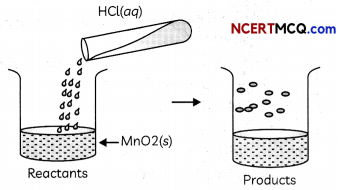
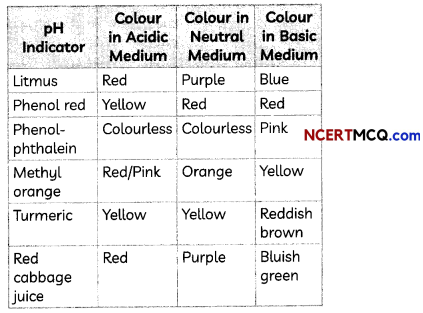
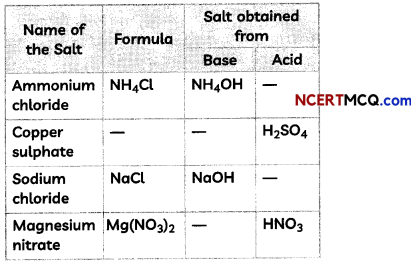
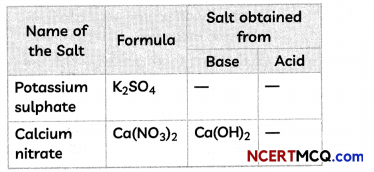
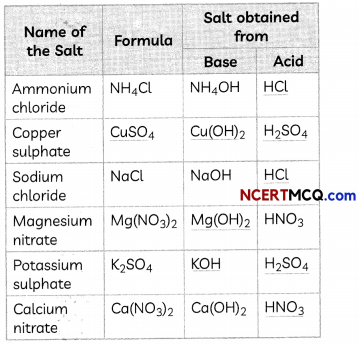
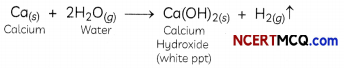
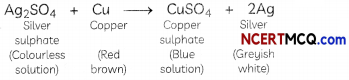
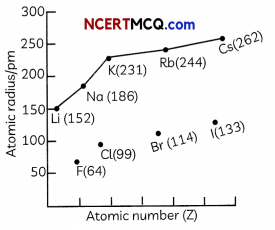
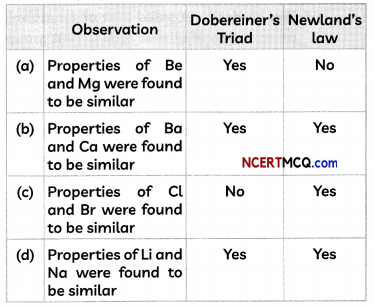
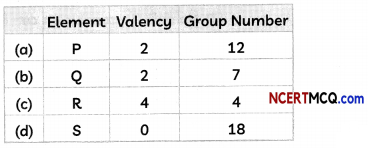
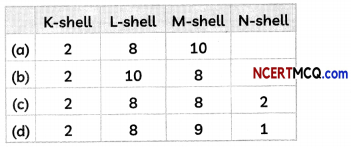
Students can also read Online Education MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Questions with Answers hope will definitely help for your board exams. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-10-science-with-answers/
Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 1 MCQ With Answers
Chemistry Class 10 Chapter 1 MCQs On Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chemical Reaction And Equation Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
Which of the following is not a physical change?
(a) Boiling of water to give water vapour.
(b) Melting of ice to give water.
(c) Dissolution of salt in water.
(d) Combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG).
Answer:
(d) Combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG).
Explanation: Since the combustion of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) produces new substances, a lot of heat is produced along with carbon dioxide and water vapour. It is also irreversible in nature. So it is a chemical change.
However, boiling of water to give water vapour, melting of ice to give water and dissolution of salt in water are physical changes, as here no new substance is formed, only the physical state of the substance changes.
A physical change does not produce a new substance although the initial and final substances appear different and it is reversible.
During a chemical change, the chemical composition of the substance changes and new substances with new properties are formed. Energy is either released or absorbed during a chemical change and it is irreversible.
Top free images & vectors for Compound chemical formula calculator in png, vector, file, black and white, logo, clipart, cartoon and transparent.
Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 MCQ Question 2.
Which of the following is (are) an endothermic process(es)?
(I) Dilution of sulphuric acid
(II) Sublimation of dry ice
(III) Condensation of water vapours
(IV) Evaporation of water
(a) (I) and (III)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Only (III)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
![]()
Class 10 Science Chapter 1 MCQ Question 3.
Strong heating of ferrous sulphate leads to the formation of a brown solid and two gases. This reaction can be categorised as:
(a) displacement and redox.
(b) decomposition and redox.
(c) displacement and endothermic.
(d) decomposition and exothermic.
Answer:
(b) decomposition and redox reaction.
Explanation: When FeSO4 is heated strong, it decomposes to form a brown solid ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide.
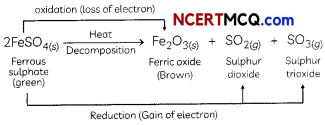
In this reaction, FeSO4 decomposes and forms new products so it is a decomposition reaction. Here FeSO4 is oxidised to Fe2O3 by loss of electrons. So this part of the reaction is oxidation reaction FeSO4 is also reduced to SO2 and SO3 by a gain of electrons.
Hence, the Heating of FeSO4 is both decomposition and Redox reaction.
Related Theory:
A reaction is called redox when both oxidation and reduction are taking place simultaneously.
The oxidation process involves:
- Gain of oxygen
- Loss of hydrogen
- Loss of electrons
Reduction process involves:
- Loss of oxygen,
- Gain of hydrogen
- Gain of electrons
The substance which loses electrons i.e. gets oxidised, acts as a reducing agent and the substance which gains electrons, i.e. it gets reduced and acts as an oxidising agent.
Alkyne Reactions Cheat Sheet Download.
Class 10 Chemical Reactions And Equations MCQ Question 4.
Which among the following is (are) double displacement reaction(s)?
(I) Pb + CuCl2 → PbCl2 + Cu
(II) Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4 + 2NaCl
(III) C + O2 → CO2
(IV) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
(a) (I) and (IV)
(b) Only (II)
(c) (I) and (II)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) only (II)
Explanation: A double displacement reaction involves the displacement of two ions of two different compounds that results in the formation of new compounds. Here, only in reaction (II), ions of both reactants are exchanged and two entirely different compounds are formed. For example.
Na2SO4 + BaCl2 → BaSO4(s) (White ppt) + 2NaCl(aq)
In a double displacement reaction, exchange of ions takes place i.e., SO42- exchange place with Cl– ion. It is also called a precipitation reaction as BaSO4 is precipitated as insoluble salt in the solution.
Ch 1 Science Class 10 MCQ Question 5.
Barium chloride on reacting with ammonium sulphate forms barium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Which of the following correctly represents the type of reaction involved?
(I) Displacement reaction
(II) Precipitation reaction
(III) Combination reaction
(IV) Double displacement reaction
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Only (IV)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
![]()
Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 1 MCQ Question 6.
When copper turnings are added to silver nitrate solution, a blue coloured solution is formed after some time. It is because copper:
(I) Displaces silver from the solution
(II) forms a blue coloured complex with AgNO3
(III) Is oxidized to Cu2+
(IV) ls reduced to Cu2+
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (III)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) (I) and (III)
Explanation: Copper is placed above silver in electrochemical series and thus reaction occurs
Cu + 2Ag+ → Cu2+ + 2Ag
Chemical Reaction And Equation MCQ Question 7.
One of the following does not happen during a chemical reaction. This is:
(a) Breaking of old bonds and formation of new bonds
(b) Formation of new substances with entirely different properties
(c) Atoms of one element change into those of another element to form new products
(d) A rearrangement of atoms takes place to form new products
Answer:
(c) atoms of one element change into those of another element to form new products. Explanation: It is not atoms but the bonds between these atoms break and form during chemical reactions. Atoms of elements can rearrange but cannot change into other elements.
Chemical Reactions And Equations MCQ Question 8.
You are given the solution of lead nitrate. In order to obtain a yellow precipitate, you should mix with it a solution of:
(a) potassium chloride
(b) potassium nitride
(c) potassium sulphide
(d) potassium iodide
Answer:
(d) potassium iodide

Explanation: Potassium iodide on reacting with lead nitrate gives yellow precipitate of Lead iodide.
2KI + Pb(NO3)2 → Pbl2 + 2KNO3
MCQ On Chemical Reactions And Equations Question 9.
In which of the following chemical equations do the abbreviations represent the correct states of the reactants and products involved at reaction temperature?
(a) 2H2(l) + O2(l) → 2H2O(g)
(b) 2H2(g) + O2(l) → 2H2O(g)
(c) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l)
(d) 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)
Answer:
Chapter 1 Science Class 10 MCQ Question 10.
Dilute hydrochloric acid is added to granulated zinc taken in a test tube. The following observations are recorded. Point out the correct observation:
(a) The surface of metal becomes shiny.
(b) The reaction mixture turns milky.
(c) Odour of a pungent-smelling gas is recorded.
(d) A colourless and odourless gas is evolved. [Diksha]
Answer:
(d) A colourless and odourless gas is evolved. Explanation: The chemical reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and granulated zinc is represented as follows:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2↑
The product, zinc chloride, does not turn the reaction milky. Hydrogen gas evolved is colourless and odourless and released by the formation of bubbles. Hence, option (d) is correct.
![]()
MCQ Of Chemical Reaction And Equation Question 11.
On heating, a blue coloured powder of copper (II) nitrate in a boiling tube, a black substance X, oxygen gas and a brown gas Y was formed. Select the option which identifies the products correctly:
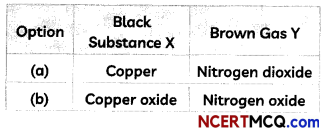
Answer:
(c) X is Copper Oxide and Y is Nitrogen Dioxide Explanation: When blue coloured powder of copper (II) nitrate is heated, it decomposes to form black coloured substance which is copper oxide, oxygen gas and brown gas nitrogen dioxide.
The chemical equation for the reaction taking place is:

Class 10 Science Ch 1 MCQ Question 12.
In the equation:
Cu + XHNO3 → CU(NO3)2 + yNO2 + 2H2O
The values of x and y are:
(a) 3 and 5
(b) 8 and 6
(c) 4 and 2
(c) 7 and 1
Answer:
(c) Cu + 4HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
Explanation: In order to find the values of x and y, we need to balance the chemical equation by equating the number of atoms of each element on both sides in the given equation.
Cu + XHNO3 → CU(NO3)2 + yNO2 + 2H2O

Equating the number of H atoms on both sides as per the law of conservation of mass, x = 4.
Putting this value in either the no. of atoms of N or O,
x = y + 2 means y = x – 2 = 4 – 2 = 2.
Therefore, x = 4 & y = 2 is the correct answer
Chemical equation balance the equation calculator finds the stoichiometric coefficients to balance chemical equations incl.
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Question 13.
In which of the following chemical equations, the abbreviations represent the correct states of the reactants and products involved at reaction temperature?
(a) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(s) + 3NH4Cl(aq)
(b) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(l) → Al(OH)3(aq) + 3NH4Cl(s)
(c) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(s) + 3NH4Cl(aq)
(d) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(aq) + 3NH4Cl(s)
Answer:
(a) AlCl3(aq) + 3NH4OH(aq) → Al(OH)3(s) + 3NH4CL(aq)
Explanation: When ammonium hydroxide solution is added to aluminium chloride solution, a white precipitate of aluminium hydroxide is formed alongwith ammonium chloride solution.
Chemical Equations And Reactions Class 10 MCQ Question 14.
The reaction 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O is an example of:
(I) displacement reaction.
(II) double displacement reaction.
(III) neutralisation reaction.
(IV) combination reaction.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (III) and (IV)
(d) (I) and (IV)
Answer:
Chemical Equation And Reaction Class 10 MCQ Question 15.
Consider the following chemical equation:
X(aq) + sodium chloride(aq) → Y(white ppt) + Sodium nitrate(aq)

Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1
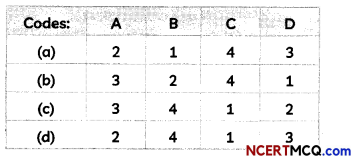
For the following questions, two statements are given: one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
![]()
Question 16.
Assertion (A): Following is a balanced chemical equation for the action of steam on iron:
4Fe + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4 + 4H2
Reason (R): The law of conservation of mass holds good for a chemical equation.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: Iron (Fe) metal does not react with cold or hot water but it reacts with steam to form a metal oxide and hydrogen.
The law of conservation of mass holds good for a chemical reaction. The statement is true but it does not explain the equation given in the Assertion.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling white flame.
Reason (R): Magnesium ribbon undergoes physical change on burning and melts.
Answer:
Question 18.
Assertion (A): While equalizing the number of atoms to balance a chemical equation, we alter the formula of the compounds or elements involved in the reaction.
Reason (R): Chemical equation is balanced by making the number of atoms of each element equal on both sides of the arrow.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Explanation: A chemical equation is balanced by making the number of atoms of each element equal on both sides of the arrow without altering the formula of the compounds or elements involved in the reaction. It is balanced by putting coefficients in front of the compounds or elements.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): The reaction of calcium oxide with water to produce slaked lime releasing a large amount of heat is a combination reaction.
Reason (R): Double displacement reactions are the reactions in which there is an exchange of ions between the reactants.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: The reaction of calcium oxide with water to produce sLaked lime releasing a large amount of heat is a combination reaction as the two reactants combine to form a single product.
Whereas, in a double displacement reaction, there will be two reactants and two products which are formed by the exchange of ions between the reactants.
![]()
Question 20.
Assertion (A): The decomposition reaction of silver chloride into silver and chlorine is an exothermic process.
Reason (R): Reactions in which energy is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions.
Answer:
Question 21.
Assertion (A): Zinc and lead displace copper from their compounds.
Reason (R): Zinc and lead are more reactive than copper.
Answer:
Competency-Based Questions (CBQs)
Question 1.
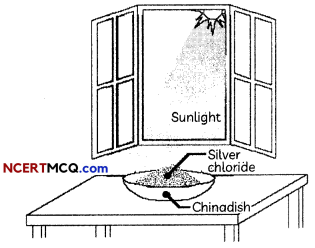
During a chemical reaction atoms of one element do not change into those of another element. Nor do atoms disappear from the mixture or appear from elsewhere. Actually, chemical reactions involve the breaking and making of bonds between atoms to produce new substances.
To demonstrate a reaction, 2 g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish and placed in sunlight.
(A) What will you observe after some time?
(B) What is this reaction known as?
(C) Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
(D) Give reasons for the observations.
Answer:
Question 2.
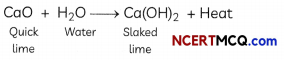
Whitewash is a very low-cost type of paint made from slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) and chalk (whiting). Chalk is calcium carbonate. Slaked lime turns into chalk by reacting with carbon dioxide in the air over several days. This causes crystallization, which binds and strengthens the coating. Various other additives can be used.

Solid calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form calcium hydroxide, accompanied by liberation of heat. This process is called slaking of lime. Calcium hydroxide dissolves in water to form a solution called lime water. Which among the following is (are) true about slaking of lime and the solution formed?
(I) It is an endothermic reaction.
(II) It is an exothermic reaction.
(III) The pH of the resulting solution will be more than seven.
(IV) The pH of the resulting solution will be less than seven.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (IV)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) (II) and (III)
Explanation: Slaking of lime is an exothermic reaction because a large amount of heat is produced during the reaction. The heat can be felt by touching the beaker from the outside. The resulting compound Ca(OH)2, which is also called slaked lime, turns red litmus solution to blue and hence, proves it to be a basic solution. Thus, the pH of this solution will be more than seven.
![]()
Question 3.
Shalini was quite interested in observing the changes that take place during chemical reactions but was always afraid of entering the chemistry lab. When she spoke to her chemistry teacher regarding this, the teacher suggested that she should perform a simple experiment under her guidance to overcome her fear and at the same time she could observe the changes that take place during a chemical reaction.
She took about 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals in a dry boiling tube and heated it over the
flame of a burner. She noticed change of colour of the ferrous sulphate crystals and could also smell the characteristic odour of burning sulphur.
(A) What change in colour did Shalini observe?
Answer:
Shalini observed that the green colour of ferrous sulphate crystals changed to white as it loses water when heated.
FeSO4.7H2O → FeSO4 + 7H2O
(B) Why did Shalini get the characteristic odour of burning sulphur?
Answer:
(C) What type of reaction takes place when ferrous sulphate is heated?
Answer:
The type of reaction taking place is the thermal decomposition reaction. The chemical equation for the reaction taking place is:
![]()
(D) Give another example of such type of reactions.
Answer:
Question 4.
The production of hydrogen from water via electrolysis is a clean process, resulting in only oxygen being produced as a by-product. If the electricity required to split the water into hydrogen and oxygen is supplied via a renewable energy source then the process is environmentally benign.The water electrolysis hydrogen (oxygen) plant is equipment that electrolyzes water to produce hydrogen and oxygen by using lye as an electrolyte.
Electrolysis of water is a decomposition reaction. The mole ratio of hydrogenand oxygen gases liberated during the electrolysis of water is:
(a) 1:1
(b) 2:1
(c) 4:1
(d) 1:2
Answer:
(b) 2:1
Explanation: The balanced chemical equation for the electrolysis of water is:

The mole ratio of hydrogen and oxygen gases Liberated during electrolysis of water is 2:1 by volume.
In a decomposition reaction, a compound is broken down into its simpler forms. During electrolysis, water is broken down into oxygen gas and hydrogen gas due to the passage of electric current through it.
![]()
Question 5.
Redox reactions are an important class of reactions. The oxidation and reduction reactions always occur simultaneously, such class of chemical reactions is named as the redox reaction or Oxidation-Reduction reaction.
The substance getting reduced in a chemical reaction is known as the oxidizing agent, while a substance that is getting oxidized is known as the reducing agent. The activity in which copper powder is taken in a china dish and heated helps in understanding redox reactions.
(A) What happens when copper powder is heated in a china dish? Explain your observation.
Answer:
When copper powder is heated in a china dish, the surface of copper powder is coated with black copper oxide as oxidation of copper takes place by addition of oxygen to copper.
2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
(B) What will you observe if hydrogen gas is passed over the heated material obtained in (A) above?
Answer:
When hydrogen gas is passed over heated material CuO, the black coating on the surface turns brown as the reverse reaction takes place and copper is formed.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
(C) Identify the substance oxidized and substance reduced in the reaction at (B) above.
Answer:
(D) Identify the correct statement:
In the reaction between lead sulphide and hydrogen peroxide shown by the equation below,
PbS + 2H2O2 → PbSO4 + 4H2O,
(a) Lead sulphide Is reduced and Hydrogen peroxide is oxidized.
(b) Lead sulphide is oxidized and Hydrogen peroxide is reduced.
(c) Lead sulphate is oxidized and water is reduced.
(d) Lead sulphate is reduced and water is oxidized.
Answer:
Question 6.
Rancidification is the process of complete or incomplete oxidation or hydrolysis of fats and oils when exposed to air, light, or moisture or by bacterial action, resulting in unpleasant taste and odor. Specifically, it is the hydrolysis or autoxidation of fats into short-chain aldehydes and ketones, which are objectionable in taste and odor. When these processes occur in food, undesirable odors and flavors can result.

Which of the following gases can be used for the storage of fresh sample of an oil for a long time?
(a) Carbon dioxide or oxygen
(b) Nitrogen or oxygen
(c) Carbon dioxide or helium
(d) Helium or nitrogen
Answer:
(d) Helium or nitrogen

Explanation: Inert gases like helium or nitrogen both can be used for the storage of fresh sample of oil for a Long time, as they do not react with most elements, including oxygen. Thus these gases create an inert environment for the oil and prevent its reaction (oxidation) with any element in the environment. Hence, stopping it from becoming rancid.
![]()
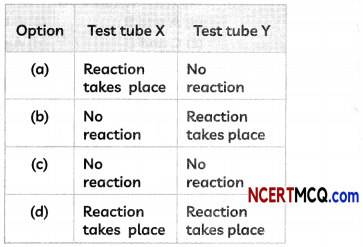
Question 7.
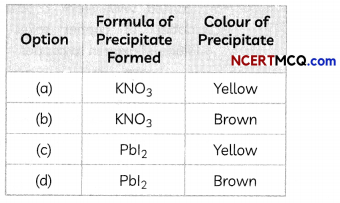
A student takes two test tubes. In the first test tube, he takes lead nitrate solution and in the second he takes a few zinc granules. He adds potassium iodide solution to lead nitrate solution in the first test tube. He adds dilute sulphuric acid in the second test tube containing zinc granules.
(A) What is observed in the first test tube on adding potassium iodide solution?
Answer:
(c) Both (II) and (III)
Explanation: When potassium iodide solution is added to lead nitrate solution in a test tube, a yellow precipitate of Lead iodide is formed. The equation of the reaction taking place is:
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) → PbI2(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
(B) Select the correct observations:
When dilute sulphuric acid is added to a few zinc granules in the second test tube,
(I) Bubbles of hydrogen gas can be seen around the zinc granules.
(II) Bubbles of carbon dioxide can be seen around zinc granules.
(III) The flask becomes hot
(IV) Colour of solution changes to blue,
(a) Only (I)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(b) Both (I) and (III)
Explanation: When diluting sulphuric acid is added to zinc granules in a conical flask, the equation of the reaction taking place is:
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq)+ H2(g)
(C) Select the incorrect statement(s):
(I) Both the reactions are accompanied by a change in colour.
(II) A precipitate is formed in the first test tube only.
(III) Gas is evolved in the second test tube only.
(IV) Both the reactions are examples of double displacement reactions.
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (I) and (IV)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (I) and (II)
Answer:
(D) Suppose we add dil hydrochloric acid in place of sulphuric acid in the second test tube. Select the correct observation:
(a) Chlorine gas will be evolved.
(b) The test tube will become cold as heat is absorbed during this reaction.
(c) Hydrogen gas will be evolved.
(d) A precipitate of zinc chloride will be formed
Answer:
(E) The type of reaction taking place when water is added slowly to a small amount of calcium oxide in a beaker is:
(I) Combination Reaction
(II) Displacement reaction
(III) Exothermic reaction
(IV) Endothermic reaction
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
Question 8.
You must have seen that your mother stores fried food items such as boondi raita, chips, mixture, banana chips and other such items properly. This is because their smell and taste change due to the oxidation of fried food items and food becomes unfit for human consumption.

Why are anti-oxidants added to fat and oil-containing food items?
Answer:
Anti-oxidants are added to fat and oil-containing food items to prevent their oxidation which is known as rancidity which makes food smell bad and changes its taste.
![]()
Question 9.
Chemical reaction, a process in which one or more substances, the reactants, are converted to one or more different substances, the products. Substances are either chemical elements or compounds. A chemical reaction rearranges the constituent atoms of the reactants to create different substances as products.
