unicellular organisms
(b) What is meant by division of labour in multicellular organisms,
(c) Name one prokaryotic and one eukaryotic unicellular organism ?
(d) Every multicellular organism has come from a single cell. Justify this statement.
(e) Write one common feature between in Amoeba and white
blood cells of humans. (CCE 2015)
Answer:
(а) Amoeba, Paramecium.
(b) Division of labour is the taking up of different functions of the system/body by different specialised components in a coordinated fashion so that the whole is benefitted without any part put to overwork. It increases efficiency. In multicellular organisms like humans there are a number of organs, tissues and cells performing different functions, e.g. contraction and movement by muscle cells, transmission of impulses by nerve cells, transport of oxygen by RBCs, protection from germs by white blood corpuscles, gamete formation by germ cells, pumping of blood by heart, extraction of wastes by kidneys, etc.
(c) Bacterium (prokaryotic, e.g., Escherichia coli), Chlamydemortas (eukaryotic).
(d) Every multicellular organism develops from a single cell called zygote, which is formed by fusion of two types of gametes.
(e) Both have irregular shape and perform endocytosis.
Question 20.
(a) Draw a neat diagram of a typical plant cell and label chloroplast and plasma membrane.
(b) State main function of
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplast.
(c) Write two differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a)
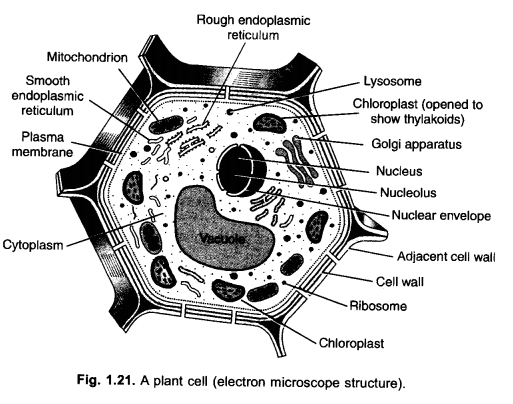
(b) Mian Function,
- Mitochondria: Aerobic respiration and energy release,
- Chloroplast: Photosynthesis.
(c)
Question 21.
What is meant by osmosis ? State the following conditions :
(a) When the cell loses water and shrinks
(b) When there is no overall movement of water. How can the plant cell withstand very dilute external media without bursting.
(CCE 2016)
Answer:
Osmosis is diffusion of water from the region of its higher concentration (pure water or dilute solution) to the region of its lower concentration (strong solution) through a semipermeable membrane.
(a) Plasmolysis due to external solution being hypertonic.
(b) External solution is isotonic.
Question 22.
A plant cell placed in very dilute solution swells up, becomes turgid but further endosmosis stops due to cell wall that begins to press the protoplasm inwardly.
(a) Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum,
(b) How is endoplasmic reticulum important for membrane biosynthesis ? (CCE 2016)
Answer:
(a)

(b) Membrane Biosynthesis: It is synthesis of cell membrane from its constituent proteins and lipids synthesised over endoplasmic reticulum and complexed by Golgi apparatus.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.