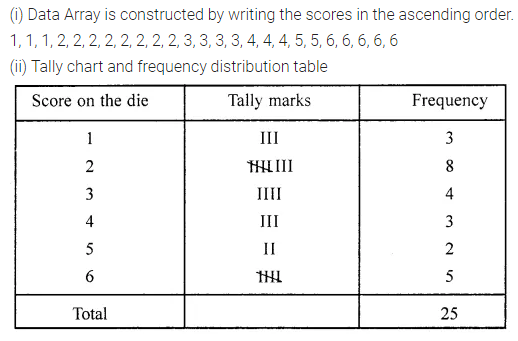
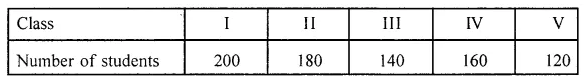
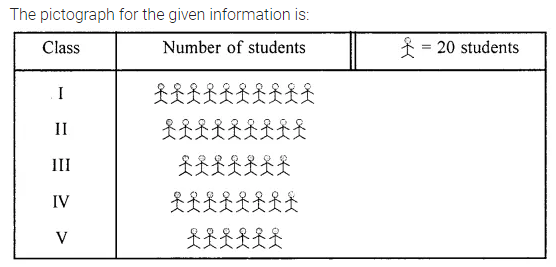
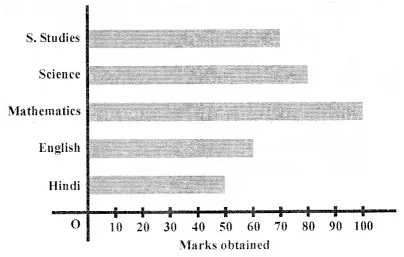
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used.
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used.
Collective Nouns Exercises for Class 4 CBSE with Answers PDF
Fundamentals
- Collective nouns—such as family, committee and class—name groups that are made up of individuals.
- A collective noun may be either singular or plural, depending on how the group acts.
- When the group acts together as one unit to do something, the group is considered singular.
- When individuals within the group act differently or do different things at the same time, the collective noun is plural.
Example:
Singular : The team practices for the game on Friday.
The jury eats lunch at the restaurant.
Plural : The team change into their street clothes after the game.
The jury often have different reactions to the case.
Presentation
Read the picture story.
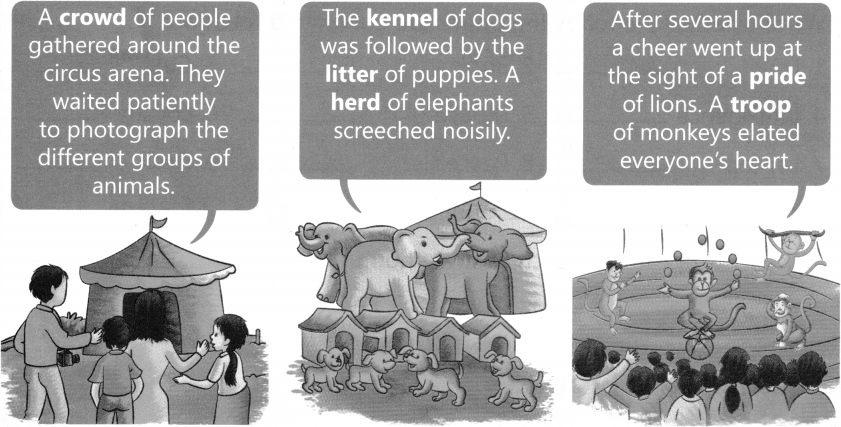
A. Answer the following questions as per the story.
1. Which group had gathered around the circus arena? ___________
2. Which group is followed by the kennel of dogs? ___________
3. Which group elated everyone’s heart? ___________
B. Write down collective nouns from the story above.
1. A group of puppies is called a ___________
2. A group of people is called a ___________
3. A group of monkey is called a ___________
4. A group of lions is called a ___________
5. A group of elephants is called a ___________
Collective Nouns Worksheet with Answers for Grade 4
A. Circle the collective noun in each sentence that is describing the subject or noun. The first one has been done for you.
1. Pulling with all their might, a team of oxen hauled rocks.
2. Schools of fish swam quickly up the cool, mountain stream.
3. Herds of elephants ate the trees bare.
4. Colonies of beavers built the dams to hold back the flowing water.
5. Packs of wolves ran through the pine forest.
6. Pods of dolphins leaped out of the ocean.
7. Hives of bees gathered sweet nectar.
B. Match the collective nouns with their groups by writing the letter in the answer column. The first one has been done for you.
| Collective Noun | Answer | Group or Unit |
| 1. An agenda | G | A. of thieves stole the money. |
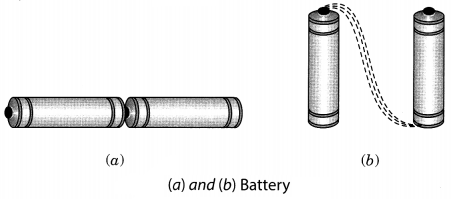
| 2. A battery | B. of kittens meowed for food. | |
| 3. Litters | C. of juicy grapes from the vines. | |
| 4. The herd | D. of elephants stomped through the lush jungle. | |
| 5. We each picked a bunch | E. of tests is hard work. | |
| 6. The gaggle | F. of geese squawked loudly. | |
| 7. A band | G. of tasks was on my desk. |
C. Write the matched pairs in a complete sentence. The first one has been done for you.
1. An agenda of tasks is on my desk.
2. ______________________
3. ______________________
4. ______________________
5. ______________________
6. ______________________
7. ______________________
D. Circle the collective noun that best fits in the sentence. The first one has been done for you.
1. The (classroom/herd) of students read the directions on the white board.
2. Sailing around the (flock/chain) of islands, the crew of sailors cheered.
3. Bears fish in the river as the (clouds/runs) of salmon swim upstream.
4. Slithering and hissing, the (pits/brigades) of snakes settled for sleep.
5. Running late, I ran up (flight/pod) of stairs in record time.
6. Looking up at the sky, I had a glimpse of the (packs/galaxies) of stars.
7. After the holidays, we had (colonies/heaps) of trash.
 This grammar section explains
This grammar section explains 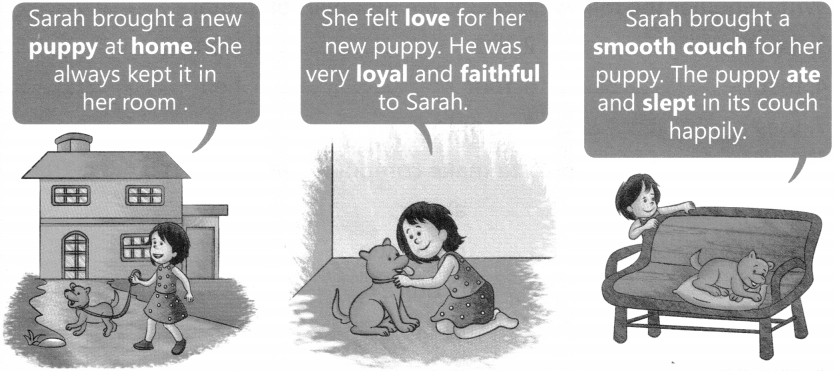
 Definition: A noun is a part of speech that is used to name a person, place, thing, quality, or action. Examples: Mango, girl, boy, cat, etc.
Definition: A noun is a part of speech that is used to name a person, place, thing, quality, or action. Examples: Mango, girl, boy, cat, etc.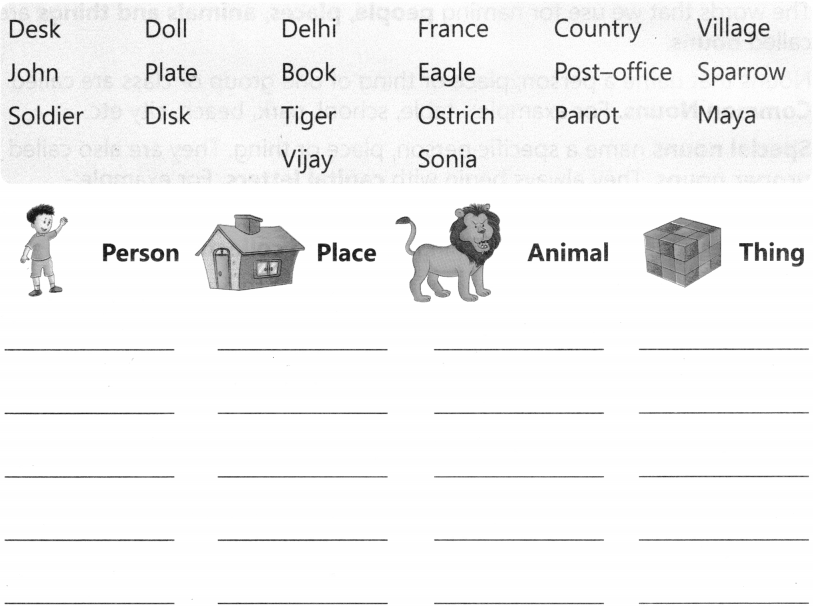









 This grammar section explains
This grammar section explains