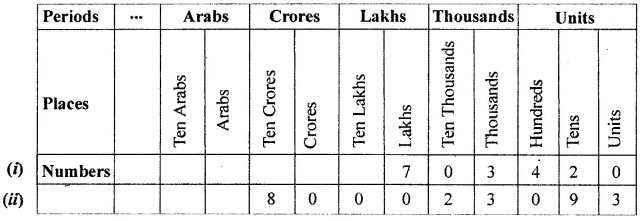
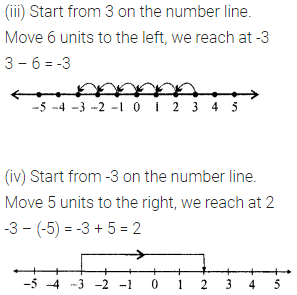
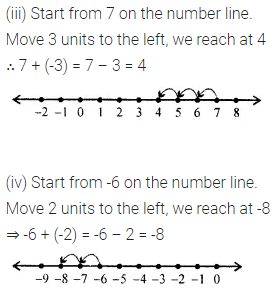
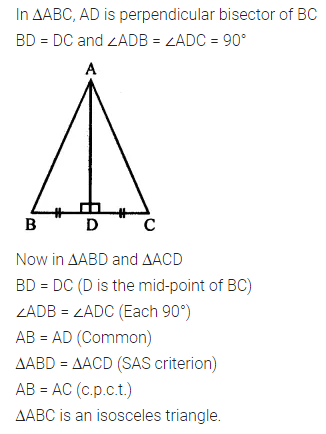
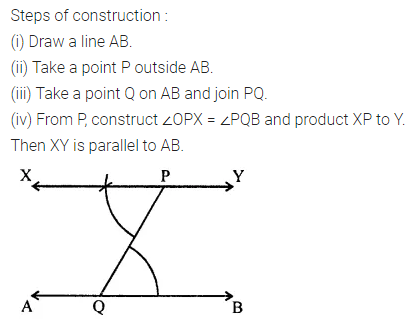
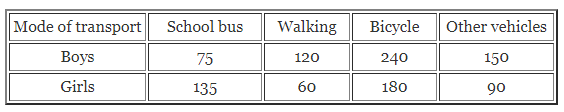
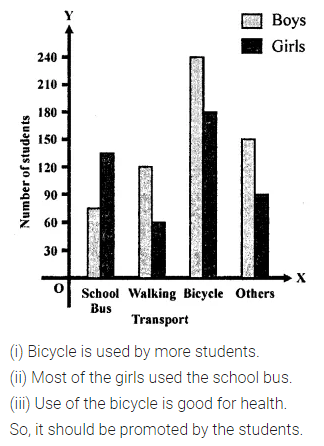
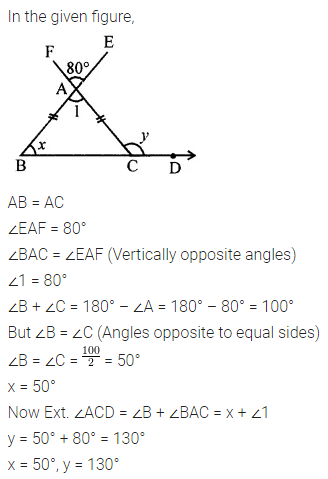
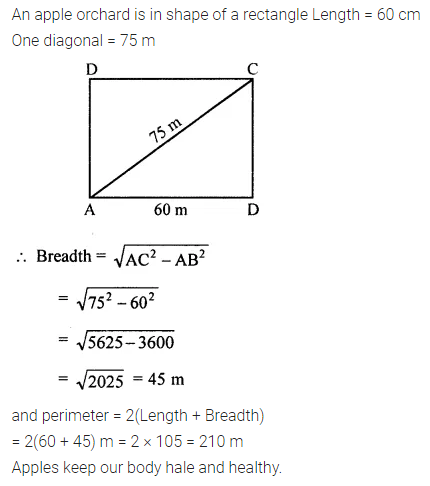
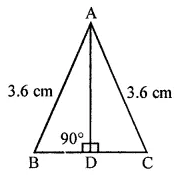
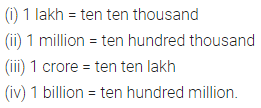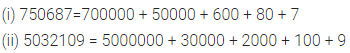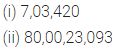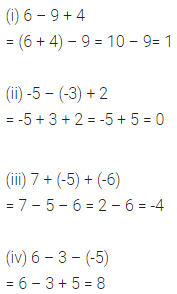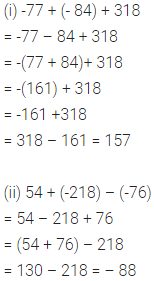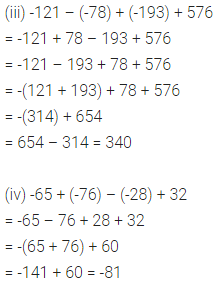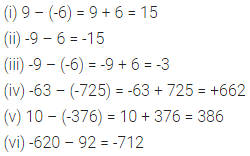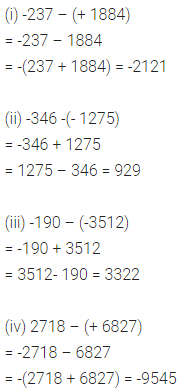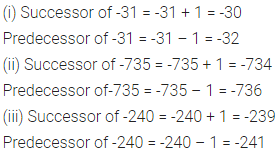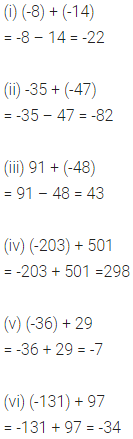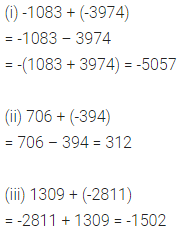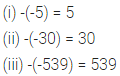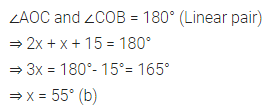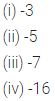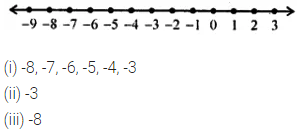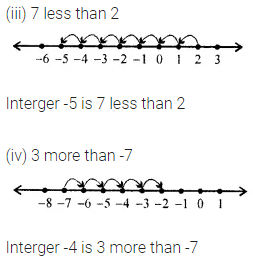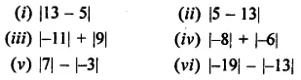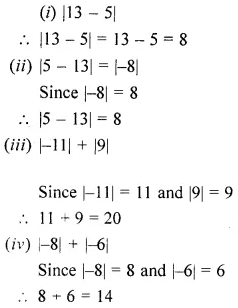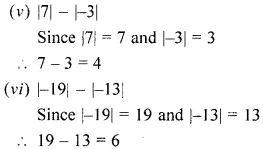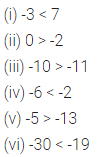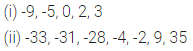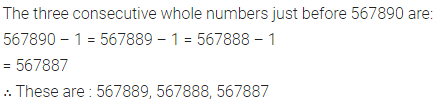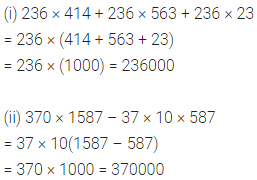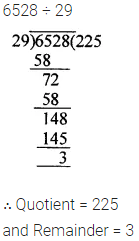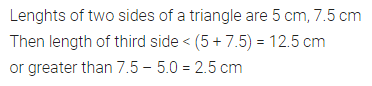ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions Chapter 3 Integers Objective Type Questions for ICSE Understanding Mathematics acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 6 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 3 Integers Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) The absolute value of 0 is ………
(ii) The sum of two negative integers is always a ……….. integer.
(iii) The smallest positive integer is ……………
(iv) The largest negative integer is ………….
(v) 17 + ………….. = 0
(vi) ……………. -15 = -10
(vii) The predecessor of -99 is …………
Solution:

Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) The sum of a positive integer and a negative integer is always a negative integer.
(ii) Zero is an integer.
(iii) The sum of an integer and its negative is always zero.
(iv) The sum of three integers can never be zero.
(v) |-7| < |-3|.
(vi) -20 is to the left of -21 on the number line.
(vii) The successor of -29 is -30.
(viii) 0 is greater than every negative integer.
(ix) The difference of two integers is always an integer.
(x) Additive inverse of a negative integer is always a positive integer.
Solution:

Question 3.
State whether the following statements are true or false. If a statement is false, write the corresponding correct statement.
(i) -8 is to the right of-10 on the number line.
(ii) -100 is to the right of -50 on the number line.
(iii) Smallest negative integer is -1.
(iv) -26 is greater than -25.
(v) -187 is the predecessor of-188.
Solution:

Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (4 to 17):
Question 4.
The integer which is 5 more than -2 is
(a) -7
(b) -3
(c) 3
(d) 7
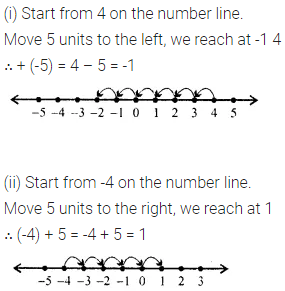
Solution:
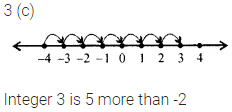
Question 5.
The number of integers between -1 and 1 is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Solution:
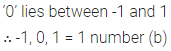
Question 6.
The number of integers between -3 and 2 are
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Solution:
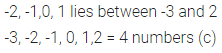
Question 7.
The number of whole numbers between -6 and 6 is
(a) 11
(b) 10
(c) 6
(d) 5
Solution:

Question 8.
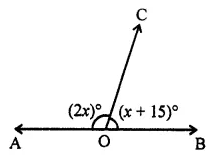
The greatest integer lying -10 and -15 is
(a) -10
(b) -11
(c) -14
(d) -15
Solution:
![]()
Question 9.
The smallest integer lying between -10 and -15 is
(a)-10
(b) -11
(c) -14
(d) -15
Solution:
![]()
Question 10.
Which of the following statement is true?
(a) |10 – 4| = |10| + |—4|
(b) Additive inverse of -5 is 5
(c) -1 lies on the right of 0 on the number line
(d) -7 is greater than -3
Solution:
![]()
Question 11.
Which of the following statement is false?
(a) -20 – (-5) = -15
(b) |-18| > |-13|
(c) 23 + (-31) = 8
(d) Every negative integer is less than 5
Solution:
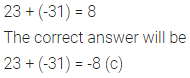
Question 12.
Which of the following statements is false?
(a) (-3) + (-11) is an integer
(b) (-19)+ 13 = 13 +(-19)
(c) (-15) + 0 = -15 = 0 + (-15)
(d) Negative of-7 does not exist
Solution:
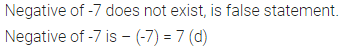
Question 13.
If the sum of two integers is -17 and one of them is -9, then the other is
(a) 8
(b) -8
(c) 26
(d) -26
Solution:
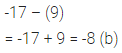
Question 14.
On subtracting -7 from -4, we get
(a) 3.
(b) -3
(c) -11
(d) none of these
Solution:
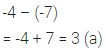
Question 15.
(-12) + 17 – (-10) is equal to
(a) -5
(b) 5
(c) 15
(d) -15
Solution:
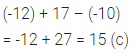
Question 16.
Which of the following statements is true?
(a) -13 > – 8 – (-6)
(b) -5 – 4 > -12 + 2
(c) (-8) – 3 = (-3) – (-8)
(d) (-15) – (-22) < (-22) – (-15)
Solution:

Question 17.
The statement “when an integer is added to itself, the sum is less than the integer” is
(a) always true
(b) never true
(c) true only when the integer is negative
(d) true when the integer is zero or positive
Solution:
![]()
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
Question 1.
Can the sum of successor and predecessor of an integer be an odd integer?
Solution:

Question 2.
What is the sum of all integers from -500 to 500?
Solution:
![]()
Question 3.
Find two positive integers such that their product is 1,00,000 and none of them contains 0 as a digit.
Solution: