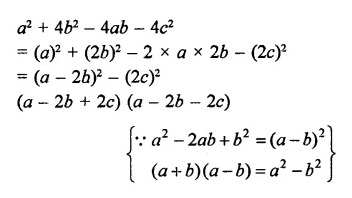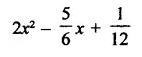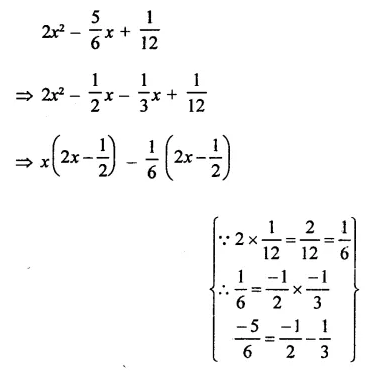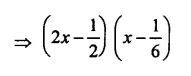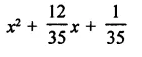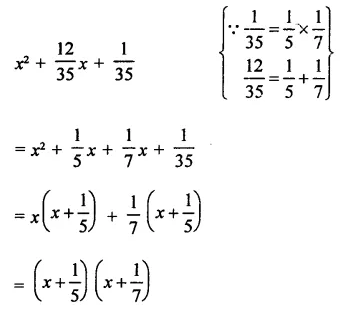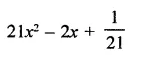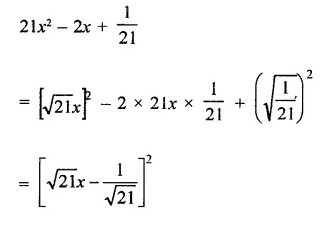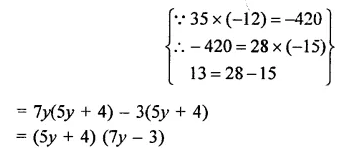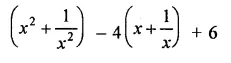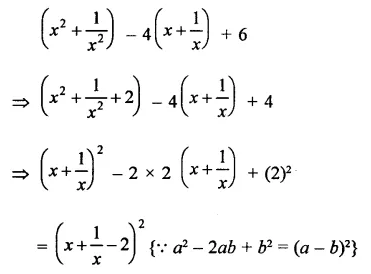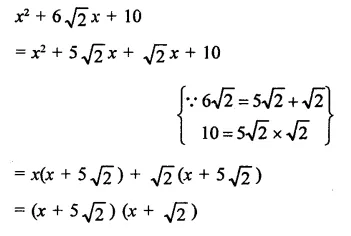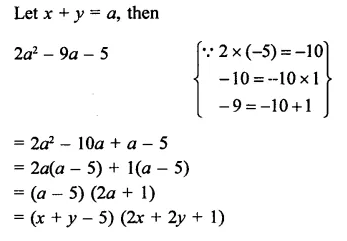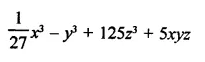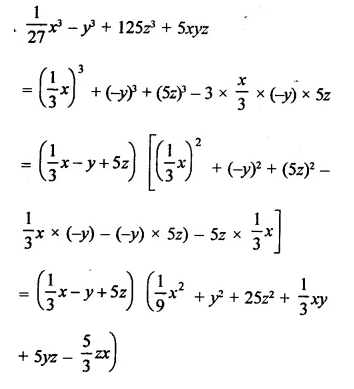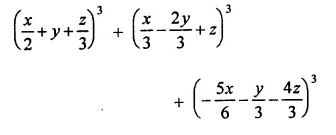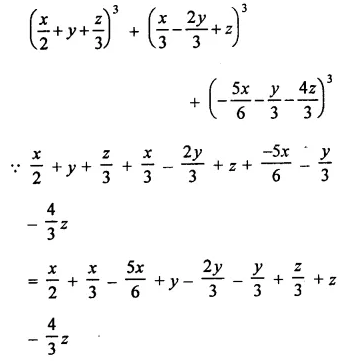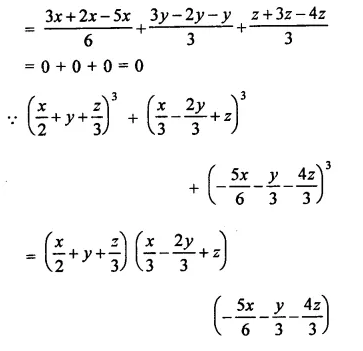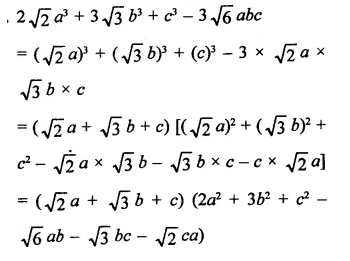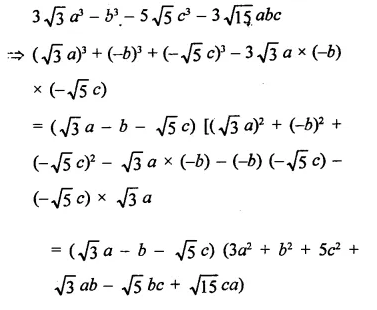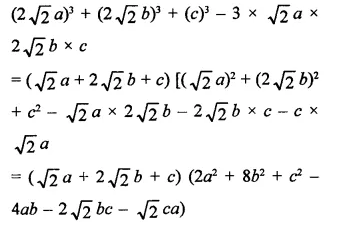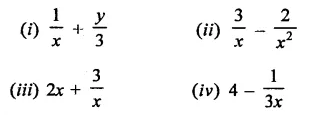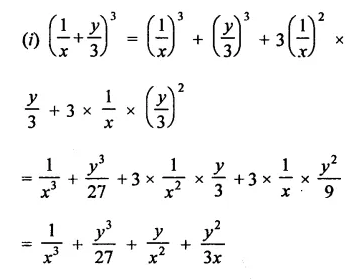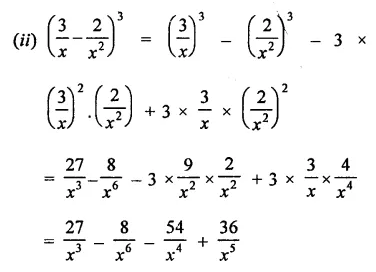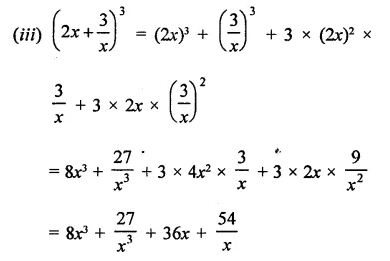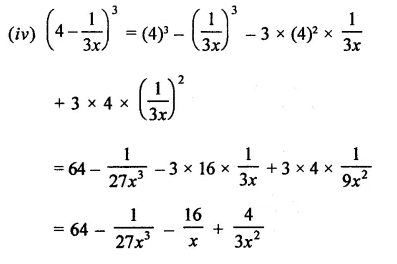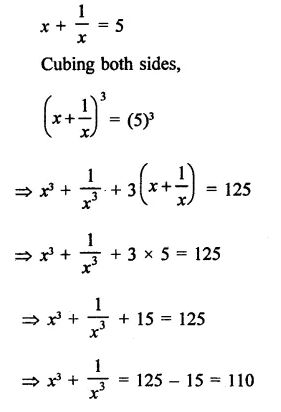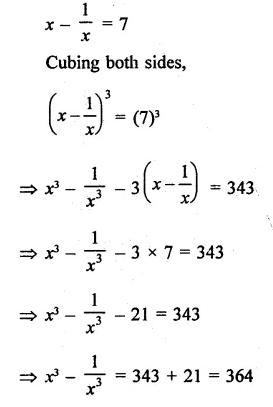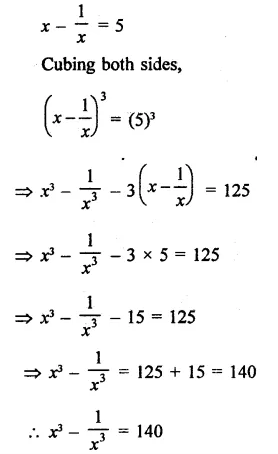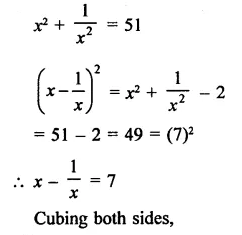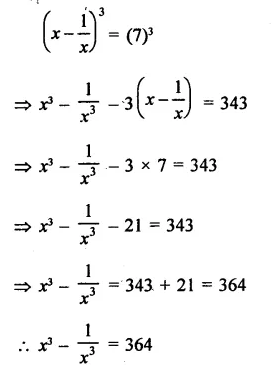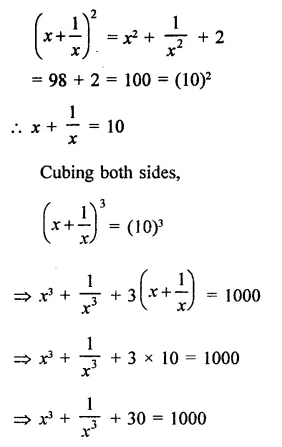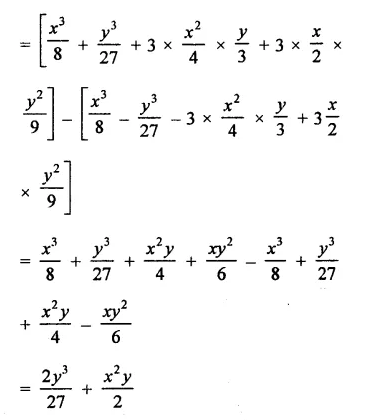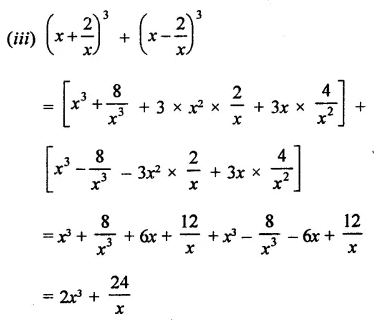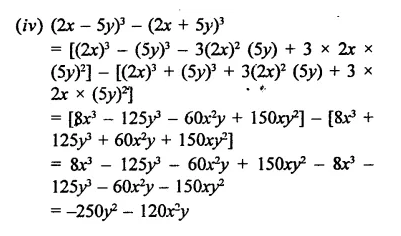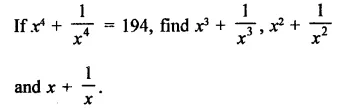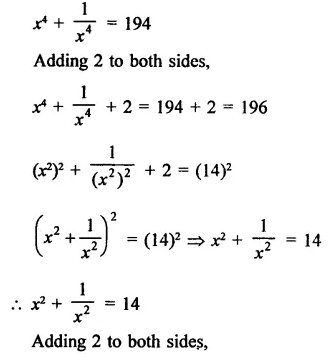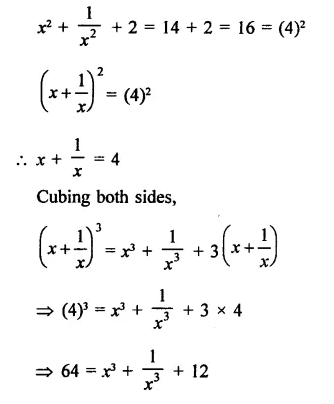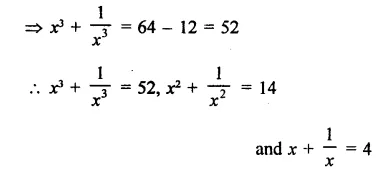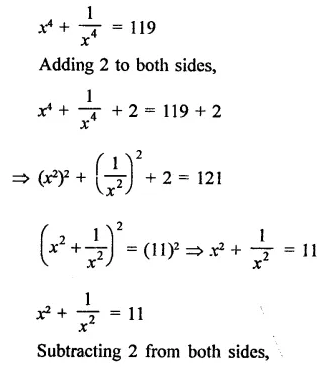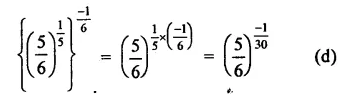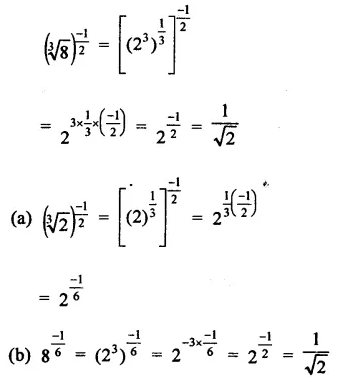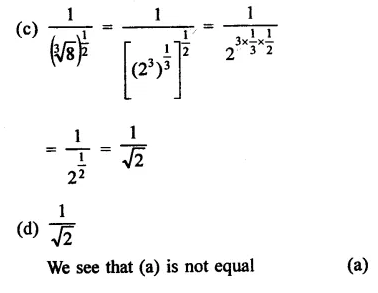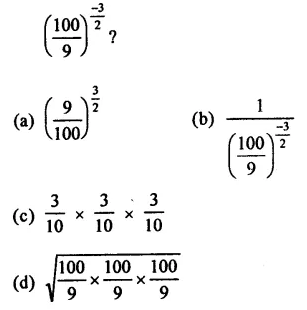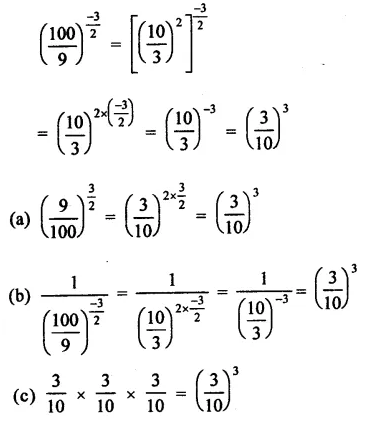