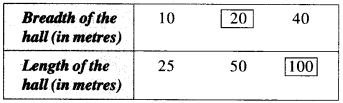
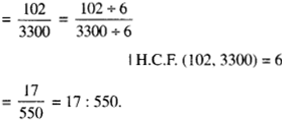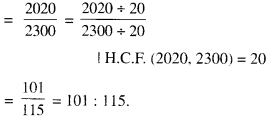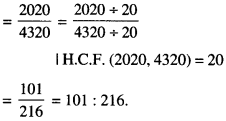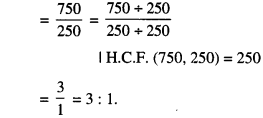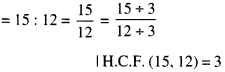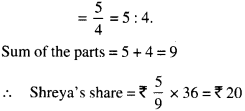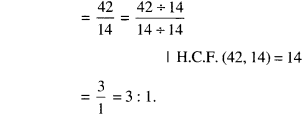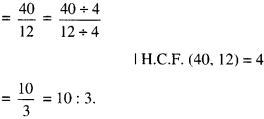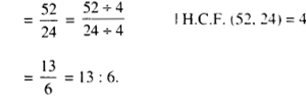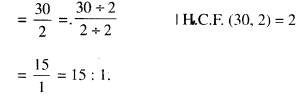In Online Education NCERT Solutions for Class 6 English Honeysuckle Poem Chapter 6 The Wonderful Words are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 6 English. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 6 English Honeysuckle Poem Chapter 6 The Wonderful Words.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | English Honeysuckle Poem |
| Chapter | Chapter 6 |
| Chapter Name | The Wonderful Words |
| Number of Questions Solved | 22 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
Online Education NCERT Solutions for Class 6 English Honeysuckle Poem Chapter 6 The Wonderful Words
Stanzas For Comprehension
Read the following extracts and answer the questions that follow choosing the best option from among the given ones.
1.
Never let a thought shrivel and die
For want of a way to say it
For English is a wonderful game
And all of you can play it
All that you do is match the words
To the brightest thoughts in your head

Paraphrase :
Do not let a thought die unexpressed for want of words. Expression is a funny game in English. Everyone can play it. All that you have to do is to find proper words to match your best thoughts.
Multiple Choice Questions.
1.
The thoughts die when
(a) they are bad
(b) they are good
(c) they are beautiful
(d) they are not expressed
2.
To give expression to the thoughts one has to
(a) work hard
(b) think well
(c) find proper words
(d) study a lot
3.
The poet feels that English has enough words
(a) to express every idea
(b) for us to learn
(c) to confuse us
(d) to write any book
4.
English is a game which is
(a) like cricket
(b) like playing cards
(c) for all persons
(d) for those who love to express themselves
5.
The adverb form of ‘wonderful’ is
(a) wonder
(b) wonderfully
(c) wondered
(d) wondering
Answers :
- (d) they are not expressed
- (c) find proper words
- (a) to express every idea
- (d) for those who love to express themselves
- (b) wonderfully
2.
So that they come out clear and true
And handsomely groomed and fed-
For many of the loveliest things
Have never yet been said.
Word-Notes :
True-exact, सही-सहीHandsomely-beautifully, सुंदरता से। Groomed-decorated, सजा हुआ।
हिन्दी अनुवाद :
ताकि वे (विचार) स्पष्ट और सही तरह अभिव्यक्त हों और उन्हें सुंदरता से सजाया और विकसित किया जा सके। क्योंकि बहुत से सुन्दरतम विचार अभी तक अभिव्यक्ति नहीं पा सके हैं।
Paraphrase :
(Work to express your best thoughts) so that they are expressed beautifully decorated and developed. The truth is that many of the most beautiful things are still waiting for an expression.
Multiple Choice Questions
1.
