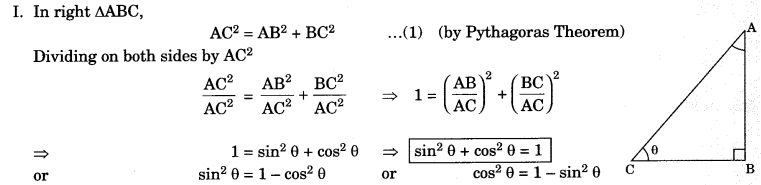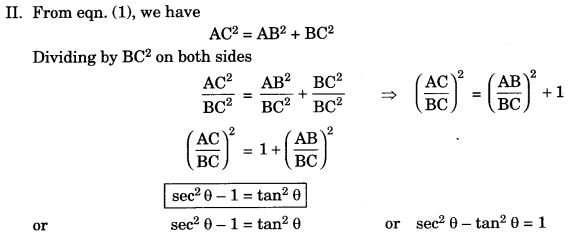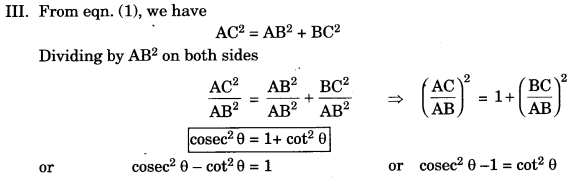
On this page, you will find Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 8 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Notes Introduction to Trigonometry
Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Notes Understanding the Lesson
The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words ‘Tri’ which means three, ‘gon’ means sides and metron meaning measure.
It means trigonometry is the study of relationship between the sides and angles
- The earliest work on trigonometry was recorded in Egypt and Babylon.
- Trigonometry was used by early astronomers to find out the distance of stars and planets from the earth.
Trigonometric Ratios
The ratios of the sides of a right triangle with respect to its acute angles are called trigonometric ratios.
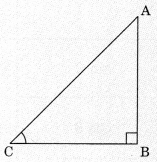
- In right triangle, side opposite to given acute angle will always be perpendicular.
- Side opposite 90° will always be hypotenuse.
- Remaining side will be base.
- The sum of two angles (except right angle) is 90°
i.e., ∠A + ∠C = 90° ( ∵ ∠B = 90°)
1. sin θ = sin θ = \(\frac{0}{\mathrm{H}}\) (O- side opposite to given angle i.e., acute angle)
2. cosine θ = cos θ = \(\frac{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{H}} \)(A-adjacent side) (H-Hypotenuse)
3. Tangent θ = tan θ =\(\frac{\mathrm{O}}{\mathrm{A}}\)
(O-side opposite to acute angle, A-adjacent side)
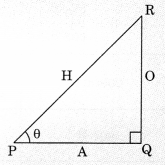
4. cosecant θ = cosec θ= \(\frac{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{O}}\)
5. secant θ = sec θ =\(\frac{\mathrm{H}}{\mathrm{A}}\)
6. cotangent θ= cot θ =\(\frac{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{O}}\)
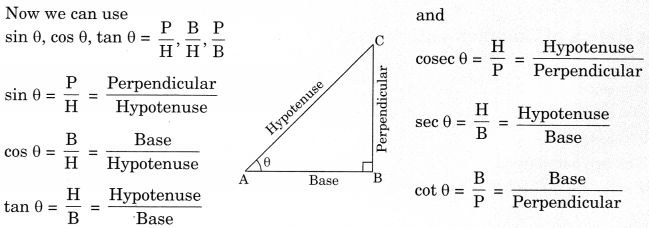

Trigonometric angles for some specific angles
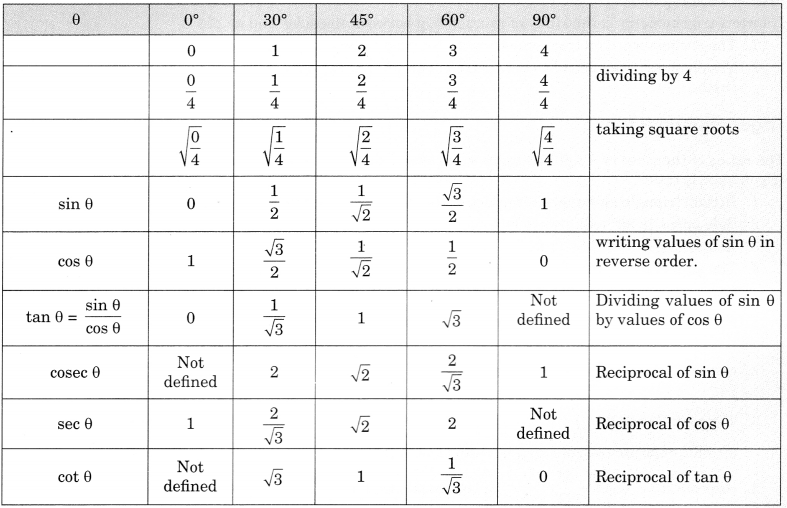
Also we can find values for some special angles as follows:
Trigonometric Identities
Identity: That equation is called an identity. If it is true for all values of the variables which involved. I. In right ΔABC,