Students can also read MCQ Questions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 7 Lifelines of the National Economy Questions with Answers hope will definitely help for your board exams. https://ncertmcq.com/tag/lifelines-of-the-national-economy-class-10-mcqs-questions/
Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 MCQ With Answers
Geography Class 10 Chapter 7 MCQs On Lifelines of the National Economy
Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
Which of the following two stations did the first train of India steam off to and when?
(a) Kolkata to Raniganj, 1874
(b) Mumbai to Thane, 1853
(c) Mumbai to Ahmedabad, 1854
(d) Chennai to Arkonam, 1856
Answer:
(b) Mumbai to Thane, 1853
Class 10 Geography Chapter 7 MCQ With Answers Question 2.
Which of the following modes of transport would one be able to find on the higher dissected terrain of mountainous regions like the Himalayas?
(a) Railways
(b) Roadways
(c) Inland waterways
(d) Airways
Answer:
(b) Roadways
Lifelines Of National Economy MCQ Question 3.
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option:
………………… is the oldest artificial port and the second most important port of the country.
(a) Mumbai port
(b) Kandla port
(c) Chennai port
(d) Ennore port
Answer:
![]()
Life Lines Of National Economy Class 10 MCQ Question 4.
Which of the following networks of pipelines bring mineral oil to the refinery of Barauni and the petrochemical complex of Haldia?
(a) Pipeline from Upper Assam oilfields to Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh)
(b) Pipeline from Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar
(c) Hazira-Vijaipur-Jagdishpur Pipeline
(d) Pipeline from Mumbai High to Goa and then to Trombay
Answer:
(a) Pipeline from Upper Assam oilfields to Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh)
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Geography Chapter 7 Question 5.
Which one of the following groups of cities is connected by the National Highway No. 1?
(a) Delhi – Amritsar
(b) Delhi – Kolkata
(c) Delhi – Mumbai
(d) Varanasi – Kanyakumari
Answer:
(a) Delhi – Amritsar
Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 MCQ Questions And Answers Question 6.
Which two extreme locations are connected by the North-South Corridor?
(a) Amritsar and Tuticorin
(b) Srinagar and Thiruvananthapuram
(c) Srinagar and Tuticorin
(d) Srinagar and Kanyakumari
Answer:
(d) Srinagar and Kanyakumari
Explanation: The North South Corridor is the one of the Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways that connects the mega cities of India.
MCQ Of Lifelines Of National Economy Question 7.
Which one of the following is not an advantage of pipeline transportation?
(a) Pipelines are used for transporting crude oil and gas from fields to refineries.
(b) Solids can be transported in slurry form through pipelines.
(c) Pipelines rule out trans-shipment losses or delays.
(d) Pipeline requires a lot of capital and extra maintenance.
Answer:
(d) Pipeline requires a lot of capital and extra maintenance.
Explanation: Pipelines do not need any extra maintenance. Its initial cost of laying is high.
MCQ On Lifelines Of National Economy Question 8.
……………… is considered as the First Class Mail by the Indian postal network.
(a) Cards and envelopes
(b) Registered periodicals
(c) Magazines and New Books
(d) Registered newspapers packets
Answer:
(a) Cards and envelopes
Class 10 Lifelines Of National Economy MCQ Question 9.
National Highways are constructed and maintained by
(a) NHAI
(b) CPWD
(c) SPWD
(d) BRO
Answer:
(b) CPWD
Explanation: National Highways link extreme parts of the country. These are the primary road systems.
Ncert Class 10 Social Science Objective Questions Question 10.
Which one of the following is the oldest port of the eastern coast of India?
(a) Kolkata (Haldia)
(b) Visakhapatnam
(c) Tuticorin
(d) Chennai (Madras)
Answer:
Lifelines Of National Economy Class 10 One Mark Questions Pdf Question 11.
Pawanhans Helicopters Ltd. Provides helicopter services to which of the following in its off-shore operations?
(a) Oil India Ltd.
(b) Oil and Natural Gas Commission
(c) NTPC
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Oil and Natural Gas Commission
![]()
Class 10 Social Science MCQ Question 12.
Air travel is not within the reach of the common people. It is only in which part of the country that special provisions are made to extend the services to the common people?
(a) Northern states .
(b) North-eastern states
(c) North-western states
(d) Coastal states
Answer:
Social Science MCQ Class 10 Question 13.
Which of the following is an example of an inland riverine port in India?
(a) Chennai
(b) Kolkata
(c) Tuticorin
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Kolkata
Explanation: Kolkata port serves a very Large and rich hinterland of Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Social Science With Answers Question 14.
Which two of the following extreme locations are connected by the east-west corridor?
(a) Mumbai and Nagpur
(b) Silchar and Porbandar
(c) Mumbai and Kolkata
(d) Nagpur and Siliguri [Diksha]
Answer:
Social MCQ Class 10 Question 15.
Which of the following is the longest National Waterway of India?
(a) The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia
(b) The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri
(c) The West-Coast Canal in Kerala
(d) None of these
Answer:
Question 16.
Which of the following ports was planned with a view to decongesting the Mumbai port?
(a) Kandla port
(b) Paradip port
(c) Tuticorin port
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru port
Answer:
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru port
Question 17.
Which one of the following is the longest National Highway?
(a) NH-7
(b) NH-8
(c) NH-1
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) NH-7
Explanation: National Highway-7 is the longest and traverses 2369 km between Varanasi and Kanyakumari via Jabalpur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Bangalore and Madurai while Delhi and Mumbai are connected by National Highway-8. The historical Sher Shah Suri Marg is called National Highway No.l connects Delhi and Amritsar.
![]()
Question 18.
Which one of the following places is NOT associated with oil refineries?
(a) Mathura
(b) Barauni
(c) Panipat
(d) Surat
Answer:
(d) Surat
Question 19.
Which of the following mode of transport is fuel-efficient and environment-friendly?
(a) Roadways
(b) Railways
(c) Airways
(d) Waterways
Answer:
(d) Waterways
Explanation: It’s the cheapest and most fuel-efficient type of transport as the friction of water is far less than that of land nor do they require road construction. Through waterways, heavy and bulky goods can be transported to distant lands.
Question 20.
Which of the following port is located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbour?
(a) Tuticorin
(b) Kochi
(c) Marmagao
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Kochi
Related Theory
Kochi is the extreme south-western port of India.
Question 21.
Which of the following organisations is responsible for construction and maintenance of the strategic roads in India?
(a) CPWD
(b) SPWD
(c) NHAI
(d) BRO
Answer:
(d) BRO
Explanation: Border Road Organisation (BRO) was established in 1960.
Question 22.
Which one of the following states is NOT connected with the HVJ pipeline?
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) Gujarat
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer:
(c) Maharashtra
![]()
Question 23.
Which one of the following major ports has been developed to decongest Kolkata port?
(a) Kandla
(b) Haldia
(c) Paradwip
(d) Marmagao
Answer:
(b) Haldia
Explanation: Haldia port was developed as a subsidiary port, in order to relieve growing pressure on the Kolkata port

Question 24.
Arrange the following options in the correct sequence:
(i) Science and technology helped improve transport.
(ii) Rapid moving and effiicient transport brought a change.
(iii) Transport and trade were restricted to a limited area.
(iv) Improved communication played a major role in this change.
Options:
(a) (i)—(ii)—(iii)—(iv)
(b) (i)—(iii)—(ii)—(iv)
(C) (iii)—(i)—(i0—(iv)
(d) (iv)—(iii)—(ii)—(i)
Identify the following on basis of the hints given.
Question 25.
identify the type of transport:
(1) Fastest mode of transport
(2) Can cover all dissected and undulating terrains
(3) Especially famous in the North Easterm states
Answer:
Airways
Question 26.
Identify the industry:
(1) Industry in India has grown substantially over the last three decades.
(2) 15 million people are directly engaged in the tourism industry.
(3) The industry promotes national integration, provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
Answer:
Tourism
Question 27.
Identify the port:
(1) It is located on the Western Coast.
(2) It is the premier iron ore exporting sea port of the country.
Answer:
Marmagao Port
Correct and Rewrite/ True-False
State whether the following statements are True or False. If false, correct the statement.
Question 28.
Roadways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
Answer:
False
Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
Question 29.
India’s first train steamed off from Mumbai to Thane in 1853 covering a distance of 34 km.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 30.
Akashwani, the national television channel of India is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world.
Answer:
False
Doordarshan.the national television channel of India is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world.
Fill in the blanks/tables with suitable information:
Question 31.
Television is a means of …………………..
Answer:
mass communication
Question 32.
…………….. is the extreme south-western port located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbour.
Answer:
Kochi
Question 33.
…………… a Government of India undertaking constructs and maintains roads in the bordering areas of the country.
Answer:
Question 34.
Complete the following table with appropriate terms in place of (a) and (b).
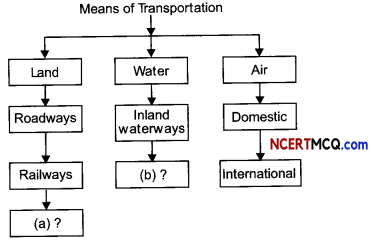
Answer:
(a) Pipelines
(b) Overseas Waterways
Question 35.
The is the largest public sector undertaking in India.
Answer:
Indian Railways government and hence it is a public sector enterprise. Railways in India bind the economic life of the country as well as accelerate the development of industries and agriculture.
Question 36.
…………. is the deepest, land-locked and well-protected port of India.
Answer:
Vishakhapatnam
Related Theory:
Railways employ a very large number of people in the country. It is monitored and run by the
![]()
Question 37.
Fill the blanks in the table with required information:

Answer:
Match the Columns Choose the correct pairs:
Question 38.
Match the following roads from column A with the organisations responsible for their construction and maintenance from column B:
| Column A (Types of Road) | Column B (Organisation) |
| (a) Super Highways | (i) Zila Parishad |
| (b) National Highways | (ii) State Public Works Department |
| (c) State Highways | (iii) Central Public Works Department |
| (d) District Roads | (iv) National Highway Authority of India |
Answer:
| Column A (Types of Road) | Column B (Organisation) |
| (a) Super Highways | (iv) National Highway Authority of India |
| (b) National Highways | (iii) Central Public Works Department |
| (c) State Highways | (ii) State Public Works Department |
| (d) District Roads | (i) Zila Parishad |
Question 39.
Match the following national highways from column A with the places/cities connected by them from column B:
| Column A (National Highways) | Column B (Places/Cities Connected) |
| (a) NH-1 | (i) Varanasi and Kanyakumari |
| (b) NH-8 | (ii) Most parts of Rajasthan |
| (c) NH-7 | (iii) Delhi and Mumbai |
| (d) NH-15 | (iv) Delhi and Amritsar |
Answer:
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Geography Chapter 7
In each of following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason (R). Select the correct answers to codes (a), (b), (c) or (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Question 40.
Assertion (A): There is a vast potential for development of tourism in all parts of the country.
Reason (R): There is a lot of scope in various fields of tourism.
Answer:
Question 41.
Assertion (A): No country can survive without international trade.
Reason (R): Resources are not space bound.
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
Explanation: Resources are space bound and thus a country has to import and export resources to be able to fulfill their needs.
![]()
Question 42.
Assertion (A): Air travel has made access easier.
Reason (R): No other mode of transport could travel across regions in the presence of big rivers, dissected relief, dense forests and frequent floods and international frontiers, etc. in the absence of air transport.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 43.
Assertion (A): 60 per cent of the country’s trade volume (68 per cent in terms of value) is moved by sea.
Reason (R): Seaways carry heavy loads to farther distances at very affordable rates.
Answer:
Question 44.
Assertion (A): The railways have become more important in our national economy than all other means of transport put together.
Reason (R): It carries the most loads and maximum number of people across the country.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(Competency Based Questions (CBQs))
Question 1.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Goods and services do not move from supply locales to demand locales on their own. The movement of these goods and services from their supply locations to demand locations necessitates the need for transport. Some people are engaged in facilitating these movements. These are known to be traders who make the products come to the consumers by transportation. Thus, the pace of development of a country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movement over space. Therefore, efficient means of transport are prerequisites for fast development.
Movement of these goods and services can be over three important domains of our earth i.e. land, water and air. Based on these, transport can also be classified into land, water and air transport expanded far and wide. Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport. Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of equally developed communication systems. Therefore, transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) Which of the following groups are involved in transport of goods and services from one nation to another?
(a) Entrepreneurs
(b) Labourers
(c) Traders
(d) Farmers
Answer:
(c) Traders
Explanation: Traders contribute to movement and transfer of goods from one place to another.
(B) Which of the following does not decide the pace of development of the country?
(a) Production of goods
(b) Production of Services
(c) Economy of the country
(d) Number of castes in a country
Answer:
(d) Number of castes in a country
(C) Which of the following supports the statement, “transport, communication and trade are complementary to each other”?
(a) World has been converted into a large village.
(b) There is fast moving transport.
(c) Transport and communication together help the trade to flourish.
(d) Transport cannot exist without trade.
Answer:
(c) Transport and communication together help the trade to flourish.
(D) Which of the following necessitates the need of transport?
(a) Communication
(b) Trade
(c) Education
(d) Lifestyle
Answer:
![]()
Question 2.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
In India, roadways have preceded railways. They still have an edge over railways in view of the ease with which they can be built and maintained. The growing importance of road transport vis-a-vis rail transport is rooted in the following reasons; construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines, roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography, roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas, Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively smaller amount of goods over short distances, it also provides door-to-door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower, road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a Link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
In India, roads are classified in the following six classes according to their capacity.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) Which of the following types of roads received special impetus under the Pradhan Mantri Grameen SadakYojana?
(a) National Highways
(b) State Highways
(c) Rural Roads
(d) District Roads
Answer:
(c) Rural Roads
(B) Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as:
(a) National highways
(b) District roads
(c) State highways
(d) Other roads
Answer:
(b) District roads
(C) Which of the following features about Roadways makes it most popular?
(I) Roads can traverse comparatively more dissected and undulating topography.
(II) Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes.
(III) Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons.
(IV) Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport.
(a) (I) only
(b) (II) only
(c) (II) & (III) only
(d) (I), (II), (III) & (IV)
Answer:
(D) In India, has preceded over railways.
(a) Waterways
(b) Airways
(c) Roadways
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(c) Roadways
Question 3.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Since the ancient period, India was one of the seafaring countries. Its seamen sailed far and near, thus, carrying and spreading Indian commerce and culture. Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods. It is a fuel-efficient and environment friendly mode of transport. India has inland navigation waterways of 14,500 km in length. Out of these only 5685 km are navigable by mechanised vessels.
The following waterways have been declared as the National Waterways by the Government The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km)-N.W. No.1
- The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km)-N.W. No.2
- The West-Coast Canal in Kerala (Kottapuram-Kollam, Udyogamandal and Champakkara canals-205 km) – N.W. No.3
- Specified stretches of Godavari and Krishna rivers along with Kakinada Puducherry stretch of canals (1078 km) – N.W. No.4
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) The National Waterway No. 1 is navigable between which of the following places?
(a) Between Sadiya and Dhubri
(b) Between Allahabad and Haldia
(c) Between Kottapuram and Komman
(d) Between Udyogamandal and Champakkara
Answer:
(b) Between Allahabad and Haldia
(B) Which of the following is the cheapest mode of transportation?
(a) Airways
(b) Waterways
(c) Roadways
(d) Railways
Answer:
(c) Waterways
(C) Fill in the blank with an appropriate option:
………………….. channel covers Kerala.
(a) West Coast Canal
(b) East Coast Canal
(c) North Coast Canal
(d) South Coast Canal
Answer:
(a) West Coast Canal
(D) Which of the following National Waterways is the longest waterway?
(a) The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia
(b) The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri
(c) The West-Coast Canal
(d) Specified stretches of Godavari and Krishna rivers along with Kakinada Puducherry stretch of canals.
Answer:
(a) The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia
Explanation: The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km)-N.W. No.1
Related Theory
- The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km)-N.W. No.2
- The West-Coast Canal in Kerala (Kottapurma-Kollam, Udyogamandal and Champakkara canals-205 km) – N.W. No.3
- Specified stretches of Godavari and Krishna rivers along with Kakinada Puducherry stretch of canals (1078 km) – N.W. No.4
![]()
Question 4.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
With a long coastline of 7,516.6 km, India is dotted with 12 major and 200 notified non¬majors (minor/intermediate) ports. These major ports handle 95 per cent of India’s foreign trade. Kandla in Kuchchh was the first port developed soon after Independence to ease the volume of trade on the Mumbai port, in the wake of loss of Karachi port to Pakistan after the Partition. Kandla also known as the Deendayal Port, is a tidal port. It caters to the convenient handling of exports and imports of highly productive granary and industrial belt stretching across the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) The New Mangalore port caters to the export of iron ore concentrates from:
(a) Chhota Nagpur Plateau Iron Ore Mines
(b) Kudremukh Iron Ore Mines
(c) Amarkantak Iron Ore Mines
(d) Jhalaabai Mines
Answer:
(b) Kudremukh Mines
Explanation: New Mangalore port. Located in Karnataka caters to the export of iron ore concentrates from Kudremukh mines.

(B) Which of the following ports did India lose to Pakistan after partition?
(a) Kandla
(b) Karachi
(c) Mumbai
(d) Haldia
Answer:
(C) Which of the following statements defines a tidal port?
(a) Tidal ports are the ports in which the water level within the port is subject to change with the ocean tides.
(b) Tidal ports are the ports in which the water level within the port is subject to change with floods.
(c) Tidal ports are the ports in which ocean water changes with sea breeze and land breeze.
(d) Tidal ports are the ports where ravines are formed on the beach.
Answer:
(D) Which of the following ports specialises in the Iron Ore exports?
(a) Tuticorin Port
(b) Chennai Port
(c) Paradip Port
(d) Kandla Port
Answer:
(c) Paradip Port
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which authority maintains and lays National Highways?
Answer:
The Central Public Works Department (CPWD) maintains and Lays National Highways.
Question 2.
What is the new arrival on the transportation map of India?
Answer:
Question 3.
What is the major objective to develop superhighways?
Answer:
One major objective of developing superhighways is to connect the megacities of India with each other.
![]()
Question 4.
Why was Jawaharlal Nehru port developed?
Answer:
Jawaharlal Nehru port was developed to decongest the Mumbai Port.
Question 5.
Why was the Haldia port set up?
Answer:
Haldia port was established to help decongest the Kolkata Seaport.
Question 6.
Suggest any one way to improve the postal system in India?
Answer:
A robust feedback system can be put in place to ensure a better customer satisfaction.
Question 7.
Name the oldest artificial sea port of India.
Answer:
Question 8.
Name the organisation which undertakes construction and maintenance of border roads.
Answer:
‘Border Roads Organisation (BRO)’ undertakes construction and maintenance of ‘border roads’.
Related Theory
Border roads are the roads constructed along the northern and north-eastern borders of our country. Border Roads Organisation (BRO) was set up in 1960 by the government of India. BRO is regarded as a symbol of nation building, national integration and an inseparable component in maintaining the security of the country.
Question 9.
Name the deepest, landlocked and well protected sea port of India.
Answer:
Vishakhapatnam is the deepest, landlocked and well protected port of India.
Related Theory
Vishakhapatnam port was originally conceived as an outlet for iron are exports.
![]()
Question 10.
Name the state related to National Waterways No. 3.
Answer:
Kerala is the state related to NationaL Waterways No. 3.
Related Theory
Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods. It is a fuel-efficient and environment-friendly mode of transport. India has inland navigation waterways of 14,500 km in length.
Question 11.
Suggest any one way to improve pilgrimage tourism through Indian Railways.
Answer:
Question 12.
Name the river which is related to National Waterway No. 1.
Answer:
The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km) is related to National Waterways No. 1.
Question 13.
Name the new port that was developed to relieve the growing pressure on the Mumbai port.
Answer:
Kandla Seaport was developed to relieve growing pressure on the Mumbai port.
Question 14.
Name the largest public sector undertaking in India.
Answer:
The Indian Railways
Question 15.
Name the sea port that was developed to relive the growing pressure on the Kolkata port.
Answer:
Haldia Seaport was developed to relive the growing pressure on the KoLkata port.
![]()
Question 16.
Name any two terminal cities connected with National Highway No.7.
Answer:
Question 17.
Name one inland riverine port.
Answer:
Kolkata Port is an inland riverine port.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science with Answers
Class 10 Social Science Geography MCQ:
