RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry Ex 7.4
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry Ex 7.4
Other Exercises
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry Ex 7.1
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry Ex 7.2
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry Ex 7.3
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry Ex 7.4
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry VSAQS
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry MCQS
Question 1.
Give the geometric representations of the following equations.
(a) on the number line
(b) on the cartesian plane.
(i) x – 2
(ii) y + 3 = 0
(iii) y = 3
(iv) 2x + 9 = 0
(v) 3x – 5 = 0
Solution:
(i) x = 2
(i) on the number line
![]()
(ii) x = 2 is a line parallel to 7-axis at a distance of 2 units to right of y-axis.
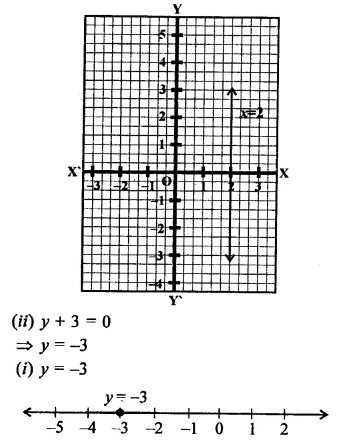
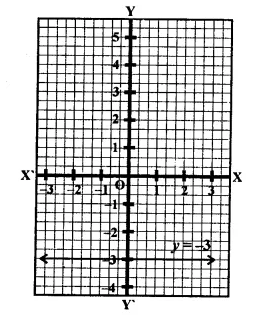
(ii) y = -3 is a line parallel to x-axis at a distance of 3 units below x-axis.
(iii) y = 3
(i) y = 3
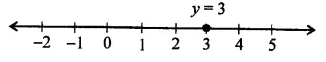
(ii) y = 3 is a line parallel to x-axis at a distance of 3 units above x-axis.
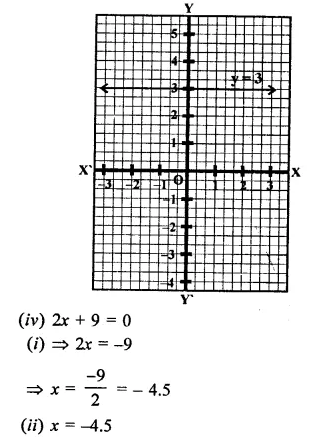
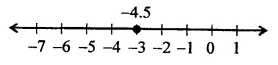
x = -4.5 is a line parallel to 7-axis at a distance of 4.5 units to left of y-axis.
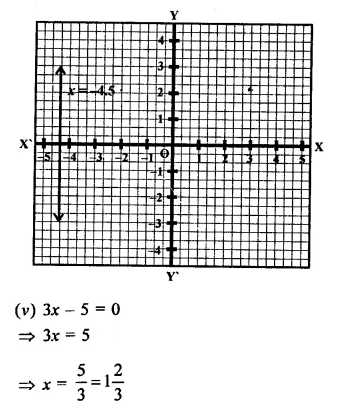
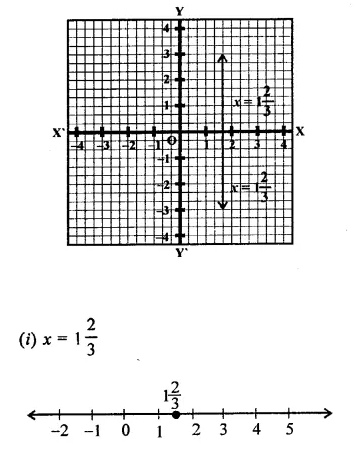
(ii) x = 1\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) is a line parallel to y-axis at a distance of 1\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) unit to right side of y-axis.
Question 2.
Give the geometrical representation of 2x + 13 = 0 as an equation in
(i) One variable
(ii) Two variables
Solution:
(i) In one variable,
2x + 13 = 0
⇒ 2x = – 13
⇒ x = \(\frac { -13 }{ 2 }\)
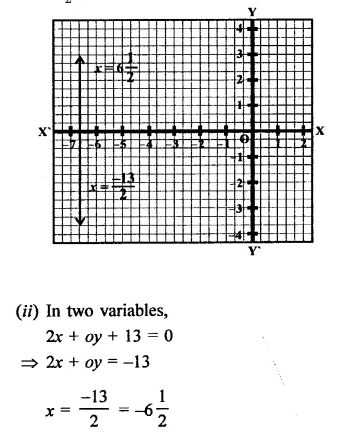
is a line parallel to y-axis at a distance of -6 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) units on the left side of y-axis.
Question 3.
Solve the equation 3x + 2 = x -8, and represent on
(i) the number line
(ii) the Cartesian plane.
Solution:
3x + 2 = x – 8
⇒ 3x – x = -8 – 2
⇒ 2x = -10
⇒ x = \(\frac { -10 }{ 2 }\) = -5
(i) on the number line s = -5
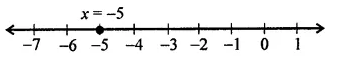
(ii) x = -5 is a line parallel to y-axis at a distance of 5 knot’s left of y-axis.
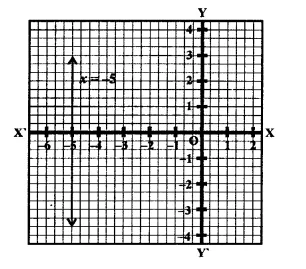
Question 4.
Write the equal of the line that is parallel to x-axis and passing through the points.
(i) (0, 3)
(ii) (0, -4)
(iii) (2, -5)
(iv) (3, 4)
Solution:
∵ A line parallel to x-axis will be of the type y = a
∴ (i) y = 3
(ii) y = -4
(iii) y = -5 and y = 4 are equations of the lines parallel to x-axis
Question 5.
Write the equation of the line that is parallel to y-axis and passing through the points.
(i) (4, 0)
(ii) (-2, 0)
(iii) (3, 5)
(iv) (-4, -3)
Solution:
∵ A line parallel to y-axis will be of the type x = a
∴ (i) x = 4, (ii) x = -2, x = 3 and x = -4 are the equations of the lines parallel to y-axis.
Hope given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 7 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry Ex 7.4 are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.