Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Physics with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 1 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Physics Standard Term 2 Set 1 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- There are 12 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper has three sections: Section A, Section B and Section C.
- Section A contains three questions of two marks each, Section B contains eight questions of three marks each, Section C contains one case study-based question of five marks. :
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks and two questions of three marks. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
- You may use log tables if necessary but use of calculator is not allowed.
Section – A (2 Marks Each)
Question 1.
Distinguish clearly between temperature and heat.
Answer:
The degree of hotness of a body is called temperature. All bodies in thermal contact with each other ultimately attain the same temperature. The flow of heat energy from one body to another due to temperature difference between the two is called heat. Two bodies in thermal equilibrium with each other may not have the same amount of heat, but they must have the same temperature.
Question 2.
A silica glass rod has a diameter of 1 cm and is 10 cm long. Estimate the largest mass that can be hung from it without breaking it. Breaking strength of glass is 50 × 106 Nm-2.
OR
What are the factors affecting Elasticity?
Answer:
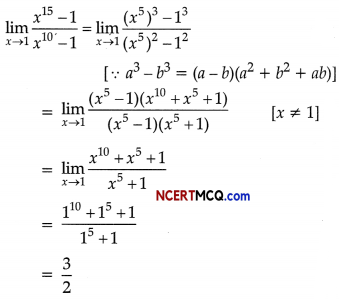
Using Stress = \(\frac{F}{A}\),
we get F = stress × A
= (50 × 106) × π × (\(\frac{10^{-2}}{2}\))2N
Largest mass = \(\frac{F}{g}\) = \(\frac{\left(50 \times 10^{6}\right)\left(\frac{\pi \times 10^{-4}}{4}\right)}{10}\)kg
= 392.7 kg
OR
Factors affecting Elasticity are –
(1) Hammering and rolling: This result is in an increase in the elastidty of material.
(2) Annealing: Annealing results in decrease in the elasticity of material.
(3) Temperature: Elastidty decreases with rise in temperature (Exception: the elasticity of invar steel (alloy) does not change with change in temperature).
(4) Impurities: This- type of effect depends upon the nature of impurities. If the added impurity is more elastic than the substance then its elasticity is increased. If the added impurity is less elastic than the substance, then its elasticity is decreased.
![]()
Question 3.
By applying the first law of thermodynamics to isobaric process, obtain relation between two specific heats of a gas.
Answer:
In an isobaric process, pressure remains constant. If an amount of heat dQ is supplied to one mole of a gas at constant pressure and its temperature increases by dT, then
dQ = CPdT
Here CP is molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure. Therefore, for an isobaric process, the first law of thermodynamics becomes:
CPdt = d\J + FcN …………… (i)
From perfect gas equation it follows that
PdV = RdT
In the eqn. (i), substituting PdV and d\J, we have
CPdT – CVdT
CP = CV + R.
Section – B (3 Marks Each)
Question 4.
Estimate the temperature of the surface of the Sun from the following data:
(i) Average radius of the earth’s orbit = 1.5 × 105 km
(ii) Average radius of the Sun = 7.0 × 105 km
(iii) Solar radiant power on the Earth = 1400 Wm-2 at Noon time
Assume the Sun to be a perfect black body will your estimate be greater or less than the actual surface temperature of the Sun ? Explain.
Answer:
Here, Radius of Sun R = 7 × 105 km
= 7 × 108 m
∴ Surface area of Sun = 4πR2
= 4π(7 × 108)2
= 6.16 × 1018 m2
σ = 5.67 × 10-8 Wm-2 K-4
Using E = AσT4,
E = (6.16 × 1018) (5.67 × 10-8)T4
= 3.49 × 1011 × T4W …………….. (i)
E = 4π2 × Solar radiant power on Earth
Here,
Radius of Earth = r = 1.5 × 105km 1.5 × 108m
E = 4π(1.5 × 108)2 × 1400
= 3.96 × 1020 watt …………….. (ii)
Equating eqn (i) and (ii), we get
3.96 × 1011 × T4 = 3.96 × 1020
T4 = \(\frac{3.96 \times 10^{20}}{3.49 \times 10^{11}}\)
T = 1.83 × 102 K.
![]()
Question 5.
In a refrigerator one removes heat from a lower temperature and deposits to the surroundings at a higher temperature. In this process, mechanical work has to be done, which is provided by an electric motor. If the motor is of 1 kW power, and heat is transferred from -3°C to 27°C, find the heat taken out of the refrigerator per second assuming its efficiency is 50% of a perfect engine.
Answer:
Given: T1 = 27°C = 27 + 273 = 300 K
T2 = -3°C = -3 + 273 = 270 K
Efficiency, η = 1 – \(\frac{\mathrm{T}_{2}}{\mathrm{~T}_{1}}\) = 1 – \(\frac{270}{300}\)
= 1 – 0.9 = 0.1 = \(\frac{1}{10}\)
Efficiency of refrigerator is 50% of perfect engine.
η = 50% of η = 0.5 × \(\frac{1}{10}=\frac{1}{20}\)
∴ Coefficient of performance,
β = \(\frac{Q_{2}}{W}=\frac{I-\eta^{\prime}}{\eta^{\prime}}\)
β = \(\frac{1-\frac{1}{20}}{\frac{1}{20}}\) = \(\frac{1-0.05}{0.05}\)
= \(\frac{0.95}{0.05}\) = 19
Q2 = 19% of work done by motor on refrigerator
= 19 × 1 kW
Q2 = 19 kJ/s
Question 6.
To what depth must a rubber ball be taken in deep sea so that its volume is decreased by 0.1%. (The bulk modulus of rubber is 9.8 × 108 Nm-2, and the density of sea water is 103 kgm-3.)
Answer:
Bulk Modulus, B = 9.8 × 108N/m2
Density of sea water (ρ) = 103kg/m3
Volume decrease (Percentage),
(\(\frac{\Delta V}{V}\) × 100) = 0.1%
\(\frac{\Delta V}{V}=\frac{0.1}{100}\)
= \(\frac{1}{1000}\) = 1 × 10-3
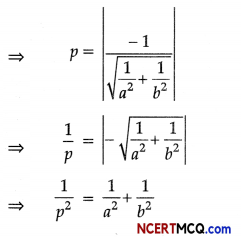
Let rubber ball be taken up to depth h
∴ change in pressure, P = hρg
Bulk Modulus,
K = \(\left|\frac{P}{\Delta V / V}\right|=\frac{h \rho g}{\Delta V / V}\)
or, h = \(\frac{B \times(\Delta V / V)}{\rho g}\)
= \(\frac{9.8 \times 10^{8} \times 1 \times 10^{-3}}{10^{3} \times 9.8}\)
h = 100 m
![]()
Question 7.
Calculate (i) r.m.s velocity, and (ii) mean kinetic energy of one gram molecule of hydrogen at S.T.P (Given, density of hydrogen at S.T.E is 0.09 kg/m3.)
Answer:
Here, ρ = 0.09 kg/m3
At S.T.E P = 1.01 × 105Pa
(i) According to kinetic theory of gases
P = \(\frac{1}{3}\)ρc2
or c = \(\sqrt{\frac{3 P}{\rho}}\)
= \(\sqrt{\frac{3 \times 1.01 \times 10^{5}}{0.09}}\)
= 1834.8 m/s
(ii) Volume occupied by one mole of hydrogen at S.T.P.
= 22.4 litres
= 22.4 × 10-3 m3
Mass of hydrogen, M = Volume × Density
= 22.4 × 10-3 × 0.09 kg
= 2.016 × 10-3 kg
Mean K.E. of one gram molecule of hydrogen at S.T.P.
= 1/2 Mc2
= 1/2 × 2.016 × 10-3 × (1834.8)2
= 3.4 × 103 J
Question 8.
A particle is moving in a straight line with S.H.M. of amplitude r. At a distance s from the mean position of motion, the particle receives a blow in the direction of motion which instantaneously doubles the velocity. Find the new amplitude.
OR
Find the time period of mass M when displaced from its equilibrium position and then released for the system shown in Fig.
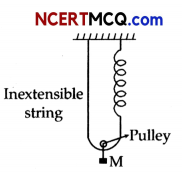
Answer:
Velocity, υ = ω\(\sqrt{r^{2}-y^{2}}\)
At y = s, let υ = υ0, then,
υ02 = ω2(r2 – s2) ………….. (i)
Due to blow, the new velocity at y = s is
υ = 2 υ0, r = r’
So, (2υ0)2 = ω2 (r’2 – s2) ………… (ii)
Dividing (ii) by (i),
4 = \(\frac{r^{\prime 2}-s^{2}}{r^{2}-s^{2}}\)
On solving r’= \(\sqrt{4 r^{2}-3 s^{2}}\)
OR
Mg = T + T {system is in equilibrium}
∴ Mg = 2T
because of mass hanging spring elongated by 21. Where / is the distance moved by hanging mass
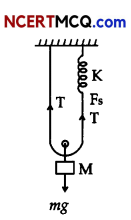
T = Fs (In the spring)
T = 2 kl
∴ Mg = 2(2kl) = 2k(2l)
displacing mass through y distance downwards Restoring force
F = Mg – 2k(2l + 2y)
= Mg – (2k)(2l) – 4ky
or F = Mg – Mg – 4ky = -4ky [1]
M \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d t^{2}}\) = -4ky [1]
\(\frac{d^{2} y}{d t^{2}}\) = –\(\frac{4 k}{M}\)y {comparing with \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d t^{2}}\) = – ω2y)
∴ ω = \(\sqrt{\frac{4 k}{M}}\) or T = \(\frac{2 \pi}{\omega}\) 2π\(\sqrt{\frac{M}{4 k}}\)
![]()
Question 9.
The pattern of standing waves formed on a stretched string at two instants of time are shown in Fig.
The velocity of two waves superimposing to form stationary waves is 360 ms1 and their frequencies
are 2.56 Hz.
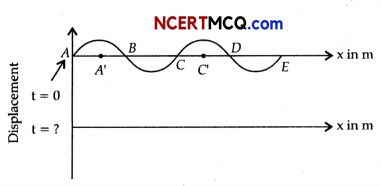
(a) Calculate the time at which the second curve is plotted.
(b) Mark nodes and anti-nodes on the curve.
(c) Calculate the distance between A and C’.
Answer:
Given: frequency of wave, v = 256 Hz
Time period, T = \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{256}\)
= 3.9 × 10-3 s
(a) Time taken to pass through mean position
t = \(\frac{T}{4}\)
= \(\frac{3.9 \times 10^{-3}}{4}\)
= 9.8 × 10-4
(b) Nodes- A, B, C, D, E (zero displacement) Anti-nodes-A’,C’ (maximum displacement)
(c) At A’, C’, there are consecutive anti-nodes, so distance between A’ and C’,
λ \(\frac{v}{v}=\frac{360}{256}\)
λ = 1.41m
Question 10.
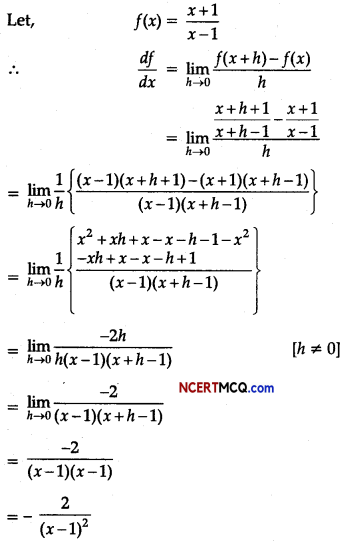
Show that the motion of a particle represented by y = sin ωt – cos ωt is simple harmonic with a period of 2π/ω.
Answer:
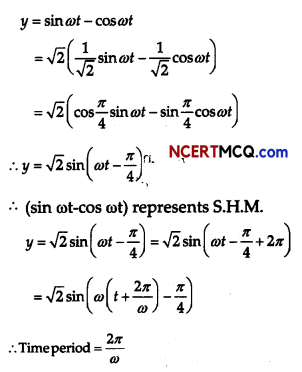
Question 11.
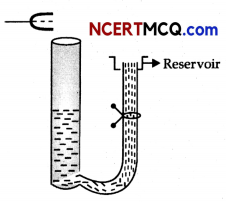
A tuning fork vibrating with a frequency of 512 Hz is kept close to the open end of a tube filled with water. The water level in the tube is gradually lowered. When the water level is 17 cm below the open end, maximum intensity of sound is heard. If the room temperature is 20°C, calculate
(a) speed of sound in air at room temperature
(b) speed of sound in air at 0°C
(c) if the water in the tube is replaced with mercury, will there be any difference in your observations?
OR
Show that when a string fixed at its two ends vibrates in 1 loop, 2 loops, 3 loops and 4 loops, the frequencies are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3 : 4.
Answer:
Let us consider the following diagram
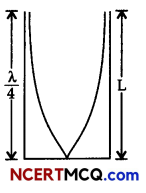
For maximum intensity-
(a) L = \(\frac{\lambda}{4}\)
or λ = 4 L
υ = vλ = v × 4L
= 512 × 4 × 17 × 10-2
= 348.16 m/s
(b) As, υ ∝ √T (T = Temperature)
\(\frac{v_{20}}{v_{0}}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{273+20}{273+0}}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{293}{273}}\)
\(\frac{v_{20}}{v_{0}}\) = 1.04
or υ0 = \(\frac{v_{20}}{1.04}\) = \(\frac{348.16}{1.04}\) = 334.8 m/s
Water and mercury in tube reflects the sound into air column to form stationary wave and reflection is more in mercury than water as mercury is more denser than water. So, intensity of sound heard will be larger but reading does not change as medium in tube (air) and running fork are same.
![]()
OR
OR
Length for each loop = \(\frac{\lambda}{2}\)
Now, L = \(\frac{n \lambda}{2}\)
λ = \(\frac{2 L}{n}\) …………… (1)
But υ = vλ or λ = \(\frac{v}{\mathrm{v}}\)
Putting in eqn. (1),
\(\frac{v}{v}=\frac{2 L}{n}\)
v = \(\frac{n}{2 L}\)
v = \(\frac{n}{2 L} \sqrt{\frac{T}{\mu}}\) [∵ υ = \(\sqrt{\frac{T}{\mu}}\)]
for n = 1,v1 = \(\frac{1}{2 L} \sqrt{\frac{T}{m}}=\) v0
for n = 2, v2 = \(\frac{2}{2 L} \sqrt{\frac{T}{m}}=\) = 2v0
Therefore,
v1 : v2 : v3 : v4 = n1 : n2 : n3 : n4
v1 : v2 : v3 : v4 =1 : 2 : 3 : 4