NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 5 |
| Chapter Name | Separation of Substances |
| Number of Questions Solved | 10 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
(Pages 44-45)
Question 1.
Why do we need to separate different components of a mixture? Give two examples.
Answer:
We need to separate different substances present in a mixture for the following purposes :
(1) To remove the unuseful or harmful component.
For example – removing tea leaves after making tea.
(2) To obtain the useful component – For getting wheat/rice grains after separating husk, dirt, etc.
(3) To remove impurities for getting a pure sample,
For example – obtaining sugar crystals from jaggery (gur) or salt from seawater.
Question 2.
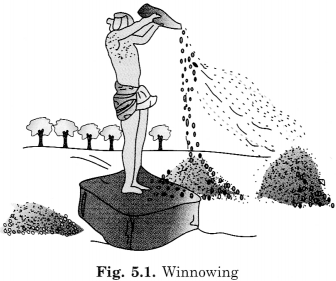
What is winnowing? Where is it used?
Answer :
Winnowing is the process of separating wheat or rice grains from the husk. Wheat grains and husk are different in weight, husk is lighter than wheat. When the mixture is allowed to fall down from a height, the wind carries the lighter husk with it and the heavy wheat grains fall vertically down on the ground.
Question 3.
How will you separate husk or dirt particles from a given sample of pulses before cooking?
Answer :
Husk or dirt particles are separated from pulses before cooking by hand-picking.
Question 4.
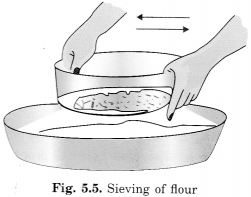
What is sieving? Where is it used?
Answer :
Sieving is the method to separate particles of different sizes. Undesirable particles can be separated from grains by this method. The size of holes in the sieves depends upon the size of the particles. In cashew nut factories, the cashew nuts of different sizes are separated by sieving. Jewellers also separate pearls of different sizes by this method.

Sieving flour before consuming is not a good practice. We should consume it along with the husk because husk provides roughage which is useful for our body in proper bowel movement.
Question 5.
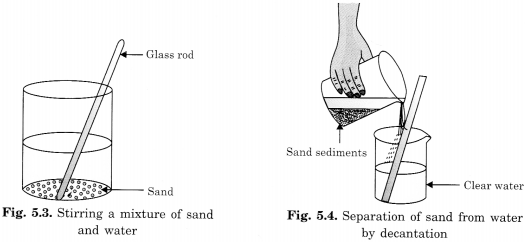
How will you separate sand and water from their mixture?
Answer:
This can be done by taking a beaker or a glass tumbler half-filled with the given sample of water. Water is stirred thoroughly before keeping it undisturbed for some time. The sand being heavy settles down at the bottom of the beaker. Now, the clear water is poured into another beaker without disturbing the layer of sand with the help of a glass rod.
Question 6.
Is it possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour? If yes, how will you do it?
Answer :
Yes, we can separate sugar from wheat flour by sieving. In the mixture of sugar and wheat flour, sieving allows the fine flour particles to pass through the holes of the sieve, while the sugar particles remain on the sieve.
Question 7.
How would you obtain clear water from a sample of muddy water?
Answer:
Muddy water is cleared by the process of loading. Take a piece of alum, tied with a thread, it is swirled in water; then after some time, the water becomes clear on standing. The water becomes clear because the mud particles get loaded by the alum particles and become heavy. The loaded mud particles settle down at the bottom of the container. The water, therefore, becomes clear and can be decanted for further use.
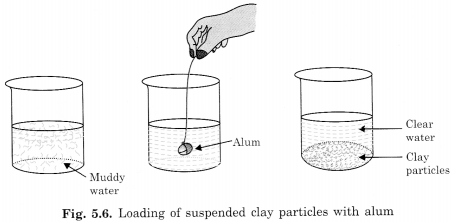
Question 8.
Fill in the blanks:
(a) The method of separating seeds of paddy from its stalks is called ………………………..
(b) When milk, cooled after boiling, is poured onto a piece of cloth the cream (malai) is left behind on it. This process of separating cream from milk is an example of ………………………..
(c) Salt is obtained from seawater by the process of ………………………..
(d) Impurities settled at the bottom when muddy water was kept overnight in a bucket. The clear water was then poured off from the top. The process of separation used in this example is called ………………………..
Answer:
(a) threshing
(b) filtration
(c) evaporation
(d) decantation
Question 9.
True or false:
(a) A mixture of milk arid water can be separated by filtration.
(b) A mixture of powdered salt and sugar can be separated by the process of winnowing.
(c) Separation of sugar from tea can be done with filtration.
(d) Grain and husk can be separated with the process of decantation.
Answer :
(a) False
(b) False
(c) False
(d) False
Question 10.
Lemonade is prepared by mixing lemon juice and sugar in water. You wish to add ice to cool it. Should you add ice to the lemonade before or after dissolving sugar? In which case would it be possible to dissolve more sugar?
Answer:
We should add ice to the lemonade after dissolving sugar. It would be possible to dissolve more sugar before adding ice.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.