Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 6 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Standard Term 2 Set 6 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- There are 12 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- This question paper has three sections: Section A, Section B and Section C.
- Section A contains three questions of two marks each, Section B contains eight questions of three marks each, Section C contains one case study-based question of five marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks and two questions of three marks. You have to attempt only one of the chokes in such questions.
- You may use log tables if necessary but use of calculator is not allowed.
SECTION – A
(Section A contains 3 questions of 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
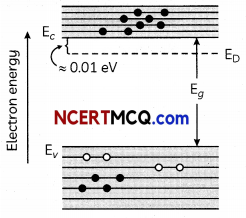
How is an n-type semiconductor formed?
Draw the energy band diagram n-type semiconductor. Name the majority charge carriers in it. (2)
Answer:
If pentavalent impurity atoms of Bi, Sb or P are doped in a tetravalent crystal of silicon or Germanium, we get a n-type semiconductor. Electrons are the majority charge carriers in a n-type semiconductor.
Question 2.
Name the characteristics of electromagnetic waves that:
(A) increases
(B) remains constant in the electromagnetic spectrum, as one moves from radioactive region towards ultraviolet region. (2)
Answer:
As one moves from radioactive region towards ultraviolet region,
(A) the frequency of the electromagnetic waves increases.
(B) The speed of the electromagnetic waves remains constant.
Related Theory
Speed of electromagnetic wave remains constant in the vacuum. Every massless object will travel with the speed of light.
![]()
Question 3.
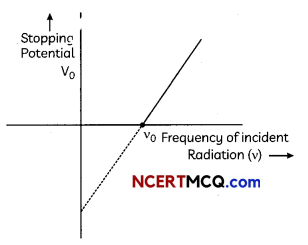
Explain with the help of Einstein’s photoelectric equation any two observed features in photoelectric effect which cannot be explained by wave theory.
OR
Consider a metal exposed to light of wavelength 600 nm. The maximum energy of the electron doubles when light of wavelength 400 nm is used. Find the work function in eV. (2)
Answer:
Features of photoelectric equation which cannot be explained by wave theory :
(A) The wave theory could not explain the instantaneous process of photoelectric effect.
(B) ‘Maximum kinetic energy’ of the emitted photo electrons is independent of intensity of incident light.
Related Theory
Einstein gives the correction in photoelectric effect and give Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
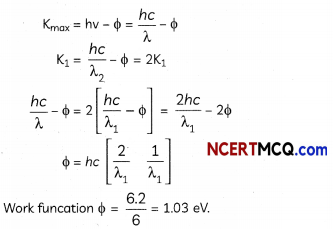
OR
Let the maximum energies of emitted electrons are K1 and K2 when 600 nm and 400 nm visible light are used according to question
K1 = 2K1
SECTION – B
(Section B consists of 8 questions of 3 marks each.)
Question 4.
In compound microscope, length of microscope is 21.5 cm, focal length of objective is 1.6 cm, focal length of eye piece is 2.1 cm and if final image is formed at infinity, then find the distance of the object from objective lens? (3)
Answer:
Here,
v = 21.5 – 2.1
= 19.4 cm
because the image formed by the objective should lie at the focus of the eyepiece, from relation,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{f}\)
= \(\frac{f-v}{v f}\)
⇒ u = \(\frac{v f}{f-v}\)
= \(\frac{1.6 \times 19.4}{1.6-19.4}\)
= -1.74 cm
![]()
Question 5.
In a single slit diffraction pattern, how does the angular width of central maxima change when
(A) Silt width is decreased
(B) Distance between the slit and screen is increased and
(C) Light of short visible wavelength is used? Justify your answer. (3)
Answer:
(A) Angular width of centrol ,maximum
2θ = \(\frac{2 \lambda}{d}\)
where d is slit width.
if slit width decreases, angular width increases.
(B) It does not depend upon D. So, it will not have any effect.
(C) Angular width
2θ = \(\frac{2 \lambda}{d}\)
∴ If Light of smaller wavelength is used then angular width decreases.
Question 6.
Spectra are produced due to electronic transitions from higher energy level to lower energy level.
(A) Name the series spectra produced by hydrogen.
(B) Which series lies in the visible region.
(C) Write down the Balmer formula for the wavelength of Hα line. (3)
Answer:
(A) Lyman, Balmer, Paschen, Brackett and Pfund series.
(B) Balmer series.
(C) Wavelength of Ha line \(\frac{1}{\lambda}\) = R \(\frac{1}{2^{2}}-\frac{1}{n^{2}}\)
![]()
Question 7.
Two convex lenses of an astronomical telescope of focal length 5 cm and 20 cm respectively, are shown in the given figure.

(A) Which of the given lenses will be used as an objective lens?
(B) How should the lenses adjusted to have the telescope in its normal adjustment position?
(C) What will be the magnifying power of the telescope in its normal adjustment position? (3)
Answer:
(A) Because of the larger focal length and larger radius, the lens B should be used as an objective Lens.
(B) In normal adjustment, the distance between objective and eyepiece will be
fo + fe = 20 + 5
= 25 cm
The distance required to be increased between the two lenses.
= 25 – 15 = 10 cm
(C) Magnifying power of the telescope in normal adjustment will be,
m = \(\frac{f_{0}}{f_{e}}\) = \(\frac{20 \mathrm{~cm}}{5 \mathrm{~cm}}\) = 4
Question 8.
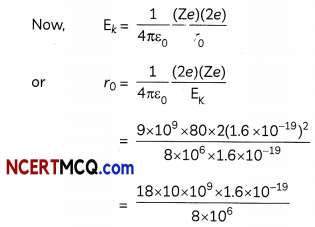
A projectile of mass m, charge Ze, initial speed v and impact parameter b is scattered by a heavy nucleus of charge Ze. Obtain a relation between minimum distance s of particle from nucleus an impact parameter using conservation of angular momentum and energy. Show that if b = 0, s becomes distance of closest approach. (Ignoring size of nucleus and recoil motion).
OR
Considering that the protons and neutrons have equal masses, calculate how many times nuclear matter is denser than water. Take the value of nuclear radius R = 1.2 × 10-15 A1/3 metre and mass of the nucleus = 1.67 × 10-27 kg. (3)
Answer:
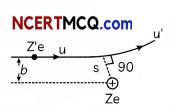
Angular momentum of the projectile at α from the nucleus = mvb
At point of minimum distance (s) from nucleus velocity v’ of projectile is normal to radius vectors.
Angular momentum of projectile at minimum nucleus = mv’s
By Law of Conservation of angular momentum, mv’s = mvb
⇒ V’ \(\frac{v b}{s}\)
By Conservation of Energy
(KE + PE) act as = (KE + PE) at distance s
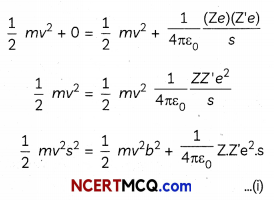
Dividing by \(\frac{1}{2}\) mv2 equation (i)
b2 + \(\frac{1}{2 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \frac{Z Z^{\prime} e^{2}}{m v^{2}}\) = s2
s = \(\frac{1}{2 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \frac{Z Z^{\prime} e^{2}}{m v^{2}}\)
which is distance of closest approach.
OR
Density pf nucleus
ρn = \(\frac{m}{\frac{4}{3} \pi R^{3}}\) = \(\frac{3 m}{4 \pi R^{3}}\)
ρn = \(\frac{3 \times 1.67 \times 10^{-27}}{4 \times 3.14 \times\left(1.20 \times 10^{-15}\right)^{3}}\)
pn = 2.307 × 1017 kg m-3
Density of water ρw = 103 kg m-3
> \(\frac{\rho_{n}}{\rho_{w}}\) = \(\frac{2.307 \times 10^{17}}{10^{3}}\) = 2.307 × 1014
![]()
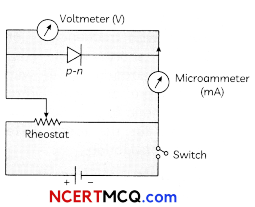
Question 9.
Draw a circuit diagram showing the biasing of an LED and state the factors which control wavelength of light and intensity of light emitted by a diode. (3)
Answer:
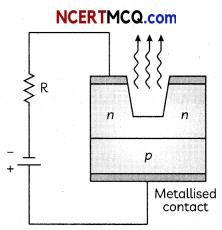
Wavelength of light is controlled by the band gap of semiconductor material.
Intensity of ammeter by the diode concentration of impurity in the junction diode.
Related Theroy
The p-n junctions can be designed so that current through them changes either by causing electron excitation by light photons or conversely through electron excitation by a suitable bias voltage resulting in emission of light photons.
Question 10.
You are given three lenses of power 0.5 D, 4 D and 10 D to design a telescope.
(A) Which lenses should be used as objective and eyepiece? Justify your answer.
(B) Why is the aperture of the objective preferred to be large?
OR
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 800 nm and 600 nm is used to obtain the interference fringes in a Young’s double slit experiment on a screen placed 1.4 m away. If the two slits are separated by 0.28 mm, calculate the least distance from the central bright maximum where the bright fringes of the two wavelengths coincide. (3)
Answer:
(A) Magnification,
m = \(\frac{f_{0}}{f_{e}}\)
= \(\frac{P_{e}}{P_{0}}\)
Therefore, the lens of 0.5 D should be used as objective and the lens of 10 D should be used as eye-piece in order to achieve higher magnification.
(B) The aperture of the objective lens is made larger so, that it receives as much light as coming from the distant object and the resolving power of the telescope increases.
OR
Given:
λ1 = 800 nm
= 800 × 10-9 m
λ2 = 600 nm
= 600 × 10-9 m
D = 1.4 m
d = 0.28 mm
= 0.28 × 10-3m
Suppose n1thaximum corresponds to wavelength λ1 and it coincides with n2th maximum corresponding to wavelength λ2.
∴ n1\(\frac{\lambda_{1} D}{d}\) = n2\(\frac{\lambda_{2} \mathrm{D}}{d}\)
or \(\frac{n_{1}}{n_{2}}=\frac{\lambda_{2}}{\lambda_{2}}\) = \(\frac{600}{800}=\frac{3}{4}\)
Thus, 3rd maximum corresponding to wavelength 800 nm coincides with 4th maximum corresponding to wavelength 600 nm.
And the minimum distance is given by,
Xmin = n1\(\frac{\lambda_{1} D}{d}\)
\(\frac{3 \times 800 \times 10^{-9} \times 1.4}{0.28 \times 10^{-3}}[ /latex]
Xmin = 12mm
![]()
Question 11.
Write three characteristic features in photoelectric effect which cannot be explained on the basis of wave theory of light, but can be explained only by using Einstein’s equation. (3)
Answer:
(A) Existence of threshold frequency: According to wave theory, there should not exist any threshold frequency but Einstein’s theory explains the existence of threshold frequency.
(B) Dependence of kinetic energy on frequency of incident light: According to wave theory, the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons should depend on intensity of incident light and not on frequency whereas Einstein’s equation explains that it dependence on frequency and not on intensity of the incident light.
(C) Instantaneous emission of electrons: According to wave theory there should be time lag between emission of electrons and incident of light whereas Einstein’s equation explains why there is no time lag between incident of light and emission of electrons.
Related Theory
Some features cannot be explained in photoelectric current. So, Einstein gave his correction to explain the effect.
![]()
SECTION – C
(Section C consists one case study-based question of 5 marks.)
Question 12.
The wave theory of light was first put forward by Christian Huygen. During that period, everyone believed in Newton’s corpuscular theory, which had satisfactorily explained the phenomenon of reflection, refraction, the rectilinear propagation of light and the fact that light could propagate through vacuum. Huygen’s model was accepted when Thomas Young performed the interference experiment.
(A) Which one of the following phenomena is not explained by Huygen’s construction of wave front?
(i) Refraction
(ii) Reflection
(iii) Diffraction
(iv) Origin of spectra
(B) When light waves suffer reflection at the interface from air to glass, the change in phase of reflected waves is equal to:
(i) Zero
(ii) [latex]\frac{\pi}{2}\)
(iii) π
(iv) 2π
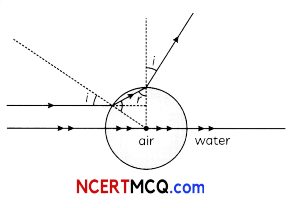
(C) In the given diagram a wavefront AB moving in air is incident on a plane glass surface xy. Its position CD after refraction through the glass slab is shown also along with normal drawn at A and D.
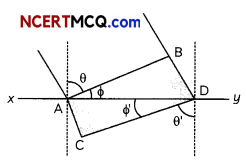
The refractive intex of glass will be equal
(i) \(\frac{\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
(ii) \(\frac{A B}{C D}\)
(iii) \(\frac{B D}{A D}\)
(iv) \(\frac{A C}{A D}\)
(D) Select the right options in the following:
(i) Christian Huygen’s a contemporary
of Newton established the wave theory of light by assuming that light waves were transverse.
(ii) Maxwell provided the compelling theoretical evidence that light is transverse wave.
(iii) Thomas Young experimentally proved the wave behaviour of light and Huygen’s assumption.
(iv) All the statements given above, correctly answers the question.
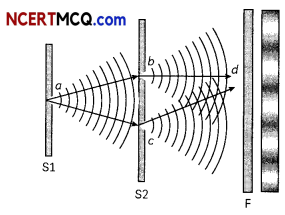
(E) The diagram below shows two sources, A and B, vibrating in phase in the same uniform medium and producing circular wave fronts.
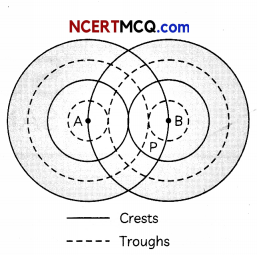
Which phenomenon occurs at point P?
(i) Destructive interference
(ii) Constructive interference
(iii) Reflection
(iv) Refraction (5)
Answer:
(A) (d) Origin of spectra
Explanation: The Huygen’s construction of wavefront does not explain the phenomena of origin of spectra.
(B) (c) π
Explanation: When a light wave suffers reflection at the interface from air to glass, it experiences a change in phase because the refractive index of glass is more than air, as we know that air is a rarer medium and glass is denser medium. So, the change in phase of the reflected wave is π.
Caution
Students are often confused about the phase change in reflection. When a light wave travels from rarer to denser than the phase of the incident wave change with angle it and when it travels from denser to rare then the phase of the incident wave does not change.
(C)(a) \(\frac{B D}{A C}\)
Explanation: BD = V1t,
AC = V2t
\(\frac{\sin \theta}{\sin \phi}\) = \(\frac{\left(\frac{B D}{A D}\right)}{\left(\frac{A C}{A D}\right)}\)
\(\frac{\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{AC}}\) = \(\frac{v_{1} t}{v_{2} t}\)
= \(\frac{v_{1}}{v_{2}}=\frac{\mu_{2}}{\mu_{1}}\)
= \(\frac{\mu_{2}}{\mu_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{BD}}{\mathrm{AC}}\)
Caution
Students are often confused in the geometry of the diagram. They should observe the angles and the common arm of the triangle.
(D) (b)
Maxwell provided the compelling theoretical evidence that light is transverse wave
Explanation: In Huygens principle the wave theory was established by assuming that the waves were longitudinal. So, (a) is wrong.
In Maxwell’s theory of light, he stated that light is a transverse wave and conducted multiple experiments to prove. So, (b) is correct.
Thomas Young conducted his double slit experiment and tried to prove the wave nature of light by proving that light undergoes interference which is a phenomenon showed by waves. He never proved the type of wave light is, i.e., transverse or longitudinal. So, (c) is wrong.
These statements mostly highlight the wave nature of light. They do not comment on the particle nature of light or the dual nature of light established. Hence, they clearly do not answer the question “what is light” correctly. So, option (D) is also wrong.
![]()
(E) (b) Constructive interference Explanation: Wave fronts for a source represents locus of points at same phase. A and B are vibrating in phase. Hence, all the wave fronts shown in the diagram are in the same phase. At P, there are wave fronts of both A and B. Hence, the waves of A and B are at same phase at P. Hence, constructive interference occurs at P.

 Read the following text carefully and answer question number 8 and 9 given below:
Read the following text carefully and answer question number 8 and 9 given below: