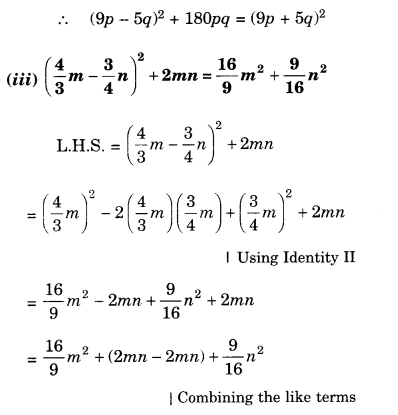
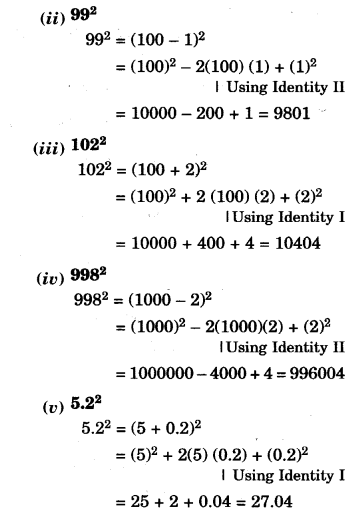
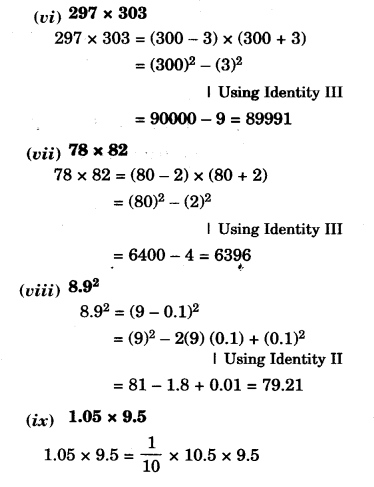
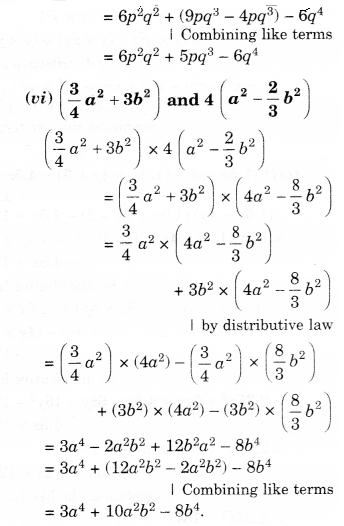
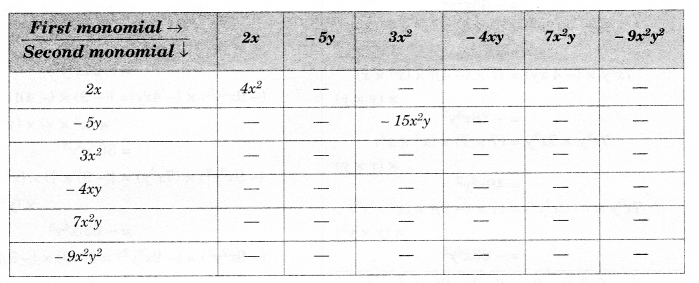
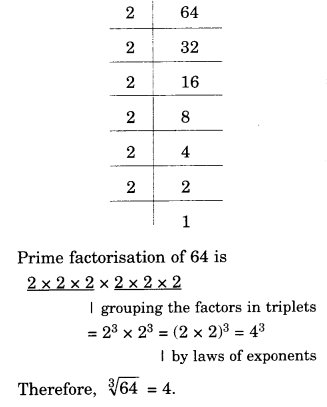
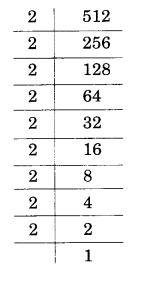
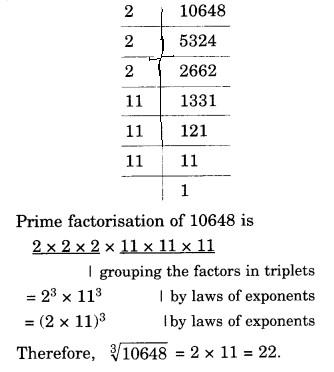
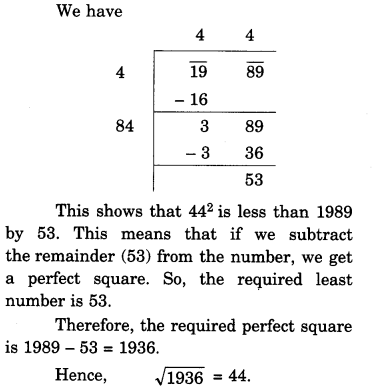
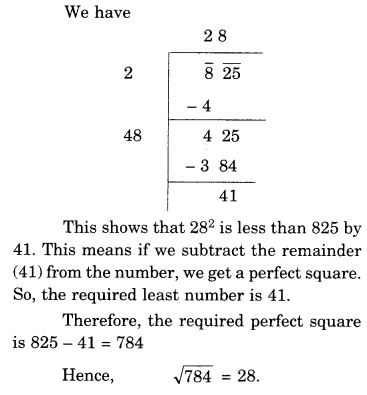
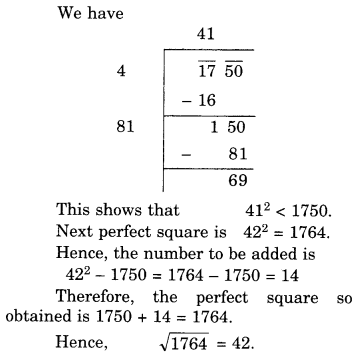
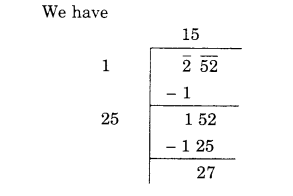
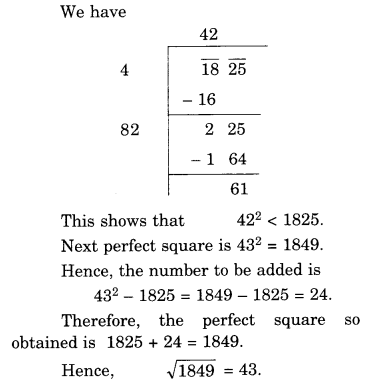
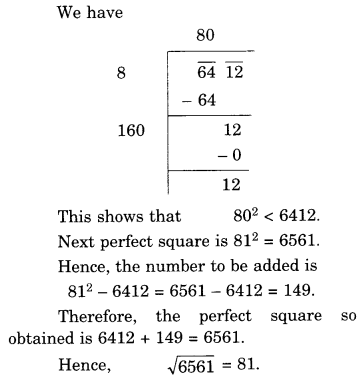
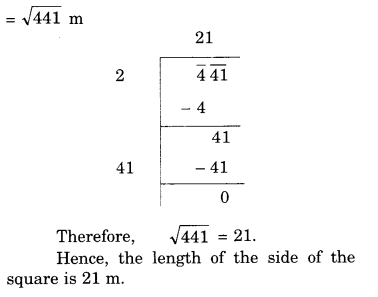
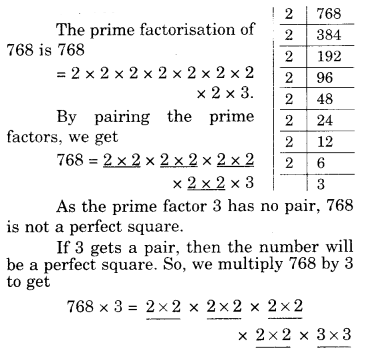
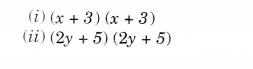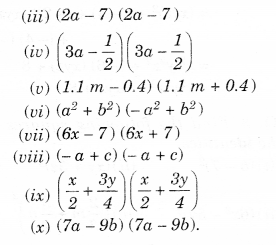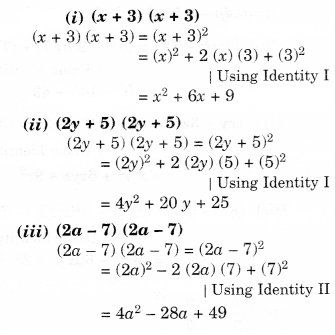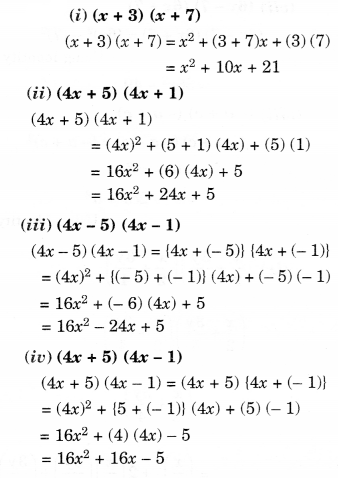