Chemical reactions must be distinguished from physical changes. Physical changes include changes of state, such as ice melting to water and water evaporating to vapour. If a physical change occurs, the physical properties of a substance will change, but its chemical identity will remain the same. However, if water, as ice, liquid, or vapour, encounters sodium metal (Na), the atoms will be redistributed to give the new substances molecular hydrogen (H2) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH). By this, we know that a chemical change or reaction has occurred.
(A) Which of the following are physical changes?
(I) Melting of wax
(II) Burning of wax
(III) Rusting of iron
(IV) Evaporation of water
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
Explanation: Melting of wax and evaporation of water are physical change as they undergo only change in their physical states without any change in their chemical composition. Whereas, burning of wax is a chemical change as carbon dioxide and water are formed when wax is burned. Rusting of iron is also a chemical change as iron undergoes oxidation in the presence of moisture to form rust or iron oxide.
(B) A chemical reaction does not involve:
(a) Formation of new substances having entirely different properties than that of the reactants
(b) Breaking of old chemical bonds and formation of new chemical bonds
(c) Rearrangement of the atoms of reactants to form new products
(d) Changing of the atoms of one element into those of another element to form new products
Answer:
(C) Quick lime is used in whitewashing because
(a) It is cheap
(b) It forms limestone with water which has a nice color.
(c) It forms slaked lime with water which reacts with atmospheric carbon dioxide to form limestone.
(d) It is easy to use
Answer:
(D) Which of the following are endothermic processes?
(I) Burning of natural gas
(II) Dilution of an acid
(III) Evaporation of water
(IV) Sublimation of camphor (crystals)
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (IV) and (IV)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(E) The following reaction is used for the preparation of oxygen gas in the laboratory
![]()
Which of the following statement about the reaction is correct?
(a) It is a displacement reaction and endothermic in nature.
(b) it is a decomposition reaction and exothermic in nature.
(c) It is a decomposition reaction and endothermic in nature.
(d) It is a photochemical decomposition reaction and exothermic in nature.
Answer:
((c) It is a decomposition reaction and endothermic in nature.
Explanation: It is a decomposition reaction as a single reactant splits up into two products, namely, KCl and O2, by absorbing energy in the form of heat.
It is an endothermic reaction as heat is absorbed in this reaction.
Question 10.
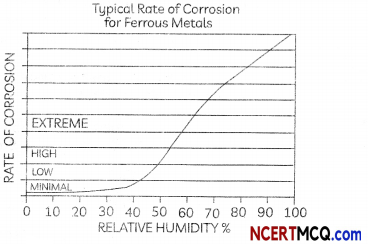
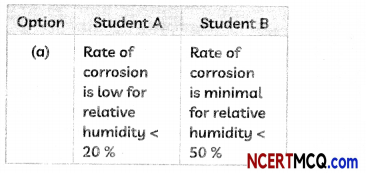
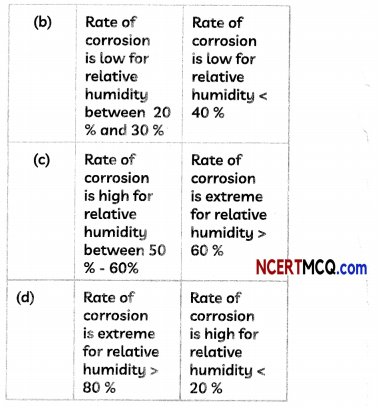
Many materials over time can be prone to corrosion and wear Iron is one such metal. Having a protective later and proper preparation can certainly help materials last longer and have other properties integrated into it.
A substance X used for coating iron articles is added to a blue solution of a reddish-brown metal Y. the colour of the solution gets discharged. Identify X and Y and also the type of reaction.
Answer:
We are given that the metal Y is reddish brown in colour. This metal is copper and the blue solution of Y is copper sulphate. Also, zinc is used in protecting iron articles and this process is called galvanisation. As Zinc is more reactive than copper it displaces copper from its salt solution, copper sulphate.
Zn + CUSO4 → ZnSCO4 + Cu
So, X is zinc, while Y is copper.
Question 11.
Double displacement reactions may be defined as the chemical reactions in which one component each of both the reacting molecules is exchanged to form the products. During this reaction, the cations and anions of two different compounds switch places, forming two entirely different compounds.
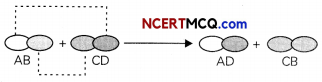
Double displacement reactions generally take place in aqueous solutions in which the ions precipitate and there is an exchange of ions.
Double displacement reactions can be further classified as neutralization and precipitation reactions.
(A) What is the precipitate formed on mixing the solution of barium chloride and sodium sulphate?
(a) Barium sulphate
(b) Sodium chloride
(c) Barium sulphite
(d) Sodium sulphite
Answer:
(a) Barium Sulphate
Explanation: When a solution of barium chloride is mixed with a solution of sodium sulphate, a precipitate of barium sulphate is formed along with sodium chloride.
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) + NaCl(aq)
(B) When Potassium iodide solution is added to lead(II) nitrate solution,
(I) lead (II) iodide precipitates out of the solution as a yellow solid
(II) Potassium nitrate precipitates out of the solution as a yellow solid
(III) Potassium displaces lead from lead nitrate solution.
(IV) Exchange of lead and potassium ions takes place
(a) Both (I) and (III)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (I) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(C) Identify the precipitate obtained by the reaction between lead nitrate and sodium sulphate.
(a) PbS
(b) Pb(SO4)2
(c) PbSO4
(d) NaNO2
Answer:
(c) PbSO4
Explanation: Lead nitrate reacts with sodium sulphate solution to form a precipitate of lead sulphate and sodium nitrate.
Pb(NO3)2(aq)+ Na2SO4(aq) → PbSO4(s) + 2NaNO3(aq)
This is a double displacement reaction as the exchange of lead and sodium ions is taking place.
(D) Which one of the following is true about a double displacement reaction?
(I) Electrolysis of water is an example of this reaction.
(II) Two compounds exchange ions to form new compounds.
(III) Only a single product is formed.
(IV) Reaction between magnesium oxide and dilute hydrochloric acid is an example for this reaction.
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(E) Identify the incorrect statement regarding double displacement reactions:
(a) All double displacement reactions are precipitation reactions.
(b) All neutralization reactions between acids and bases are double displacement reactions
(c) The reaction between vinegar and baking soda is an example of a double displacement reaction.
(d) Reaction between silver nitrate solution and sodium chloride solution is an example of a double displacement reaction.
Answer:
![]()
Question 12.
Thermite is a pyrotechnic composition of metal powder fuel and metal oxide. When ignited by heat, thermite undergoes an exothermic oxidation-reduction reaction. Most varieties are not explosive but can create brief bursts of high temperature in a small area. Its form of action is similar to that of other fuel-oxidizer mixtures, such as black powder. Thermites have diverse compositions. Fuels include aluminium, magnesium, titanium, zinc, silicon, and boron. Aluminium is common because of its high boiling point. Oxidizers include boron(III) oxide, silicon(IV) oxide, chromium(III) oxide, manganese(IV) oxide, iron(III) oxide, iron(II, III) oxide, copper(II) oxide, and lead(ll,IV) oxide.

In this reaction mention the substance getting oxidized and the substance getting reduced.
Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
Answer:
Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen while packing them as nitrogen is an inert gas and prevents fried food materials from getting rancid.
Question 13.
A synthesis or combination reaction is a reaction in which simple compounds combine to make a more complex one. The opposite of a combination reaction is a decomposition reaction in which a single substance splits into two or more substances. We also have a single displacement reaction (in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound) and a double displacement reaction (in which the exchange of ions takes place between two compounds). Having a thorough understanding of the types of reactions will be useful for predicting the products of an unknown reaction.
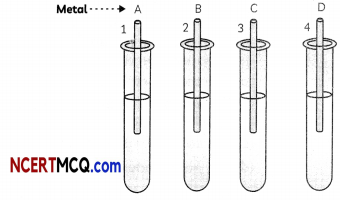
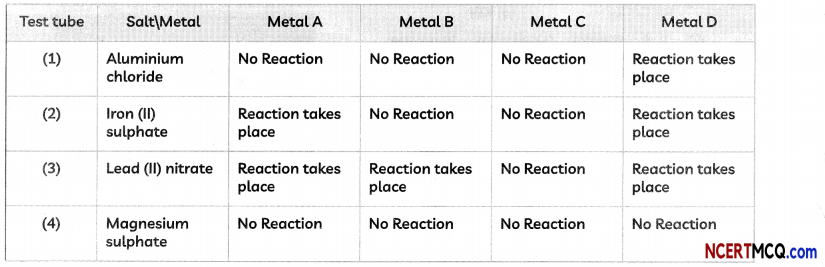
(A) A student performed several experiments and then noted down his observations in a tabular form as given below:
| S.No. Observation | Conclusion Regarding the type of Reaction Taking Place |
| (I) When copper powder is heated in a china dish, the surface of the copper powder turns black | Combination Reaction |
| (II) Hydrogen gas is . evolved when Iron reacts with dil. HCl. | Decomposition Reaction |
| (III) A black precipitate is formed along with sulphuric acid solution when hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through copper sulphate solution | Double Displacement Reaction |
| (IV) When electricity is passed through molten aluminium chloride aluminium metal is formed along with a gas. | Displacement Reaction |
Select the option that correctly describes the conclusions made by the student regarding type of reaction taking place:
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (I) and (III)
(c) Both (II) and (III)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Explanation : When barium chloride solution is added to copper sulphate soLution, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed alongwith copper chloride solution.
This is an example of precipitation reaction as a precipitate of barium sulphate is formed. It is also a double displacement reaction as the Ba2+ and Cu2+ ions form new compounds by exchanging their ions. The equation of the reaction talcing place is:
BaCl2(aq) + CuSO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) + CuCl2(aq)
(B) When a metal X, which is used for coating iron articles, is added to a blue solution of a reddish brown metal Y, the color of the solution gets discharged.
Select the option which correctly identifies the metals X and Y and the type of reaction taking place.
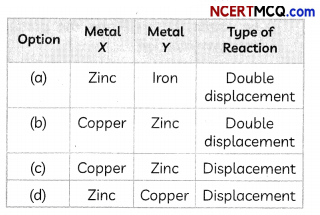
Answer:
(C) The type of reaction taking place when barium chloride solution is added to copper sulphate solution is:
(I) Combination reaction
(II) Displacement reaction
(III) Double Displacement reaction
(IV) Precipitation reaction
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (II) and (IV)
(d) Both (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(D) Identify the incorrect statement:
(a) Burning of natural gas is a decomposition reaction.
(b) Burning of hydrogen gas in air is a combination reaction
(c) Reaction between most metals and dilute hydrochloric acid is a displacement reaction.
(d) Reaction between an acid and a base is an example of double displacement reaction.
Answer:
(E) Which of the following statement(s) are correct?
(I) The precipitation reactions produce insoluble salts.
(II) Neutralization reactions are single displacement reactions.
(III) Decomposition reactions can be carried out only in presence of heat or light.
(IV) Displacement reactions are opposite of combination reactions.
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(a) Only (I)
Explanation: Precipitation reactions are the reactions in which an insoluble substance or precipitate is formed. Neutralization reactions are the reactions between an acid and a base and are double displacement reactions. Decomposition reactions require energy in the form of heat, light or electricity. Decomposition reactions are the opposite of combination reactions.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What happens when sodium sulphate solution is added to barium chloride solution?
Answer:
When sodium sulphate solution is added to barium chloride solution, a white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.
The equation of the reaction taking place is:
Na2SO4((aq) + BaCl2(aq) →BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
![]()
Question 2.
An aqueous solution of metal nitrate P reacts with sodium bromide solution to form yellow ppt of compound Q which is used in photography. Q on exposure to sunlight undergoes decomposition reaction to form metal present in P along with reddish-brown gas. Identify P & Q.
Answer:
As the compound Q is formed by the reaction between P (metal nitrate solution) and sodium bromide solution, Q is silver bromide which is used in photography.
Further, Q undergoes decomposition in the presence of sunlight to form silver and bromine gas. As silver is formed above, the metal nitrate is silver nitrate.
P – silver nitrate (AgNO3)
Q – silver bromide (AgBr).
Question 3.
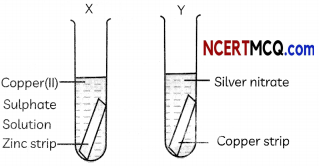
What can be seen when a strip of copper metal is placed in a solution of silver nitrate?
Answer:
When a strip of copper metals is placed in a solution of silver nitrate, copper displaces silver from silver nitrate solution as copper is a more reactive metal than silver. Copper nitrate is formed with a shiny greyish-white deposit of silver on the copper strip.
2AgNO3 + Cu → Cu(NCO3)2 + 2Ag
Question 4.
Name and state the law which is kept in mind when we balance chemical equations.
Answer:
The law which is kept in mind when we balance chemical equations is the law of conservation of mass which states that “Matter can neither be created nor be destroyed”. It means that the total mass of atoms of reactants = the total mass of atoms of products, as atoms can neither be created nor be destroyed.
![]()
Question 5.
Hydrogen being a highly inflammable gas and oxygen being a supporter of combustion, yet water, a compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen is used to extinguish fire. Why?
Answer:
The compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen is water (H20) which has properties that are different from properties of H2 and O2 as it is formed by the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen gases. While hydrogen and oxygen are gases at room temperature, water is a liquid at room temperature.
Question 6.
If copper metal is heated over a flame, it develops a coating. What is the colour and composition of the coating?
Answer:
Question 7.
Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the following reaction: carbon monoxide reacts with hydrogen gas at 340 atm to form methyl alcohol.
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between sodium chloride and silver nitrate indicating the physical state of the reactants and the products.
Answer:
When silver nitrate solution is added to sodium chloride solution, a white precipitate of silver chloride is formed along with sodium nitrate solution.
AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq)
Question 9.
Complete and balance the following:
Fe2O3 + Al →
Answer:
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science with Answers
Class 10 Science Chemistry MCQ: