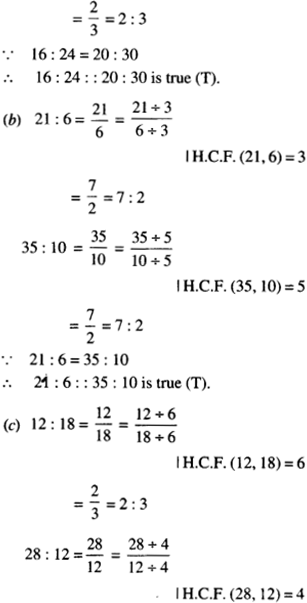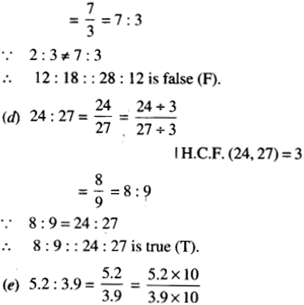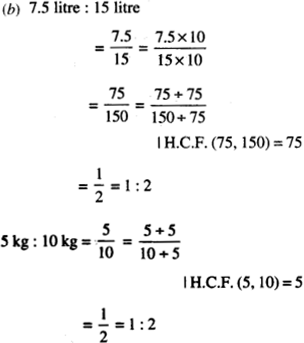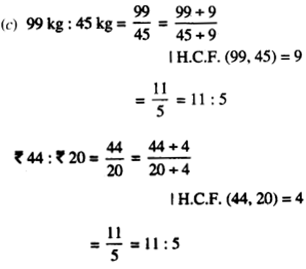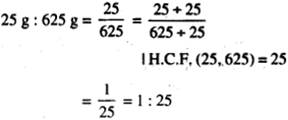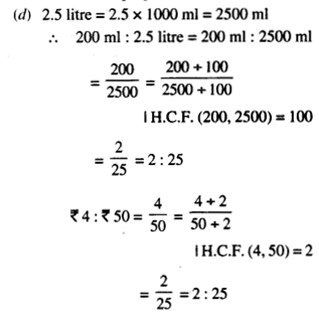NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.2 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.2.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 1 |
| Chapter Name | Integers |
| Exercise | Ex 1.2 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 4 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.2
Question 1.
Write down a pair of integers whose:
(a) the sum is -7
(b) the difference is -10
(c) the sum is 0.
Solution:
(a) (-15) and 8
(b) 15 and 25.
(c) (-49) and 49
Question 2.
(a) Write a pair of negative integers whose difference gives 8.
(b) Write a negative integer and a positive integer whose sum is -5.
(c) Write a negative integer and a positive integer whose difference is -3.
Solution:
(a) (-10) and (-18)
(b) (-10) and 5
(c) (-1) and 2
Question 3.
In a quiz, team A scored – 40, 10,0 and team B scored 10, 0, – 40 in three successive rounds. Which team scored more? Can we say that we can add integers in any order?
Solution:
Total scores of team A = (- 40) + 10 + 0 = – 40 + 10 + 0 = – 30
and, total scores of team B = 10 + 0 + (- 40) = 10 + 0 – 40 = – 30
Since the total scores of each team are equal.
∴ No team scored more than the other but each has an equal score.
Yes, integers can be added in any order and the result remains unaltered.
For example, 10 + 0 + (-40) = -30 = -40 + 0 + 10
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks to make the following statements true:
- (-5) + (-8) = (+8) + (……)
- -53 + …… = -53.
- 17 + …… = 0
- [13 + (-12)] + (…… ) = 13 + [(-12) + (- 7)]
- (- 4) + [15 + (- 3)] = [(-4) + 15] + …….
Solution:
- (-5) + (-8) = (-8) + (- 5)
- -53 + 0 = -53
- 17 + (- 17) = 0
- [13 + (- 12)] + (- 7) = 13 + [(- 12) + (-7)]
- (- 4) + [15 + (- 3)] = [(- 4) + 15] + (- 3).
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.2 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.