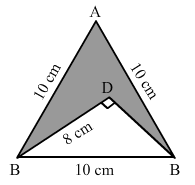
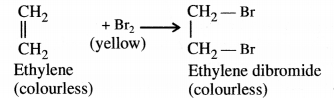
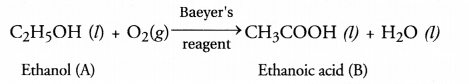
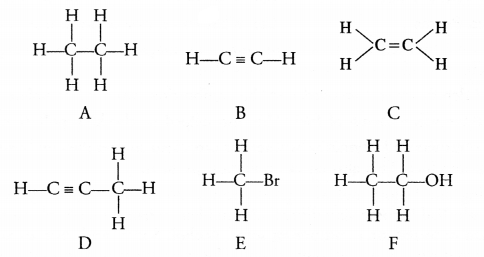
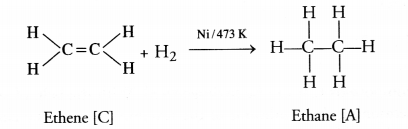
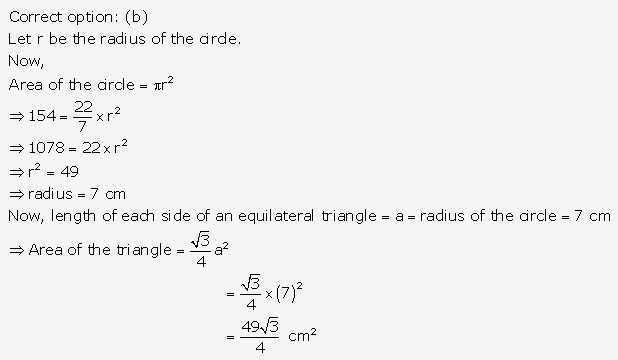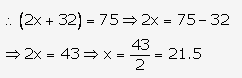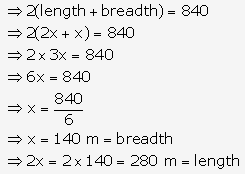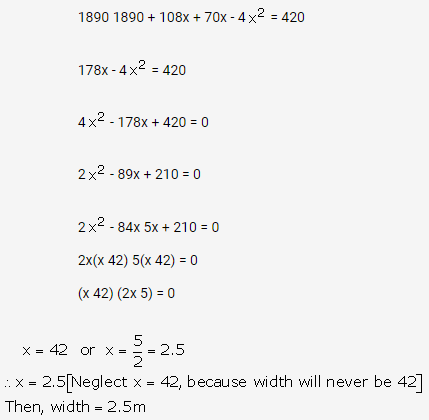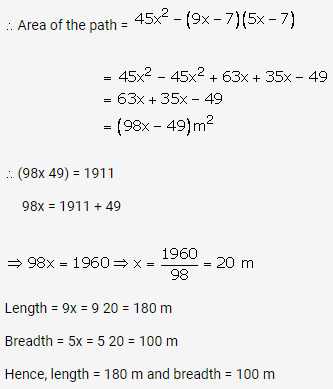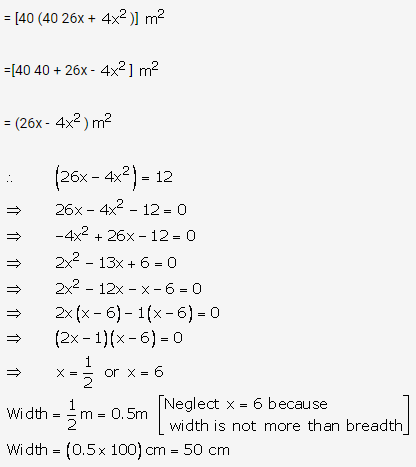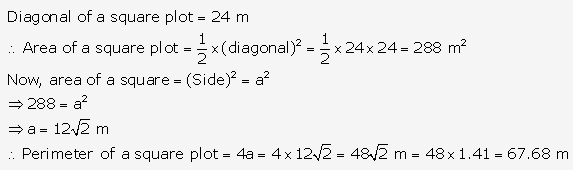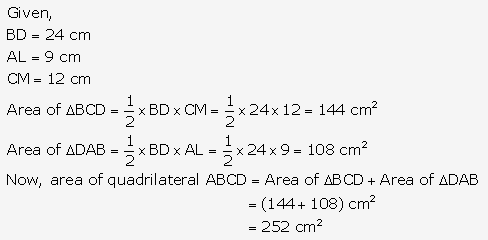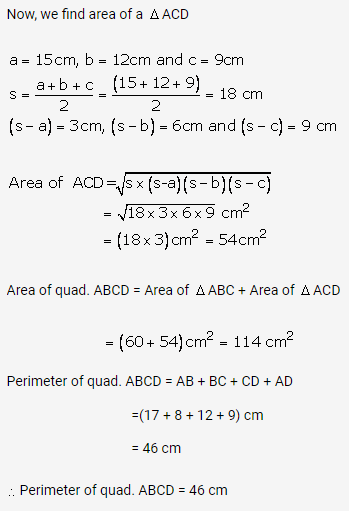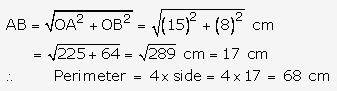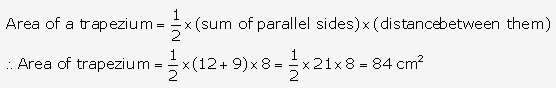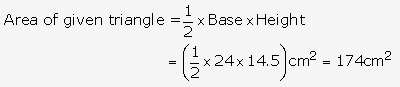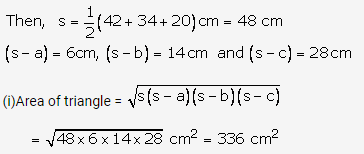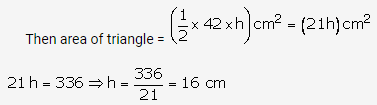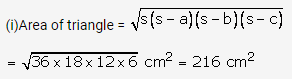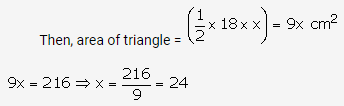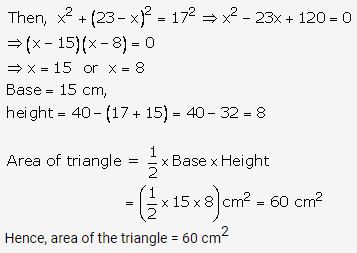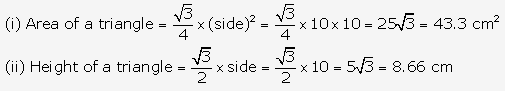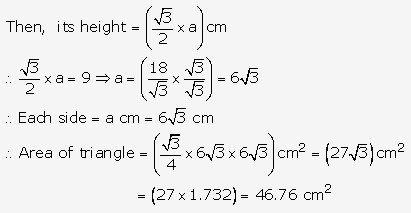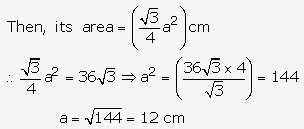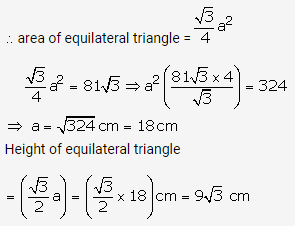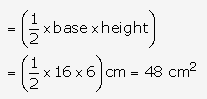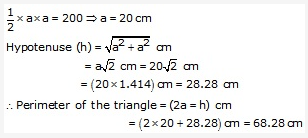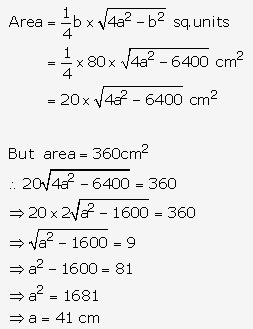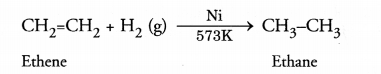