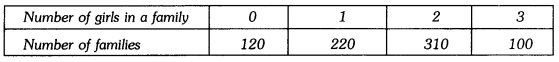
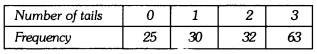
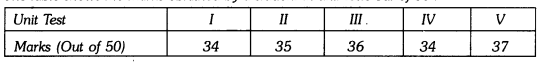
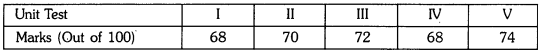
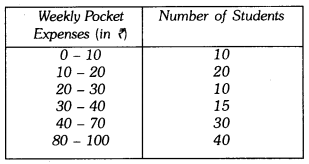
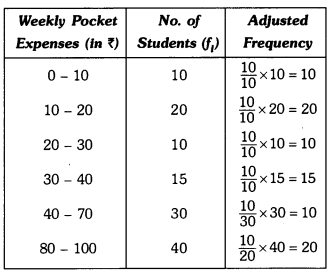
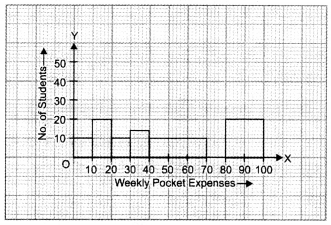
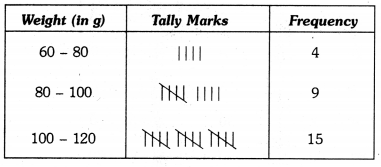
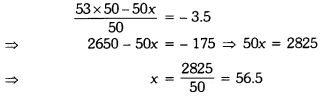In this page, we are providing Why Do we Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 13 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do we Fall Ill with Answers will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-9-science/
Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Extra Questions and Answers Why Do we Fall Ill
Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do we Fall Ill with Answers Solutions
Why Do we Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions Question 1.
What are infectious or communicable diseases?
Answer:
The diseases which are caused by infectious agents are called as infectious diseases as they can spread from one person to another through some medium or by direct contact.
Example: Pneumonia, common cold, tuberculosis, etc.
Why Do We Fall Ill Extra Questions Question 2.
What are congenital diseases?
Answer:
The diseases which are present in a person since birth are called congenital diseases.
Example: colour blindness.
Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions Pdf Question 3.
Give one local and one general effect of the inflammation process.
Answer:
Swelling or pain is a local effect. Fever or headache is a general effect.
Class 9 Why Do We Fall Ill Extra Questions Question 4.
Name the organism causing the following diseases:
(a) Kala-azar
(b) Sleeping sickness
Answer:
Kala-azar is caused by Leishmania; Sleeping sickness is caused by Trypanosoma.
Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Extra Questions And Answers Question 5.
It was diagnosed that a patient has lost the power of fighting any infection.
(i) Name the disease the patient is suffering from.
(ii) Name the pathogen responsible for the disease.
Answer:
(i) AIDS.
(iii) HIV is the causative organism of AIDS. [HIV-Human immunodeficiency virus]
Extra Questions Of Why Do We Fall Ill Question 6.
What is immunity?
Answer:
The ability of the body of a person to fight against the disease causing organisms is called immunity. Name any disease that can be prevented by using vaccines.
Class 9 Science Ch 13 Extra Questions Question 7.
The diseases which can be prevented by using vaccines.
Answer:
The diseases which can be prevented by using vaccines are polio, small pox, diphtheria, tetanus, measles, etc.
Extra Questions Of Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9 Question 8.
What are principles of treatment of a disease?
Answer:
The principles of treatment are:
- reducing the effects of the disease.
- to kill the cause of the disease.
Extra Questions On Why Do We Fall Ill Question 9.
How do children in many parts of India get immune to hepatitis-A by the time they are five year old?
Answer:
The children become immune to hepatitis A virus as they are exposed to hepatitis A virus present in the water they drink.
Ch 13 Science Class 9 Extra Questions Question 10.
Name the causative organisms of tuberculosis and cholera.
Answer:
Tuberculosis: Caused by bacterium called as Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Cholera is caused by a bacterium called as Vibrio cholera
Why Do we Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 1
Extra Questions Why Do We Fall Ill Question 1.
What are the differences between acute and chronic diseases?
Answer:
Acute disease:
- The disease which lasts for only very short periods of time is called acute disease.
- They get over soon and do not get much time to affect the health more adversely. Example: Common cold
Chronic disease:
- The disease which can last for a long time, even as much as a lifetime is called chronic disease.
- They have a long-term effect on the health of a person. Example: Elephantiasis
Class 9 Science Why Do We Fall Ill Extra Questions Question 2.
What is a pandemic disease? Give one example.
Answer:
The disease which affects the health of human population all over the world is called a pandemic disease. For example, AIDS.
Class 9 Biology Chapter 13 Extra Questions Question 3.
Mention the symptoms because of which you will visit a doctor and why?
Answer:
High fever, headache, tiredness, loose motion, cough and cold, loss of appetite and body weight are some of the symptoms for which we will visit a doctor because the doctor would be able to ascertain the disease caused on the basis of the symptoms produced and give medication accordingly.
Class 9 Biology Why Do We Fall Ill Extra Questions Question 4.
Why is DPT called triple antigen?
Answer:
DPT is called as triple antigen as it affects three antigens to produce the antibodies against them. The diseases are: Diphtheria, Pertussis and Tetanus.
Extra Questions From Why Do We Fall Ill Question 5.
What are the symptoms shown by a person if the
(i) lungs get infected?
(ii) stomach is infected?
Answer:
(i) Cough, breathlessness, tiredness are the symptoms produced if the lungs of a person get affected by a disease.
(ii) Loose motion, vomiting and stomachache are the symptoms produced when the stomach of a person gets affected by a disease.
Question 6.
“In our country majority of children are already immune to hepatitis A without giving its vaccine to them.” Justify this statement giving reasons.
Answer:
Majority of the children are already exposed to the hepatitis A virus by the time they are five years old because the water which the children generally drink contains the hepatitis A virus. The immune system thus helps to develop immunity against the virus.
Question 7.
List any four factors that must be taken care of by an individual for keeping good health.
Answer:
The four factors which must be taken care by an individual for keeping good health are:
- Proper nourishing balanced diet
- Clean and hygienic environment
- Good social environment
- Proper sanitation and cleanliness
Question 8.
Why are antibiotics effective against bacteria?
Answer:
Antibiotics block the biochemical pathways of the bacteria which inhibit their growth and kill them. For example: Penicillin blocks the pathway involved in the synthesis of cell wall which protects the bacteria. This inhibits their growth and kills them.
Question 9.
Influenza or common cold spreads faster and is difficult to control. Explain.
Answer:
Influenza and common cold are infectious diseases which are spread through air, so it becomes difficult to control them.
Question 10.
Why are overcrowded and poorly ventilated areas, major factors in the spread of air-borne diseases?
Answer:
In poorly ventilated and overcrowded areas, the little droplets containing air-borne microbes thrown by an infected person on coughing or sneezing, can be easily inhaled by a healthy person standing close by. This can start a new infection in the healthy person. Hence, such areas are major factors in the spread of air-borne diseases.
Question 11.
(a) Name the organ into which the malarial parasite enters after a mosquito bite.
(b) Give two examples of air-borne diseases.
Answer:
(a) The malarial parasite enters the liver of the healthy person after mosquito bite.
(b) Common cold and pneumonia are some air-borne diseases.
Question 12.
What are non-infectious diseases? Give two examples of non-infectious diseases.
Answer:
The diseases which do not spread from one person to the other person in the community are called as non-infectious diseases. They are caused due to internal factors.
Example: Cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, etc.
Question 13.
Identify infectious and non-infectious diseases from the diseases given below: Tuberculosis, goitre, marasmus and typhoid.
Answer:
- Infectious diseases are tuberculosis and typhoid.
- Non-infectious diseases are goitre and marasmus.
Question 14.
Write the symptoms and diseases associated with the following:
(a) when microbes attack the lungs
(b) when the virus enters the liver
Answer:
(a) Tuberculosis may occur when microbes attack the lungs. The symptoms would be persistent cough, blood in sputum, prolonged low fever.
