Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Maths MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 MCQ With Answers
Maths Class 11 Chapter 3 MCQs On Trigonometric Functions
MCQ On Trigonometry For Class 11 Pdf Question 1.
The value of cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × cos (x + y) is
(a) sin (x + y)
(b) sin² (x + y)
(c) sin³ (x + y)
(d) sin4 (x + y)
Answer
Answer: (b) sin² (x + y)
Hint:
cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × cos(x + y)
{since cos(x + y) = cos x × cos y – sin x × sin y }
= cos² x + cos² y – 2cos x × cos y × (cos x × cos y – sin x × sin y)
= cos² x + cos² y – 2cos² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y
= cos² x + cos² y – cos² x × cos² y – cos² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y
= (cos² x – cos² x × cos² y) + (cos² y – cos² x × cos² y) + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y
= cos² x(1- cos² y) + cos² y(1 – cos² x) + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y
= sin² y × cos² x + sin² x × cos² y + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y (since sin² x + cos² x = 1 )
= sin² x × cos² y + sin² y × cos² x + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y
= (sin x × cos y)² + (sin y × cos x)² + 2cos x × cos y × sin x × sin y
= (sin x × cos y + sin y × cos x)²
= {sin (x + y)}²
= sin² (x + y)
Trigonometry MCQ Class 11 Question 2.
If a×cos x + b × cos x = c, then the value of (a × sin x – b²cos x)² is
(a) a² + b² + c²
(b) a² – b² – c²
(c) a² – b² + c²
(d) a² + b² – c²
Answer
Answer: (d) a² + b² – c²
Hint:
We have
(a×cos x + b × sin x)² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b²
⇒ c² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b²
⇒ (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² – c²
Trigonometry Class 11 MCQ Question 3.
If cos a + 2cos b + cos c = 2 then a, b, c are in
(a) 2b = a + c
(b) b² = a × c
(c) a = b = c
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 2b = a + c
Hint:
Given, cos A + 2 cos B + cos C = 2
⇒ cos A + cos C = 2(1 – cos B)
⇒ 2 cos((A + C)/2) × cos((A-C)/2 = 4 sin²(B/2)
⇒ 2 sin(B/2)cos((A-C)/2) = 4sin² (B/2)
⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2sin (B/2)
⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2cos((A+C)/2)
⇒ cos((A-C)/2) – cos((A+C)/2) = cos((A+C)/2)
⇒ 2sin(A/2)sin(C/2) = sin(B/2)
⇒ 2{√(s-b)(s-c)√bc} × {√(s-a)(s-b)√ab} = √(s-a)(s-c)√ac
⇒ 2(s – b) = b
⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b
⇒ a + c – b = b
⇒ a + c = 2b
Trigonometric Functions Class 11 MCQ Question 4.
The value of cos 5π is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -1
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) -1
Hint:
Given, cos 5π = cos (π + 4π) = cos π = -1
Class 11 Trigonometry MCQ Questions Question 5.
In a triangle ABC, cosec A (sin B cos C + cos B sin C) equals
(a) none of these
(b) c/a
(c) 1
(d) a/c
Answer
Answer: (c) 1
Hint:
Given cosec A (sin B cos C + cos B sin C)
= cosec A × sin(B+C)
= cosec A × sin(180 – A)
= cosec A × sin A
= cosec A × 1/cosec A
= 1
Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 MCQ With Answers Question 6.
If the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5, then the ratio of the greatest side to the smallest side is
(a) 4 : (√5 – 1)
(b) 5 : 4
(c) (√5 – 1) : 4
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 4 : (√5 – 1)
Hint:
Given, the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5
⇒ x + 4x + 5x = 180
⇒ 10x = 180
⇒ x = 180/10
⇒ x = 18
So, the angle are: 18, 72, 90
Since a : b : c = sin A : sin B : sin C
⇒ a : b : c = sin 18 : sin 72 : sin 90
⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1)/4 : {√(10 + 2√5)}/4 : 1
⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1) : {√(10 + 2√5)} : 4
Now, c /a = 4/(√5 – 1)
⇒ c : a = 4 : (√5 – 1)
MCQ On Trigonometry For Class 11 Pdf Download Question 7.
The value of cos 180° is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -1
(d) infinite
Answer
Answer: (c) -1
Hint:
180 is a standard degree generally we all know their values but if we want to go theoretically then
cos(90 + x) = – sin(x)
So, cos 180 = cos(90 + 90)
= -sin 90
= -1 {sin 90 = 1}
So, cos 180 = -1
MCQ Of Trigonometry Class 11 Question 8.
