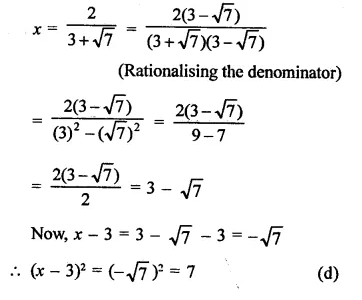
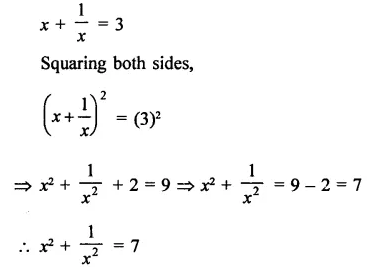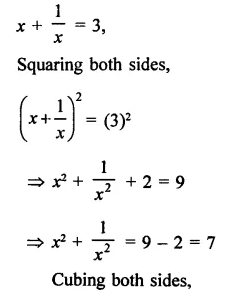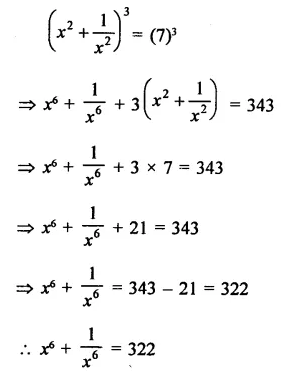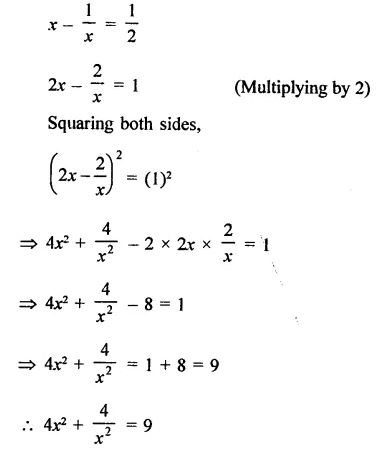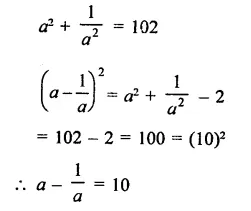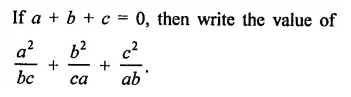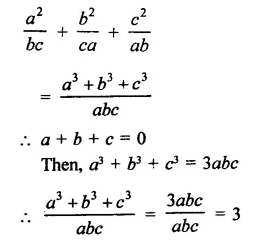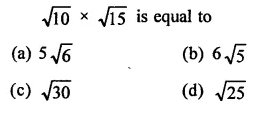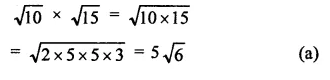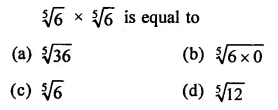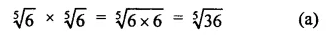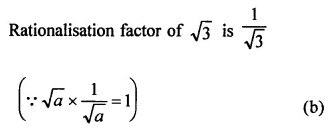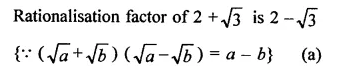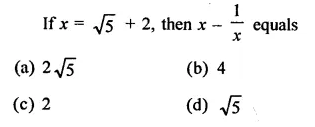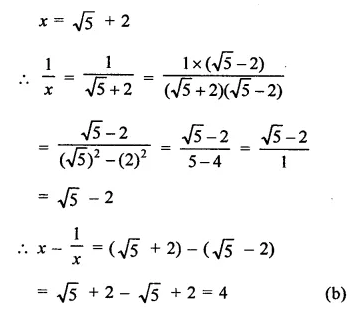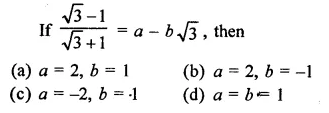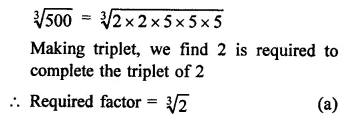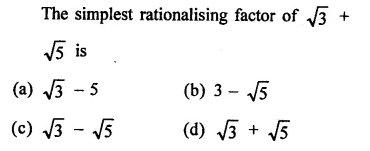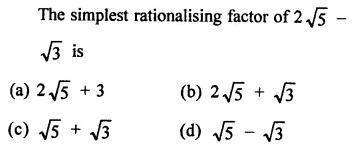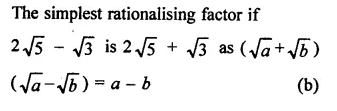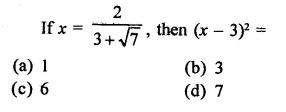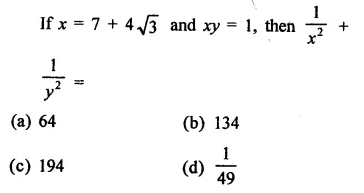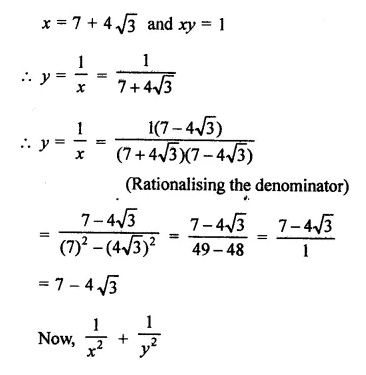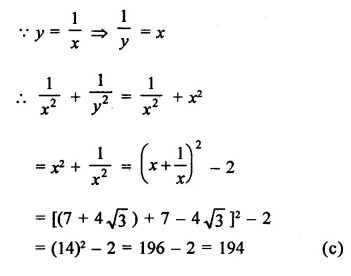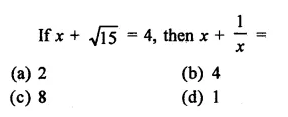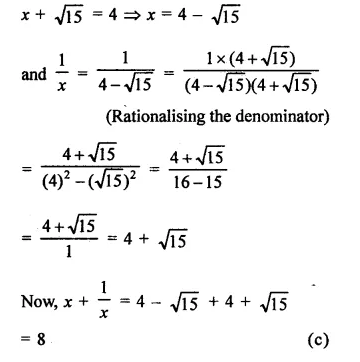