(b) Jaundice may occur when the virus enters the liver. The symptoms would be headache, high fever, loss of appetite and dark yellow coloured urine.
Question 15.
Why does a person suffering from the disease HIV-AIDS dies even due to small infection?
Answer:
The HIV damages the immune system of the person suffering from AIDS. Due to this the body of the person is unable to fight against even the small infections. The immune system of the person becomes very weak and ultimately leads to the death of the person due to several infections.
Why Do we Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions Short Answer Type 2
Question 1.
(a) Define disease.
(b) Explain briefly the two groups of diseases.
Or
Differentiate between infectious and non-infectious diseases.
Answer:
(a) Disease refers to any condition that disturbs the normal functioning of the living organism. It is a condition of disturbed ease when an individual feels uncomfortable.
(b) The two groups of diseases are infectious diseases and the non-infectious diseases.
Infectious diseases:
- These diseases are caused by infectious agents. These can spread from one person to another through some medium or by direct contact.
- Example: Pneumonia, common cold, tuberculosis, etc.
Non-infectious diseases:
- These do not spread form one person to the other person in the community. They are caused due to
- internal factors.
Example: Cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, etc.
Question 2.
What are acute and chronic diseases? Which one of the two is more harmful and why? Give an example in support of your answer.
Answer:
Acute disease:
- The disease which lasts for only very short periods of time is called acute disease.
- They get over soon and do not get much time to affect the health more adversely. Example: Common cold
Chronic disease:
- The disease which can last for a long time, even as much as a lifetime is called chronic disease.
- They have a long-term effect on the health of a person. Example: Elephantiasis
Chronic diseases are more harmful as they persist for a long time and thus adversely affect the general health of the person suffering from them.
Question 3.
Giving reasons, justify that it is difficult to prepare antiviral medicines than antibiotics.
Or
Why is it difficult to prepare anti-viral medicines than antibiotics?
Or
Explain why antibiotics do not work against viruses but work against many group of bacteria.
Answer:
Antibiotics are the chemicals which usually block the biochemical pathways of the bacteria. This inhibits their growth and kills them. But, the viruses do not have their own biochemical pathways as present in the bacteria. Viruses use the host machinery to multiply themselves. So, it becomes difficult to prepare anti-viral vaccines in order to inhibit their growth.
Question 4.
How do diseases spread through air? Name two such diseases.
Answer:
The diseases spread through air when little droplets thrown out by an infected person who sneezes or coughs are inhaled by a healthy person. This results in a new infection in the healthy person.
Example: Common cold, pneumonia and tuberculosis.
Question 5.
Why does a person who has suffered once from small pox cannot suffer with it again?
Answer:
The immune system of our body responds against the disease causing small pox virus when it encounters it for the first time. This interaction is slower and less vigorous, but the immune system remembers the virus specifically. Whenever the immune system encounters the virus after this first response, the interaction is more vigorous and the immune system completely eliminates the virus. Thus, the small pox virus is not able to affect the person who has suffered from it once.
Question 6.
How is the principle of immunisation implemented for eliminating polio?
Answer:
The polio vaccine which is administered to the children in the form of polio drops contains the weakened polio causing pathogen which is not able to cause the disease but enables the immune system of the child to produce antibodies against the polio virus. Subsequent encounter of the child to the polio virus activates the immune system which kills the polio virus and protects the immunised child from the disease. Thus, principle of immunisation helps in eliminating polio.
Question 7.
Give the cause and the remedy of:
(a) Hepatitis
(b) AIDS
(c) Malaria
Answer:

Question 8.
“Being disease free is not the same as being healthy.” Explain the statement by giving an example.
Answer:
Disease refers to any condition that disturbs the normal functioning of the living organism. It is a condition of disturbed ease when an individual feels uncomfortable. Being disease-free is a concept which applies to individual sufferer.
Even a disease free person can be considered as having a poor health if the person is unfit in terms of social and mental health. So, health is a concept which applies to societies and communities.
For example: a disease free person suffering from mental stress and tension cannot be considered as healthy.
Question 9.
A person was bitten by a stray dog. After some days his nature gets irritated, he started fearing water.
(a) Name the disease.
(b) Is there any vaccine available?
(c) Is there any plan of your local authority for the control of this disease?
Answer:
(a) The disease caused due to bite of a stray dog is rabies.
(b) Yes, anti-rabies vaccine is available.
(c) Local authorities have planned immunisation of the stray dogs against the disease.
Question 10.
It was diagnosed that the body of a patient had lost his power of fighting any infection. Name the disease the patient was suffering from. Which microbe is responsible for this disease? Give two ways by which it spreads from one person to another.
Answer:
The disease is called AIDS (Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) and the microbe which is responsible for the disease is a virus called HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus). The ways to control the disease are:
- Creating awareness among people regarding the modes of spread of the disease.
- Use of disposable syringes in hospitals and clinics.
- Avoiding sexual contact with multiple partners.
Question 11.
Give two examples for each of the following:
(a) Acute diseases
(b) Chronic diseases
(c) Infectious diseases
(d) Non-infectious diseases
Answer:
(a) Acute diseases: Common cold, eye flu
(b) Chronic diseases: Tuberculosis (TB), asthma
(c) Infectious diseases: Chicken pox, small pox
(d) Non-infectious diseases: Goitre, Cancer
Question 12.
Name two diseases caused by Protozoans. What are their causal organisms.
Answer:
Malaria is caused by Plasmodium and Kala-azar caused by Leishmania Symptoms of malaria are: high fever and shaking chills that can range from moderate to severe, profuse sweating, headache, nausea, vomiting, etc. Symptoms of Kala-azar are breathing difficulty, recurrent fever and skin sores.
Question 13.
Which bacterium causes peptic ulcers? Who discovered the above pathogen for the first time?
Answer:
Heliobacterium pylori cause peptic ulcers. This pathogen was discovered for the first time by Marshall and Warren.
Question 14.
What is an antibiotic? Give two examples.
Answer:
The chemicals secreted by some microorganisms which can kill the bacteria and other disease causing pathogens are called antibiotic. Example: Penicillin, Streptomycin
Question 15.
Fill in the blanks
(a) Pneumonia is an example of ________ disease.
(b) Many skin diseases are caused by ________
(c) Antibiotics commonly block biochemical pathways important for the growth of ________
(d) Living organisms carrying the infecting agents from one person to another are called ________
Answer:
(a) Communicable
(b) Fungi
(c) Bacteria
(d) Vector
Question 16.
Name the target organs for the following diseases
(a) Hepatitis targets ________
(b) Fits or unconsciousness targets ________
(c) Pneumonia targets ________
(d) Fungal disease targets ________
Answer:
(a) Liver
(b) Brain
(c) Lungs
(d) Skin
Question 17.
Who discovered Vaccine’ for the first time? Name two diseases which can be prevented by using vaccines.
Answer:
Edward Jenner discovered vaccine for the first time. Polio, small pox, typhoid, etc. can be prevented by vaccines.
Question 18.
Fill in the blanks:
(a) ________ disease continues for many days and causes effect the on body.
(b) ________ disease continues for a few days and causes short term effect on the body.
(c) ________ is defined as physical, mental and social well-being and comfort.
(d) Common cold is an ________ disease.
(e) Many skin diseases are caused by ________
Answer:
(a) Chronic, long-term
(b) Acute
(c) Health
(d) Infectious
(e) Fungi
Question 19.
Classify the following diseases as infectious or non-infectious.
(a) AIDS
(b) Tuberculosis
(c) Cholera
(d) High blood pressure
(e) Heart disease
(f) Pneumonia
(g) Cancer
Answer:
(a) infectious
(b) infectious
(c) infectious
(d) non-infectious
(e) non-infectious
(f) infectious
(g) non-infectious
Question 20.
Name any two groups of microorganisms from which antibiotics can be extracted.
Answer:
Bacteria and fungi are the microorganisms from which antibiotics can be extracted.
Question 21.
Name any three diseases transmitted through vectors.
Answer:
Filariasis, Dengue, Chikungunya, Malaria, Kala-azar
Why Do we Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
(a) Give definition of health.
(b) State and explain in brief the four major factors which cause disease.
Answer:
(a) ‘Health’ is defined as a state of physical, emotional, mental and social well being of a person.
(b) The four factors whose non availability or absence can cause disease are:
(i) Proper nourishing food: If the person does not get proper nourishing food and a balanced diet, then disease may affect the person.
(ii) Proper hygienic conditions and cleanliness: If the surroundings are not hygienic and the public cleanliness is ignored in a society, then the individuals living there become more prone to diseases.
(iii) Good social conditions: The society in which the person lives should cater towards a healthy mind set of the members of the society. A bad social environment makes the individuals of the society develop an unhealthy attitude.
(iv) Good economic conditions: Poverty is a major cause of diseases and poor economic conditions increase the chances of spread of diseases in the society due to inadequate food and unhygienic conditions.
Question 2.
(a) Doctors diagnosed that Radha was suffering from HIV-AIDS. List any two methods by which she might have come in contact with the disease. Name the organ affected by this disease.
(b) Why antibiotics cannot be used for its treatment? Justify your answer.
Answer:
(a) AIDS can spread by four ways: Sexual contact, Transfusion of AIDS infected blood, use of infected syringe and from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy or through breast feeding.
(b) Antibiotics block the biochemical pathways of the microorganism in order to inhibit their growth and kill them. But, the viruses do not employ such biochemical pathways of their own. They utilise the host machinery to multiply themselves. So, antibiotics cannot be used for the treatment of the viral diseases like AIDS.
Question 3.
(a) If a person is suffering from jaundice, name the mode of its transmission and the organ affected by the disease.
(b) List one general mode of prevention of jaundice.
(c) It has been observed that despite the availability of the vaccine of Hepatitis A in the market, it may not be necessary to be given to children by the time they are 5 years old. Why?
Answer:
(a) Mode of transmission of Jaundice: Contaminated water Organ affected by Jaundice: Liver
(b) Access to pure drinking water can prevent jaundice.
(c) Most of the children of India are already exposed to the hepatitis A virus through the drinking water and their immune system helps to develop immunity against the disease by the time they are five years old. So, it is not necessary to give them the hepatitis A vaccine.
Question 4.
Give an account of malaria, giving its causative agent, symptoms and control measures.
Answer:
Malaria is a protozoan disease caused by Plasmodium species. It gets transmitted by a vector called as the female Anopheles mosquito. The symptoms of malaria are high fever and body ache. The patient feels chills and shivering at regular time intervals. The disease can be controlled by eliminating the breeding grounds of mosquitoes, using mosquito nets or mosquito repellents at home, taking a dose of quinine medicine as prescribed by the doctor.
Question 5.
(a) Name two air-borne diseases. How does the disease causing microbes spread through air?
(b) How does HIV virus spread from a patient to a healthy person?
(c) How does the immune system of our body function?
Answer:
(a) Common cold, tuberculosis, pneumonia are some air-borne infections. They spread from one person to another when an infected person releases droplets into air while coughing or sneezing and these droplets get inhaled by a healthy person standing close by. The microbes start a new infection in the healthy person.
(b) HIV can spread by the following ways: Sexual contact, transfusion of AIDS infected blood, from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy or through breast feeding, use of infected syringe.
(c) The immune system gets activated on encountering a disease causing microbe or on infection and recruits many cells to the affected tissue by a process called as inflammation. This results in pain, swelling, fever, etc., but ultimately it results in killing the disease causing microbe and prevent spread of infection.
Question 6.
(a) Discuss briefly the principle of immunisation.
(b) Mention any two diseases that can be prevented by immunisation.
Answer:
(a) The process by which immunity or resistance to a disease is developed in an individual by administration of biological preparations called vaccines is known as immunisation. In this process, a harmless or dead pathogen is introduced in the body of the organism by vaccination. The immune system of the organism gets activated and produces antibodies against the pathogen to kill it.
These antibodies remain in the memory of the immune system of the individual and in the case of any subsequent infection by the same microbe, these antibodies act quickly and more vigorously to kill the microbe. In this way, the microbe is not able to infect the person and the person gets immunised against the disease.
(b) Two diseases prevented by immunisation are: Measles and polio. Some other diseases which can be prevented by vaccination are diphtheria, pertusis, whooping cough, hepatitis, tetanus, etc.
Question 7.
Explain giving reasons
(а) Balanced diet is necessary for maintaining healthy body.
(b) Health of an organism depends upon the surrounding environmental conditions.
(c) Our surrounding area should be free of stagnant water.
(d) Social harmony and good economic conditions are necessary for good health.
Answer:
(a) Balanced diet provides raw materials and energy in appropriate amount needed for the proper growth and development of the body. It contains the nutrients like the protein, carbohydrates, fats, minerals etc., in the right amount which helps in the proper growth and functions. This ensures a good health of the individual.
(b) The physical, mental and the social well being of a person is affected by the surrounding environmental conditions. Since, these factors determine the health of a person, we can say that the health of a person depends on the environmental conditions. For example, Unhygienic surroundings as breeding grounds for disease causing organisms and their vectors can harm our health.
(c) Stagnant water is a source of many water-borne diseases and acts as breeding place for many insect vectors which can cause diseases in human beings. So, our surrounding area should be free of stagnant water.
(d) Social harmony ensures that the mental tensions and problems do not surround a person and friendly relations are maintained among the individuals of the society. They strive for the growth and well being of each other and thus better health is maintained in such environment and surroundings. Better economic conditions enable a person to invest more to attain good health by eating nutritive food, ensure protection from diseases, get better medical facilities, etc. So, health of a person is better maintained if economic conditions are good.
Question 8.
What is a disease? How many types of diseases have you studied? Give examples.
Answer:
Any condition that disturbs the normal functioning of the organism or its organs is called a disease. Diseases can be classified as acute, chronic, infectious, non-infectious, etc. The diseases which are for short duration are called acute whereas the diseases which persist for a long time are called chronic diseases, example common cold (acute) and tuberculosis (chronic).
The diseases which can be transmitted from one person to another are called infectious diseases whereas the ones which cannot be transmitted are called non-infectious diseases, example cancer and goitre respectively.
Question 9.
What do you mean by disease symptoms? Explain giving two examples.
Answer:
The physical disturbances or the visual changes which indicate the existence of a disease are called the symptoms of the disease.
Example:
- High fever and chills is a symptom of malaria.
- Appearance of lesions on the skin is a symptom of chickenpox.
Question 10.
Why is the immune system essential for our health?
Answer:
Immune system is essential as it helps our body to fight against disease causing microbes. It protects our body by secreting chemicals called antibodies or other substances which protect us from harmful microbes.
Question 11.
What precautions will you take to justify “prevention is better than cure”?
Answer:
The precautions which can be taken to protect ourselves from the disease are:
- Maintaining personal hygiene as well as clean surroundings.
- Being aware about diseases, their symptqms and the organism which causes then.
- Eating a balanced diet.
- Timely vaccination and regular medical, check-up.
Question 12.
Why do some children fall ill more frequently than others living in the same locality?
Answer:
The reasons due to which some children fall ill more frequently than others living in the same locality can be:
- Poor and inefficient immune system.
- Unhealthy food habits and not taking balanced diet.
- Not maintaining personal hygiene.
Question 13.
Why are antibiotics not effective for viral disease?
Answer:
The mode of action of the antibiotics is blocking the biosynthetic pathways of the bacteria and other microbes. However, viruses do not have such biochemical pathways or have very few biochemical mechanisms of their own, hence viruses are unaffected by antibiotics.
Question 14.
Becoming exposed to or infected with an infectious microbe does not necessarily mean developing noticeable disease. Explain.
Answer:
Becoming exposed to or infected with an infectious microbe does not necessarily mean developing noticeable disease because the immune system becomes active when it encounters a pathogen. If the immune system of the organism is able to ward off the disease causing microbe, then the disease will not occur and the person will remain disease-free. So, a strong immune system can ensure that we do not suffer from diseases even if we are exposed to infectious microbes.
Question 15.
Give any four factors necessary for a person to be healthy.
Answer:
The four factors necessary for a person to be healthy are:
- Proper nourishment and a balanced diet which help to provide a strong immune system.
- Maintaining personal hygiene to protect ourselves from infectious microbes.
- Timely vaccination against various diseases.
- Maintaining community hygiene and clean surroundings will to prevent the incidence of waterborne and the air-borne diseases.
Question 16.
Why is AIDS considered to be a ‘Syndrome’ and not a disease?
Answer:
The causative organism of AIDS is a virus called the HIV which gets transmitted through sexual contact, transfusion of contaminated blood, intravenous syringes used by drug addicts and from a mother suffering with AIDS to her child, spread to lymph nodes all over the body. The virus attacks the immune system of the organism and makes it so weak that it cannot fight against even the minor infections. Due to this even a small cold can develop into pneumonia or minor stomach infection may lead to severe diarrhoea and blood loss in stools.
Ultimately the immune system becomes very weak and leads to the death of the person suffering from AIDS. Many diseases simultaneously develop in such a person, so there is no specific disease symptom but a number of symptoms occur in the person. This group of symptoms are called as ‘syndrome’. So, AIDS is not a disease, it is a syndrome.
Why Do we Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1.
The symptoms seen in a patient are high fever, constipation and stomach pain. A doctor wants to confirm whether the patient is suffering from Amoebiasis or typhoid. How can the doctor confirm it?
Answer:
The doctor can advise the patient to get a widal test done which helps to confirm the presence of typhoid causing microorganism in the body. If typhoid is ruled out then the patient is most likely to suffer from Amoebiasis.
Question 2.
Name the disease:
(a) that spreads by sexual contact but not by casual contact like handshake.
(b) that can be caused by virus, bacteria or protozoa.
(c) that can be caused due to bite of stray dog.
Answer:
(a) AIDS
(b) Diarrhoea
(c) Rabies
Question 3.
A mother who had suffered from chicken pox in her childhood, is now taking care of her child, who is suffering from the same disease. What are the chances of her mother having chicken pox? Explain.
Answer:
The mother will not suffer from chicken pox as she has become immune to chicken pox. During the first infection, her immune system develops antibodies against chicken pox. These antibodies respond with more vigour during the next infection, eliminate the microbe and thus prevent the person from the disease.
Question 4.
Name the disease:
(a) in which the liver of the person is the target.
(b) in which saliva of the infected animal spreads infection.
(c) against which BCG vaccine is given.
(d) for which widal test is done.
(e) in which sexual contact spreads the disease but not the physical contact in form of handshakes or hugging.
Answer:
(a) Jaundice and hepatitis
(b) Rabies
(c) Tuberculosis
(d) Typhoid
(e) AIDS
Question 5.
The immune system of a patient has been damaged by a virus. What is the probable disease which would have led to this effect on the immune system? What are the ways by which the pathogen would have been transferred into the individual?
Answer:
The disease is most likely to be AIDS caused by the HIV virus which damages the immune system of the person.
AIDS can be spread in four ways: Sexual contact, transfusion of AIDS infected blood, from an infected i mother to her baby during pregnancy or through breast feeding.
Question 6.
A patient bitten by a stray animal complained of excessive salivation, restlessness and a fear of water. What can be the probable disease and its cause? How can such disease be treated or controlled?
Answer:
The patient is probably suffering from rabies caused by the rabies virus. The disease can be controlled by ensuring proper vaccination of stray animals like dogs. The disease can be treated by timely administration of anti rabies vaccine.
Question 7.
A patient went to a doctor and complained of having a persistent cough, blood in sputum, breathlessness and loss of body weight. Name the disease and the causative microbe. How is the disease transmitted? Which vaccine is given to develop resistance against the disease?
Answer:
The disease from which the patient is suffering is Tuberculosis (T.B.) and the causative microbe is . a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis.. The disease gets transmitted when a healthy person inhales the droplets released by an infected person on coughing, sneezing or while talking. The vaccine i called BCG is given to develop resistance against the disease.
Question 8.
A child was suffering from loose motions, frequent vomiting, feeling of nausea and watery diarrhoea which led to an excessive loss of fluids from his body. Name the disease and its causative microbe. What measures, can be taken to treat this disease? How can one avoid getting infected by the disease?
Answer:
The person is infected with disease called cholera which is caused by a virus called Vibrio cholerae. The measures which can be taken for treatment of the disease are: Giving ORS-Oral rehydration solution to the patient and giving antibiotics prescribed by the doctor. The disease can be avoided by eating clean and hygienic food and timely immunisation against the disease.
Why Do we Fall Ill Class 9 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1.
An HIV infected employee was dismissed from service by the employer. The colleagues of the employee in the office intervened and convinced the boss of the company to reinstate the services of the employee as HIV is not transmitted by mere physical contact. They told the employer that such person should not be made a victim of social stigma on contracting the disease.
(i) Name the disease which the employee was suffering from.
(ii) How does the disease get transmitted from one person to another?
(iii) What values are shown by the colleagues of the employee?
Answer:
(i) AIDS: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.
(ii) The disease gets transmitted by four ways:
(a) Sex with multiple partners.
(b) Transfusion of HIV contaminated blood.
(c) Use of HIV contaminated syringe.
(d) From infected mother to her child at the time of delivery of the baby.
(iii) The values shown by the colleague of the employee are: awareness, helpfulness, empathy and knowledge about their rights.
Question 2.
Rohit and’ Mayank are roommates in the hostel. Mayank is an avid reader of science magazines and articles. Mayank immediately took Rohit to a doctor when Rohit complained of tiredness, nausea, vomiting and pale eyes. What is the probable disease Rohit was suffering from? Name the causative microbe. What values are shown by Mayank?
Answer:
The symptoms of Rohit show that he was suffering from Jaundice. The microbe which causes the disease is virus. The values shown by Mayank are awareness, scientific temper, concern for others and helpful nature.
Question 3.
The parents of a new bom child were afraid to take their child for vaccination as someone told them that the vaccine contains harmful germs. However, when they consulted Dr. Shweta, she listened to them patiently and then cleared their doubts about vaccines. She told them that the vaccines only contain dead germs or inactivated germs which do not cause the disease. How do the dead germs in vaccines protect from diseases? What are the values shown by Dr. Shweta?
Answer:
The dead or the inactivated germs in the vaccines stimulate our immune system to develop antibodies against the disease causing microbes present in the vaccine and store the antibodies for action during any subsequent infection. In this way the vaccines provide immunity to the person against the disease. The values shown by Dr. Shweta are concern for others, helpfulness and patience.
Question 4.
Megha’s told her that he had been feeling tired, breathless, had persistent cough and blood was coming out in his sputum. She told him that these are symptoms of an infectious disease and advised him to consult a doctor. She also took him for diagnostic tests prescribed by the doctor. The helps was diagnosed as suffering from an infectious disease. He took the medicines prescribed by the doctor and got cured of the disease.
(i) Name the most likely disease and microbe from which the help suffered?
(ii) How does the disease get transmitted?
(iii) What are the values depicted by Megha?
Answer:
(i) The disease is most likely Tuberculosis caused by bacteria.
(ii) The disease gets transmitted when a healthy person inhales the droplets released into air by an infected person while coughing or sneezing.
(iii) Megha shows a helpful nature, scientific attitude, concern for others and sympathetic nature.
Question 5.
The municipality of an area advised the residents of the area to eliminate the breeding grounds of mosquitoes and use mosquito repellents in homes to avoid a disease which results in chills and recurring fever in patients. The children of the area formed teams which inspected the surrounding areas and put few drops of oil or petrol on stagnant water pools of the area.
(i) Name the disease, causative organism and the vector of the disease which was spreading in the area.
(ii) How do the drops of petrol or oil on stagnant water prevent the spread of the disease?
(iii) What are the values shown by the students?
Answer:
(i) The disease is Malaria caused by Plasmodium and transmitted by the vector female Anopheles mosquito.
(ii) The drops of oil or petrol in the stagnant water pools kill the larvae of the mosquito as they will not be able to breathe.
(iii) The values shown by the children are: public good, helpful attitude, scientific temper and work for social good.