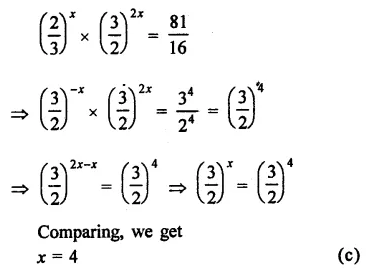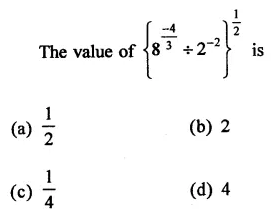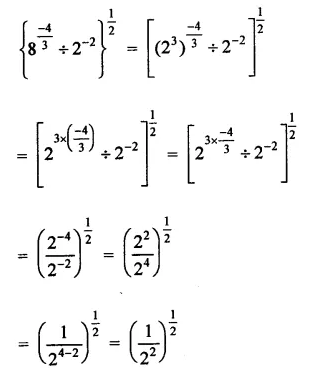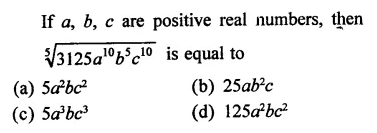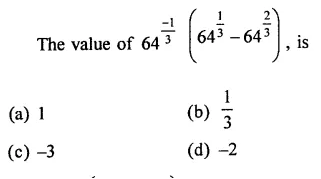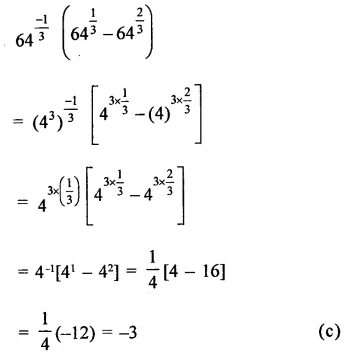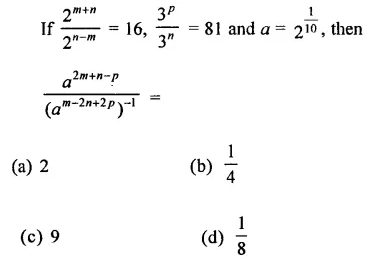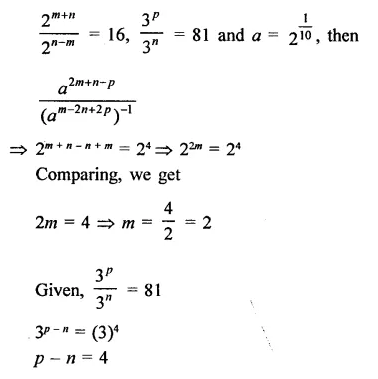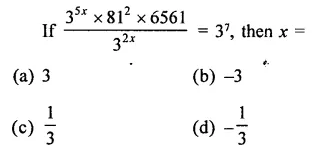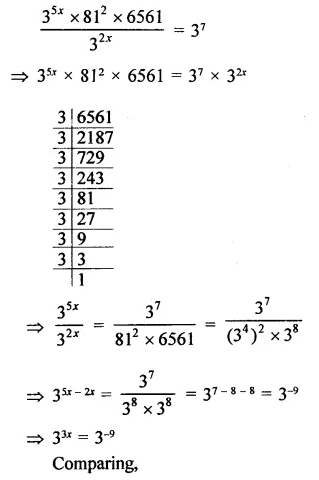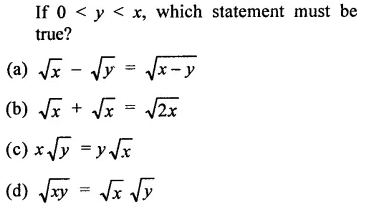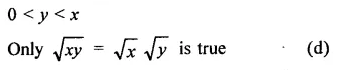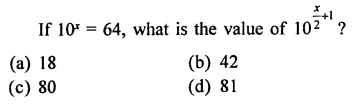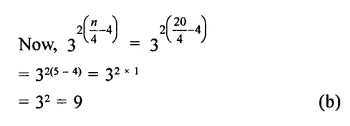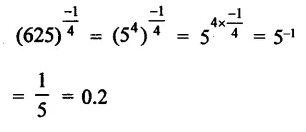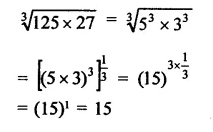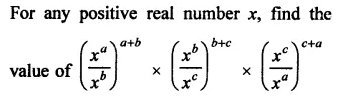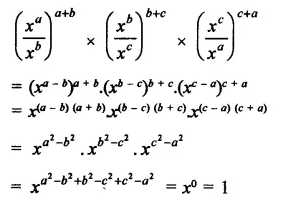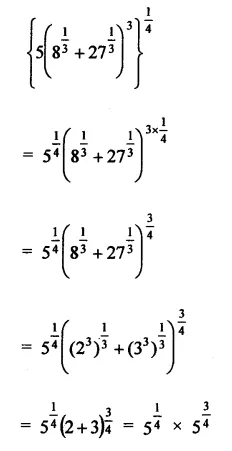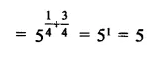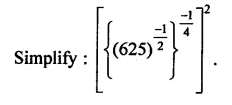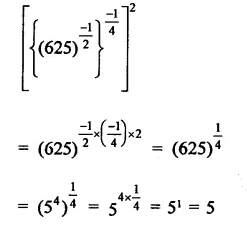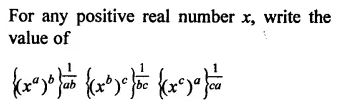