We have given detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 3 शब्द परिचयः 3 Textbook Questions and Answers come in handy for quickly completing your homework.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 3 शब्द परिचयः 3
Class 6th Sanskrit Chapter 3 शब्द परिचयः 3 Textbook Questions and Answers
अभ्यासः
प्रश्न 1.
(क) उच्चारणं कुरुत- (उच्चारण कीजिए- Read it out.)
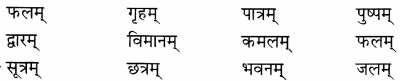
(ख) चित्राणि दृष्ट्वा पदानि उच्चारयत- (चित्रों को देखकर शब्दों का उच्चारण कीजिए Look at the pictures and pronounce these words.)

उत्तर:
(क) छात्र स्वयं उच्चारण करें। ये सभी शब्द नपुंसकलिङ्ग हैं।
(ख) छात्र चित्रों को देखकर पदों का उच्चारण करें। उच्चारण करते समय चित्र की ओर ध्यान दें ताकि पद का अर्थ याद रहे। उच्चारण शुद्ध हो। प्रत्येक पद का उच्चारण यदि दो बार
करें, तो लाभ होगा। सभी नपुंसकलिङ्ग पद हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
(क) वर्णसंयोजनं कृत्वा पदं कोष्ठके लिखत- (वर्णों को जोड़कर शब्द कोष्ठक में लिखिए Combine the letters and write down the word in the box.)

(ख) अधोलिखितानां पदानां वर्णविच्छेदं कुरुत- (निम्नलिखित पदों का वर्ण-विच्छेद कीजिए Separate the letters in the words given below.)

उत्तर:
(क) खनित्रम्, पुराणानि, पोषकाणि, कङ्कतम्।

प्रश्न 3.
चित्राणि दृष्ट्वा संस्कृतपदानि लिखत- (चित्र देखकर संस्कृत शब्द लिखिए- Look at the pictures and write the -words in Sanskrit.)

उत्तर:
(क) आम्रम्
(ख) पर्णम्
(ग) व्यजनम्
(घ) करवस्त्रम्
(ङ) सूत्रम्
(च) छत्रम्
प्रश्न 4.
चित्रं दृष्ट्वा उत्तरं लिखत- (चित्र देखकर उत्तर लिखिए- Look at the pictures and write the answer.)

उत्तर:
(क) मयूरौ नृत्यतः।
(ख) एते क्रीडनके स्तः।
(ग) बालिकाः पठन्ति।
(घ) पुष्पाणि विकसन्ति।
प्रश्न 5.
निर्देशानुसारं वाक्यानि रचयत- (निर्देशानुसार वाक्य बनाएँ- Transform the sentences as directed.)
यथा- एतत् पतति। (बहुवचने) — ………………… एतानि पतन्ति।
(क) एते पणे स्तः। (बहुवचने) — …………………
(ख) मयूरः नृत्यति। (बहुवचने) — …………………
(ग) एतानि यानानि। (द्विवचने) — …………………
(घ) छात्रे लिखतः। (बहुवचने) — …………………
(ङ) नारिकेलं पतति। (द्विवचने) — …………………
उत्तर:
(क) एतानि पर्णानि सन्ति।
(ख) मयूराः नृत्यन्ति।
(ग) एते याने।
(घ) छात्राः लिखन्ति।
(ङ) नारिकेले पततः।
प्रश्न 6.
उचितपदानि संयोज्य वाक्यानि रचयत- (उचित पदों का मेल करके वाक्य बनाइए- Match the appropriate words and frame sentences.)
कोकिले — विकसति
पवनः — नृत्यन्ति
पुष्पम् — उत्पतति
‘खगः — वहति
मयूराः — गर्जन्ति
सिंहाः — कूजतः
उत्तर:
(क) कोकिले कूजतः।
(ख) पवनः वहति।
(ग) पुष्पम् विकसति।
(घ) खगः उत्पतति।
(ङ) मयूराः नृत्यन्ति।
(च) सिंहाः गर्जन्ति।
Class 6th Sanskrit Chapter 3 शब्द परिचयः 3 Additional Important Questions and Answers
प्रश्न 1.
चित्रं दृष्ट्वा संस्कृतपदं लिखत। (प्रत्येक चित्र देखकर संस्कृत पद लिखिए। Look at each picture and write down the word in Sanskrit.)
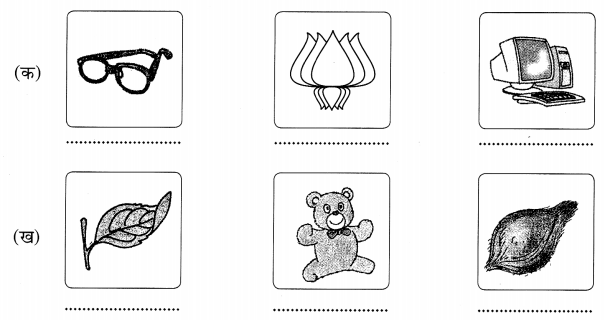
उत्तर:
(क) उपनेत्रम् – कमलम् – सङ्गणकम्
(ख) पर्णम् – क्रीडनकम् – नारिकेलम्
प्रश्न 2.
वर्णसंयोजनम् कुरुत। (वर्णसंयोग कीजिए- Join the alphabets.)

उत्तर:
(i) सङ्गणकम्
(ii) सूत्रम्
(iii) उद्यानम्
(iv) क्रीडनकम्
(ख) वर्णविच्छेदं कुरुत। (वर्ण-विच्छेद कीजिए- Separate the alphabets.)
पर्णम् = ………………….
वातायनम् = ………………….
कङ्कतम् = ………………….
कदलीफलम् = ………………….
उत्तरम्-

प्रश्न 3.
अधोदत्ताम् तालिकां पूरयत। (निम्नलिखित तालिका को पूरा कीजिए- Complete the table given below.)

उत्तर:


उत्तर:

प्रश्न 4.
संस्कृतेन लिखत- (संस्कृत में लिखिए– Write down the word in Sanskrit.)
यथा — खेत – क्षेत्रम्
(क) छाता …………….
(ख) नारियल …………….
(ग) छुरी …………….
(घ) कुञ्जी …………….
(ङ) कंघा …………….
उत्तर:
(क) छत्रम्
(ख) नारिकेलम्
(ग) छुरिका
(घ) कुञ्चिका
(ङ) कङ्कतम्/ककतम्
प्रश्न 5.
प्रत्येकं स्तम्भात् उचितं पदम् आदाय वाक्यानि रचयत। (प्रत्येक स्तम्भ से उचित पद लेकर वाक्य बनाइए- Frame sentences by picking out the appropriate word from each column.)

उत्तर:

प्रश्न 6.
अधोदत्तायां तालिकायाम् रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयत। (तालिका में रिक्त स्थान भरिए- Fill in the blanks in the table given below.)

उत्तर:

बहुविकल्पीयप्रश्नाः
प्रश्न 1.
उचित विकल्पं चित्वा वाक्यपूर्तिं कुरुत। (उचित विकल्प चुनकर वाक्य पूरे कीजिए। Complete the sentences by picking out the correct option.)
(क)
(i) ……….. आम्राणि मधुराणि। (एतत्, एते, एतानि)
(ii) ………. उद्यानम् सुंदरम्। (सः, सा, तत्)
(ii) ………. बसयाने कुत्र गच्छतः। (ते, सा, तानि)
(iv) ………. कोकिला कूजति। (एषः, एषा, एतत्)
(v) ………. जनाः गच्छन्ति। (सः, तौ, ते)
उत्तर:
(i) एतानि
(ii) तत्
(iii) ते
(iv) एषा
(v) ते
(ख)
(i) अत्र ………. अस्ति। (विश्रामगृह, विश्रामगृहम्, विश्रामगृहः)
(ii) …………. विकसति। (कमलम्, कमल, कमलः)
(iii) ………. मधुराणि सन्ति। (कदलीफलम्, कदलीफले, कदलीफलानि)
(iv) ………. कुत्र स्त? (पुस्तकम्, पुस्तके, पुस्तकानि)
(v) ………. चलति। (व्यञ्जनम्, व्यजनः, व्यजनम्)
उत्तर:
(i) विश्रामगृहम्
(ii) कमलम्
(iii) कदलीफलानि
(iv) पुस्तके
(v) व्यजनम्
प्रश्न 2.
उचितं विकल्पं चित्वा चित्रस्य समक्षं लिखत। (उचित विकल्प चुनकर चित्र के सामने लिखिए।Pick out the correct option and write down in front of the picture.)
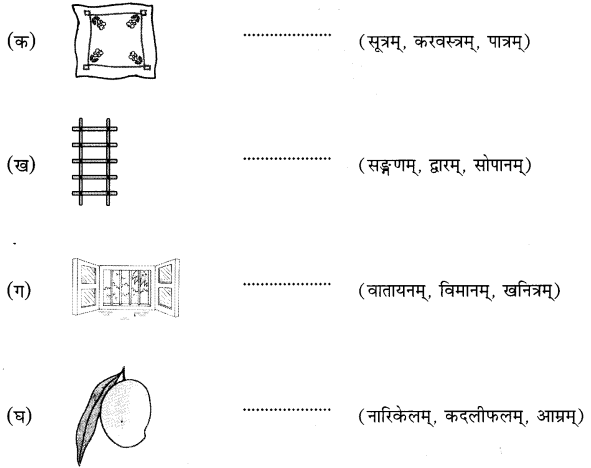
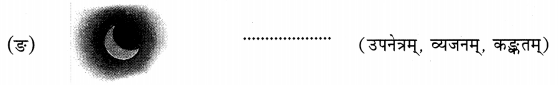
उत्तर:
(क) करवस्त्रम्
(ख) सोपानम्
(ग) वातायनम्
(घ) आम्रम्
(ङ) व्यजनम्
प्रश्न 3.
उचित-विकल्पेन रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयत। (उचित विकल्प द्वारा रिक्त स्थान भरिए। Fill in the blanks with the correct option.)
(क)
(i) पुष्पाणि …………….. (विकसति, विकसतः, विकसन्ति)
(ii) बालिके कुत्र …………….. ? (गच्छति, गच्छतः, गच्छन्ति)
(iii) ………………. पतन्ति । (पर्णाः, पर्णम्, पर्णानि)
(iv) ……………….. कुत्र अस्ति? (उद्यान, उद्यानम्, उद्यानानि)
(v) …………….. अत्र अस्ति। (वातायन, वातायनः, वातायनम्)
उत्तर:
(i) विकसन्ति
(ii) गच्छतः
(iii) पर्णानि
(iv) उद्यानम्
(v) वातायनम्।
(ख)
(i) पर्णम् ………….। (पतति, उत्पतति)
(ii) सुवर्णकारः अंगुलीयकम् ………….। (चालयति, रचयति)
(iii) सौचिकः ………….। (सीव्यति, सूचयति)
(iv) अजाः ………….। (चरन्ति, कूजन्ति)
(v) जवनिका …………… (चलति, दोलति)
उत्तर:
(i) पतति
(ii) रचयति
(iii) सीव्यति
(iv) चरन्ति
(v) दोलति।