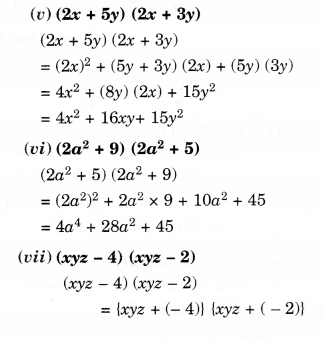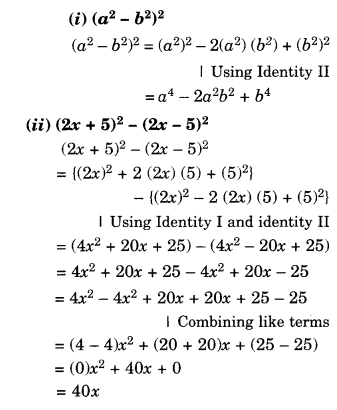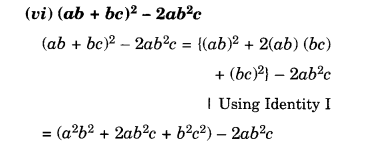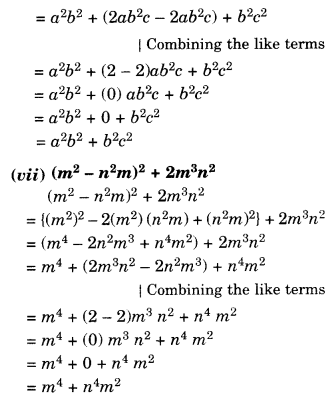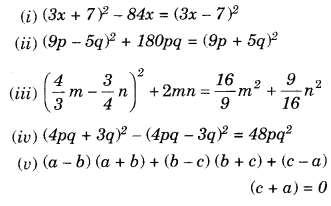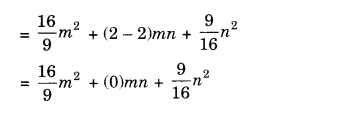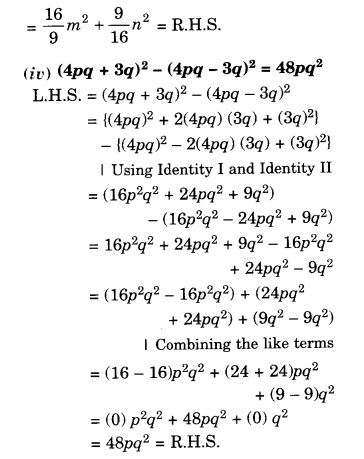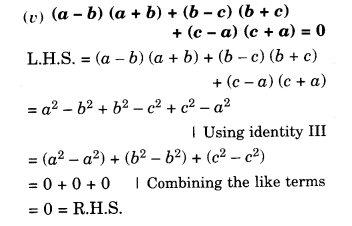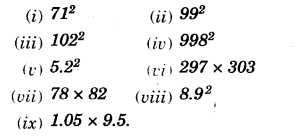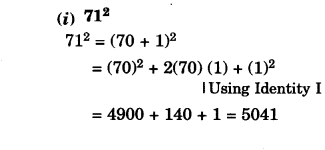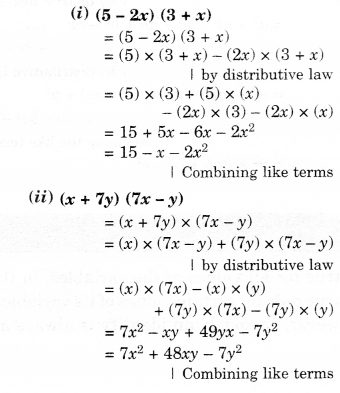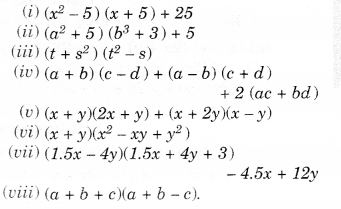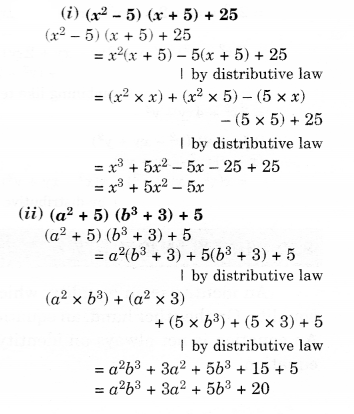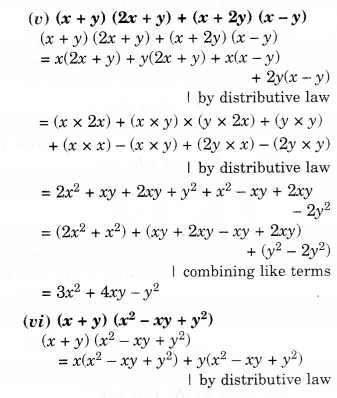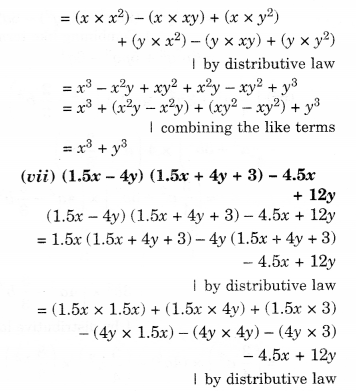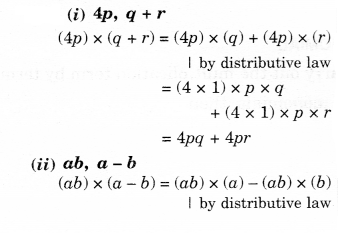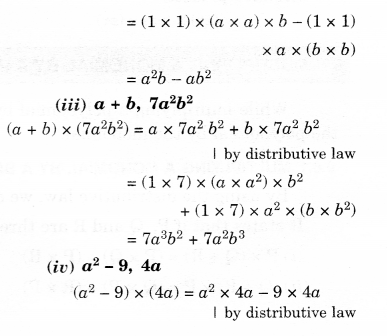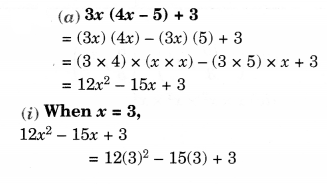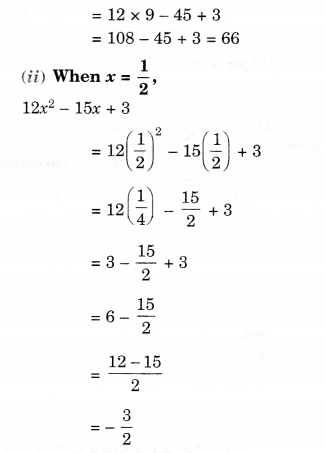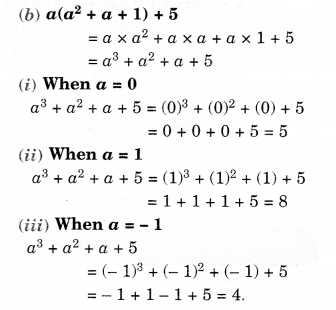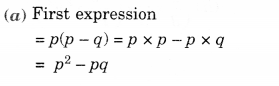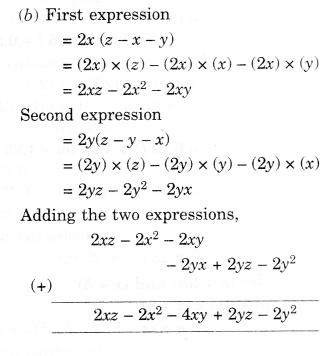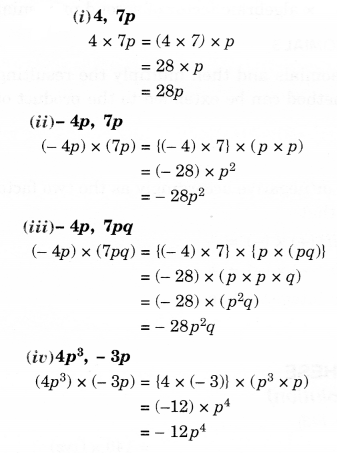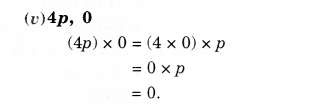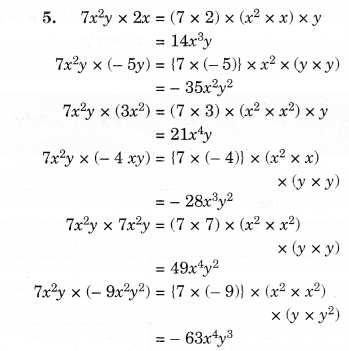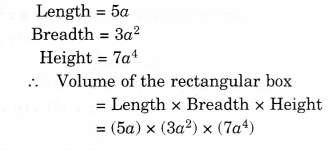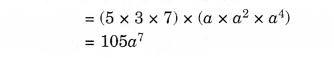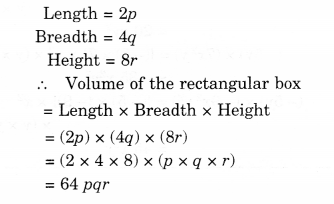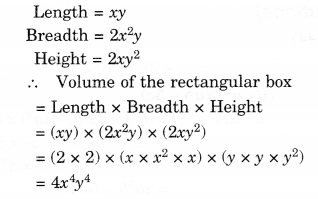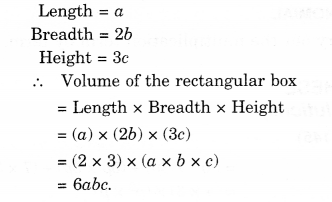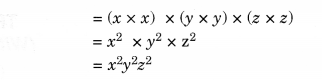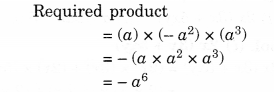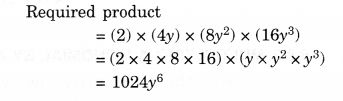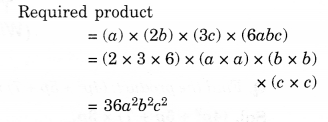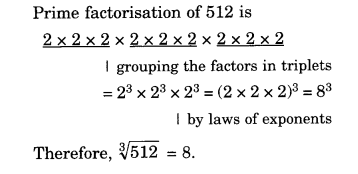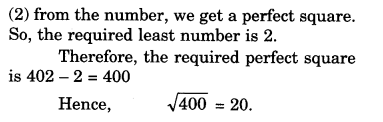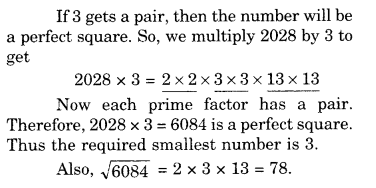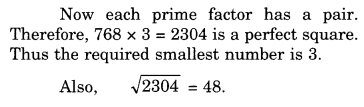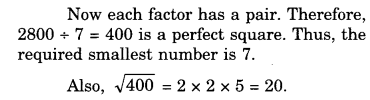NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.2 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.2.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 10 |
| Chapter Name | Visualising Solid Shapes |
| Exercise | Ex 10.2 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 4 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.2
Question 1.
Look at the given map of a city.
Answer the following.
(a) Colour the map as follows: Bluewater, Red-fire station, Orange-Library, Yellow-schools, Green-Parks, Pink-Community Centre, Purple-Hospital, Brown-Cemetery.
(b) Mark a green X’ at the intersection of Road ‘C’ and Nehru Road, Green Y’ at the intersection of Gandhi Road and Road A.
(c) In red, draw a short street route from Library to the bus depot.
(d) Which is further east, the city park or the market?
(e) Which is further south, the primary school or the Sr. Secondary School?
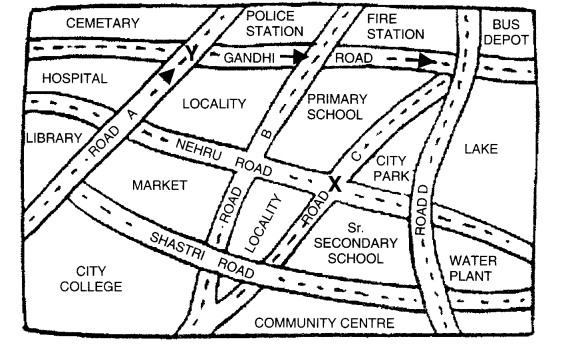
Solution.
(a) Please color yourself.
(b) See the above figure.
(c) See the above figure.
(d) City Park.
(e) Senior Secondary school.
Question 2.
Draw a map of your classroom using a proper scale and symbols for different objects.
Solution.
Please draw yourself.
Question 3.
Draw a map of your school compound using a proper scale and symbols for various features like playground main building, garden etc.
Solution.
Please draw yourself.
Question 4.
Draw a map giving instructions to your friend so that she reaches your house without any difficulty.
Solution.
Please draw yourself.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.2 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.