NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Literature Chapter 2 Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Literature Chapter 2 Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger.
All our solutions for Chapter 2 – Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger are prepared considering the latest CBSE syllabus, and they are amended from time to time. Our free NCERT Textbook Solutions for CBSE Class 10 English will strengthen your fundamentals in this chapter and can help you to score more marks in the examination. Refer to our Textbook Solutions any time, while doing your homework or while preparing for the exam.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | English Literature |
| Chapter | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Literature Chapter 2 Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger
TEXTUAL EXERCISES
(Page 12 & 16)
Question 1.
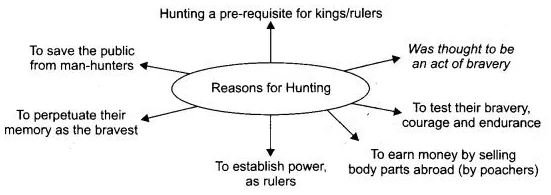
Why do people hunt ? Complete the web chart giving various reasons for the same :
Answer:
Question 2.
Read these lines and guess the answers to the questions given below :
It was Mrs. Packletide’s pleasure and intention that she should shoot a tiger … The compelling motive … was the fact that Loona Bimberton had recently … personally procured tiger-skin and a heavy harvest of Press photographs could successfully counter that sort of thing.
(a) Why did Mrs. Packletide want to kill a tiger ? (V. Imp.)
(b) What does it tell you about her ?
(c) What is the tone of the storywriter ?
(d) Do you think she was successful in her mission ?
(e) What do you think the story is all about ?
Answer:
(a) Mrs. Packletide wanted to kill a tiger to counter the fame and prestige of Loona Bimberton. She had acquired these in flying in an aeroplane. She couldn’t tolerate her increased social prestige than hers. So out of jealousy she decided to kill a tiger.
(b) This all tells us that Mrs. Packletide is a woman full of jealousy for other women. She can’t tolerate the idea that other women should outweigh her in any thing.
(c) The tone of the storywriter is humorous and taunting. At every available point Mrs. Packletide is derided and made fun of.
(d) Mrs. Packletide was not successful in her mission. She had decided publicly to belittle Loona Bimberton in organizing a luncheon party in her honour and offering her a tiger-claw brooch. But Loona Bimberton had declined to attend this party. However, she accepted the tiger-claw brooch unwillingly. Mrs. Packletide was, however, successful in ‘hunting’ the tiger though she had to pre-arrange it.
(e) The story is all about her feeling jealous of Loona Bimberton and hunting the tiger.
Question 3.
Answer the following questions in your own words :
(a) Why did Mrs. Packletide wish to kill a tiger ? (V. Imp.) (CBSE 2015)
Or
Why does Mrs. Packletide want to kill a tiger ? (CBSE 2012)
Or
Why does Mrs. Packletide want to kill a tiger ? How does she realise her ambition ? (CBSE 2015)
(b) What made her decide to give a party in Loona Bimberton’s honour ? What did she intend to give Loona on her birthday ? (V. Imp.)
Or
Why did Mrs. Packletide decide to give a party in the honour of Loona Bimberton ? What did she plan to present Loona on her birthday ? (CBSE 2012)
(c) How was the tiger shooting arranged ? What kind of a tiger was chosen for the purpose ? (CBSE 2015)
(d) In what way did the villagers help Mrs. Packletide shoot the tiger ?
(e) Who was Miss Mebbin ? Was she really devoted to Mrs. Packletide ? How did she behave during the tiger shooting ? (V. Imp.)
(f) Mrs. Packletide was a good shot. Discuss.
(g) What comment did Miss Mebbin make after Mrs. Packletide had fired the shot ? Why did Miss Mebbin make this comment ? How did Mrs. Packletide react to this comment ? (V. Imp.)
(h) How did the villagers react to the tiger’s death ?
(i) Do you think Mrs. Packletide was able to achieve her heart’s desire ? Give reasons for your answer.
(j) How did Miss Mebbin manage to get her week-end cottage 1 Why did she plant so many tiger lilies in her garden ? (V. Imp.)
Or
How did Mrs. Louisa Mebbin manage to acquire a week-end cottage for herself ? (CBSE 2015)
(k) “The incidental expenses are so heavy”, she confides to inquiring friends. Who is the speaker ? What is she referring to here ? (V. Imp.)
Answer:
(a) Mrs. Packletide wished to kill a tiger to counter the fame of Loona Bimberton who had flown in an aeroplane. She couldn’t tolerate her increased social prestige than hers. So to counter it she thought a tiger hunt would put her above her in social circles. So she decided to hunt a tiger to achieve that status. She arranged for the kill through payment and with the help of the villagers and Miss Mebbin.
(b) The feeling of belittling Loona Bimberton by hunting a tiger made her decide to give a party. She intended to offer Loona Bimberton a tiger-claw brooch on her birthday.
(c) Mrs. Packletide offered ? one thousand to the villagers to arrange an old tiger for hunting. She took Louisa Mebbin with her as her hunting companion and paid her for this work. A very old tiger who couldn’t even kill for his food was chosen for the purpose.
(d) The villagers helped Mrs. Packletide a lot in shooting the tiger. They arranged for an old tiger. Then they posted the children to see that the tiger didn’t stray in other hunting grounds. They also asked women crossing the forest not to sing loudly. This was to avoid that the tiger was not disturbed in his sleep.
(e) Miss Louisa Mebbin was Mrs. Packletide’s paid companion. She charged money for sitting with Mrs. Packletide while she hunted the tiger. She was not devoted to Mrs. Packletide at all. She behaved very arrogantly during the tiger hunting. She said that Mrs. Packletide shouldn’t pay if the tiger didn’t touch the goat. Then she pointed out that the shot of Mrs. Packletide killed the goat and the tiger died due to heart failure. She threatened to tell all this to Loona Bimberton to extract money from her.
(f) Mrs. Packletide was not a good shot as her shot killed the goat and not the tiger who was the target.
(g) Miss Mebbin said that Mrs. Packletide’s shot had killed the goat while there was no trace of shot on the tiger’s body. The tiger had died due to heart-failure caused by the sudden report of the rifle. Miss Mebbin made this comment just to blackmail Mrs. Packletide for more and more money. Mrs. Packletide was annoyed at this discovery.
(h) The villagers celebrated the hunt of the tiger by Mrs. Packletide. They started beating the tom-toms. This made Mrs. Packletide very glad and excited.
(i) No, Mrs. Packletide was not able to achieve her heart’s desire because Loona Bimberton declined to attend the luncheon party. Mrs. Packletide had decided to arrange it in her honour. Also she had decided to belittle her in offering her a tiger-claw brooch.
(j) Miss Mebbin blackmailed Mrs. Packletide. She threatened her that unless she bought her the week end cottage, she would tell Loona Bimberton the secret of her tiger hunt. Mrs. Packletide gave in for fear of being exposed and humiliated. She paid the money and Miss Mebbin managed to get the cottage. Miss Mebbin planted many tiger-lilies in her garden as the tiger was behind her acquiring this cottage. Tiger-lilies were synonymous for the tiger.
(k) The speaker of these lines is Mrs. Packletide. She refers to the ‘expenses’ that she met in buying Louisa Mebbin a cottage. These ‘expenses’ also include the money that she paid to the villagers for arranging a tiger.
Question 4.
Discuss the following questions in detail and write the answers in your notebooks :
(a) Do you think the tiger shooting organized by the villagers was a serious affair ? Give f reasons for your answer.
(b) Do you think the writer is trying to make fun of the main characters in the story i.e. Mrs. Packletide, Miss Mebbin and Loona Bimberton ? Pick out instances from the story that point to this fact.
(c) A person who is vain is full of self importance and can only think of himself / herself and can go to great lengths to prove his / her superiority. Do you think Mrs. Packletide is vain ? Give reasons in support of your answer.
(d) Sometimes writers highlight certain negative aspects in society or human beings by making fun of it. This is called satire. In your groups discuss whether you would classify this story as a satire. Give reasons to support your answer.
(e) How does the writer create humour in this story ?
Or
How does the writer create humour in the story Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger’ ? (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
(a) Yes, I think the tiger shooting organized by the villagers was a serious affair because tiger hunting is illegal. Doing anything to help in illegal deeds is also criminal. So the villagers can be challaned in helping in arranging the tiger for hunt illegally. Secondly, tigers are on the extinction list. The hunt becomes a serious criminal act on the part of Mrs. Packletide and the villagers.
(b) I think the writer is trying to make fun of these main characters. The language and tone used for this suggests taunt, derision and fun in an implied manner. The instances are :
For Mrs. Packletide : “Not that the lust to kill had suddenly descended … could successfully counter that sort of thing,” “her movements and motives were … Loona Bimberton.”
For Miss Mebbin : “If it’s an old tiger … money”, “Her energetic intervention had saved many a rouble … sympathetic hands,” “How you shot the goat … pleasant laugh”, “Loona Bimberton would,” said Miss Mebbin,” “I have seen a week-end cottage … have the money.”
For Loona Bimberton : “… that Loona Bimberton had recently been carried eleven miles … of nothing else,” “As for Loona Bimberton, she refused to look … repressed emotions,” “The luncheon party she declined … dangerous.”
(c) Mrs. Packletide is very vain and jealous by nature. She can never tolerate the growing social prestige of Loona Bimberton being carried in an aeroplane. So Mrs. Packletide is so much full of self-importance that she thinks of herself only. She can’t give the No. 1 place to any other woman and at any cost at social level. So she spends so much money. She is forced also to buy Louisa Mebbin a cottage just to keep (up) her foolish sense of social superiority.
(d) Meant for discussion at class level.
The story is essentially a satire on womanhood. The hollowness of Mrs. Packletide, the hypocrisy of Loona Bimberton and their giving more importance to false notions are ridiculed by the author. The doings of Louisa Mebbin and how she blackmails Mrs. Packletide also satirise these traits in women. In fact, all the three women have been satirised humorously in such a way that their hypocrisy and affectation are clearly understood.
(e) The author creates humour through the use of satirical language and creating undertones (through phrases) in description of various aspects of the story. The phrases are: ‘It was Mrs. Packletide’s pleasure and intention’; ‘her sudden deviation’; ‘stimulated the sporting and commercial instinct of the villagers’ ; ‘The one great anxiety was lest he should die of old age’.
Humour is also created through situations. These are : Mrs. Packletide and Louisa Mebbin are on the hunting platform. But they have small sized playing cards to play ‘solitaire’; women asked to hush up their singing lest the tiger should get disturbed in sleep ; villagers’ celebrating the hunting through thumping of tom-toms ; Mrs. Packletide’s hiding the facts of the case calling through ‘incidental expenses’.
This humour is also created through satirical and ironical treatment by the author.
Question 5.
Choose extracts from the story that illustrate the character of the people listed in the table given below. There are some words given to help you. You may add words of your own. One has been done as an example :
vain jealous competitive shrewd manipulative stingy materialistic spiteful

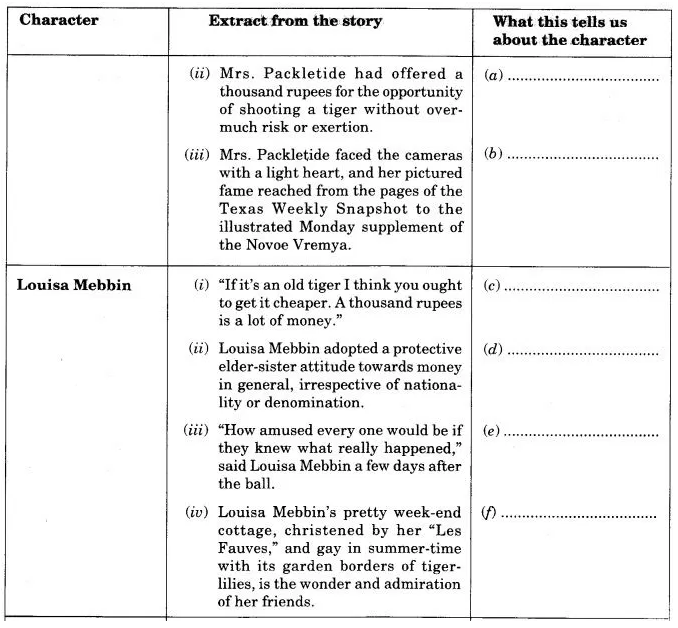

Answer:
(a) shrewd, manipulative, opportunistic, cunning planner
(b) vain, stingy, spiteful, proud, self-willed
(c) competitive, shrewd, materialistic, calculative Cd) competitive, shrewd, materialistic, vain
(e) shrewd, spiteful, exploitative, manipulative.
(f) shrewd, manipulative, opportunistic, materialistic
(g) vain, jealous, shrewd, stingy, spiteful, haughty
(h) revengeful, stingy, spiteful, vain, haughty
Question 6.
There are many amusing lines in the story. Here are a few of them. Rewrite each one in ordinary prose so that the meaning is retained. One has been done for you as an example :
(a) It was Mrs. Packletide’s pleasure and intention that she should shoot a tiger.
Mrs. Packletide wanted to shoot a tiger
……………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Mrs. Packletide had already arranged in her mind the lunch she would give at her house in Curzon Street, ostensibly in Loona Bimberton’s honour, with a tiger-skin rug occupying most of the foreground and all of the conversation.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
(c) Mothers carrying their babies home through the jungle after the day’s work in the fields hushed their singing lest they might curtail the restful sleep of the venerable herd-robber.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
(d) Louisa Mebbin adopted a protective elder-sister attitude towards money in general, irrespective of nationality or denomination.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
(e) Evidently the wrong animal had been hit, and the beast of prey had succumbed to heart-failure, caused by the sudden report of the rifle, accelerated by senile decay.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
(f) As for Loona Bimberton, she refused to look at an illustrated paper for weeks, and her letter of thanks for the gift of a tiger-claw brooch was a model of repressed emotions.
……………………………………………………………………………………..
Answer:
(b) Mrs. Packletide would arrange a luncheon party in her house to honour Loona Bimberton with a tiger-skin rug and conversation about it.
(c) Mothers were asked to come home through the jungle silently so that the tiger was not disturbed in his sleep.
(d) Louisa Mebbin behaved like an elder sister about money.
(e) Clearly the goat had been killed and the tiger died due to heart failure caused by the noise of the rifle shot and old age.
(f) Loona Bimberton refused to look at the illustrated magazines for weeks. Her letter of thanks for the gift of a tiger-claw brooch showed her repressed emotions.
Question 7.
An oxymoron is a figure of speech that combines normally-contradictory terms. The most common form of oxymoron involves an adjective-noun combination of two words like—failed success.
Writers often use an oxymoron to call attention to an apparent contradiction. For example, Wilfred Owen’s poem The Send-off refers to soldiers leaving for the front line, who “lined the train with faces grimly gay.” The oxymoron ‘grimly gay’ highlights the contradiction between how the soldiers feel and how they act: though they put on a brave face and act cheerful, they feel grim. Some examples of oxymorons are—dark sunshine, cold sun, living dead, dark light, almost exactly etc.
The story ‘Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger’ has a number of oxymorons. Can you identify them and write them down in your notebooks ?
Answer:
The following are some oxymorons in the story :
over-much, elaborate carelessness, grand attack, venerable herd-robber, disagreeably pleasant.
Students on their own can find more oxymorons in the story.
Question 8.
WRITING TASK
(a) Years later Mrs. Packletide writes her autobiography. As Mrs. Packletide, write about the tiger episode with the help of the clues given below.
(b) In groups of four construct the dialogues and enact the following situations from the story :
- Mrs. Packletide and the headman of the village/other villagers discussing the details of the tiger shooting.
- Miss Mebbin blackmailing Mrs. Packletide into gifting her a cottage.
- Loona Bimberton and a lady-friend discussing Mrs. Packletide’s hunting success.
Answer:
(a) Loona Bimberton’s being carried in an aeroplane was the talk of the town. She had become very famous due to it and her social prestige had gone onto the top. I couldn’t digest it as her applause had created jealousy in me. Day and night I felt how to counter it. So I thought that a tiger hunt would take me on a higher social pedestal than Loona. I lost no time in arranging a tiger hunt with the help of the villagers who were just thirsty for money.
I paid ₹ one thousand to the villagers for getting an aged tiger in the village forest. A goat with a loud bleat was tied at a convenient place to attract the tiger.
A suitable platform was built in a tree. On the night of the hunt I sat with Louisa Mebbin, my paid companion.
As per pre-arranged plan the tiger came near the goat. He lay flat to regain his strength before attacking his prey. I lost no time in firing the shot. I saw that both the goat and the tiger had been killed. ‘I am on the top’, I simply felt it in my blood.
It was Louisa Mebbin who told me that I had killed the goat with my shot and not the tiger. The tiger had died due to heart failure caused by the rifle shot and old age. She proved herself very cunning and crafty. She blackmailed me that she would tell this fact to Loona Bimberton. This hit my self-esteem. I had no choice except to bow down to her indirect demand. I had to buy a week-end cottage in Dorking for her to shut her mouth to give out the secret of the tiger hunt.
(b) Students to construct the dialogues on their own and enact the same on the given situations. One sample dialogue construction is given below which can be enacted by them at class level :
Mrs. Packletide and the headman of the village/other villagers discussing the details of the tiger shooting.
A (Mrs. Packletide) : Well, gentlemen, I have decided to hunt a tiger in your village. For that I shall be needing your help. Don’t worry about money. What do you say?
B (village headman) : Yes, madam. When you have talked of money, we shall do whatever you say. I think my village people shall fully cooperate.
C (other villagers) : Yes, madam. We are with the headman. Whatever you decide, we shall do.
A (Mrs. Packletide) : For this I shall pay you one thousand. You shall have to arrange for a very weak tiger. You all will direct it on the hunting night to come to his bait. For bait you’ll arrange a goat with a good bleating sound and tie it at a point near the platform in a tree.
B (village headman) : Excuse me, madam. Where shall the platform be built?
A (Mrs. Packletide) : It should be near the place where the goat is to be tied. I and another madam shall sit on this platform in a tree. You all will direct the tiger towards the goat. When I see the tiger coming near the goat, I shall shoot at once.
C (other villagers) : What’ll happen in case the tiger strays out before the date of hunting?
A (Mrs. Packletide) : That’s your responsibility. But one thing. You’re never to disclose whatever we decide now to anybody, come what may.
B (village headman) : You needn’t worry, madam. I am asking the children to see that the tiger doesn’t stray out. Equally all the women have been asked not to sing loudly while coming home through the jungle. It is not to disturb the tiger in his sleep.
A (Mrs. Packletide) : That would be very nice. Please see that whatever we decide actually occurs. If there gets any lapse, you know the consequences…
C (All the villagers) : Yes, madam. You needn’t worry. We shall celebrate the tiger hunt with playing tom-toms.
A (Mrs. Packletide) : Good bye.
Question 9.
LISTENING TASK
Listen to the passage on lion hunting and answer the questions given below :
1. The Maasai tribe in Africa hunt lions because
- they live near the forests of Africa
- they view it as a sign of bravery and personal achievement
- they are a hunting tribe
- they adorn their bodies with body parts of the lion.
2. Solo hunting has been banned because
- it is dangerous –
- of the declining lion population
- too many hunters have been killed
- it creates pride in the minds of the successful hunters.
3. The hunting of lionesses is discouraged because
- they bear the cubs
- they run much faster
- they are more fierce
- they cannot be spotted easily.
4. The Maasai warriors chase a lion with rattle bells to
- awaken it
- make it run faster
- make it angry
- frighten it.
5. The Maasai use three parts of the lion. They are
- the mane, tail and claws
- the mane, nails and claws
- the mane, tail and nails
- the whiskers, tail and claws.
6. The tail is given to
- the strongest warrior
- the fastest warrior
- the youngest warrior
- the bravest warrior.
Answer:
- 2. they view it as a sign of bravery and personal achievement
- 2. of the declining lion population
- 1. they bear the cubs
- 3. make it angry
- 3. the mane, tail and nails
- 1. the strongest warrior
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Literature Chapter 2 Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Literature Chapter 2 Mrs. Packletide’s Tiger, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.