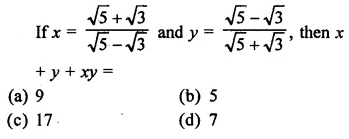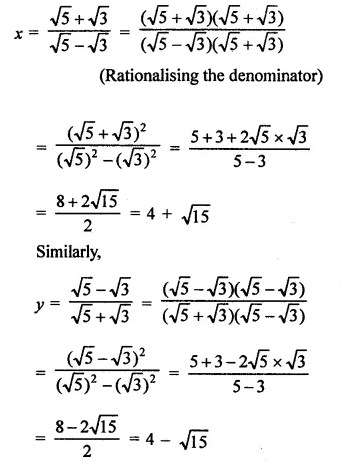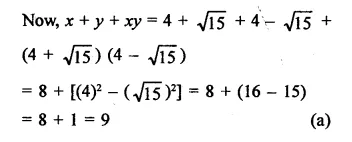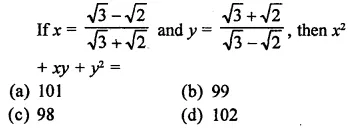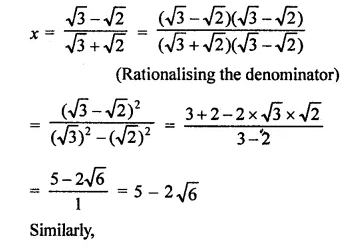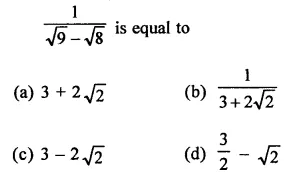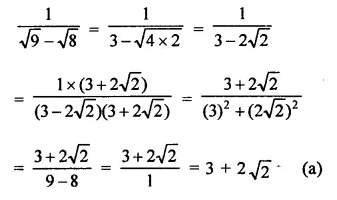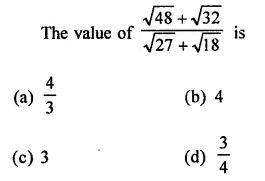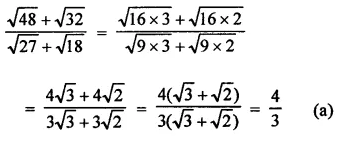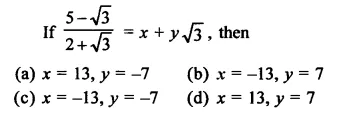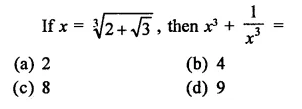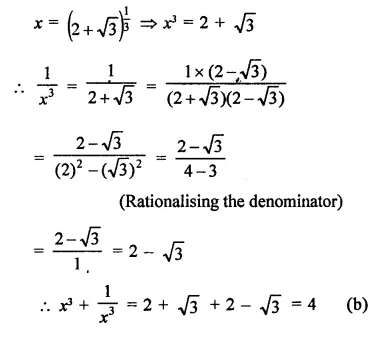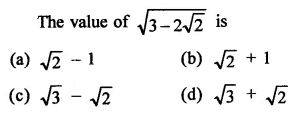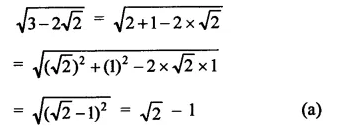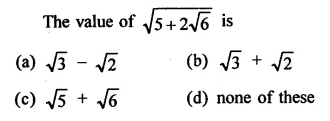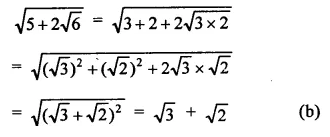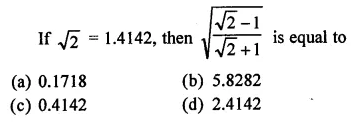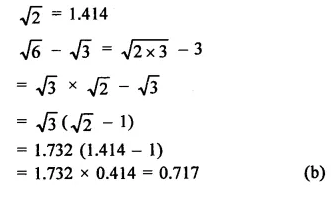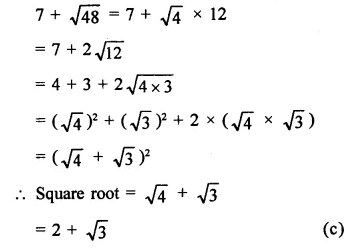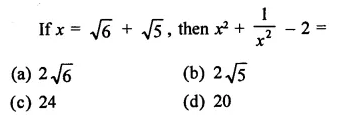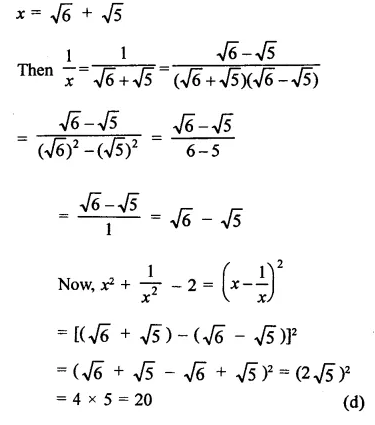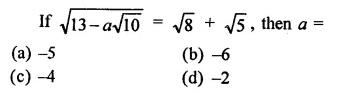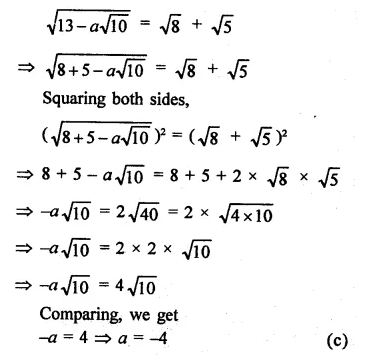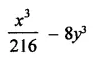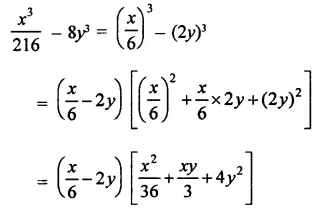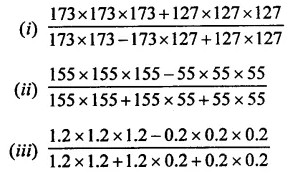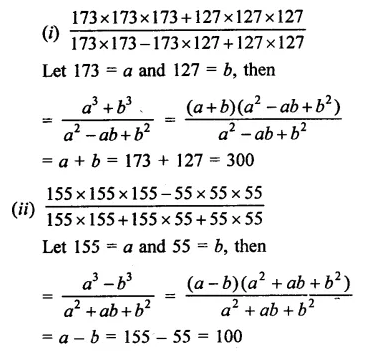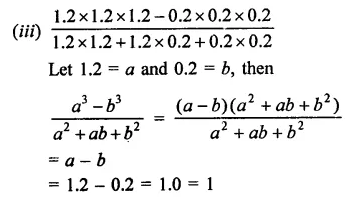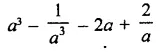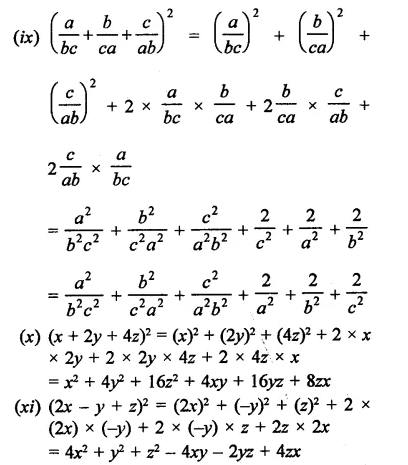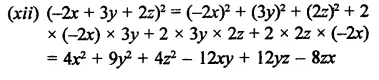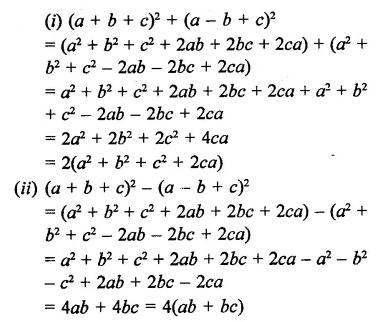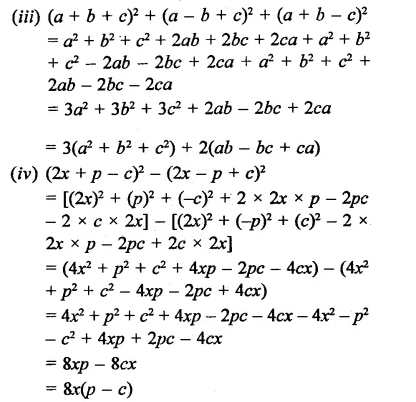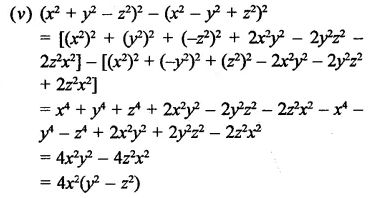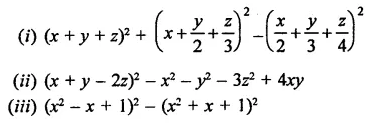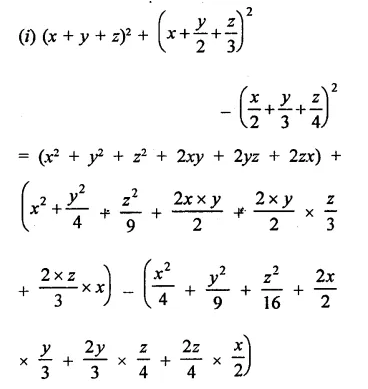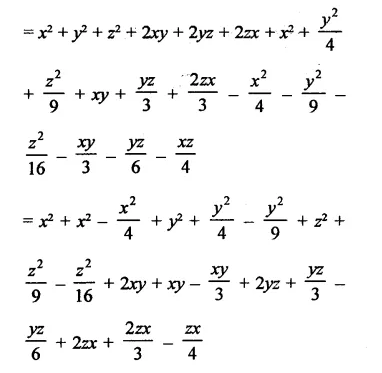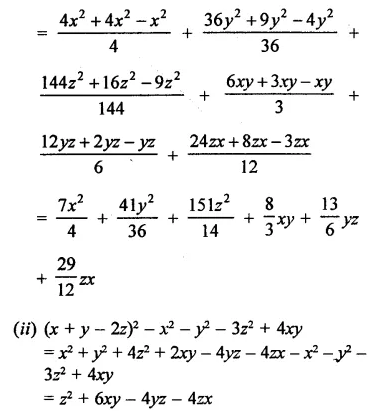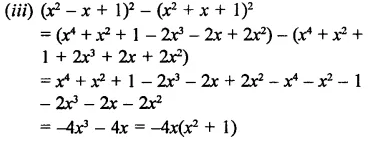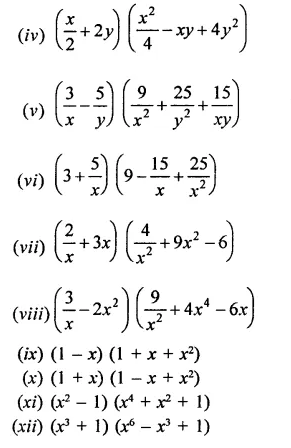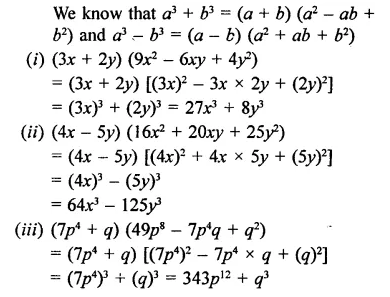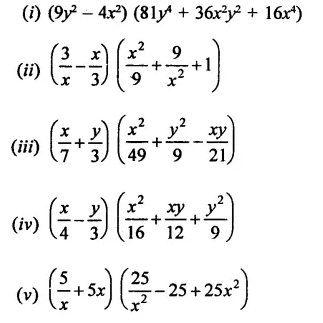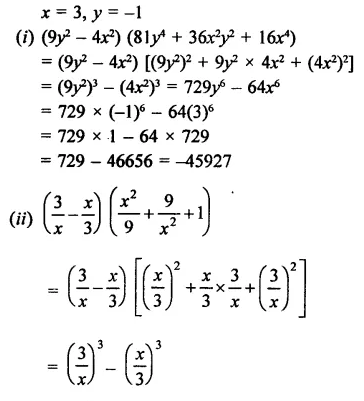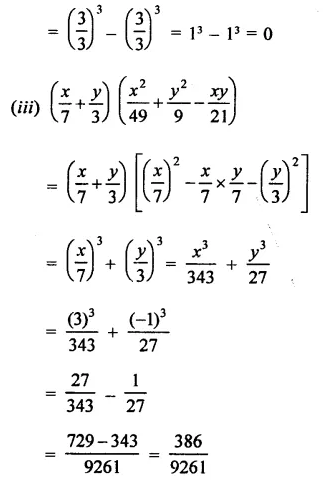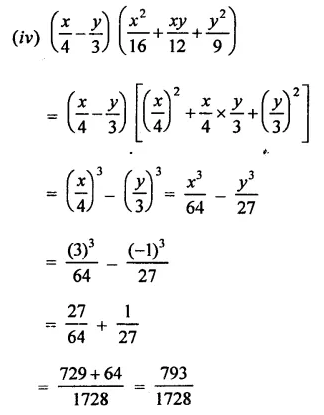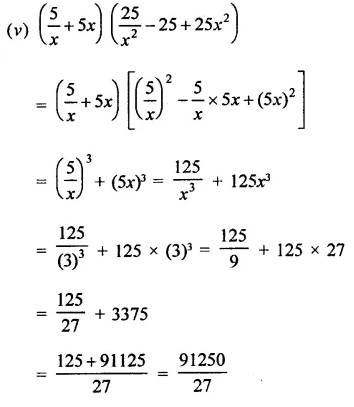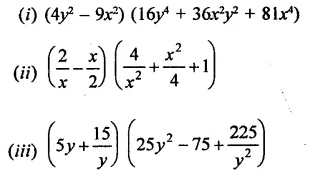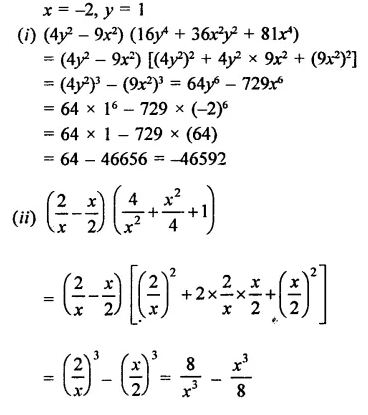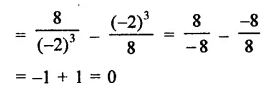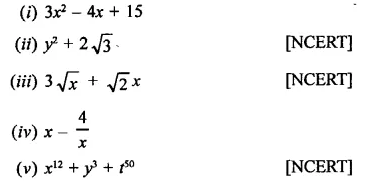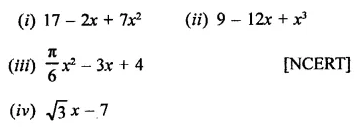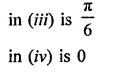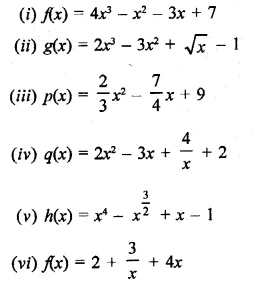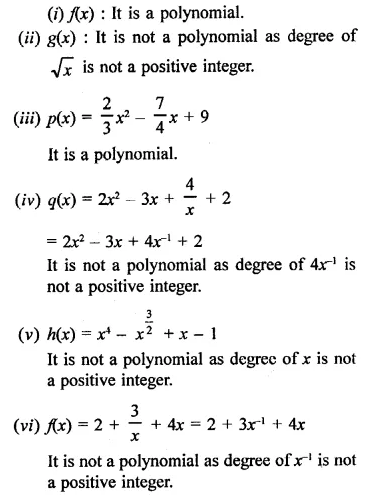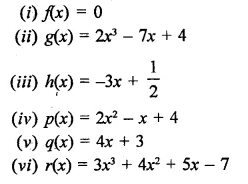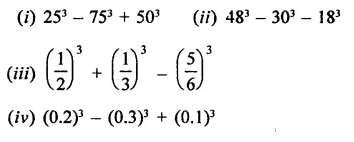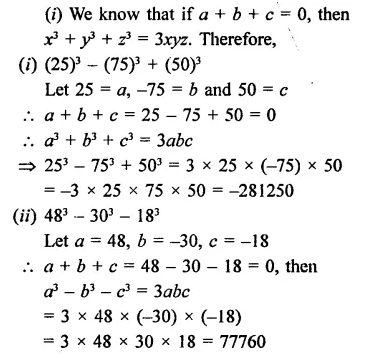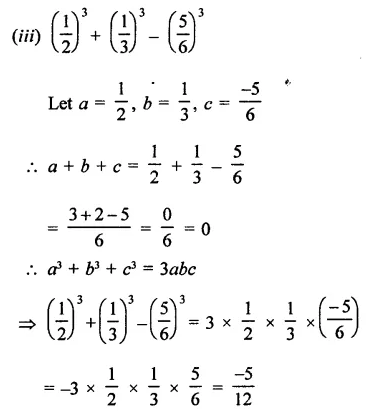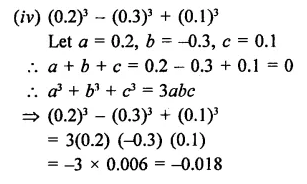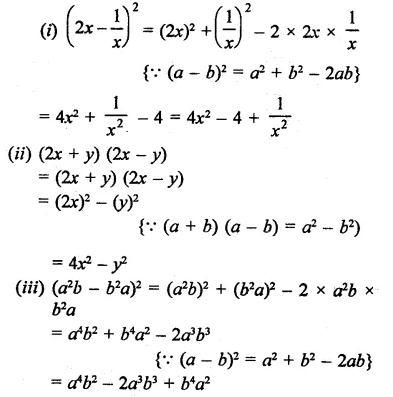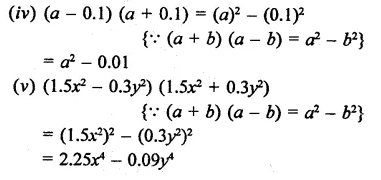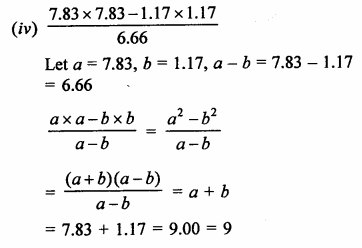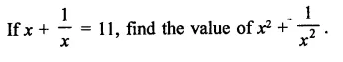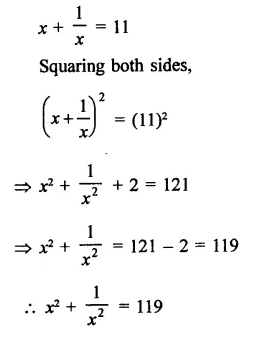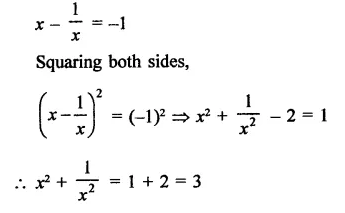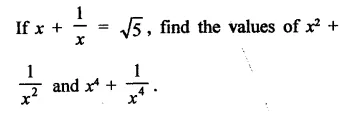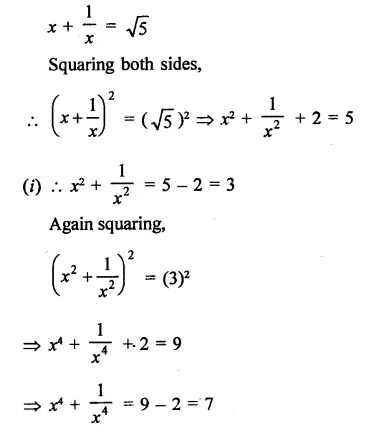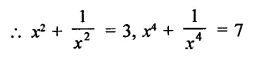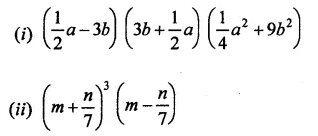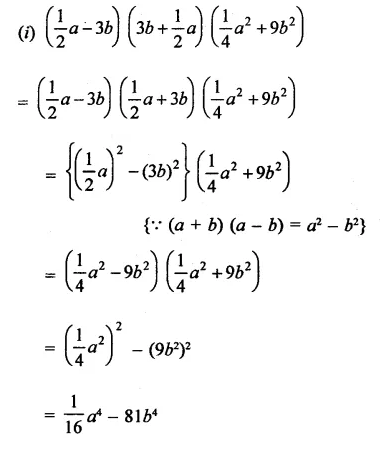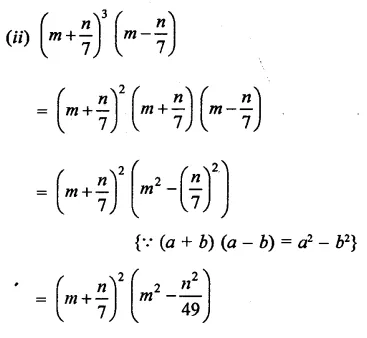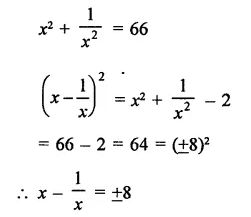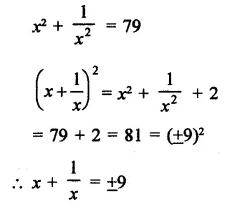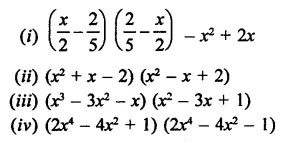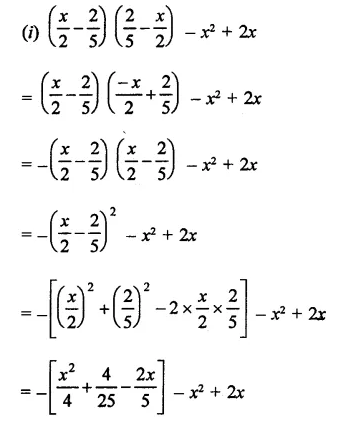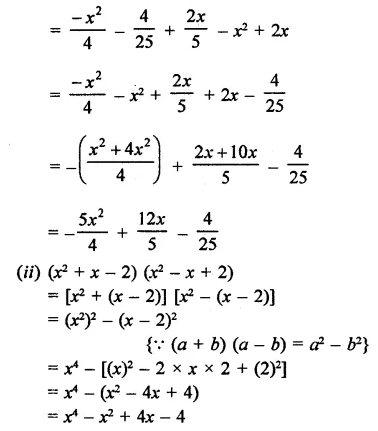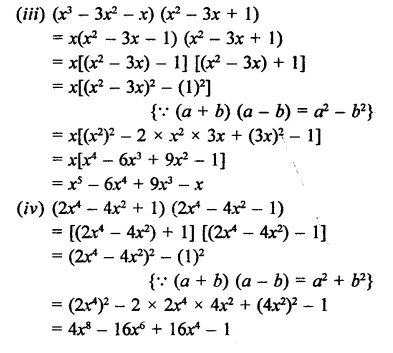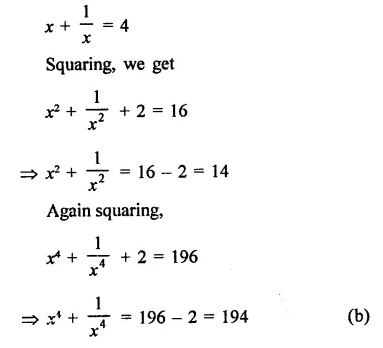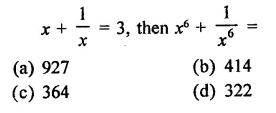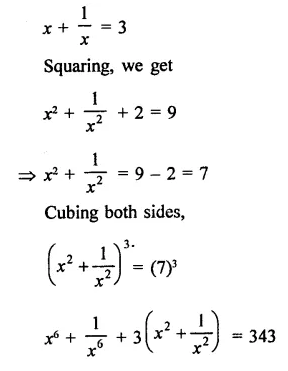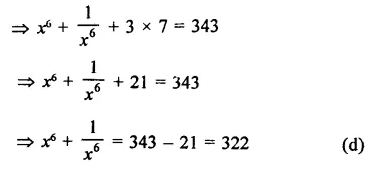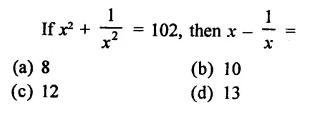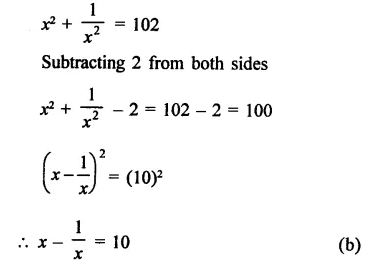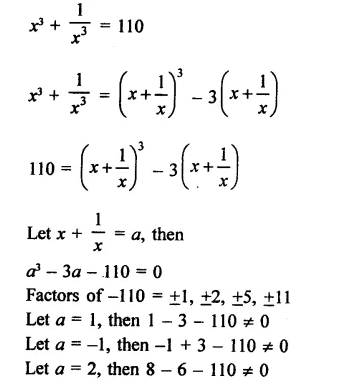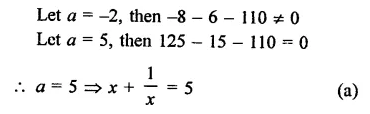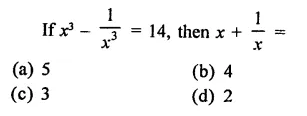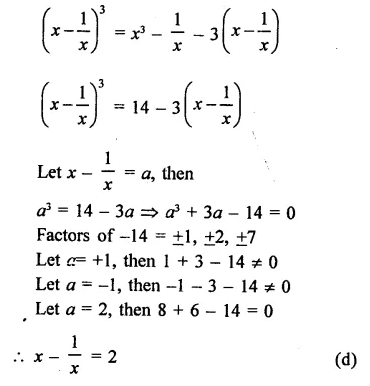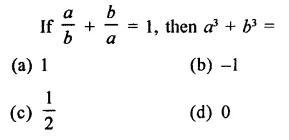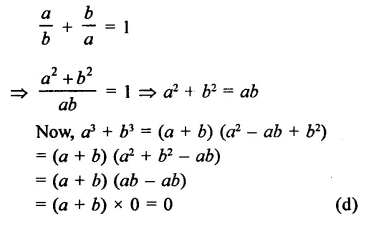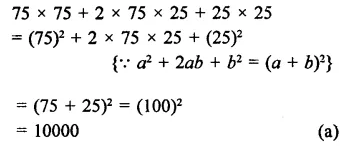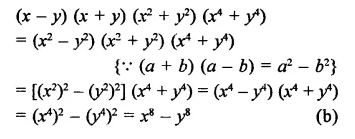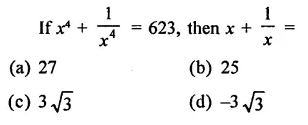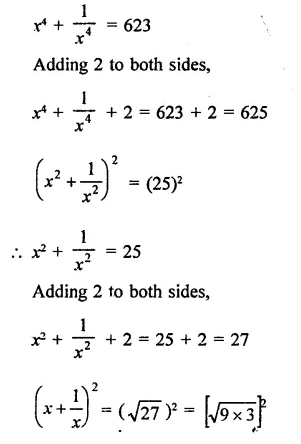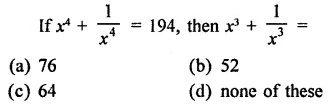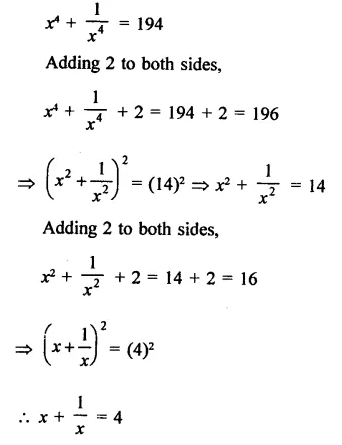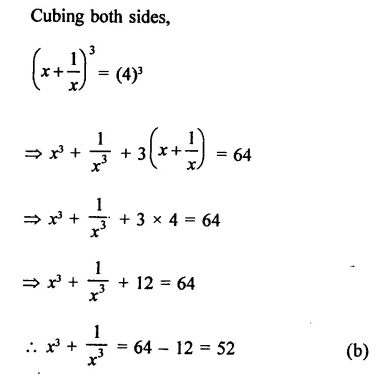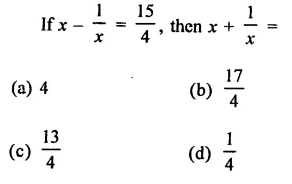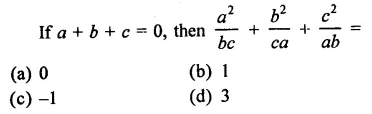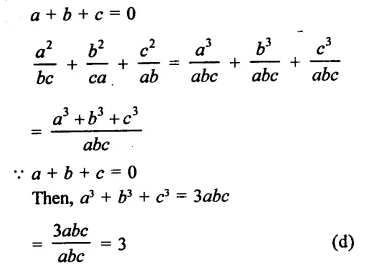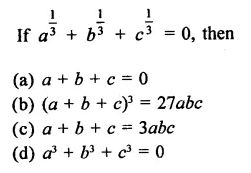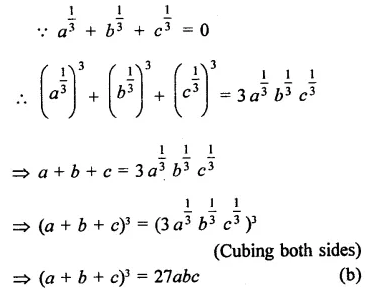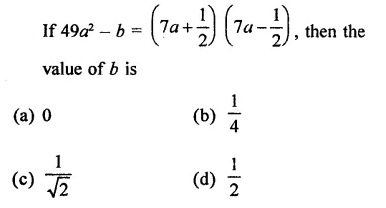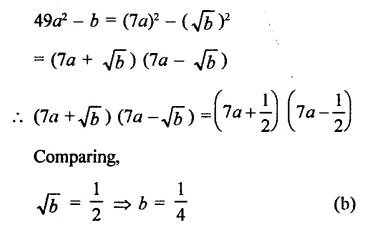RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 3 Rationalisation Ex 3.2
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 3 Rationalisation Ex 3.2
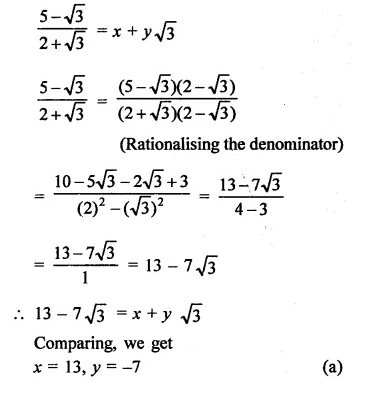
Question 1.
Rationalise the denominators of each of the following(i – vii):
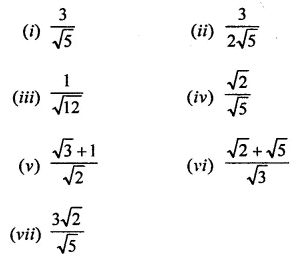 >
>
Solution:
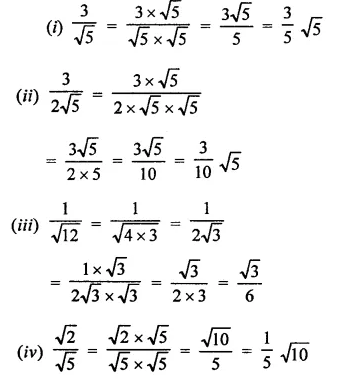
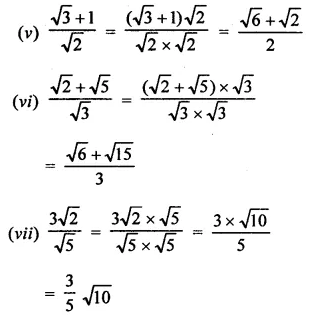
Question 2.
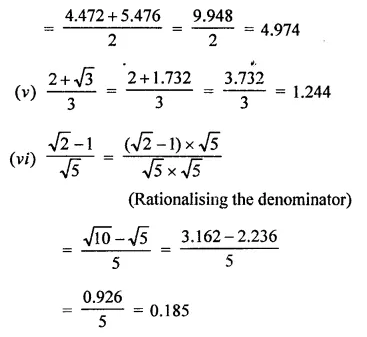
Find the value to three places of decimals of each of the following. It is given that
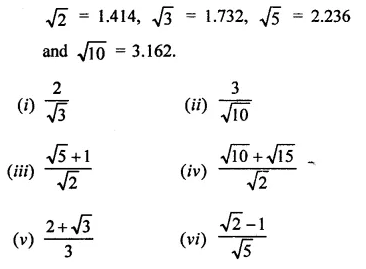
Solution:
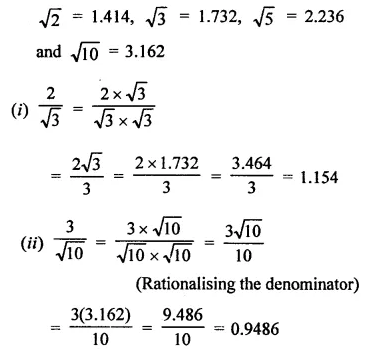
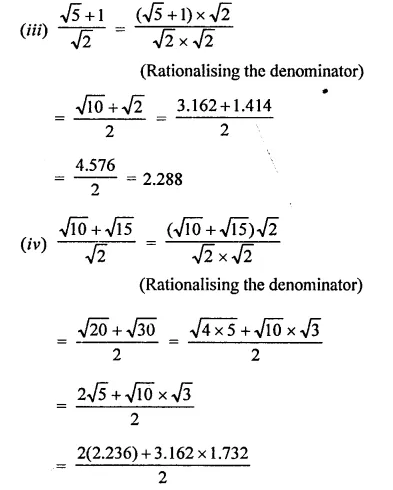
Question 3.
Express each one of the following with rational denominator:
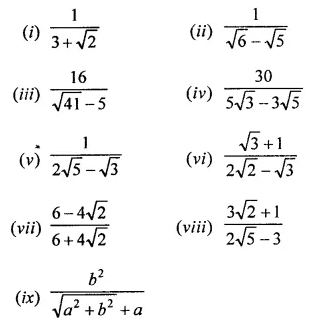
Solution:
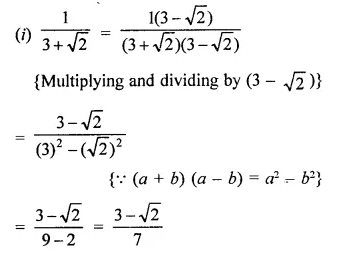
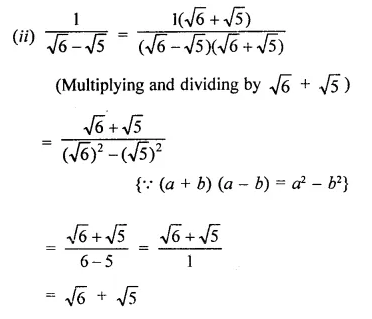
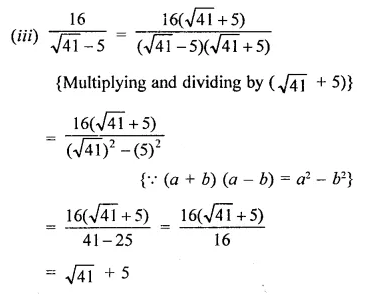
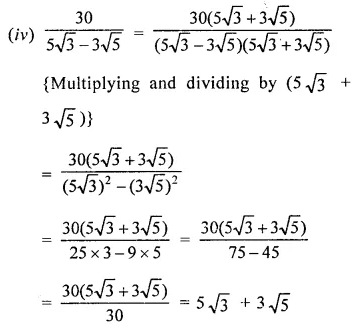
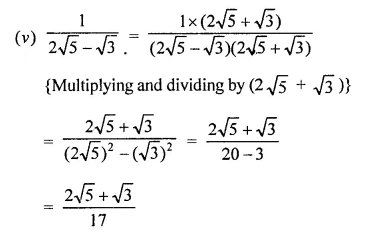
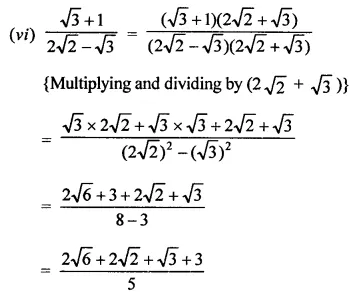
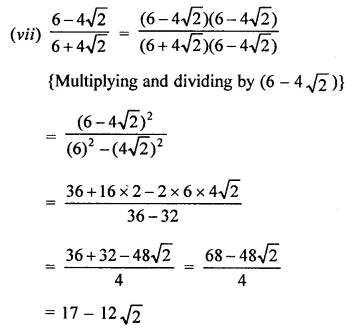
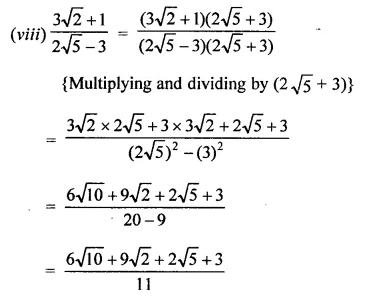
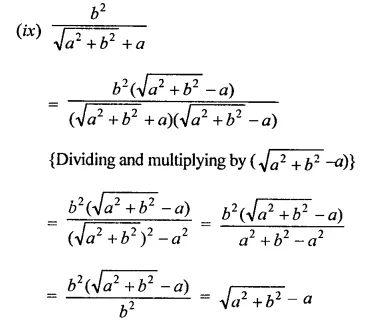
Question 4.
Rationales the denominator and simplify:
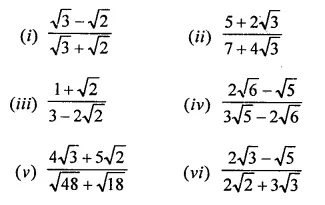
Solution:
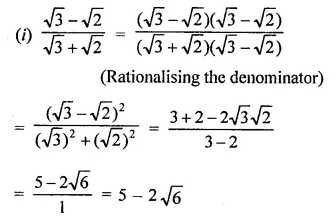
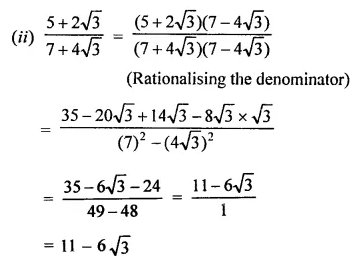
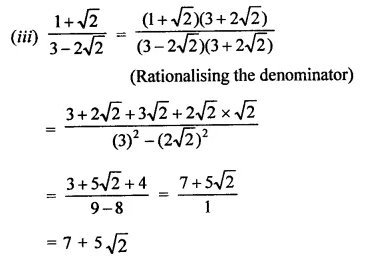
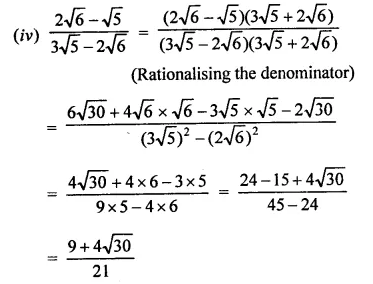
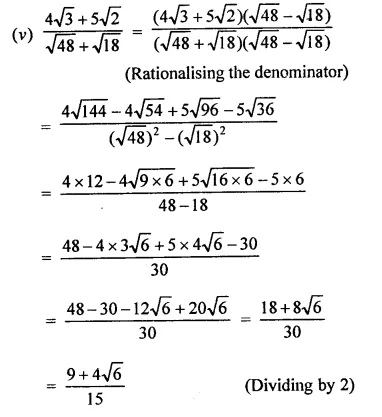
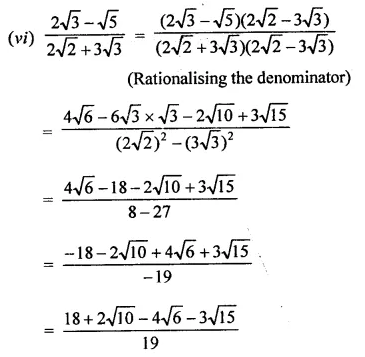
Question 5.
Simplify:
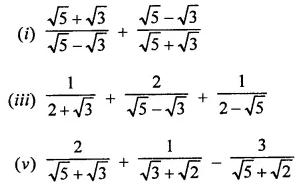
Solution:
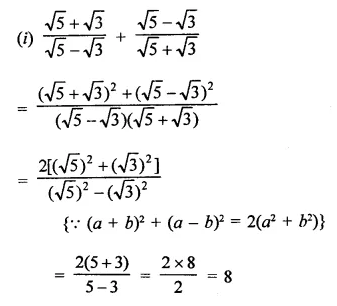
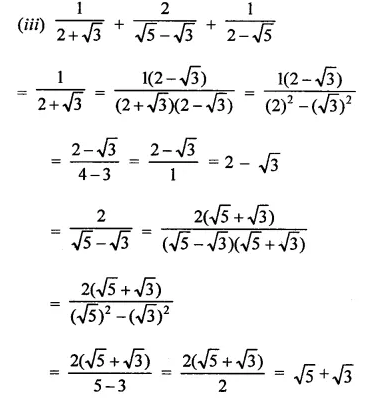
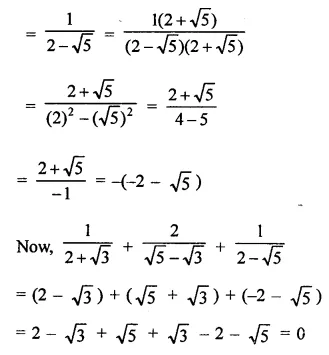
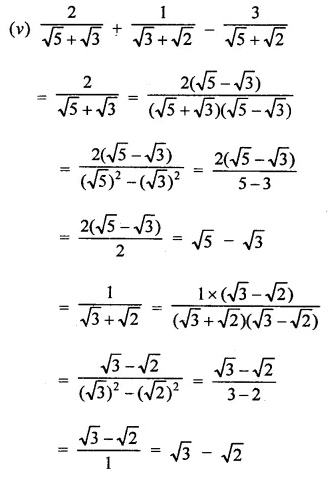
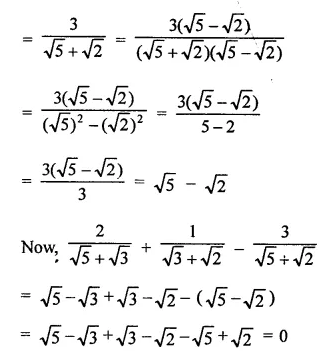
Question 6.
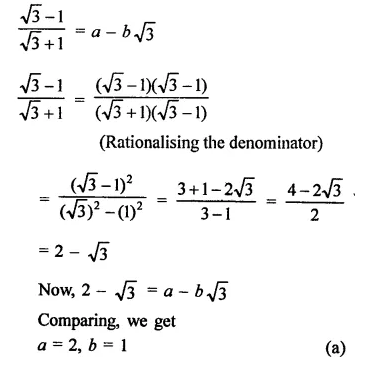
In each of the following determine rational numbers a and b:
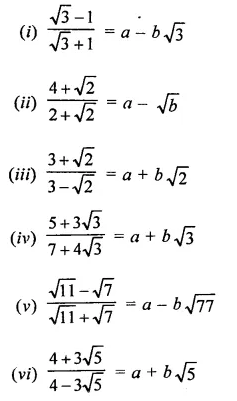
Solution:
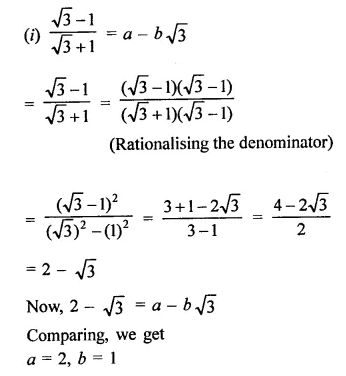
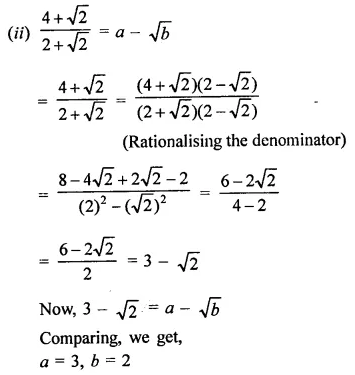
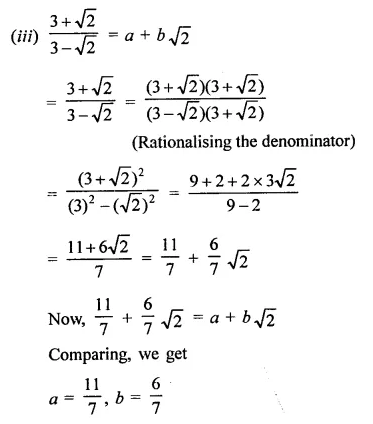
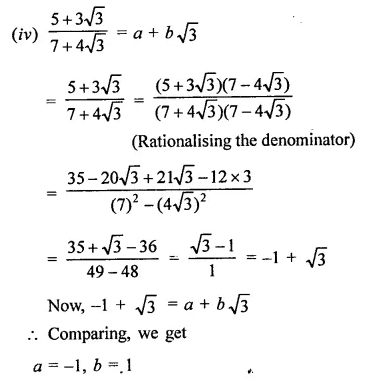
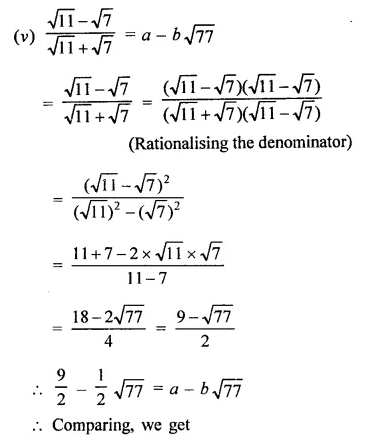
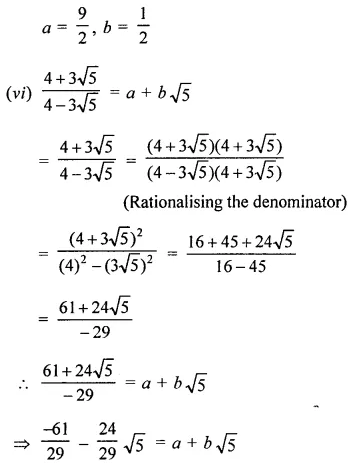
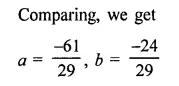
Question 7.
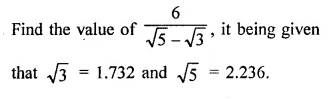
Solution:
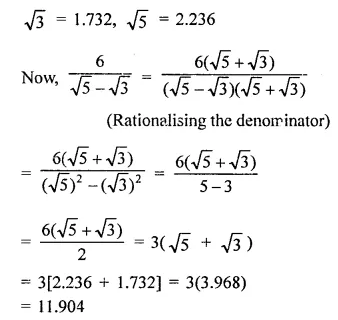
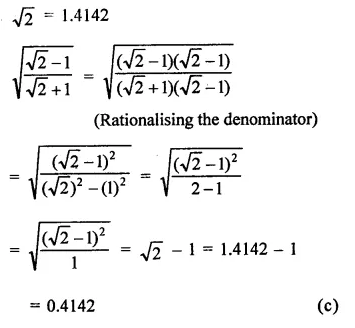
Question 8.
Find the values of each of the following correct to three places of decimals, it being given that \(\sqrt { 2 } \) = 1.4142, \(\sqrt { 3 } \) = 1-732, \(\sqrt { 5 } \) = 2.2360, \(\sqrt { 6 } \) = 2.4495 and \(\sqrt { 10 } \) = 3.162.

Solution:
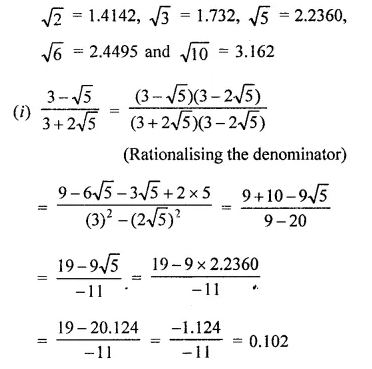
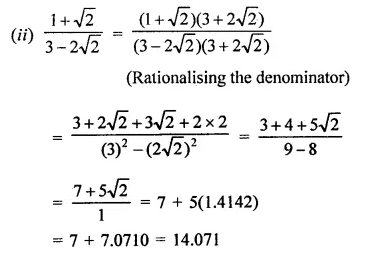
Question 9.
Simplify:
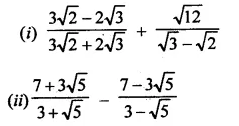
Solution:
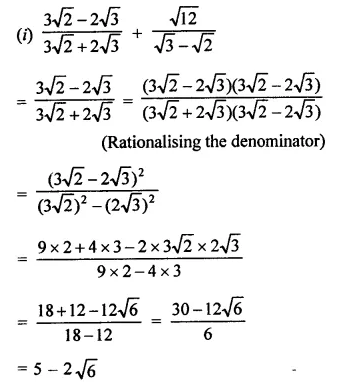
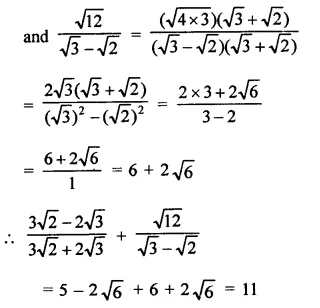
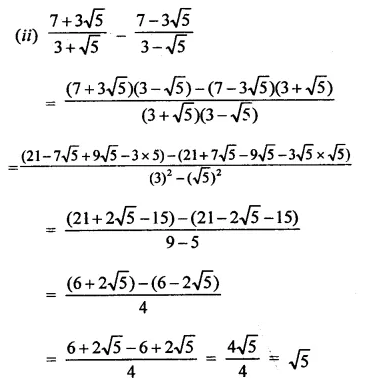
Question 10.

Solution:
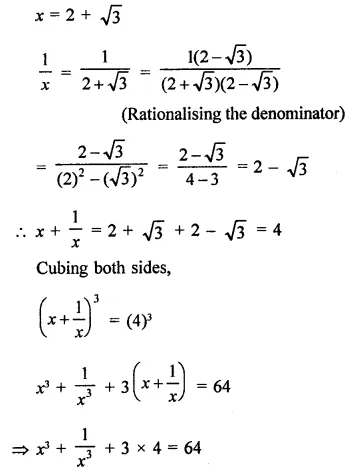

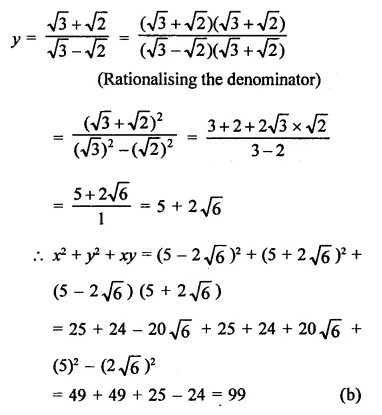
Question 11.

Solution:
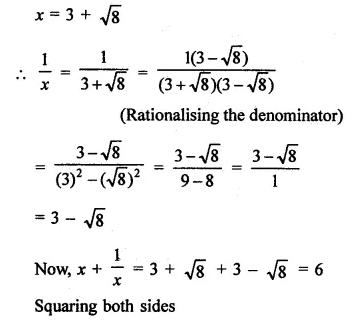
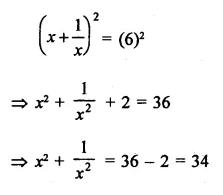
Question 12.

Solution:
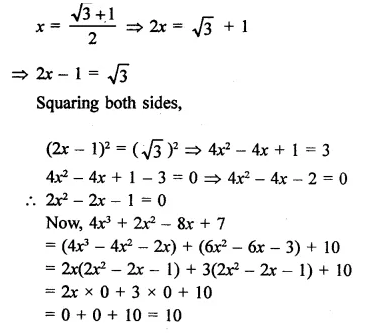
Hope given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 3 Rationalisation Ex 3.2 are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.