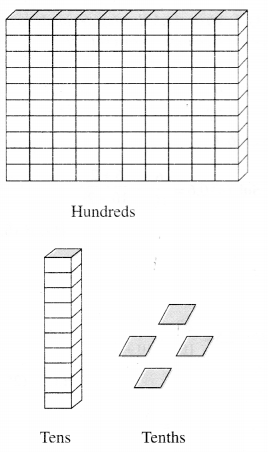
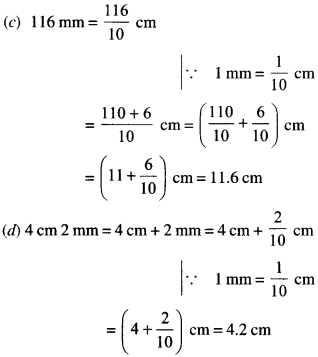
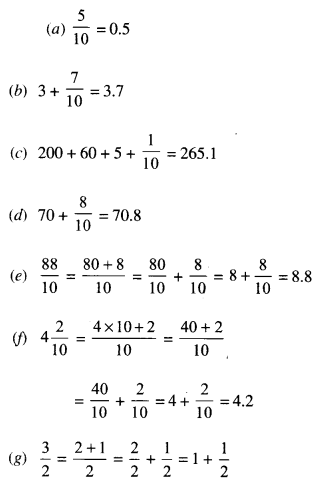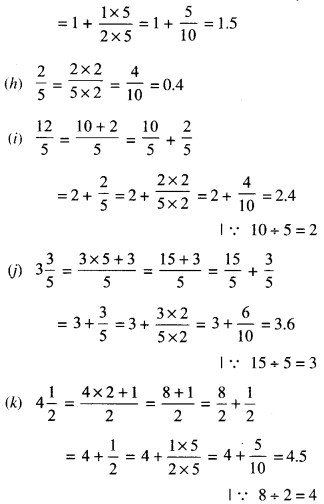CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 1 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 1.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 1
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Physics |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 1 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
-
Time Allowed : 3 HoursMax. Marks : 70General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all.
- This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section E.
- Section A contains five questions of 1 mark each. Section B contains five questions of 2 marks each. Section C contains twelve questions of 3 marks each. Section D contains one value based question of 4 marks and Section E contains three questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 1 question of 2 marks, 1 question of 3 marks and all the 3 questions of 5 marks weightage. You have to attempt only 1 of the choices in such questions.
- You may use the following values of physical constants wherever necessary :
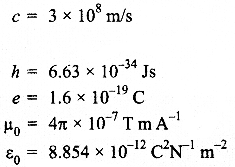

Questions :
SECTION : A
Question 1.
Define the term self-inductance of a coil. Write its S.I. unit
Question 2.
Which basic mode of communication is used for telephonic communication?
Question 3.
Why do the electrostatic field lines not form closed loops?
Question 4.
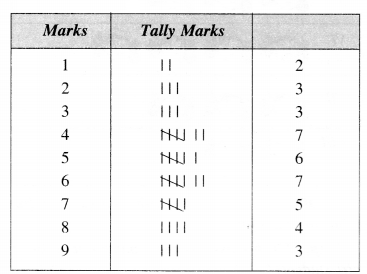
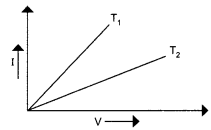
1-V graph for a metallic wire at two different temperatures, T1 and T2 is as shown in the figure. Which of the two temperature is lower and why?
Question 5.
Why does bluish colour predominate in a clear sky?
SECTION : B
Question 6.
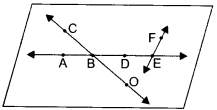
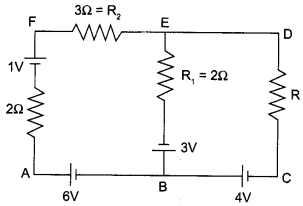
Use Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the potential difference between the points A and D when no current flows in the arm BE.
Question 7.
When an electron in hydrogen atom jumps from the excited state to the ground state, how would the de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electron change? Justify your answer.
Question 8.
You are given two converging lenses of focal lengths 1.25 cm and 5 cm to design a compound microscope. If it is desired to have a magnification of 30, find out the separation between the objective and the eyepiece.
OR
A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 150 cm and eyepiece of focal length 5 cm. What is the magnifying power of the telescope for viewing distant objects in normal adjustment? If this telescope is used to view a 100 m tall tower 3 km away, what is the height of the image of the tower formed by the objective lens?
Question 9.
Calculate the shortest wavelength in the Balmer series of hydrogen atom. In which region (infra-red, visible, ultraviolet) of hydrogen spectrum does this wavelength lie?
Question 10.
Write two factors which justify the need of modulation.
SECTION : C
Question 11.
Draw a circuit diagram of a C.E. transistor amplifier. Briefly explain its working and write the expression for
(i) current gain
(ii) voltage gain of the amplifier.
Question 12.
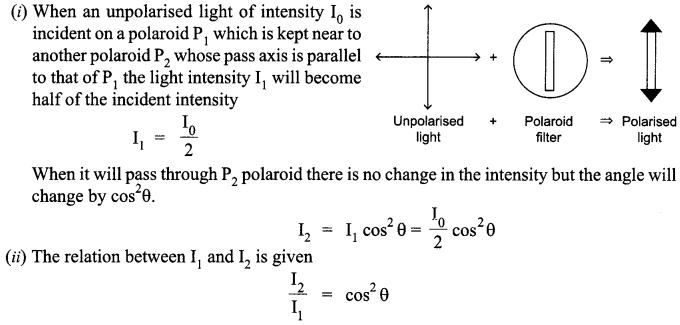
State clearly how an unpolarised light gets linearly polarized when passed through a Polaroid.
(i) Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on a Polaroid P1 which is kept near another Polaroid P2 whose pass axis is parallel to that of P1. How will the intensities of light, I1 and I2, transmitted by the Polaroids P1 and P2 respectively, change on rotating P1 without disturbing P2?
(ii) Write the relation between the intensities I1 and I2.
Question 13.
Define modulation index. Why is its value kept, in practice, less than one? A carrier wave of frequency 1.5 MHz and amplitude 50 V is modulated by a sinusoidal wave of frequency 10 kHz producing 50% amplitude modulation. Calculate the amplitude of the AM wave and frequencies of the side bands produced.
Question 14.
A uniform magnetic field B is set up along the positive X – axis. A particle of charge ‘q’ mass ‘m’ moving with a velocity v enters the field at the origin in X – Y plane such that it has velocity components both along and perpendicular to the magnetic field B. Trace, giving reason, the trajectory followed by the particle. Find out the expression for the distance moved by the particle along the magnetic field in one rotation.
Question 15.
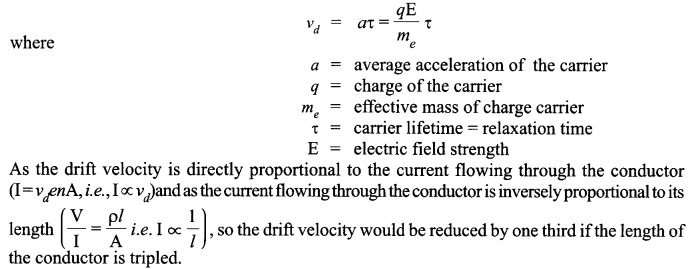
Find the relation between drift velocity and relaxation time of charge carriers in a conductor. A conductor of length L is connected to a d.c. source of emf ‘E’. If the length of the conductor is tripled by stretching it, keeping ‘E’ constant, explain how its drift velocity would be affected.
Question 16.
(a) Determine the value of phase difference between the current and the voltage in the given series LCR circuit.
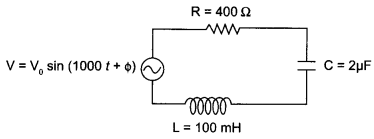
(b) Calculate the value of the additional capacitor which may be joined suitably to the capacitor C that would make the power factor of the circuit unity.
Question 17.
Write the expression for the generalized form of Amperes Circuital law. Discuss its significance and describe briefly how the concept of displacement current is explained through charging/ discharging of a capacitor in an electric circuit.
Question 18.
(a) Describe briefly three experimentally observed features in the phenomenon of photoelectric effect.
(b) Discuss briefly how wave theory of light cannot explain these features.
OR
(a) Write the important properties of photons which are used to establish Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
(b) Use this equation to explain the concept
(i) threshold frequency and
(ii) stopping potential.
Question 19.
Use Huygens principle to show how a plane wavelength propagates from a denser to rarer medium. Hence verify Snell’s law of refraction.
Question 20.
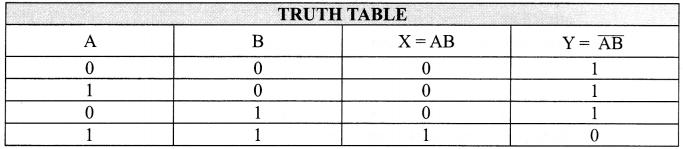
Identify the gates P and Q shown in the figure . Write the truth table for the combination of the gates shown.
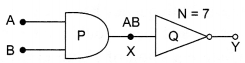
Name the equivalent gate representing this circuit and write its logic symbol.
Question 21.
(a) Write three characteristic properties of nuclear force.
(b) Draw a plot of potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of their separation. Write two important conclusions that can be drawn from the graph.
Question 22.
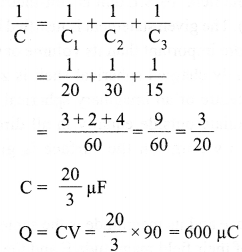
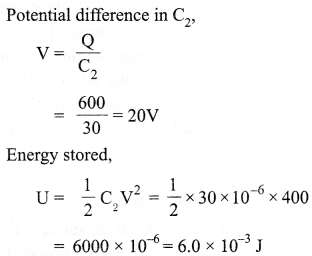
Calculate the potential difference and the energy stored in the capacitor C2 in the circuit shown in the figure. Given potential at A is 90 V, C1 = 20 µF, C2 = 30 µF and C3 = 15 µF.
![]()
SECTION : D
Question 23.
One morning an old lady tried bare-footed to replace the fuse wire fitted with power supply mains for her house. Suddenly she cried and collapsed on the floor. Her family members cried loudly for help. Her neighbour heard the cries and rushed to the spot wearing rubber soul shoes on. He took a wooden stick and used it to switch off the main supply.
Answer the folio wing questions :
- What are the voltage and frequency of mains supply in India?
- These days most of the electrical devices we use require a.c. voltage. Why?
- Can a transformer be used to step up d.c. voltage ?
- Write two qualities displayed by neighbour by his action.
SECTION : E
Question 24.
(a) Define electric flux. Write its S.I. unit. “Gauss’s law in electrostatics is true for any closed surface, no matter what its shape or size is”. Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
(b) Use Gauss’s law to prove that electric field inside a uniformly charged spherical shell is zero.
OR
(a) Derive the expression for the energy stored in a parallel plate capacitor. Hence obtain the expression for the energy density of the electric field.
(b) A fully charged parallel plate capacitor is connected across an uncharged identical capacitor. Show that the energy stored in the combination is less than that stored initially in the single capacitor.
Question 25.
Explain, using a labelled diagram, the principle and working of a moving coil galvanometer. What is the function of
(i) uniform radial magnetic field,
(ii) soft iron core?
Define the terms :
(i) current sensitivity and
(ii) voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer. Why does increasing the current sensitivity not necessarily increase voltage sensitivity?
OR

Question 26.
(a) Consider two coherent sources S1 and S2 producing monochromatic waves to produce interference pattern. Let the displacement of the wave produced by S1 be given by y1 = a cos mt and the displacement by S2 be y2 = a cos (ωt + Φ). Find out the expression for the amplitude of the resultant displacement at a point and show that the intensity at that point will be I = 4a2 cos2 Φ/2. Hence establish the conditions for constructive and destructive interference.
(b) What is the effect on the interference fringes in Young’s double slit experiment when
(i) the width of the source slit is increased,
(ii) the monochromatic source is replaced by a source of white light.
OR
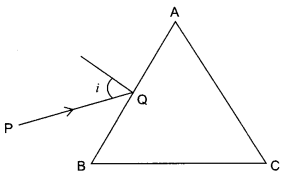
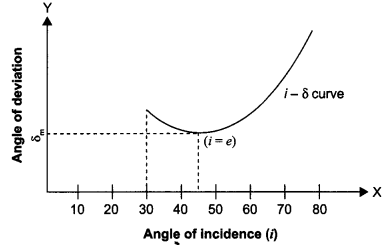
(a) A ray ‘PQ’ of light is incident on the face AB of a glass prism ABC (as shown in the figure) and emerges out of the face AC. Trace the path of the ray. Show that ∠i + ∠e = ∠A + ∠δ. Where δ and e denote the angle of deviation and angle of emergence respectively.
Plot a graph showing the variation of the angle of deviation as a function of angle of incidence. State the condition under which ∠δ is minimum.
(b) A ray of light passing through an equilateral triangular prism from air undergoes minimum deviation when angle of incidence is 3/4th of the angle of prism. Calculate the speed of light in the prism.
Answers :
SECTION : A
Answer 1.
L = Φ / I . If I = 1 then L = Φ i.e self inductance L of a coil is numerically equal to the amount of magnetic flux (Φ) linked with the coil when unit current flows through the coil. The S.I. unit of self inductance is henry (H) or weber per ampere.
![]()
Answer 2.
The basic mode of communication used in telephony is the point-to-point communications mode, which takes place through a link between a single transmitter and receiver.
Answer 3.
Electrostatic field lines originate from positive charge and terminate at negative charge.
Answer 4.
For the given figure the slope of a V – I graph is I/V = 1/R . Here the smaller the slope larger is the resistance . As the resistance of a metal increases with the increase in temperature, so resistance at T2 is more and T1 is lower.
Answer :
The light is scattered by air molecules. According to Lord Rayleigh the intensity of scattered light I ∝ 1/λ4. As λblue < λred Therefore blue colour scattered more in sky.
SECTION : B
Answer 6.
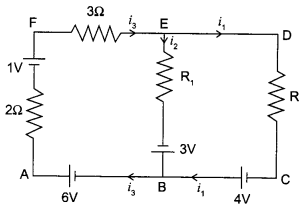
According to Kirchhoff’s junction law at B
i3 = i1 + i2
i3 = i1
As i3 = 0 (given)
Applying second law to loop AFEB, electronic network shown in the figure.
∴ i3 x 2 + i3 x 3 + i2 R1 = 1+3 + 6
∴ i3 = i1 = 2A
From A to D along AFD
∴ VAD = 2 i3 – 1 + 3 x i3
= (4 – 1 + 6)V
= 9V
Answer 7.
In an hydrogen atom, the negatively charged electron revolves in a circular orbit around the heavy positively charged nucleus. The centripetal force required by the electron is produced by the attractive force exerted by the nucleus on it. The energy is radiated, when an electron jumps from higher to lower energy orbit and the energy is absorbed, when jumps from lower to higher energy orbit.
![]()
It is called Bohr’s frequency condition.
Answer 8.
Given, f0 = 5 cm , fe = 1.25 cm and m = 30
Let S be tube length (distance between the objective and the eyepiece).

Thus, the height of the image would be 31.58 m.
Answer 9.
The formula for wavelength (λ) by Balmer series is :
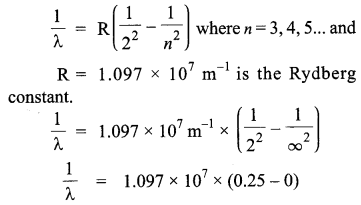

Answer 10.
Two factors that justify the need for modulation of low frequency signals to high frequency signals are :
- increase in range of communication base band signals suffer from attenuation and so cannot be transmitted over long distances, and
- the antenna height and aperture is inversely proportional to the radiated signal frequency, implying that higher frequencies result in smaller antennas.
SECTION : C
Answer 11.
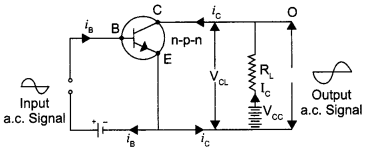
The purpose of this circuit is to amplify a small a.c input signal, such as an audio or radio signal. A small a.c. voltage is applied to the input through a coupling capacitor. The ratio of the a.c. component of the output to the a.c. component of the input, is known as gain.
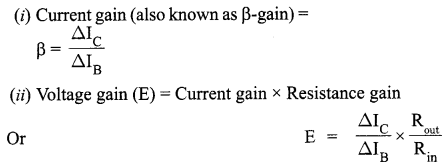
Answer 12.
Polaroid filters are made of a special material that is capable of blocking of the two planes of vibration of an electromagnetic wave. In this sense, a Polaroid serves as a device that filter out one-half of the vibrations upon transmission of the light through the filter. When unpolarised light is transmitted through a Polaroid filter, it emerge with one-half the intensity and with vibrations in a single plane; it emerges as polarized light.
Answer 13.
The modulation index p, can be defined as the ratio between the amplitude of the modulating signal and the amplitude of the carrier signal. A modulation index above 1 causes over-modulation, causing the carrier to experience 180° phase reversals. These reversals give rise to additional side and audio signal will be distorted during reception.
Given,
carrier wave frequency = 1.5 MHz, amplitude (V m) = 50 V
sinusoidal wave frequency = 10 kHz
amplitude modulation = 50%

Thus, amplitude of the AM wave = 250 volt
Now,
f USB = 1.5 x 1000+ 10 kHz
⇒ 1500 + 10 = 1510 kHz
f LSB = 1.5 x 1000 -10 = 1490 kHz
Answer 14.
Field at an axial point of a circular coil.
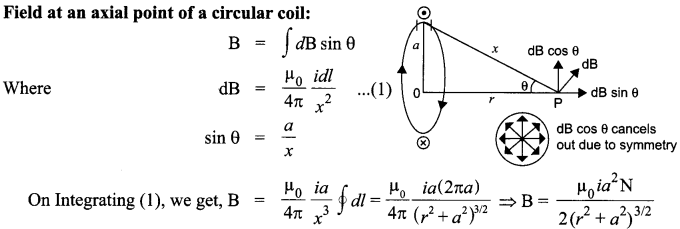
Where N is the number of turns of the circular coil. If M =iA is the magnetic moment of the coil, then
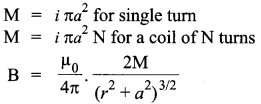
∵ a = 0, For small loop,

Where p is electric dipole moment.
Answer 15.
The drift velocity of electrons can be formulated as :
Answer 16.
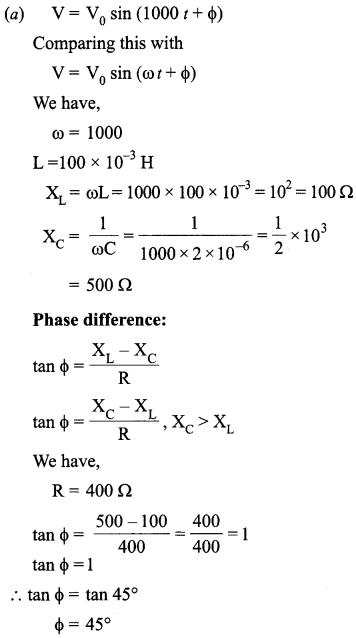
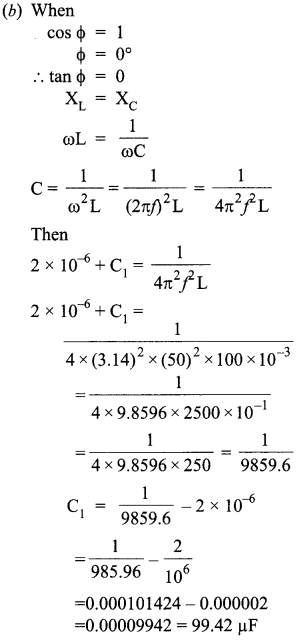
Answer 17.
Generalized form of Ampere Circuital Law :
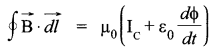
It signifies that the source of magnetic field is not just due to the conduction of electric current due to flow of charge but also due to the time rate of change of electric field called displacement current.
Displacement current :
During charging and discharging of a capacitor the electric field between the plates will change so there will be a change of electric flux (displacement current) between the plates.
Answer 18.
(a)
(i) The photoelectric effect will not occur when the frequency of the incident light is less than the threshold frequency. Different materials have different threshold frequencies and most elements have threshold frequencies in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
(ii) The maximum KE of a stream of photo electrons increases linearly with the frequency of the incident light above the threshold frequency.
(iii) The rate at which photo electrons are emitted from a photosensitive surface is directly proportional to the intensity of incident light when the frequency is constant.
(b) Classical wave theory cannot explain :
(i) The existence of threshold frequency because it predicts that electrons would absorb enough energy to escape and there would not be any threshold frequency.
(ii) The almost immediate emission of photo electrons as, according to this theory, electrons require a period of time before sufficient energy is absorbed by it to escape from the metal; however such a thing does not happen practically; and
(iii) The independence of KE of photo electrons on intensity and dependence on frequency because it cannot explain why maximum KE is dependent on frequency and independent of intensity.
OR
(i) The important property of photons that is useful in establishing Einstein’s photoelectric equation is their ability to hold on to the electrons of an atom by their forces of attraction.
(ii) Einstein’s photoelectric equation states that :

Answer 19.
Medium 1

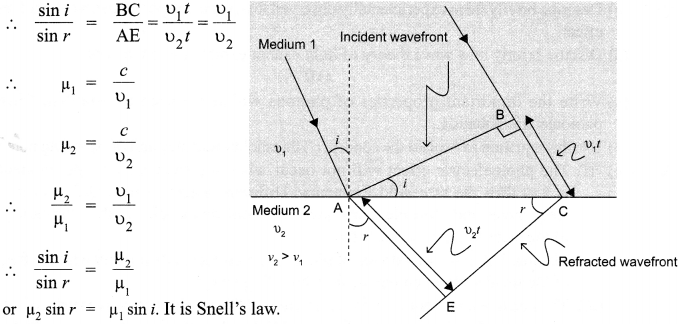
Answer 20.
Logic gate P is AND gate and logic Q is NOT gate.
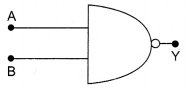
The combination is NAND
Answer 21.
(a)
(i) Nuclear forces are short range forces.
(ii) Nuclear forces are primarily attractive and extremely strong.
(iii) Nuclear forces are charge independent
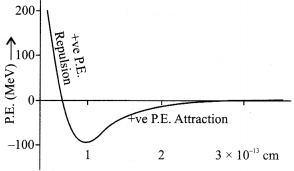
(b) Nuclear forces is of attractive nature when separation between the nuclei is greater than 1 fm and of repulsive nature when separation is less than 1 fm.
Answer 22.