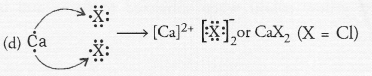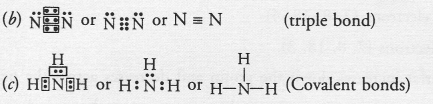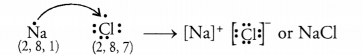RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 17 Perimeter and Areas of Plane Figures Test Yourself
These Solutions are part of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10. Here we have given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 17 Perimeter and Areas of Plane Figures Test Yourself.
Other Exercises
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 17 Perimeter and Areas of Plane Figures Ex 17A
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 17 Perimeter and Areas of Plane Figures Ex 17B
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 17 Perimeter and Areas of Plane Figures MCQ
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 17 Perimeter and Areas of Plane Figures Test Yourself
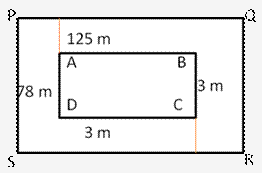
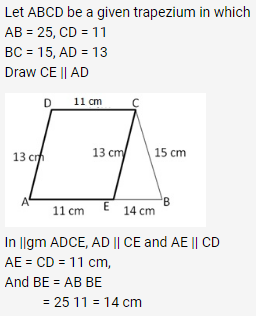
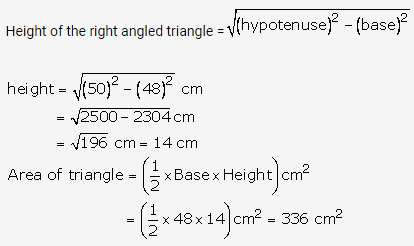
Question 1.
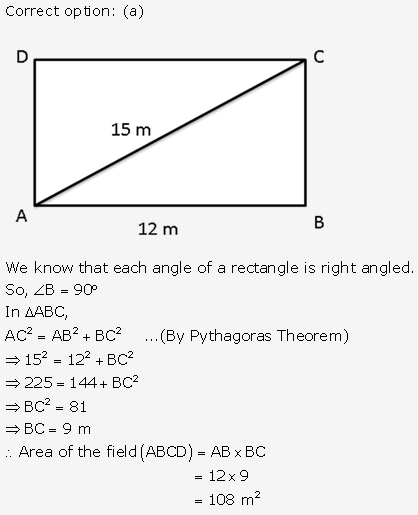
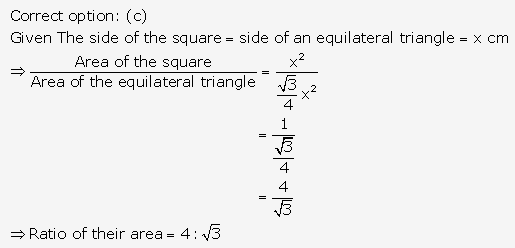
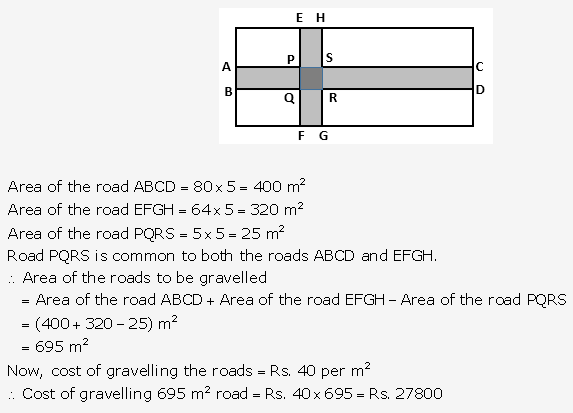
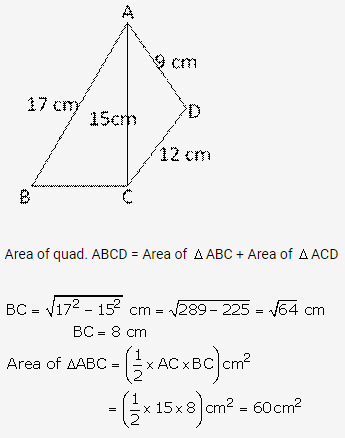
Solution:

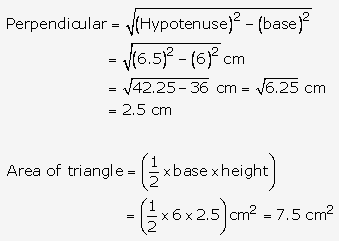
Question 2.
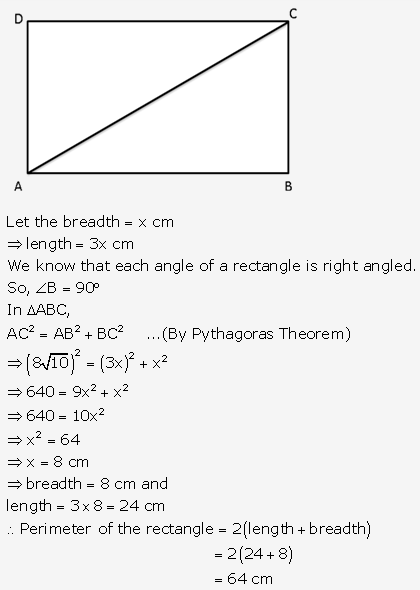
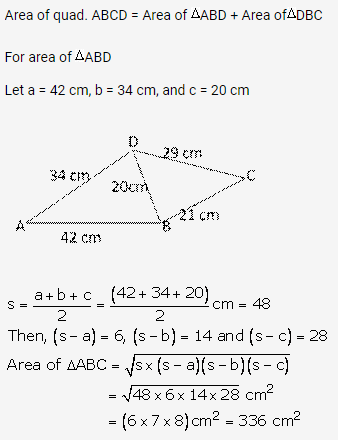
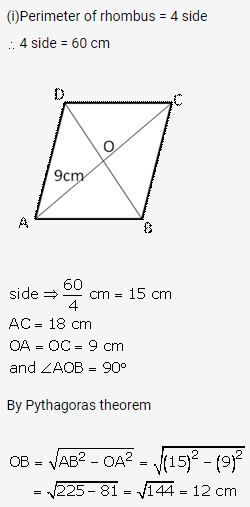
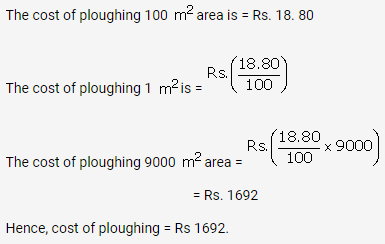
Solution:

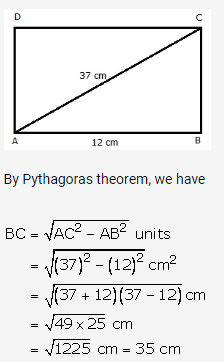
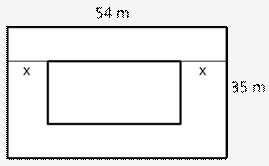
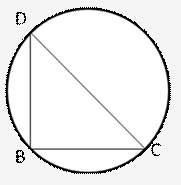
Question 3.
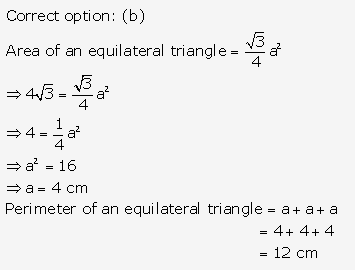
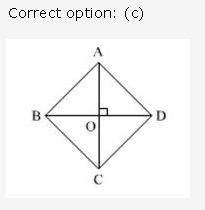
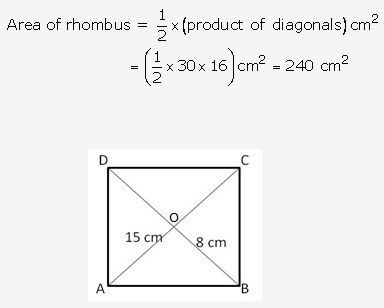
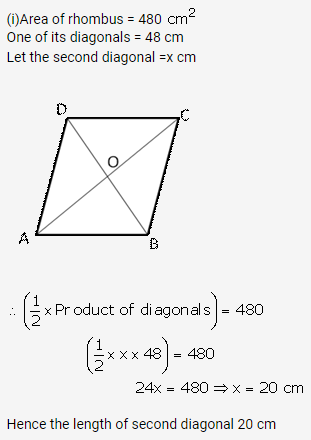
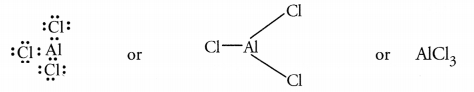
Solution:

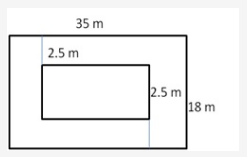
Question 4.
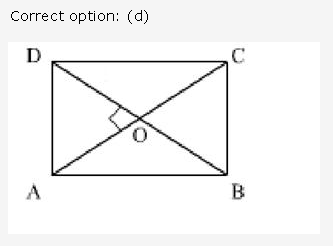
Solution:

Question 5.
Solution:
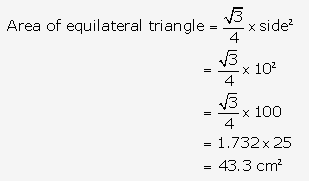
Question 6.
Solution:
Question 7.
Solution:
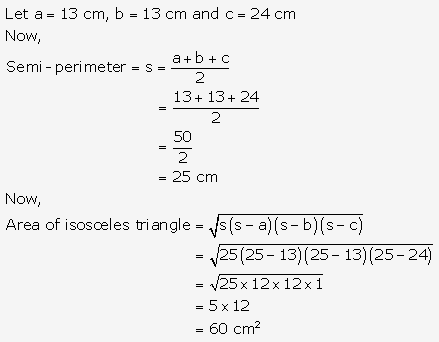
Question 8.
Solution:

Question 9.
Solution:
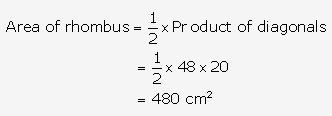
Question 10.
Solution:

Question 11.
Solution:

Question 12.
Solution:
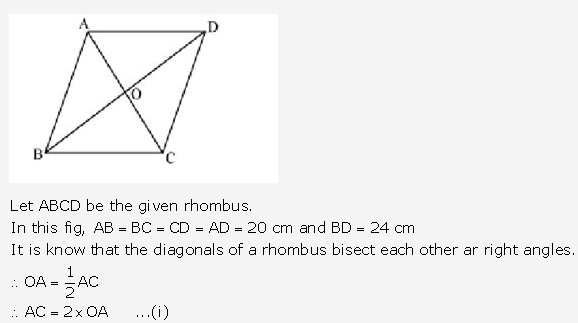

Question 13.
Solution:
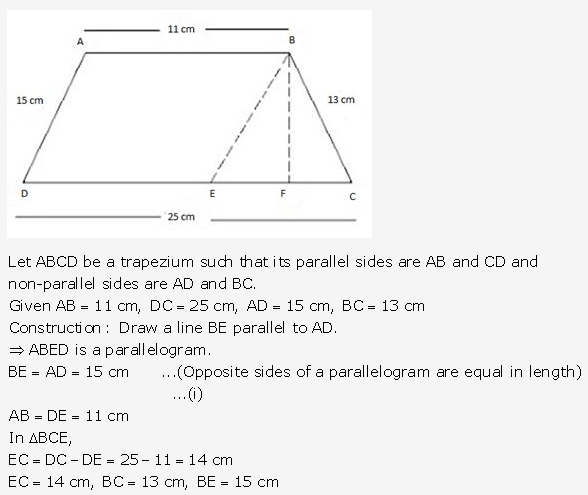

Question 14.
Solution:

Question 15.
Solution:

Question 16.
Solution:


Question 17.
Solution:

Question 18.
Solution:
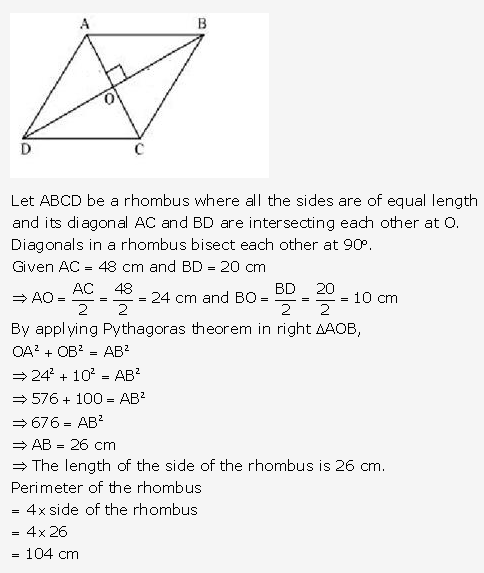
Question 19.
Solution:

Question 20.
Solution:
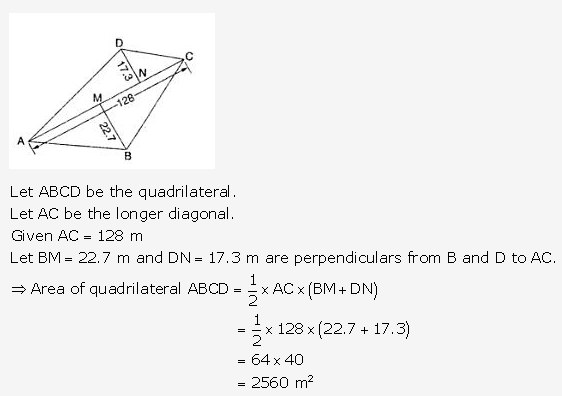
Hope given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 10 Chapter 17 Perimeter and Areas of Plane Figures Test Yourself are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.