In this page, we are providing Water Class 6 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 14 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Water with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-6-science/
Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Extra Questions and Answers Water
Extra Questions for Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Water with Answers Solutions
Water Class 6 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Water Class 6 Questions And Answers Question 1.
Can you name some activities where water is used for recreation?
Answer:
River rafting, swimming, water games, water park, etc.
Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Extra Questions Question 2.
Name some sources of water.
Answer:
Hand pump, tube well, river, pond, lake, ocean, etc.
Ncert Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Extra Questions Question 3.
From where do lakes and ponds get their water?
Answer:
Rains
Water Class 6 Worksheet With Answers Question 4.
Name two main processes which transfer water present on the earth into water vapour continuously.
Answer:
Evaporation and transpiration.
Water Class 6 Extra Questions And Answers Question 5.
What name is given to the process in which rainwater is made to percolate into the ground efficiently?
Answer:
Rainwater harvesting
Class 6 Science Water Extra Questions Question 6.
What is the ultimate source of water?
Answer:
Rain
Water Class 6 Extra Questions Question 7.
What are the different forms of precipitation?
Answer:
Rain, snow and dew.
Class 6 Water Extra Questions Question 8.
What will happen if there is a continuous rain?
Answer:
This results into floods.
Class 6 Science Ch 14 Extra Questions Question 9.
Name the process which is involved in the formation of dew?
Answer:
Condensation
Ncert Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Extra Questions Question 10.
Name the condition given to the extreme dryness in an area due to lack of rains for a long period.
Answer:
Drought
Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Worksheet Question 11.
What is the main source of groundwater?
Answer:
Rainwater
Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Extra Question Answer Question 12.
List one use of water.
Answer:
Water is essential for the germination of seeds.
Extra Questions On Water Class 6 Question 13.
Name the term used for falling of water drops from sky.
Answer:
Precipitation
Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Questions And Answers Question 14.
Name the states where roof top water harvesting is used to collect water.
Answer:
Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan.
Water Class 6 Worksheet With Answers Pdf Question 15.
What is the process of changing water into vapour called?
Answer:
Vapourization
Water Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
What is glacier?
Answer:
A glacier is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. The rivers get their water from the melting of these glaciers.
Question 2.
Why is water important for us?
Answer:
- Water regulates body temperature by the process of respiration and evaporation.
- All metabolic reactions in the body take place in aqueous medium.
- It transports minerals and food materials in plant’s and animal’s body.
Question 3.
What is water cycle?
Answer:
Water constantly moves from the earth to the air and back again. The constant circulation of water is known as the water cycle.
Question 4.
What are the different ways by which water vapour is put into the atmosphere?
Answer:
Water in oceans, lakes and ponds get evaporated due to atmospheric heat. Factories and thermal power stations produce a lot of steam and put it into the atmosphere. Plants lose water through transpiration. Animals lose water through respiration, sweating and excretion. All this vapour accumulates in the atmosphere.
Question 5.
What is precipitation?
Answer:
When water drops come together in the air, it becomes heavy and begin to fall. Falling of water drops is called precipitation.
Question 6.
What are the two main techniques of rainwater harvesting?
Answer:
The two main techniques of rainwater harvesting are:
- Roof-top rainwater harvesting
- Rainwater harvesting from open spaces around buildings.
Question 7.
How does rainwater become saline?
Answer:
Water is a universal solvent because it dissolves a large number of substances. When rain falls, it dissolves common salts and many other substances and minerals present on the earth. The rainwater passes through different layers of earth, rocks, dissolves large amount of salt and other minerals. Thus it becomes salty.
Question 8.
Explain the roof-top rainwater harvesting.
Answer:
In this technique, the rainwater from the roof-top is collected in a storage tank with the help of pipes. Here it is filtered and then sent into a pit. The water in the pit seeps or percolates slowly into the ground to recharge the groundwater.
Question 9.
How does water cycle help in maintaining global climate?
Answer:
Water cycle plays an important role in the world climate. Ocean absorb vast quantities of heat and help in global warming. By absorbing heat, water evaporates and on condensation releases heat. This absorption and releasing of heat in the form of energy drives weather pattern in the short-term and regulate the climate for long time.
Water Class 6 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
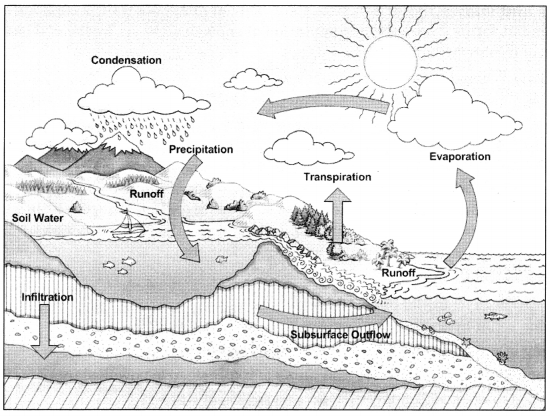
Explain the process of water cycle in nature with the help of suitable diagram.
Answer:
Water constantly moves from the earth to the air and back again. The constant circulation of water is known as the water cycle. The water in seas, rivers, lakes, ponds or streams evaporates because of the heat of the sun. Plants also give out large amounts of water from their leaves. The water vapour rises up. The air higher up in the atmosphere is cooler.
This cools the water vapour and its condenses to form tiny drop of water. These drops of water together form clouds. As the clouds get cooled further, the water drops become bigger and heavier. When they become too heavy, they fall on the earth as rain and fill the sources of water like river, ponds, streams, etc.
Question 2.
List the uses of water.
Answer:
Uses of water are:
- It is needed for drinking, bathing, washing, cleaning of vessels, toilets, flushing, etc.
- Our body contains about 70% of water. Hence, water is essential for our life.
- Water helps animals and plants to keep themselves cool.
- Water is required for irrigation.
- Water is used to generate electricity.
- Water is used for recreational activity.
- Water is habitat of many aquatic plants and animals.
Question 3.
Explain about the sources of water.
Answer:
Sources of water can be classified as:
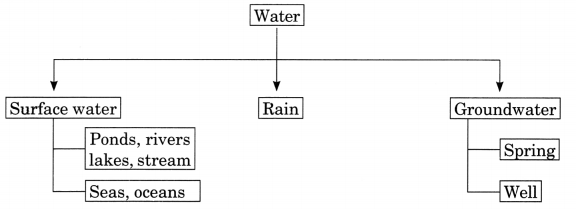
• Surface-water: Rivers, lakes, ponds, streams, oceans, etc., are surface water which is continually replenished by rainwater runoff and melting of glaciers. Most of the human activities, like drinking, washing, farming, etc., rely on freshwater supply. Two-third of Earth’s surface is covered with oceans and seas. Water from these sources are not fit for drinking or any other human activities. Surface water act as natural habitat for many plants and animals.
• Groundwater: Water present beneath Earth’s surface in soil pore spaces and in fractures of rock formations. It is stored there and moves slowly through geologic formation of soil, sand and rocks called aquifers. Groundwater is mainly replenished through seepage of rainwater and surface water.
• Rain: Rain is liquid water in form of droplets that have condensed from the atmospheric water vapour and then precipitated, i.e., become heavy enough to fall under gravity.
• Glaciers and snow: Glacier is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. It forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its melting. Glacial ice is the largest reservoir of freshwater on Earth.
Question 4.
What is drought? When does drought occur?
Answer:
Drought is a long period without rains leading to severe shortage of water in the region.
The soil continues to lose water by evaporation and transpiration. The water lost by soil is usually made up by rains. If, however, it does rain at all or the rainfall is very low for a long period, the loss of water from the soil is not made up and hence the soil becomes dry.
Due to lack of rains, the water level in the lakes and ponds also goes down and some of them may even dry up completely. In the absence of rains, no water seeps into the ground and hence the level of groundwater in wells, etc., falls drastically. Due to this groundwater also becomes scarce. In this way, a prolonged period of no rains or very low rains causes all around shortage of water leading to drought.
Question 5.
How is rain useful to us?
Answer:
Rainwater is useful to us in the following ways: ,
- Rains bring relief by cooling the environment after hot summer days.
- The sowing of many crops depends on the arrival of rains during monsoon.
- Rains provide water in the rivers and dams of hydroelectric power plants.
- Rains fill the lakes and ponds which acts as source of water.
- Rains are also responsible for recharging the groundwater and thus maintaining water table.
Water Class 6 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
What are the factors affecting rate of evaporation?
Answer:
(a) Temperature: Higher is the temperature higher will be the rate of evaporation.
(b) Wind velocity: Higher is the wind velocity higher will be the rate of evaporation.
(c) Surface area: Larger is the surface area, i.e., exposed area, larger will be the rate of evaporation.
(d) Humidity: Humidity is the presence of moisture in air. Higher is the humidity, less will be the the rate of evaporation.
Question 2.
How does water kept under the shade of a tree also gets evaporated?
Answer:
Air around us gets heated from sunlight. This warm air provides heat for evaporation of water kept in
the shade.
Question 3.
What will happen if we are lost in a sea and drink lot of sea water to quench our thirst?
Answer:
The sea water is highly saline. Drinking this water will cause diarrhoea and loss of too much water from our body through frequent urination. Thus, will cause dehydration and ultimately death.
Question 4.
In what ways does water serves to sustain life?
Answer:
Water controls various biological processes like, transpiration, ingestion, excretion, digestion, etc. Moreover 70% of our body weight comprises of water.
Question 5.
Dissolve two spoons of common salt in half a cup of water. Now, if you want to get the salt back, what will you do?
Answer:
To get the salt back from its solution, the solution is heated in a container till all the water gets evaporated. The white powdery substance that is retained back is the salt
Water Class 6 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1.
On a summer vacation, Ria went to her village to spent her holidays. After staying there for some days she realised the problem of shortage of water faced by the villagers. She along with her father went to the office of water supply department of her village and conveyed them the problem of water shortage.
The officer of water supply department assured Ria and her father that they will do something to overcome this shortage but the villagers must also adopt water conservation practices to use water judiciously. Ria thought to make villagers aware of water conservation practices with some interesting play so that they could understand its importance.
(a) Where did Ria went in her summer vacation?
(b) What did she observed there?
(c) What do mean by water conservation?
(d) What practices could help in conserving water?
(e) What values of Ria is shown here?
Answer:
(a) Ria went to her village in summer vacation.
(b) She observed water shortage there.
(c) Water conservation refers to strategies and activities made to manage fresh water as a sustainable resource to meet current and future human demand.
(d) (i) Use water judiciously.
(ii) Use water from washing machine, bathing and moping in watering plants or flushing toilets.
(iii) Check leaking pipes and get it’repaired.
(iv) Use high-efficiency toilets that use less water in a flush.
(v) Water the plants at night to reduce loss of water due to evaporation.
(e) Ria is an intelligent, responsible, understanding, sensible and innovative girl.
Question 2.
Whenever Sajia returns from school she empties her water bottle in the potted plant instead of throwing it in the sink. She always keep her eyes on her housemaid that the water after mopping the house must be used for watering the plants in the garden.
(a) Can you suggest any other use of the water left after mopping?
(b) What is the function of water in plants?
(c) What values of Sajia is shown here?
Answer:
(a) We can use the water after mopping in flushing the toilets.
(b) Water in plants help in transportation, maintaining turgidity, photosynthesis and cooling through transpiration.
(c) Sajia is eco-friendly, responsible and intelligent girl.