NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.5 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.5.
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Ex 5.1
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Ex 5.2
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Ex 5.3
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Ex 5.4
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Ex 5.6
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Ex 5.7
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Ex 5.8
- Understanding Elementary Shapes Class 6 Ex 5.9
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 5 |
| Chapter Name | Understanding Elementary Shapes |
| Exercise | Ex 5.5 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 4 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.5
Question 1.
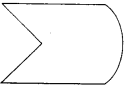
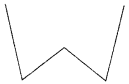
Which of the following are models for perpendicular lines :
(a) The adjacent edges of a table top.
(b) The lines of a railway track.
(c) The line segments forming the letter “L”.
(d) The letter V.
Solution :
(a) and (c) are models for perpendicular lines.
Question 2.
Let \(\overline { PQ }\) be the perpendicular to the line segment \(\overline { XY }\) . Let \(\vec { PQ }\) and \(\overline { XY }\) intersect in the point A. What is the measure of ∠PAY ?
Solution :
The measure of ∠PAY is 90°.
Question 3.
There are two “set-squares ” in your box. What are the measures of the angles that are formed at their comers? Do they have any angle measure that is common?
Solution :
One is a 30° – 60° – 90° set square; the other is a 45° – 45° – 90° set square. The angle of measure 90° (i.e., a right angle) is common between them.
Question 4.
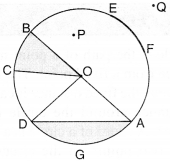
Study the diagram. The line l is perpendicular to line m.
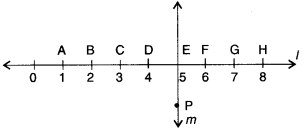
(a) Is CE = EG?
(b) Does PE bisect CG?
(c) Identify any two line segments for which PE is the perpendicular bisector.
(d) Are these true?
(i) AC > EG
(ii) CD = GH
(iii) BC < EH.
Solution :
(a) CE= CD + DE
= 1 + 1=2 units
EG = EF + FG
= 1 + 1=2 units
∴ CE= EG
(b) ∴ CE = EG
∴ E is the mid-point of CG.
∴ Line PE bisects line segment CG
(c) ∴ DE = EF = 1 unit
∴ PE is the perpendicular bisector of line segment DF
∴ BE = EH = 3 units
∴ PE is the perpendicular bisector of BH
(d)
(i) true
(ii) true
(iii) true
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.5 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.5, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.