The passage is taken from
(a) The Wonderful Words
(b) Beauty
(c) A House, A Home
(d) The Kite
2.
The author of the poem is
(a) L.M. Halli
(b) Mary O’ Neill
(c) Peter Dixon
(d) Shure
3.
The poem is about
(a) a groom
(b) a girl
(c) words
(d) beauty
4.
The ‘loveliest things’ are
(a) money
(b) fame
(c) beauty
(d) great ideas
5.
The noun form of ‘fed’ is
(a) feed
(b) feeding
(c) food
(d) feeling
Answers :
- (a) The wonderful words
- (b) Mary O’ Neill
- (c) words
- (d) great ideas
- (c) food
3.
Words are the food and dress of thought
They give it its body and swing
And everyone’s longing today to hear
Some fresh and beautiful thing ;
But only words can free a thought
From its prison behind your eyes
May be your mind is holding now
A marvellous new surprise !
Word-Notes :
Swing-rhythm/progression/impetus/freedom, लय/ गति/ शक्ति/ स्वतंत्रा Longing-desiring, इछुक। Holding-keeping, रखे हुए। Marvellous wonderful, शानदार।
हिन्दी अनुवाद :
शब्द विचारों के शरीर और वस्त्र हैं। वे उन्हें उनका रूप, शक्ति और स्वतंत्रता प्रदान करते हैं। और आज हर व्यक्ति कोई ताजी और सुन्दर बात सुनने की कामना करता है, पर केवल शब्द ही तुम्हारी आँखों के पीछे छिपे कारागार से उन्हें मुक्ति दिला सकते हैं, हो सकता है इस समय भी तुम्हारे मस्तिष्क में कोई शानदार नया विचार सुरक्षित है।
Paraphrase :
Thoughts survive on words. They are their food and clothing. They give them the body and force. Everybody wants to hear some new and beautiful things today. Only the words can free a thought imprisoned in the mind. May be your mind is even now holding back a new and beautiful thought.
Multiple Choice Questions.
1.
If the words are the body, the thought is its
(a) dress
(b) food
(c) soul
(d) swing
2.
According to the poet, everyone wants to hear
(a) good music
(b) fine words
(c) a new poem
(d) new and noble thoughts
3.
The words can free a thought which is
(a) in a prison
(b) in the mind
(c) in the eyes
(d) nowhere
4.
the real beauty is in
(a) new and beautiful ideas
(b) beautiful words
(c) beautiful expression
(d) surprising words
5.
The word longing is a
(a) gerund
(b) verb
(c) noun
(d) adjective
Answers :
- (c) soul
- (d) new and noble thoughts
- (b) in the mind
- (a) new and beautiful ideas
- (c) noun
Textual Questions
Question 1.
With your partner, complete the following sentences in your own words using the ideas in the poem.
- Do not let a thought shrivel and die because ________ .
- English is a ________ with words that everyone can play.
- One has to match ________ .
- Words are the ________ of thought.
Answer :
- it may be a ‘marvellous new surprise’ which everyone is longing to hear.
- wonderful game of matching thoughts.
- the words to the brightest thought in the mind.
- food and dress of thought.
Question 2.
In groups of four discuss the following lines and their meanings.
- All that you do is match the words To the brightest thoughts in your head
- For many of the loveliest things Haye never yet been said
- And everyone’s longing today to hear Some fresh and beautiful thing
- But only words can free a thought From its prison behind your eyes
Answer :
- You have only to find the nearest possible words which seem to trans¬late your best thoughts.
- Many of the most beautiful ideas are still waiting for proper expres¬sion.
- Today everyone is very eager to hear something new and beautiful.
- Words are imprisoned in the mind. They will remain so until and un¬less you find proper words to give them expression. This alone will give them freedom from the prison of mind.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 6 English Honeysuckle Poem Chapter 6 The Wonderful Words help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 6 English Honeysuckle Poem Chapter 6 The Wonderful Words, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest