NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 |
| Chapter Name | Getting to Know Plants |
| Number of Questions Solved | 13 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
(Page 64)
Question 1.
Correct the following statements and rewrite them in your notebook :
(a) Stem absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
Answer:
Roots absorb water and minerals from the soil.
(b) Leaves hold the plant upright.
Answer:
The stem holds the plant upright.
(c) Roots conduct water to the leaves.
Answer:
Stem conducts water to the leaves.
(d) The number of petals and sepals in a flower is always equal.
Answer:
The statement is not correct
(e) If the sepals of a flower are joined together its petals are also joined.
Answer:
The statement is correct.
(f) If the petals of a flower are joined together, then the pistil is joined to the petal.
Answer:
The statement is correct.
Question 2.
Draw a leaf, a taproot, and a flower, you have studied for Table 7.3 (NCERT Book, Page 61).
Answer :
(a) Leaf
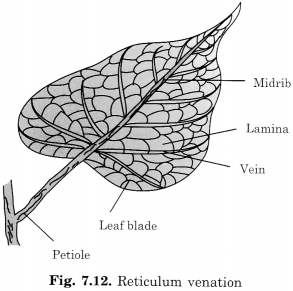
(b) Taproot

(c) Flower
Question 3.
Can you find a plant in your house or in your neighbourhood, which has a long but weak stem? Write its name. In which category will you place it?
Answer :
Yes, money plant. It belongs to creepers.
Question 4.
What is the function of a stem?
Answer :
A stem in a plant performs the following functions:
- It bears leaves, buds, flowers, fruits, etc.
- It conducts water from roots to the leaves and other parts and food from leaves to the roots.
- In some plants, it is also modified to store food.
- It upholds the plant upright.
Question 5.
Which of the following leaves have reticulate venation? Wheat, tulsi, maize, grass, coriander (dhania), China rose.
Answer :
Leaves having reticulate venation are Tulsi, Coriander (dhania), China rose.
Question 6.
If a plant has a fibrous root, what type of venation do its leaves have?
Answer :
Parallel’venation.
Question 7.
If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation, what kind of roots will it have?
Answer:
If a plant has leaves with reticulate venation then it will have taproots.
Question 8.
Is it possible for you to find out whether a plant has taproot or fibrous roots by looking at the impression of its leaf on a sheet of paper?
Answer :
We cannot exactly recognize a leaf without seeing it. However, we might get some idea about the leaf by touching and smelling.
Question 9.
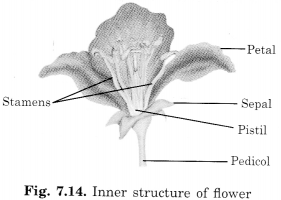
Write the names of the parts of a flower.
Answer :
Sepals, petals, stamen, pistil.
Question 10.
From the following plants, which of them have flowers? Grass, maize, wheat, chilli, tomato, tulsi, piped, shisham, banyan, mango, Jamun, guava, pomegranate, papaya, banana, lemon, sugarcane, potato, groundnut.
Answer :
| S.No | Name of the plant | Whether seen | Whether have flowers | |||
| Yes | No | |||||
| 1. | Grass | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 2. | Maize | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 3. | Wheat | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 4. | Chilli | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 5. | Tomato | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 6. | Tulsi | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 7. | Pipal | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 8. | Shisham | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 9. | Banyan | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 10. | Mango | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 11. | Jamun | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 12. | Guava | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 13. | Pomegranate | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 14. | Papaya | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 15. | Banana | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 16. | Lemon | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 17. | Sugarcane | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 18. | Potato | Yes | ✓ | |||
| 19. | Groundnut | Yes | ✓ | |||
Question 11.
Name the part of the plant which produces its food. Name this process.
Answer :
Leaves of the plant produce food by the process of photosynthesis.
Question 12.
In which part of a flower in which one has joined sepals and the other has separate sepals.
Answer :
Pistil. The ovary is the lowermost part of the pistil.
Question 13.
Name two flowers, in which one has joined sepals and the other has separate sepals. ,
Answer :
Flowers with joined sepals are in rose, ladyfingers, brinjal.
Flower with separate sepals in mustard and datura.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.