NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science History Chapter 4 The Mughal Empire are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science History Chapter 4 The Mughal Empire.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Social Science History |
| Chapter | Chapter 4 |
| Chapter Name | The Mughal Empire |
| Number of Questions Solved | 17 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science History Chapter 4 The Mughal Empire
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
IMAGINE
You have inherited a kingdom. (Remember Babur and Akbar were about your age when they became rulers). How would you make your kingdom stable and prosperous?
Answer.
We would make our kingdom stable and prosperous in the following manner:
- We shall appoint an advisory council to advise on the matters of ruling and administration.
- A foolproof tax system will be started at reasonable rates.
- Government enterprises will be set up to ensure regular income to the state.
- Joint venture undertakings would be set up at a minimum rate of profit to the state exchequer.
LET’S RECALL
Question 1.
Match the following:
Mansab Marwar
Mongol Governor
Sisodiya Rajput Uzbeg
Rathor Rajput Mewar
Nur Jahan Rank
Subadar Jahangir
Answer.
Mansab Rank
Mongol Uzbeg
Sisodiya Rajput Mewar
Rathor Rajput Marwar
Nur Jahan Jahangir
Subadar Governor
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The capital of Mirza Hakim, Akbar’s half-brother, was …………
- The five Deccan Sultanates were Berar, Khandesh, Ahmadnagar, …………, and …………..
- If zat determined a mansabdar’s rank and salary, sawar indicated his …………….
- Abul Fazl, Akbar’s friend and counsellor, helped him frame the idea of ……………. so that he could govern a society composed of many religions, cultures, and castes.
Answer.
- Kabul.
- Bijapur, Golconda.
- Cavalrymen.
- Sulh-i-kul
Question 3.
What were the central provinces under the control of the Mughals?
Answer.
Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh.
Question 4.
What was the relationship between the man Sardar and the jagir?
Answer.
- Mansabdar were the nobles or the rank holders. They were not paid salaries Instead they were given the right to collect revenue from the land granted to them. These lands were called jagirs.
- Often mansabdars had to serve outside their jagirs therefore the revenue from their jagir was collected by their servants.
LET’S UNDERSTAND
Question 5.
What was the role of the zamindar in the Mughal administration?
Answer.
Role of the Zamindar in Mughal administration:
- Zamindars were described as all types of intermediary whether they were local headmen of the villages or the powerful chieftains.
- They collected taxes from peasants and deposited the same with the treasury of the empire.
Question 6.
How were the debates with religious scholars important in the formation of Akbar’s ideas on governance?
Answer.
The debates with religious scholars, of India today do not pose a challenge to national integration because today, we have a democratic, republic government appointed by the common people of the land through elections.
Question 7.
Why did the Mughals emphasise their Timurid and not their Mongol descent?
Answer.
The Mughals did not like to be known as Mongols. Genghis Khan’s memory was associated with the massacre of people and invasional instinct. It was also linked with Uzbegs, their Mongol competitors.
They preferred their Timurid ancestry. Their great ancestor had captured Delhi in 1398. They were proud of their genealogy. Each ruler had his picture made with Timur.
LET’S DISCUSS
Question 8.
How important was the income from land revenue to the stability of the Mughal Empire?
Answer.
Land revenue was the backbone of the Mughal Empire. Without it nothing could be done. The king could not pay the salary of his soldiers. Neither could he do any welfare work. The administrative expenditure was so vast and this could be met with this revenue only. Hence, revenue was important to strengthen the empire.
Question 9.
Why was it important for the Mughals to recruit mansabdars from diverse backgrounds and not just Turanis and Iranis?
Answer.
It was important for the Mughals to recruit mansabdars from diverse backgrounds and not just Turanis and Iranis because of the following reasons:
- It had a positive effect on the emotions of the people of India (Hindustan—the subcontinent).
- The people of the subcontinent were more conversant with the status of land and taxes to be imposed on it.
Question 10.
Like the Mughal Empire, India today is also made up of many social and cultural units. Does this pose a challenge to national integration?
Answer.
No. This does not pose any challenge to national integration. Unity in diversity is the special feature of India. Indians may belong to different regions, cultures, castes and creed. But this does not mean that they are different people. They are one and are proud of being born in India.
Sometimes social conflicts arise no doubt but they are solved in an amicable way. Whenever there is an external threat, all Indians come together. The Kargil war is worth mentioning here. India fought and won the war in the last. That was the time when everyone was filled with patriotic feelings. There was only one goal, Le. to win the war and that India did with the help of her brave heroes.
Question 11.
Peasants were vital for the economy of the Mughal Empire. Do you think that they are as important today? Has the gap in the income between the rich and the poor in India changed a great deal from the period of the Mughals?
Answer.
Peasants are still very important as they are the producers of food and the agrarian industrial raw material:
- Peasants pay the land revenue increasing the government revenue.
- There is a change in the gap between the rich and the poor today as compared to the Mughal period mainly because of change in the social, economic situation of the country.
- Now the country is one political entity with rights and duties for all the citizens and the government working for the welfare of the citizens.
LET’S DO
Question 12.
The Mughal Empire left its impact on the different regions of the subcontinent in a variety of ways. Find out if it had any impact in the city, village, or region in which you live.
Answer.
I live in Delhi. It was the capital of the Mughal Empire. The Empire changed the face of the city. We see the Red Fort, Chandni Chowk, Jama Masjid, Humayun’s tomb, the Mughal garden, etc. in the city. These were the contributions of the Mughal emperors who made the city so rich and colourful.
INTEXT QUESTIONS WITH THEIR ANSWERS
Question 1.
Do you think this painting suggests that the Mughals claimed kingship as a birthright? (NCERT Page 46)
Answer.
Yes.
Question 2.
Did the annexation of Golconda and Bijapur in Aurangzeb’s reign end hostilities in the Deccan? (NCERT Page 47)
Answer.
No, the uncertain situation still persisted and he had to personally manage the affairs of Deccan. He even had to face guerrilla warfare.
Question 3.
Can you identify the Jesuit priests in this picture? (NCERT Page 55)
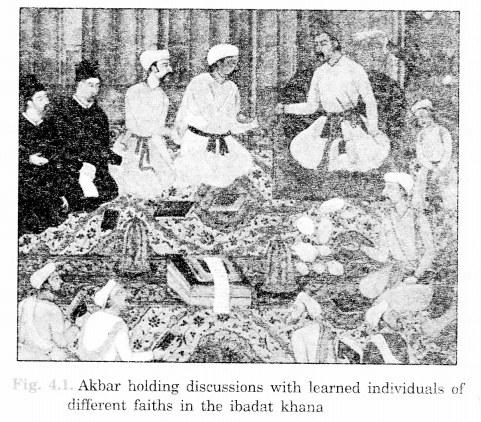

Answer.
The Jesuit priests in this picture are in black and long gowns.
Question 4.
Find out more about Akbar’s other contemporaries—the ruler of England, Queen Elizabeth I (1558-1603); the Safavid ruler of Iran, Shah Abbas (1588-1629); and the more controversial Russian ruler, Czar Ivan IV Vasilyevich, also called “Ivan the Terrible” (1530-1584). (NCERT Page 57)
Answer.
- Akbar: Universal peace
- Queen Elizabeth: Democratic attitude
- Shah Abbas: Liberal
- Czar Ivan: Ruthless dictator
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science History Chapter 4 The Mughal Empire help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science History Chapter 4 The Mughal Empire, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.