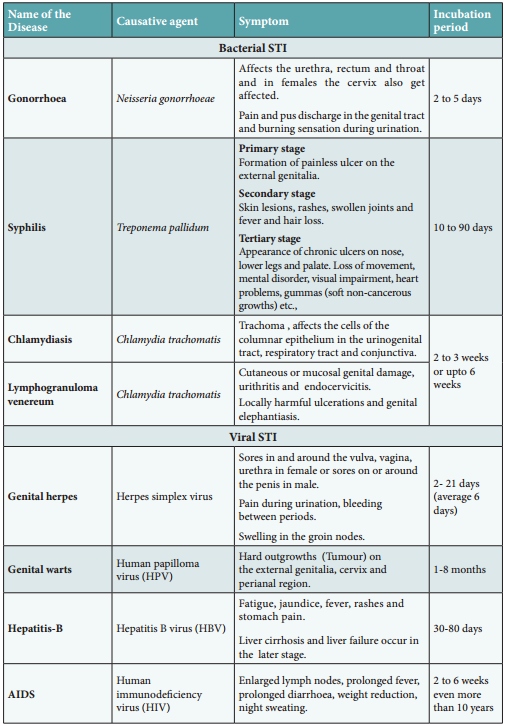
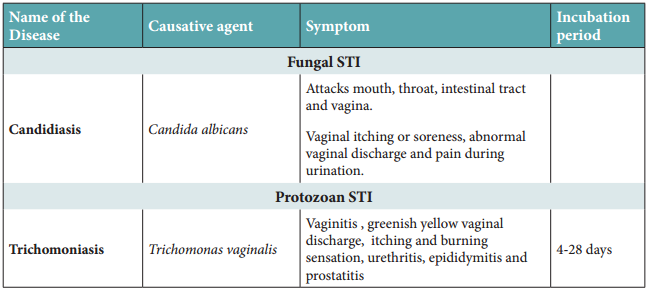
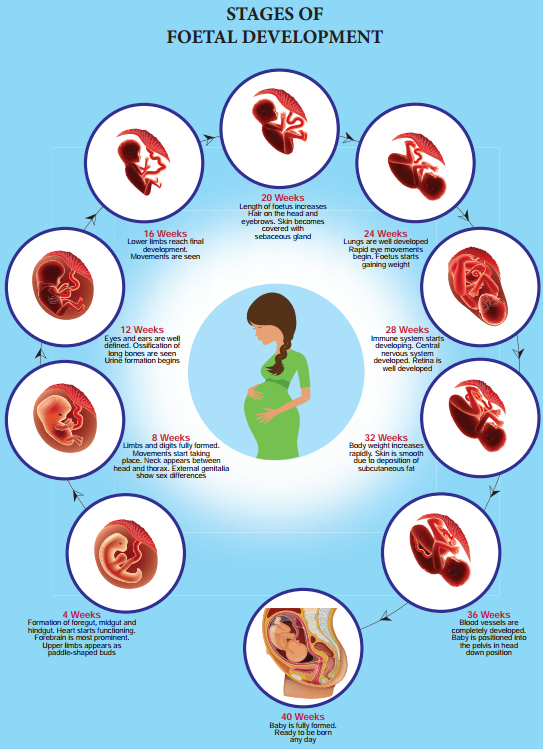
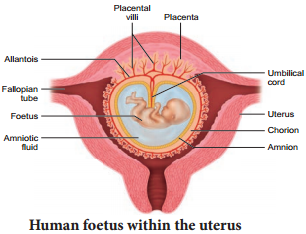
Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Assisted Reproductive Technology (Art)
A collection of procedures, which includes the handling of gametes and/or embryos outside the body to achieve pregnancy is known as Assisted Reproductive Technology. It increases the chance of pregnancy in infertile couples. ART includes intra-uterine insemination (IUI), in vitro fertilization, (IVF) Embryo transfer (ET), Zygote intra-fallopian transfer (ZIFT), Gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT), Intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), Preimplantation genetic diagnosis, oocyte and sperm donation and surrogacy.
Intra-uterine insemination (IUI)
This is a procedure to treat infertile men with low sperm count. The semen is collected either from the husband or from a healthy donor and is introduced into the uterus through the vagina by a catheter after stimulating the ovaries to produce more ova. The sperms swim towards the fallopian tubes to fertilize the egg, resulting in normal pregnancy.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) or Test tube baby
In this technique, sperm and eggs are allowed to unite outside the body in a laboratory. One or more fertilized eggs may be transferred into the woman’s uterus, where they may implant in the uterine lining and develop. Excess embryos may be cryopreserved (frozen) for future use. Initially, IVF was used to treat women with blocked, damaged, or absent fallopian tubes. Today, IVF is used to treat many causes of infertility.
The basic steps in an IVF treatment cycle are ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization, embryo culture, and embryo transfer. Egg retrieval is done by minor surgery under general anesthesia, using ultrasound guide aftr 34 to 37 hours of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) injection.
The eggs are prepared and stripped from the surrounding cells. At the same time, sperm preparation is done using a special media. After preparing the sperms, the eggs are brought together.
10,000-1,00,000 motile sperms are needed for each egg. Then the zygote is allowed to divide to form 8 celled blastomere and then transferred into the uterus for a successful pregnancy. The transfer of an embryo with more than 8 blastomeres stage into uterus is called Embryo transfer technique.
Zygote intra-fallopian transfer (ZIFT)
As in IVF, the zygote upto 8 blastomere stage is transferred to the fallopian tube by laparoscopy. The zygote continues its natural divisions and migrates towards the uterus where it gets implanted.
Intra uterine transfer (IUT)
Embryo with more than 8 blastomeres is inserted into uterus to complete its further development.
Gamete intra-fallopian transfer (GIFT)
Transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the fallopian tube. In this the eggs are collected from the ovaries and placed with the sperms in one of the fallopian tubes. The zygote travels toward the uterus and gets implanted in the inner lining of the uterus.
Intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
In this method only one sperm is injected into the focal point of the egg to fertilize. The sperm is carefully injected into the cytoplasm of the egg. Fertilization occurs in 75 – 85% of eggs injected with the sperms. The zygote is allowed to divide to form an 8 celled blastomere and then transferred to the uterus to develop a protective pregnancy.
Surrogacy
Surrogacy is a method of assisted reproduction or agreement whereby a woman agrees to carry a pregnancy for another person, who will become the newborn child’s parent after birth. Though in vitro fertilization (IVF), embryos are created in a lab and are transferred into the surrogate mother’s uterus.
Male infertility
Azoospermia is defined as the absence of spermatozoa in the ejaculate semen on atleast two occasions and is observed approximately in 1% of the population.
Micro-testicular sperm extraction (TESE)
Microsurgical sperm retrieval from the testicle involves a small midline incision in the scrotum, through which one or both testicles can be seen. Under the microscope, the seminiferous tubules are dilated and small amount of testicular tissue in areas of active sperm production are removed and improved for sperm yield compared to traditional biopsy techniques.