Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Wave Optics with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Wave Optics Class 12 Physics MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 MCQ With Answers
Physics Class 12 Chapter 10 MCQs On Wave Optics
Wave Optics MCQ Questions With Answers Question 1.
What happens if one of the slits, say S1 in Young’s double , slit experiment-is covered with a glass plate which absorbs half the intensity of light from it?
(a) The bright fringes become less-bright and the dark fringes have a finite light intensity
(b) The bright fringes become brighter and the dark fringes become darker
(c) The fringe width decreases
(d) No fringes will be observed
Answer
Answer: (a) The bright fringes become less-bright and the dark fringes have a finite light intensity
Wave Optics Class 12 MCQ Question 2.
What happens to the interference pattern the two slits S1 and S2 in Young’s double experiment are illuminated by two independent but identical sources?
(a) The intensity of the bright fringes doubled
(b) The intensity of the bright fringes becomes four times
(c) Two sets of interference fringes overlap
(d) No interference pattern is observed
Answer
Answer: (d) No interference pattern is observed
MCQ On Wave Optics Class 12 Question 3.
What is the reason for your answer to the above question?
(a) The two sources do not emit light of the same wavelength
(b) The two sources emit waves which travel with different speeds
(c) The two sources emit light waves of different amplitudes
(d) There is not constant phase difference between the waves emitted by the two sources
Answer
Answer: (d) There is not constant phase difference between the waves emitted by the two sources
Wave Optics MCQ Questions With Answers Pdf Question 4.
A single slit diffraction pattern is obtained using a beam of red light What happened the red light is replaced by the blue light?
(a) There is no change in diffraction pattern
(b) Diffraction fringes become narrower and crowded
(d) Diffraction fringes become broader and farther apart
(d) The diffraction pattern disappear
Answer
Answer: (b) Diffraction fringes become narrower and crowded
Wave Optics Class 12 MCQ Pdf Question 5.
When a polaroid is rotated, the intensity of light varies but never reduces to zero. It shows that the incident light is:
(a) unpolarised
(b) completely plane polarised
(c) partially plane polarised
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) partially plane polarised
MCQ Of Wave Optics Class 12 Question 6.
When a polaroid is rotated, the intensity of light does not vary. The incident light may be:
(a) unpolarised
(b) completely polarised
(c) partially plane polarised
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) unpolarised
Wave Optics Class 12 MCQ Questions Question 7.
In Young’s double slit experiment, a maximum is obtained when the path difference between the interfering waves is (n ∈ l):
(a) nλ
(b) n \(\frac{λ}{2}\)
(c) (2n + 1) \(\frac{λ}{2}\)
(d) (2n – 1) \(\frac{λ}{4}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) nλ
Wave Optics Objective Questions Question 8.
For sustained interference, we need two sources which
emit radiations :
(a) of the same intensity
(b) of the same amplitude
(c) having a constant phase difference
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) having a constant phase difference
Wave Optics MCQ Class 12 Question 9.
Two sources of light are said to be coherent when both give out light waves of the same:
(a) amplitude and phase
(b) intensity and wavelength
(c) speed
(d) wavelength and a constant phase difference
Answer
Answer: (d) wavelength and a constant phase difference

Wave Optics MCQ Questions Question 10.
The intensity of light emerging from the two slits, in Young’s experiment is in the ratio 1 : 4. The ratio of,the intensity of the minimum to that of the consecutive maximum will be:
(a) 1 : 4
(b) 1 : 9
(c) 1 : 16
(d) 2 : 3
Answer
Answer: (b) 1 : 9
MCQ Questions On Wave Optics Question 11.
Poisson’s bright spot was discovered by:
(a) Fresnel
(b) Rayleigh
(c) Poisson
(d) Fraunhoffer
Answer
Answer: (c) Poisson
MCQ Wave Optics Class 12 Question 12.
The theory of expanding universe is confirmed by the observation of the spectral lines of the star, which shows :
(a) green shift
(b) red shift
(c) violet shift
(d) yellow shift
Answer
Answer: (b) red shift
Wave Optics MCQ Questions With Answers Pdf Download Question 13.
The application of Doppler effect are:
(a) Doppler spectrometer
(b) Doppler radius
(c) Doppler velocimeter
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
MCQs On Wave Optics Question 14.
Which of the following is conserved when light waves interefere?
(a) phase
(b) intensity
(c) amplitude
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (d) none of these
Question 15.
In Young double slit experiment, a minimum is obtained when the phase difference of the superposing waves, is (n ∈ l):
(a) nπ
(b) (n + \(\frac{1}{2}\))π
(c) (2n + 1)π
(d) zero
Answer
Answer: (c) (2n + 1)π
Question 16.
The angle of minimum deviation of a prism depends upon the aggie of:
(a) incidence
(b) reflection
(c) prism
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (c) prism
Question 17.
he minimum value of the refractive index is:
(a) zero
(b) 1
(c) less than 1 but not zero
(d) more than 1
Answer
Answer: (c) less than 1 but not zero
Question 18.
Polarization of light prove the :
(a) corpuscular nature of light
(b) quantum nature of light
(c) Transverse wave nature of light
(d) Longitudinal wave nature of light
Answer
Answer: (c) Transverse wave nature of light
Question 19.
Out of the following Statements which is not correct?
(a) When unpolarised light passes through Nicol’s prism, the emergent light is elliptically polarized
(b) Nicol’s prism works on the principle of double refraction and T.l.R.
(c) Nicol’s prism can be used both the produce and analyse polarized light
(d) Calcite and Quartz are both double refracting crystal
Answer
Answer: (a) When unpolarised light passes through Nicol’s prism, the emergent light is elliptically polarized
Question 20.
Polaroid glasses is used in sun glasses because :
(a) It reduces the light intensity to half on account of polarization
(b) It is fashionable
(c) It has good colour
(d) It is cheaper
Answer
Answer: (a) It reduces the light intensity to half on account of polarization
Question 21.
In vacuum, the speed of light depends upon :
(a) frequency
(b) velocity
(c) wave length
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Question 22.
The fringe width (β) of a diffraction pattern and the slit width d are related as:
(a) β ∝ d
(b) β ∝\(\frac{1}{d}\)
(c) β ∝ √d
(d) β ∝ \(\frac{1}{d^2}\)
Answer
Answer: (b) β ∝\(\frac{1}{d}\)
Question 23.
C.V. Raman was awarded the Nobel prize for his work associated with which of the following phenomenon of radiations?
(a) scattering
(b) diffraction
(c) interference
(d) polarisation
Answer
Answer: (a) scattering
Question 24.
Light takes 10-10 to cross a glass slab. What is the thickness of the glass slab?
(a) 2 cm
(b) 3 cm
(c) 2.5 cm
(d) 3.5 cm
Answer
Answer: (b) 3 cm
Question 25.
In Young’s double slit experiment, the central point on the screen is:
(a) bright
(b) dark
(c) first bright and later dark
(d) first dark and later bright
Answer
Answer: (a) bright
Question 26.
Between the slit is id\ the distance between the slit and the screen is α, with light of wavelength λ, the number of fringe observed per metre on the screen is:
(a) \(\frac{δy}{α}\)
(b) \(\frac{Dα}{λ}\)
(c) \(\frac{α}{Dλ}\)
(d) \(\frac{λd}{D}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{δy}{α}\)
Question 27.
In Young’s double slit experiment the distance between the slit and the screen is doubled and the separation between the slit is reduced to half. The fringe width:
(a) is doubled
(b) become four time
(c) is halfed
(d) remain unchanged
Answer
Answer: (b) become four time
Question 28.
In a Young’s double slit experiment the distance between the slit is 1 mm and the distance of screen from the slit is 1 m. If light of wavelength 6000 A is used then the fringe width is:
(a) 0.4 mm
(b) 0.5 mm
(c) 0.6 mm
(d) 0.8 mm
Answer
Answer: (c) 0.6 mm
Question 29.
A person cannot see object clearly beyond 50 cm. The pow er of the lens to correct his vision is :
(a) +0.5 dioptre
(b) -0.5 dioptre
(c) -2 dioptre
(d) +2 dioptre
Answer
Answer: (c) -2 dioptre
Question 30.
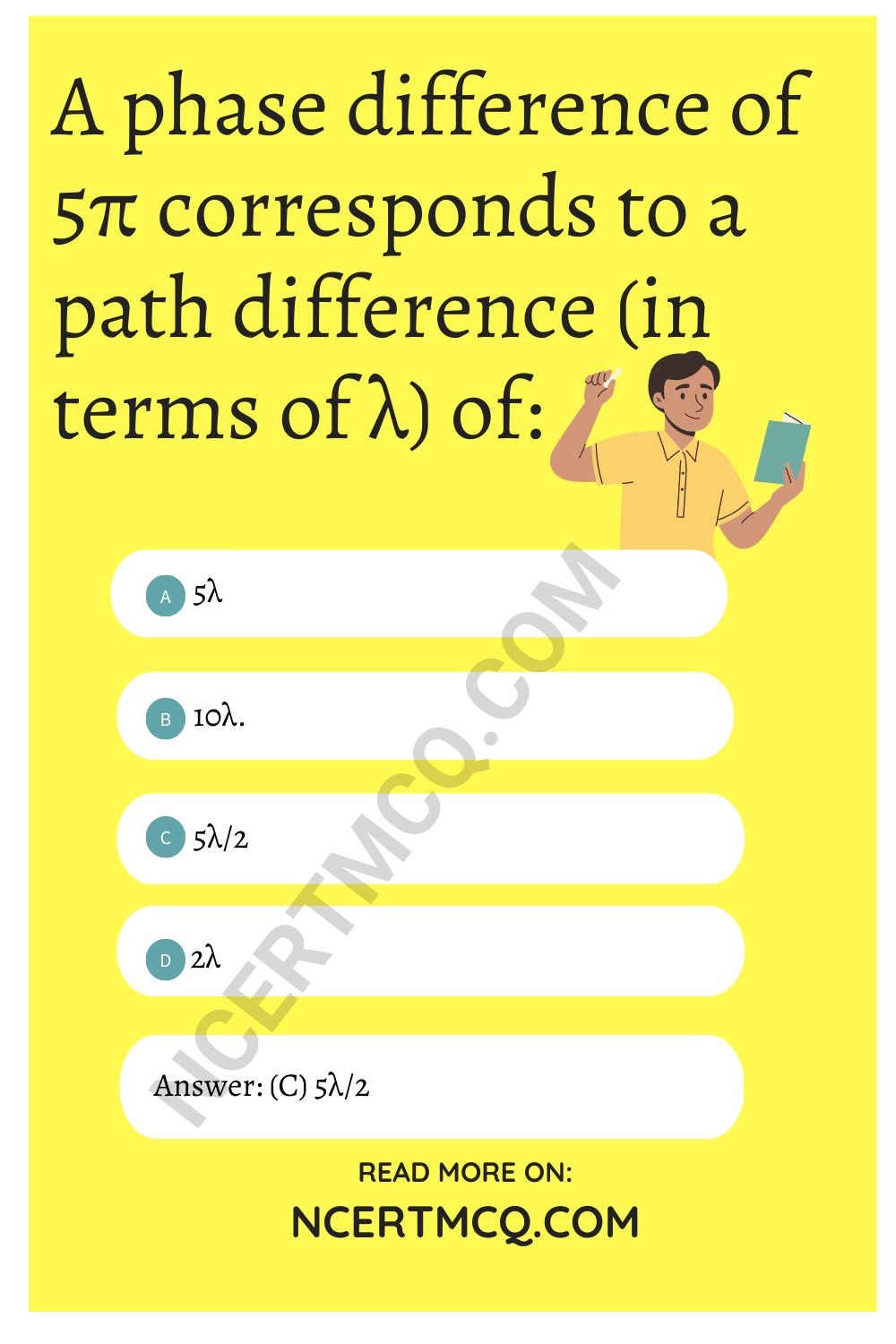
A phase difference of 5π corresponds to a path difference (in terms of λ) of:
(a) 5λ
(b) 10λ.
(c) 5λ/2
(d) 2λ
Answer
Answer: (c) 5λ/2
Question 31.
A polaroid produces a strong beam of light which is :
(a) circularly polarised
(b) elliptically polarised
(c) plane polarised
(d) unpolarised
Answer
Answer: (c) plane polarised
Question 32.
Images of a distant lamp seen through a fire cloth rotate on rotating the cloth. This is due to the phenomenon of:
(a) interference
(b) diffraction
(c) polarisation
(d) scattering
Answer
Answer: (b) diffraction
Question 33.
A young’s double slit experiment uses a monochromatic source. The shape of interference fringes formed on a screen is :
(a) parabola
(b) straight line
(c) circle
(d) hyperbola
Answer
Answer: (b) straight line
Question 34.
A monochromatic light is refracted from air into a glass of refractive index µ. The ratio of the wavelengths of the incident and the refracted waves is:
(a) 1 : µ
(b) 1 : µ²
(c) µ : 1
(d) µ² : 1
Answer
Answer: (c) µ : 1
Question 35.
The focal length of the lens is 50 cm; then its power is:
(a) +2D
(b) +1D
(c) -2D
(d) -1D
Answer
Answer: (a) +2D
Question 36.
In the above question, the number of the lens is:
(a) +2
(b) +1
(c) -2
(d) -1
Answer
Answer: (a) +2
Question 37.
The refractive index of diamond is about:
(a) 1
(b) 1.42
(c) 2.42
(d) 4.24
Answer
Answer: (c) 2.42
Question 38.
Two lenses having power +6 D and -4 D are placed in contact. The power of the combination is
(a) -2D
(b) -4D
(c) +4D
(d) +2 D
Answer
Answer: (d) +2 D
Question 39.
Diffraction was discovered by :
(a) Grimaldi
(b) Thomas Young
(c) Malus
(d) Huygens
Answer
Answer: (a) Grimaldi
Question 40.
The electromagnetic wave theory of light fails to explain :
(a) compton effect
(b) photoelectric effect
(c) neither (a) nor (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
Answer: (a) compton effect
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 10 Wave Optics with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Wave Optics CBSE Class 12 Physics MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 12 Physics MCQ:
- Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 MCQ
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Class 12 MCQ
- Current Electricity Class 12 MCQ
- Moving Charges and Magnetism Class 12 MCQ
- Magnetism and Matter Class 12 MCQ
- Electromagnetic Induction Class 12 MCQ
- Alternating Current Class 12 MCQ
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 MCQ
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 MCQ
- Wave Optics Class 12 MCQ
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 MCQ
- Atoms Class 12 MCQ
- Nuclei Class 12 MCQ
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits Class 12 MCQ
- Communication Systems Class 12 MCQ