SECTION : D
Answer 23.
- The voltage and frequency of mains supply in India are 220 V and 50 Hz respectively.
- Most electrical devices require a.c. voltage because a.c. is available by default through the mains supply and also because d.c., is actually a one-way current, is available only through batteries.
- No, a transformer cannot be used to set-up d.c. voltage because a transformer works on the magnetic effect of current and d.c. voltage does not produces any magnetic field.
- The two qualities displayed by neighbour are :
(a) preventing himself from being the earthing conductor by putting on his shoes and
(b) switching off the mains connection to prevent the old lady from acting as an earthing conductor
SECTION : E
Answer 24.
(a) The electric flux through an area is defined as the electric field multiplied by the area of the surface projected on a plane, perpendicular to the field. Its S.I. unit is volt-metres (Vm) or Newton metres square per coulomb (Nm2 C-1 ). The given statement is justified because while measuring the flux, the surface area is more important than its volume or its size.
(b) To prove that the electric field inside a uniformly charged spherical shell is zero, we place a single positive point charge ‘q’ at the centre of an imaginary spherical surface with radius R. The field lines of this point radiate outside equally in all directions. The magnitude E of the electric field at every point on the surface is given by

OR
(a) When charging parallel plate capacitor, whose plate area is A and distance between the plate is d. When charge on capacitor is q, potential difference increase 0 to V. Hence average

(b) Let the capacitance of the charged capacitor C1 by and the voltage be ∆V1

Answer 25.
The basic principle of a moving coil galvanometer is that when a current carrying coil is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a torque.
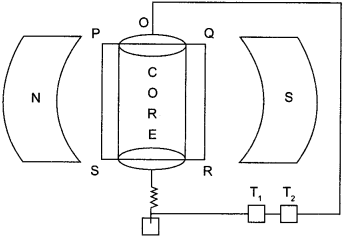
When the current I is passed through the coil, the torque experienced is given by
τ = NIAB sinθ
Where
N = no. of turns of the coil,
A = area of the coil
B = magnetic field and
θ = angle between normal of coil and magnetic field
(i) The uniform radial magnetic field allows the coil to rotate and
(ii) The soft iron core makes the magnetic field linked with the coil to be radial.
The current sensitivity is defien as the deflection produced in the galvanometer, while passing a current of 1 ampere (1amp).
Thus,
![]()
The voltage sensitivity is defined as the deflection produced in the galvanometer when a potential difference of IV is applied to the coil.
Thus,
![]()
Where, R is the resistance.
Increasing the current sensitivity does not necessarily increase the voltage sensitivity as there is an increase in the resistance as well.
OR
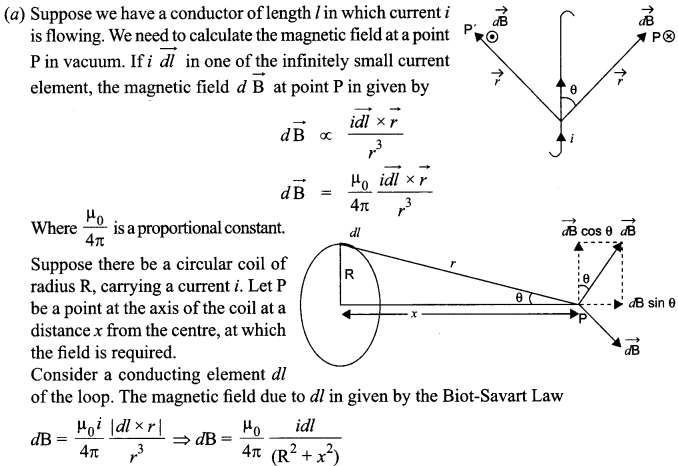
The direction of dB is perpendicular to the plane formed by dl and r. It has an x-component dBx. When the components perpendicular to the x-axis are summed over, they cancel out and we obtain null result. Thus only the x-component survives.