The perimeter of a triangle ABC is 6 times the arithmetic mean of the sines of its angles. If the side b is 2, then the angle B is
(a) 30°
(b) 90°
(c) 60°
(d) 120°
Answer
Answer: (b) 90°
Hint:
Let the lengths of the sides if ∆ABC be a, b and c
Perimeter of the triangle = 2s = a + b + c = 6(sinA + sinB + sinC)/3
⇒ (sinA + sinB + sinC) = ( a + b + c)/2
⇒ (sinA + sinB + sinC)/( a + b + c) = 1/2
From sin formula,Using
sinA/a = sinB/b = sinC/c = (sinA + sinB + sinC)/(a + b + c) = 1/2
Now, sinB/b = 1/2
Given b = 2
So, sinB/2 = 1/2
⇒ sinB = 1
⇒ B = π/2
Trigonometry Objective Questions For Class 11 Question 9:
If 3 × tan(x – 15) = tan(x + 15), then the value of x is
(a) 30
(b) 45
(c) 60
(d) 90
Answer
Answer: (b) 45
Hint:
Given, 3×tan(x – 15) = tan(x + 15)
⇒ tan(x + 15)/tan(x – 15) = 3/1
⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = (3 + 1)/(3 – 1)
⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = 4/2
⇒ {tan(x + 15) + tan(x – 15)}/{tan(x + 15) – tan(x – 15)} = 2
⇒ sin(x + 15 + x – 15)/sin(x + 15 – x + 15) = 2
⇒ sin 2x/sin 30 = 2
⇒ sin 2x/(1/2) = 2
⇒ 2 × sin 2x = 2
⇒ sin 2x = 1
⇒ sin 2x = sin 90
⇒ 2x = 90
⇒ x = 45
MCQ Questions On Trigonometry Class 11 Question 10.
If the sides of a triangle are 13, 7, 8 the greatest angle of the triangle is
(a) π/3
(b) π/2
(c) 2π/3
(d) 3π/2
Answer
Answer: (c) 2π/3
Hint:
Given, the sides of a triangle are 13, 7, 8
Since greatest side has greatest angle,
Now Cos A = (b² + c² – a²)/2bc
⇒ Cos A = (7² + 8² – 13²)/(2×7×8)
⇒ Cos A = (49 + 64 – 169)/(2×7×8)
⇒ Cos A = (113 – 169)/(2×7×8)
⇒ Cos A = -56/(2×56)
⇒ Cos A = -1/2
⇒ Cos A = Cos 2π/3
⇒ A = 2π/3
So, the greatest angle is
= 2π/3
MCQ On Trigonometry For Class 11 Question 11.
The value of tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 is
(a) tan 30
(b) tan 60
(c) 2 tan 30
(d) 2 tan 60
Answer
Answer: (b) tan 60
Hint:
Given, tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80
= tan 40 × tan 80 × tan 20
= [{sin 40 × sin 80}/{cos 40 × cos 80}] × (sin 20/cos 20)
= [{2 * sin 40 × sin 80}/{2 × cos 40 × cos 80}] × (sin 20/cos 20)
= [{cos 40 – cos 120}/{cos 120 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20)
= [{cos 40 – cos (90 + 30)}/{cos (90 + 30) + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20)
= [{cos 40 + sin30}/{-sin30 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20)
= [{(2 × cos 40 + 1)/2}/{(-1 + cos 40)/2}] × (sin 20/cos 20)
= [{2 × cos 40 + 1}/{-1 + cos 40}] × (sin 20/cos 20)
= [{2 × cos 40 × sin 20 + sin 20}/{-cos 20 + cos 40 × cos 20}]
= (sin 60 – sin 20 + sin 20)/(-cos 20 + cos 60 + cos 20)
= sin 60/cos 60
= tan 60
So, tan 20 × tan 40 × tan 80 = tan 60
MCQ Trigonometry Class 11 Question 12.
If the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5, then the ratio of the greatest side to the smallest side is
(a) 4 : (√5 – 1)
(b) 5 : 4
(c) (√5 – 1) : 4
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 4 : (√5 – 1)
Hint:
Given, the angles of a triangle be in the ratio 1 : 4 : 5
⇒ x + 4x + 5x = 180
⇒ 10x = 180
⇒ x = 180/10
⇒ x = 18
So, the angle are: 18, 72, 90
Since a : b : c = sin A : sin B : sin C
⇒ a : b : c = sin 18 : sin 72 : sin 90
⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1)/4 : {√(10 + 2√5)}/4 : 1
⇒ a : b : c = (√5 – 1) : {√(10 + 2√5)} : 4
Now, c /a = 4/(√5 – 1)
⇒ c : a = 4 : (√5 – 1)
Class 11 Maths Trigonometry MCQ Questions Question 13.
The general solution of √3 cos x – sin x = 1 is
(a) x = n × π + (-1)n × (π/6)
(b) x = π/3 – n × π + (-1)n × (π/6)
(c) x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6)
(d) x = π/3 – n × π + (π/6)
Answer
Answer: (c) x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6)
Hint:
√3 cos x-sin x=1
⇒ (√3/2)cos x – (1/2)sin x = 1/2
⇒ sin 60 × cos x – cos 60 × sin x = 1/2
⇒ sin (x – 60) = 1/2
⇒ sin (x – π/3) = sin 30
⇒ sin (x – π/3) = sinπ/6
⇒ x – π/3 = n × π + (-1)n × (π/6) {where n ∈ Z}
⇒ x = π/3 + n × π + (-1)n × (π/6)
Class 11 Maths Trigonometry MCQs Question 14.
If tan² θ = 1 – e², then the value of sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ is
(a) 2 – e²
(b) (2 – e²)1/2
(c) (2 – e²)²
(d) (2 – e²)3/2
Answer
Answer: (d) (2 – e²)3/2
Hint:
Given, tan² θ = 1 – e²
⇒ tan θ = √(1 – e²)
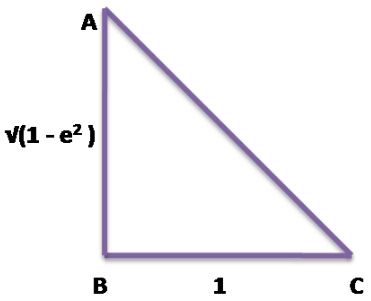
From the figure and Pythagorus theorem,
AC² = AB² + BC²
⇒ AC² = {√(1 – e²)}² + 12
⇒ AC² = 1 – e² + 1
⇒ AC² = 2 – e²
⇒ AC = √(2 – e²)
Now, sec θ = √(2 – e²)
cosec θ = √(2 – e²)/√(1 – e²)
and tan θ = √(1 – e²)
Given, sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ
= √(2 – e²) + {(1 – e²)3/2 × √(2 – e²)/√(1 – e²)}
= √(2 – e²) + {(1 – e²) × (1 – e²) × √(2 – e²)/√(1 – e²)}
= √(2 – e²) + (1 – e²) × √(2 – e²)
= √(2 – e²) × (1 + 1 – e²)
= √(2 – e²) × (2 – e²)
= (2 – e²)3/2
So, sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ = (2 – e²)3/2
Trigonometry Class 11 MCQ With Answers Question 15.
The value of cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -1
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) 1
Hint:
Given, cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65
= cos 20 + 1 – cos 110 – √2 sin65 {since cos 2x = 1 – 2sin² x}
= 1 + cos 20 – cos 110 – √2 sin65
= 1 – 2 × sin {(20 + 110)/2 × sin{(20 – 110)/2} – √2 sin65 {Apply cos C – cos D formula}
= 1 – 2 × sin 65 × sin (-45) – √2 sin65
= 1 + 2 × sin 65 × sin 45 – √2 sin65
= 1 + (2 × sin 65)/√2 – √2 sin65
= 1 + √2 ( sin 65 – √2 sin 65
= 1
So, cos 20 + 2sin² 55 – √2 sin65 = 1
Question 16.
If the radius of the circumcircle of an isosceles triangle PQR is equal to PQ ( = PR), then the angle P is
(a) 2π/3
(b) π/3
(c) π/2
(d) π/6
Answer
Answer: (a) 2π/3
Hint:
Let S be the center of the circumcircle of triangle PQR.
So, SP = SQ = SR = PQ = PR, where SP, SQ & SR are radii.
Thus SPQ & SPR are equilateral triangles.
⇒ ∠QSP = 60°;
Similarly ∠RQP = 60°
⇒ Angle at the center QSP = 120°
So, SRPQ is a rhombus, since all the four sides are equal.
Hence, its opposite angles are equal; so ∠P = ∠QSP = 120°
Question 17.
If cos a + 2cos b + cos c = 2 then a, b, c are in
(a) 2b = a + c
(b) b² = a × c
(c) a = b = c
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 2b = a + c
Hint:
Given, cos A + 2 cos B + cos C = 2
⇒ cos A + cos C = 2(1 – cos B)
⇒ 2 cos((A + C)/2) × cos((A-C)/2 = 4 sin² (B/2)
⇒ 2 sin(B/2)cos((A-C)/2) = 4sin² (B/2)
⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2sin (B/2)
⇒ cos((A-C)/2) = 2cos((A+C)/2)
⇒ cos((A-C)/2) – cos((A+C)/2) = cos((A+C)/2)
⇒ 2sin(A/2)sin(C/2) = sin(B/2)
⇒ 2{√(s-b)(s-c)√bc} × {√(s-a)(s-b)√ab} = √(s-a)(s-c)√ac
⇒ 2(s – b) = b
⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b
⇒ a + c – b = b
⇒ a + c = 2b
Question 18.
The value of 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) is
(a) sin x
(b) sin 2x
(c) sin 3x
(d) sin 4x
Answer
Answer: (c) sin 3x
Hint:
Given, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3)
= 4 × sin x × {sin x × cos π/3 + cos x × sin π/3} × {sin x × cos 2π/3 + cos x × sin 2π/3}
= 4 × sin x × {(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2} × {-(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2}
= 4 × sin x × {-(sin 2x)/4 + (3 × cos 2x)/4}
= sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 × cos 2x}
= sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 × (1 – sin 2x)}
= sin x × {-sin 2x + 3 – 3 × sin 2x}
= sin x × {3 – 4 × sin 2x}
= 3 × sin x – 4 sin 3x
= sin 3x
So, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) = sin 3x
Question 19.
If tan A – tan B = x and cot B – cot A = y, then the value of cot (A – B) is
(a) x + y
(b) 1/x + y
(c) x + 1/y
(d) 1/x + 1/y
Answer
Answer: (d) 1/x + 1/y
Hint:
Given,
tan A – tan B = x ……………. 1
and cot B – cot A = y ……………. 2
From equation,
1/cot A – 1/cot B = x
⇒ (cot B – cot A)/(cot A × cot B) = x
⇒ y/(cot A × cot B) = x {from equation 2}
⇒ y = x × (cot A × cot B)
⇒ cot A × cot B = y/x
Now, cot (A – B) = (cot A × cot B + 1)/(cot B – cot A)
⇒ cot (A – B) = (y/x + 1)/y
⇒ cot (A – B) = (y/x) × (1/y) + 1/y
⇒ cot (A – B) = 1/x + 1/y
Question 20.
The value of (sin 7x + sin 5x) /(cos 7x + cos 5x) + (sin 9x + sin 3x) / (cos 9x + cos 3x) is
(a) tan 6x
(b) 2 tan 6x
(c) 3 tan 6x
(d) 4 tan 6x
Answer
Answer: (b) 2 tan 6x
Hint:
Given, (sin 7x + sin 5x) /(cos 7x + cos 5x) + (sin 9x + sin 3x) / (cos 9x + cos 3x)
⇒ [{2 × sin(7x+5x)/2 × cos(7x-5x)/2}/{2 × cos(7x+5x)/2 × cos(7x-5x)/2}] + [{2 × sin(9x+3x)/2 × cos(9x-3x)/2}/{2 × cos(9x+3x)/2 × cos(9x-3x)/2}]
⇒ [{2 × sin 6x × cosx}/{2 × cos 6x × cosx}] + [{2 × sin 6x × cosx}/{2 × cos 6x × cosx}]
⇒ (sin 6x/cos 6x) + (sin 6x/cos 6x)
⇒ tan 6x + tan 6x
⇒ 2 tan 6x
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 11 Maths MCQ:
- Sets Class 11 MCQ
- Relations and Functions Class 11 MCQ
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 MCQ
- Principle of Mathematical Induction Class 11 MCQ
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Class 11 MCQ
- Linear Inequalities Class 11 MCQ
- Permutations and Combinations Class 11 MCQ
- Binomial Theorem Class 11 MCQ
- Sequences and Series Class 11 MCQ
- Straight Lines Class 11 MCQ
- Conic Sections Class 11 MCQ
- Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Class 11 MCQ
- Limits and Derivatives Class 11 MCQ
- Mathematical Reasoning Class 11 MCQ
- Statistics Class 11 MCQ
- Probability Class 11 MCQ