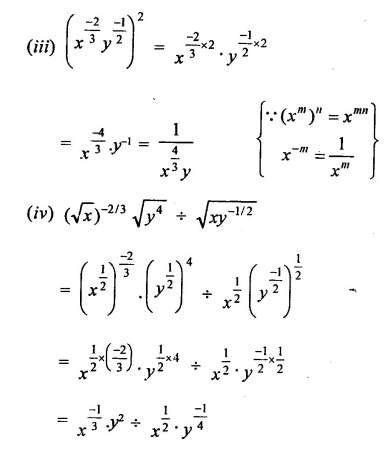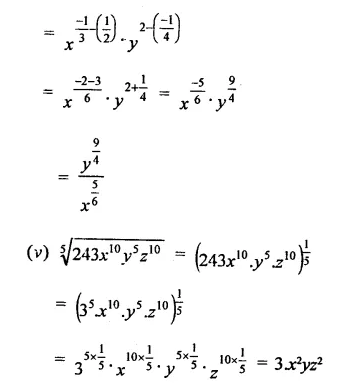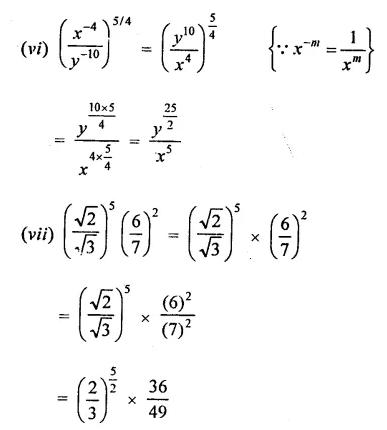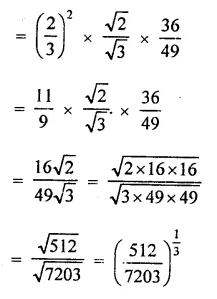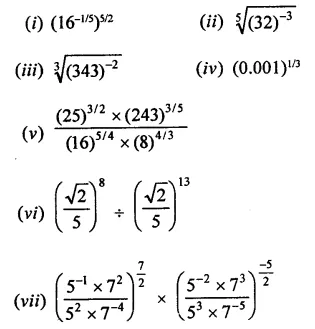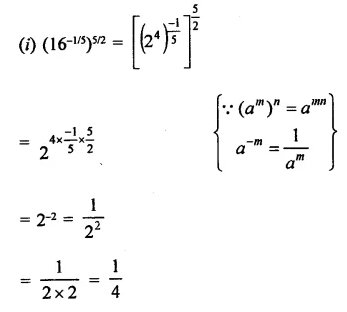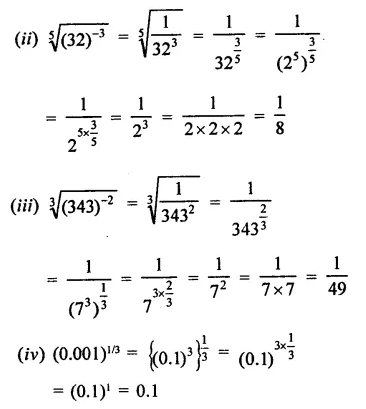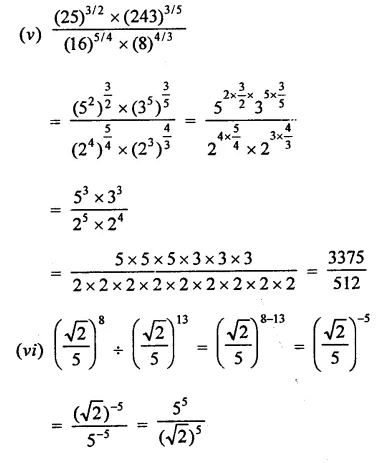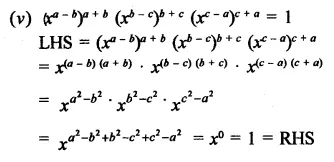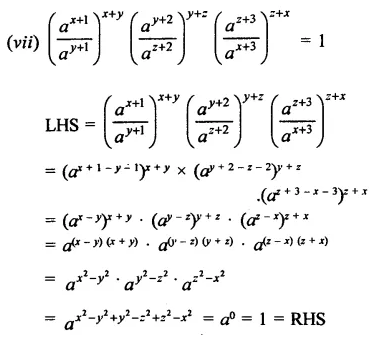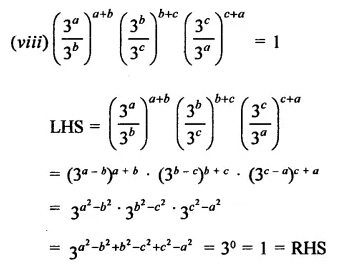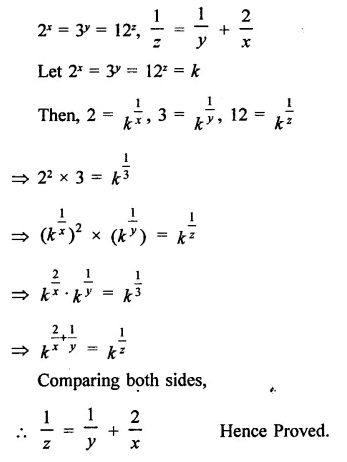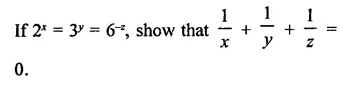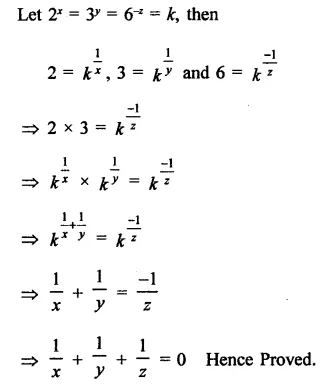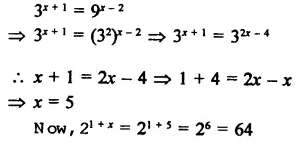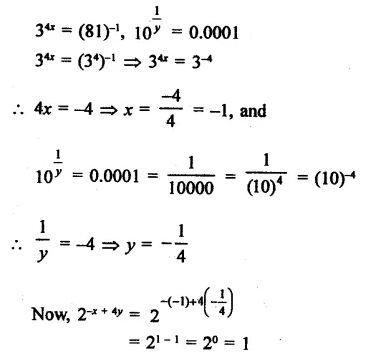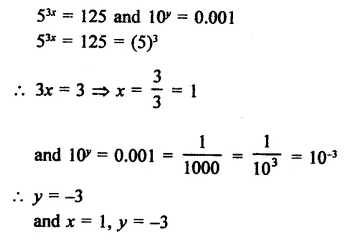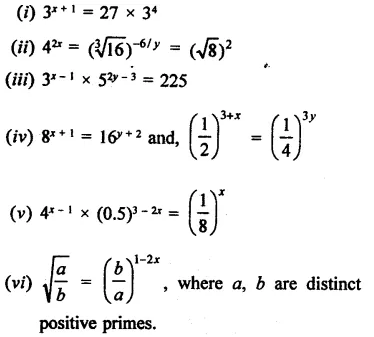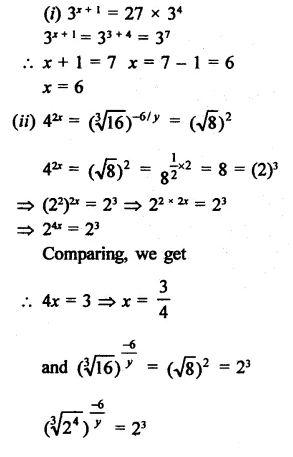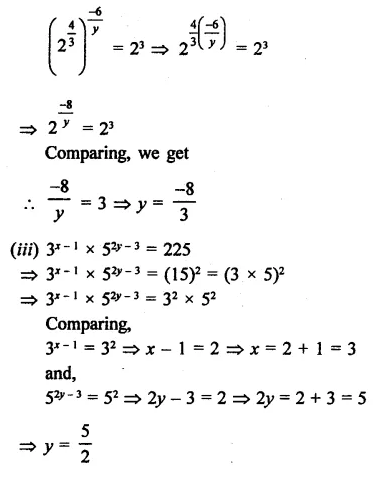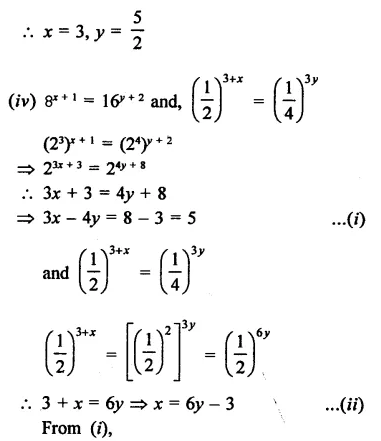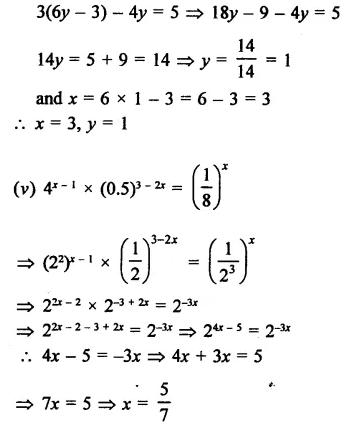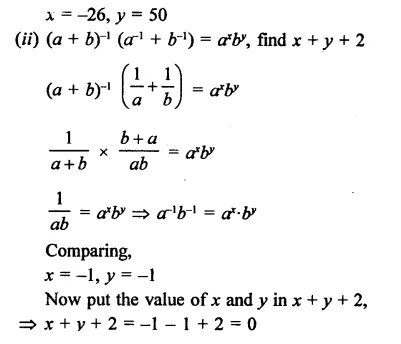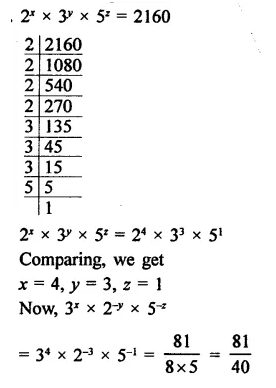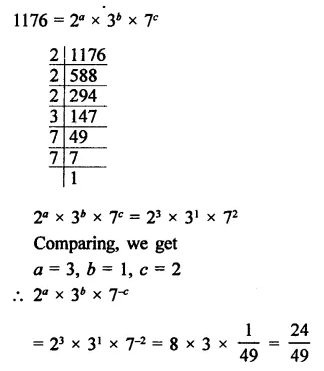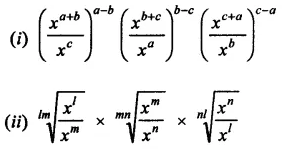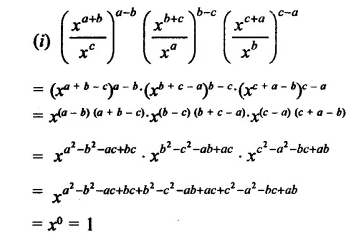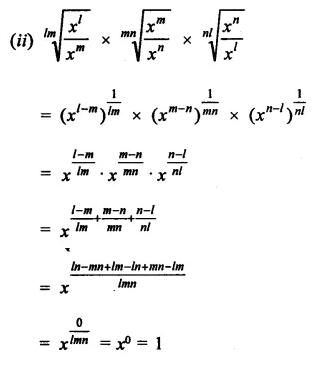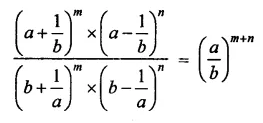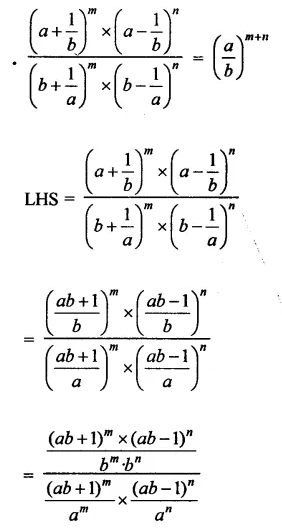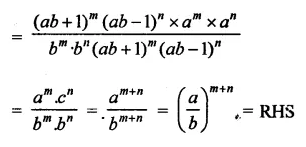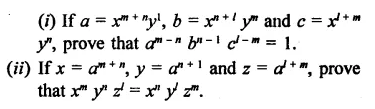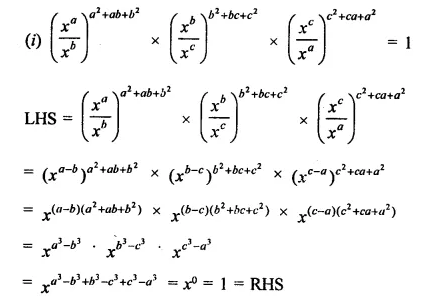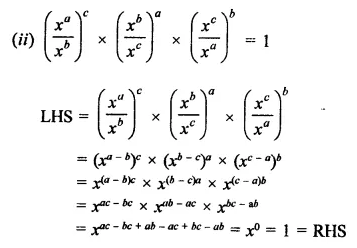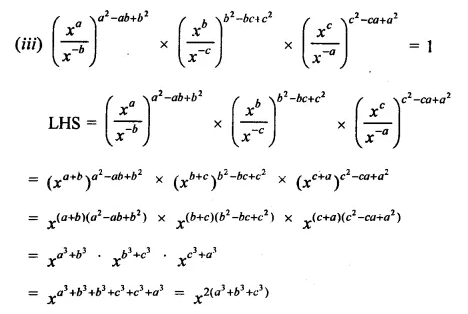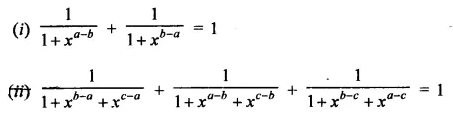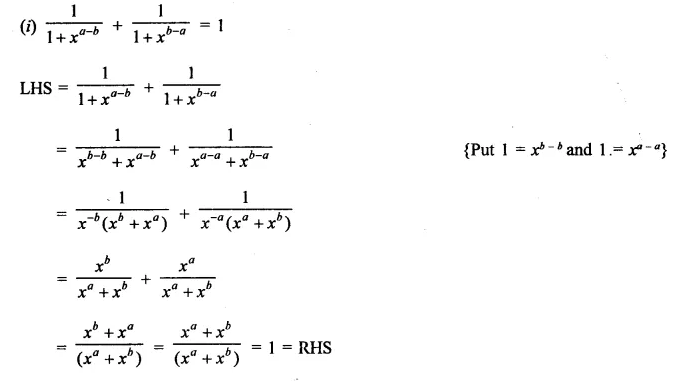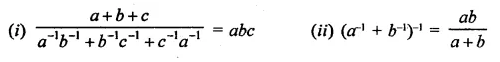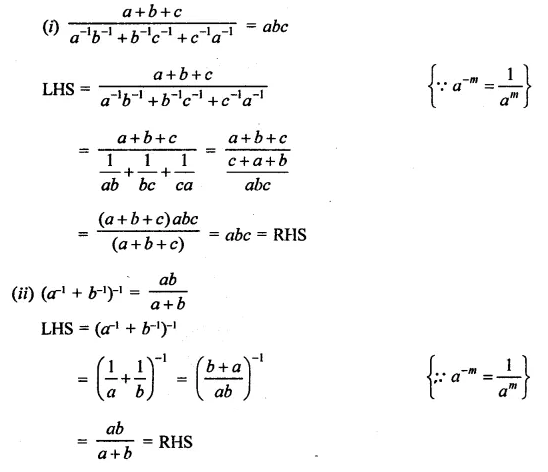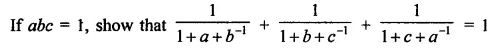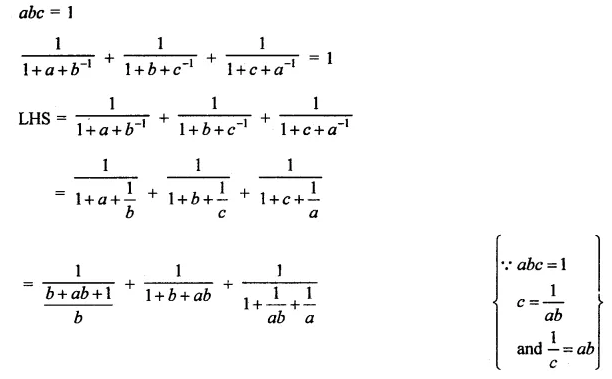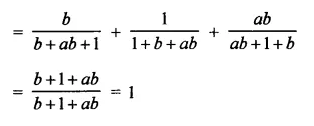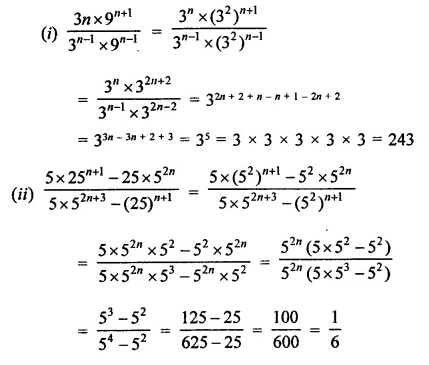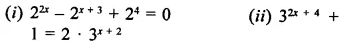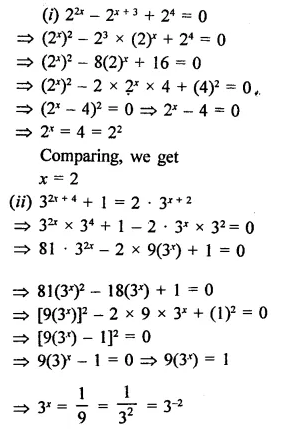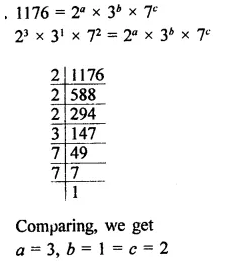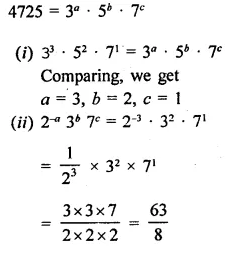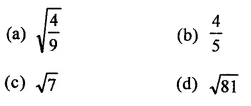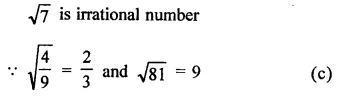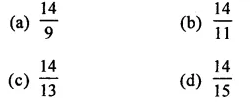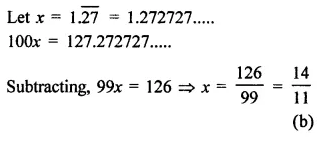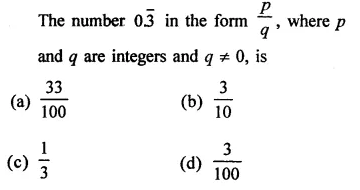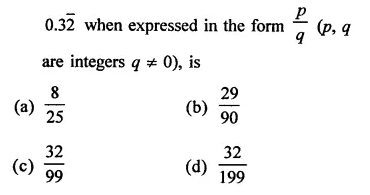RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions MCQS
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions MCQS
Other Exercises
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Ex 5.1
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Ex 5.2
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Ex 5.3
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions Ex 5.4
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions VSAQS
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions MCQS
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
Question 1.
The factors of x3 – x2y -xy2 + y3 are
(a) (x + y) (x2 -xy + y2)
(b) (x+y)(x2 + xy + y2)
(c) (x + y)2 (x – y)
(d) (x – y)2 (x + y)
Solution:
x3 – x2y – xy2 + y3
= x3 + y3 – x2y – xy2
= (x + y) (x2 -xy + y2)- xy(x + y)
= (x + y) (x2 – xy + y2 – xy)
= (x + y) (x2 – 2xy + y2)
= (x + y) (x – y)2 (d)
Question 2.
The factors of x3 – 1 +y3 + 3xy are
(a) (x – 1 + y) (x2 + 1 + y2 + x + y – xy)
(b) (x + y + 1) (x2 + y2 + 1- xy – x – y)
(c) (x – 1 + y) (x2 – 1 – y2 + x + y + xy)
(d) 3(x + y – 1) (x2 + y2 – 1)
Solution:
x3 – 1 + y3 + 3xy
= (x)3 + (-1)3 + (y)3 – 3 x x x (-1) x y
= (x – 1 + y) (x2 + 1 + y2 + x + y – xy)
= (x- 1 + y) (x2+ 1 + y2 + x + y – xy) (a)
Question 3.
The factors of 8a3 + b3 – 6ab + 1 are
(a) (2a + b – 1) (4a2 + b2 + 1 – 3ab – 2a)
(b) (2a – b + 1) (4a2 + b2 – 4ab + 1 – 2a + b)
(c) (2a + b+1) (4a2 + b2 + 1 – 2ab – b – 2a)
(d) (2a – 1 + b)(4a2 + 1 – 4a – b – 2ab)
Solution:
8a3 + b3 – 6ab + 1
= (2a)3 + (b)3 + (1)3 – 3 x 2a x b x 1
= (2a + b + 1) [(2a)2 + b2+1-2a x b- b x 1 – 1 x 2a]
= (2a + b + 1) (4a2 + b2+1-2ab-b- 2a) (c)
Question 4.
(x + y)3 – (x – v)3 can be factorized as
(a) 2y (3x2 + y2)
(b) 2x (3x2 + y2)
(c) 2y (3y2 + x2)
(d) 2x (x2 + 3y2)
Solution:
(x + y)3 – (x – y)3
= (x + y -x + y) [(x + y)2 + (x +y) (x -y) + (x – y)2]
= 2y(x2 + y2 + 2xy + x2-y2 + x2+y2 – 2xy)
= 2y(3x2 + y2) (a)
Question 5.
The expression (a – b)3 + (b – c)3 + (c – a)3 can be factorized as
(a) (a -b) (b- c) (c – a)
(b) 3(a – b) (b – c) (c – a)
(c) -3(a – b) (b – c) (a – a)
(d) (a + b + c) (a2 + b2 + c2 – ab – bc – ca)
Solution:
(a – b)3 + (b – c)3 + (c – a)3
Let a – b = x, b – a = y, c – a = z
∴ x3 + y3 + z3
x+y + z = a- b + b- c + c – a = 0
∴ x3 +y3 + z3 = 3xyz
(a – b)3 + (b – a)3 + (c – a)3
= 3 (a – b) (b – c) (c – a) (b)
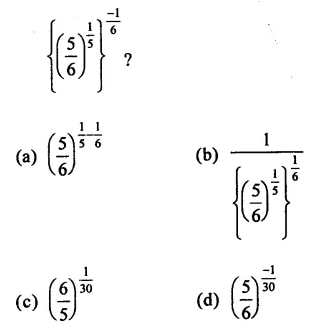
Question 6.
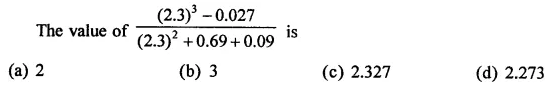
Solution:
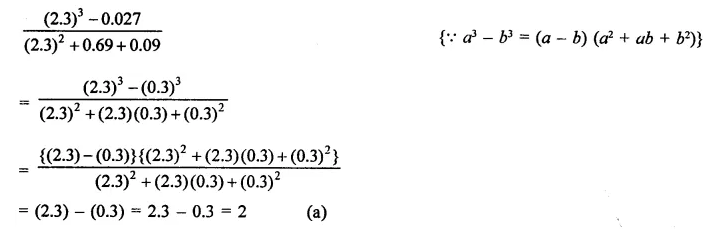
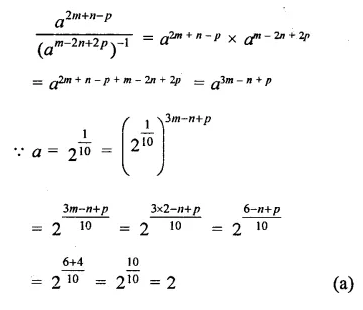
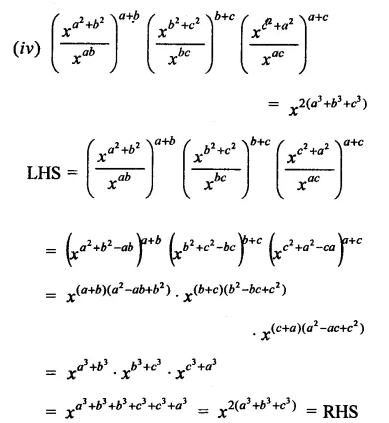
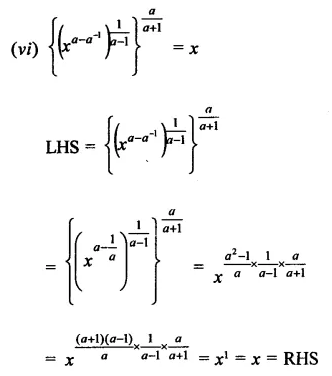
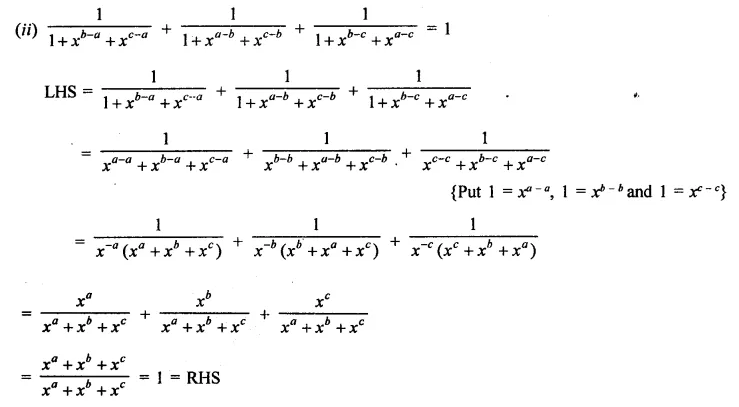
Question 7.
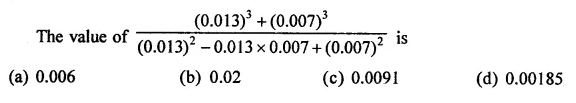
Solution:
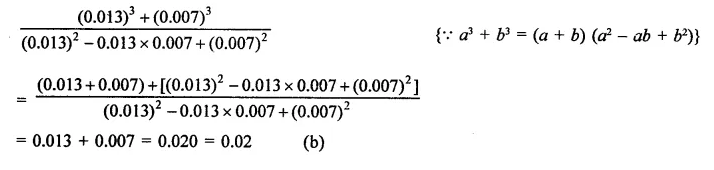
Question 8.
The factors of a2 – 1 – 2x – x2 are
(a) (a – x + 1) (a – x – 1)
(b) (a + x – 1) (a – x + 1)
(c) (a + x + 1) (a – x – 1)
(d) none of these
Solution:
a2 – 1- 2x – x2
⇒ a2 – (1 + 2x + x2)
= (a)2 – (1 + x)2
= (a + 1 + x) (a – 1 – x) (c)
Question 9.
The factors of x4 + x2 + 25 are
(a) (x2 + 3x + 5) (x2 – 3x + 5)
(b) (x2 + 3x + 5) (x2 + 3x – 5)
(c) (x2 + x + 5) (x2 – x + 5)
(d) none of these
Solution:
x4 + x2 + 25 = x4 + 25 +x2
= (x2)2 + (5)2 + 2 x x2 x 5- 9x2
= (x2 + 5)2 – (3x)2
= (x2 + 5 + 3x) (x2 + 5 – 3x)
= (x2 + 3x + 5) (x2 – 3x + 5) (a)
Question 10.
The factors of x2 + 4y2 + 4y – 4xy – 2x – 8 are
(a) (x – 2y – 4) (x – 2y + 2)
(b) (x – y + 2) (x – 4y – 4)
(c) (x + 2y – 4) (x + 2y + 2)
(d) none of these
Solution:
x2 + 4y2 + 4y – 4xy – 2x – 8
⇒ x2 + 4y + 4y – 4xy – 2x – 8
= (x)2 + (2y)2– 2 x x x 2y + 4y-2x-8
= (x – 2y)2 – (2x – 4y) – 8
= (x – 2y)2 – 2 (x – 2y) – 8
Let x – 2y = a, then
a2– 2a – 8 = a2– 4a + 2a – 8
= a(a – 4) + 2(a – 4)
= (a-4) (a + 2)
= (x2 -2y-4) (x2 -2y + 2) (a)
Question 11.
The factors of x3 – 7x + 6 are
(a) x(x – 6) (x – 1)
(b) (x2 – 6) (x – 1)
(c) (x + 1) (x + 2) (x – 3)
(d) (x – 1) (x + 3) (x – 2)
Solution:
x3 -7x + 6= x3-1-7x + 7
= (x – 1) (x2 + x + 1) – 7(x – 1)
= (x – 1) (x2 + x + 1 – 7)
= (x – 1) (x2 + x – 6)
= (x – 1) [x2 + 3x – 2x – 6]
= (x – 1) [x(x + 3) – 2(x + 3)]
= (x – 1) (x+ 3) (x – 2) (d)
Question 12.
The expression x4 + 4 can be factorized as
(a) (x2 + 2x + 2) (x2 – 2x + 2)
(b) (x2 + 2x + 2) (x2 + 2x – 2)
(c) (x2 – 2x – 2) (x2 – 2x + 2)
(d) (x2 + 2) (x2 – 2)
Solution:
x4 + 4 = x4 + 4 + 4x2 – 4x2 (Adding and subtracting 4x2)
= (x2)2 + (2)2 + 2 x x2 x 2 – (2x)2
= (x2 + 2)2 – (2x)2
= (x2 + 2 + 2x) (x2 + 2 – 2x) {∵ a2 – b2 = (a + b) (a – b)}
= (x2 + 2x + 2) (x2 – 2x + 2) (a)
Question 13.
If 3x = a + b + c, then the value of (x – a)3 + (x – bf + (x – cf – 3(x – a) (x – b) (x – c) is
(a) a + b + c
(b) (a – b) {b – c) (c – a)
(c) 0
(d) none of these
Solution:
3x = a + b + c .
⇒ 3x-a-b-c = 0
Now, (x – a)3+ (x – b)3 + (x – c)3 – 3(x – a) (x -b) (x – c)
= {(x – a) + (x – b) + (x – c)} {(x – a)2 + (x – b)2 + (x – c)2 – (x – a) (x – b) (x – b) (x – c) – (x – c) (x – a)}
= (x – a + x – b + x – c) {(x – a)2 + (x – b)2 + (x – c)2 – (x – a) (x – b) – (x – b) (x – c) – (x – c) (x – a)}
= (3x – a – b -c) {(x – a)2 + (x -b)2+ (x – c)2 – (x – a) (x – b) – (x – b) (x – c) – (x – c) (x – a)}
But 3x-a-b-c = 0, then
= 0 x {(x – a)2 + (x – b)2 + (x – c)2 – (x – a) (x – b) – (x – b) (x – c) – (x – c) (x – a)}
= 0 (c)
Question 14.
If (x + y)3 – (x – y)3 – 6y(x2 – y2) = ky2, then k =
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8
Solution:
(x + y)3 – (x – y)3 – 6y(x2 – y2) = ky2
LHS = (x + y)3 – (x – y)3 – 3 x (x + y) (x – y) [x + y – x + y]
= (x+y-x + y)3 {∵ a3 – b3 – 3ab (a – b) = a3 – b3}
= (2y)3 = 8y3
Comparing with ky3, k = 8 (d)
Question 15.
If x3 – 3x2 + 3x – 7 = (x + 1) (ax2 + bx + c), then a + b + c =
(a) 4
(b) 12
(c) -10
(d) 3
Solution:
x3 – 3x2 + 3x + 7 = (x + 1) (ax2 + bx + c)
= ax3 + bx2 + cx + ax2 + bx + c
x3 – 3x2 + 3x – 7 = ax3 + (b + a)2 + (c + b)x + c
Comparing the coefficient,
a = 1
b + a = -3 ⇒ b+1=-3 ⇒ b = -3-1=-4
c + b = 3 ⇒ c- 4 = 3 ⇒ c = 3 + 4 = 7
a + b + c = 1- 4 + 7 = 8- 4 = 4 (a)
Hope given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 5 Factorisation of Algebraic Expressions MCQS are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.