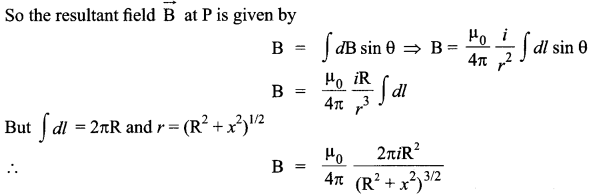
If the coil has N turns, then each turn will contribute equally to B. Then
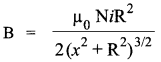
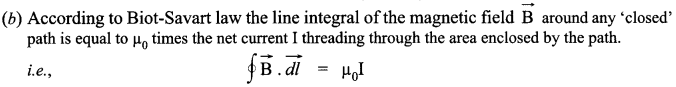
Where μ0 in the permeability of free space. Ampere’s circuital law in electromagnetism is analogous to Gauss’ law in electrostatics.
Answer 26.
(a) Let S be a narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic source of light, and Sj and S2 two similar parallel slits very close together and equidistant from S.
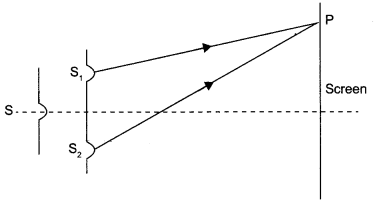
Displacement of the wave produced by S1 is given by
y1 = a cos ωt and
the displacement of the Wave produced by S2 is given by
y2 = a cos (ωt + Φ)
The resultant displacement is given by
y = y1 + y2 = a cos(ωt + Φ) + a cos (ωt + Φ)
⇒ y = 2a cos Φ/2 cos (ωt + Φ/2)
The amplitude of the resultant displacement is 2a cos Φ/2. The intensity of light is directly proportional to the square of amplitude of the wave.
The resultant intensity in given by
I = 4a cos2 Φ/2
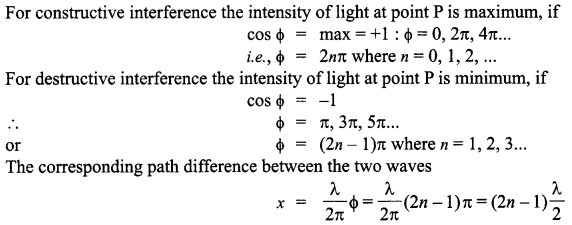
(b) (i) As the width of the slits is increased, the fringe width decreases. It is because,
![]()
(ii) The different colours of white light will produce different interference patterns but the central bright fringes due to all colours are at the same positions. Therefore, the central bright fringe is white in colour. Since the wavelength of the blue light is smallest, the fringe close to the either side of the central white fringe is blue and farthest is red.
OR
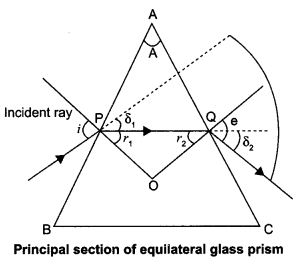
(a) Let the incident ray meet refracting face AB of the prism at point P. Ray PQ is the refracted ray inside the prism and δ1 and r1, are the angle of the deviation and refraction at interface AB. At interface AC the ray goes out of the prism. Let e be the angle of emergence. The angle of deviation at point Q is δ2 as shown in figure. Using geometry, we see that at point P,
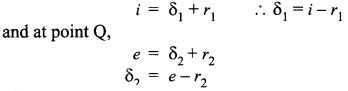

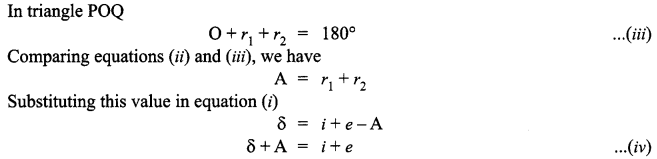
So angle of deviation produced by a prism depends upon the angle of incidence, refracting angle of prism, and the material of the prism.