Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Chemistry MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 MCQ With Answers
Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 4 MCQs On Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics Class 12 MCQ Question 1.
In chemical equation H2 (g) + I2 (g) \(\rightleftharpoons\) 2HI (g) the equilibrium constant Kp depends on
(a) total pressure
(b) catalyst used
(c) amount of H2 and I2
(d) temperature
Answer
Answer: (b) catalyst used
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 MCQ Question 2.
If the rate of a reaction is expressed by, rate = A [A]² [B], the order of reaction will be
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer
Answer: (b) 3
Percent concentration and molarity are the most commonly used solution.
MCQ On Chemical Kinetics Question 3.
In a reaction, 2X → Y, the concentration of X decreases from 0.50 M to 0.38 M in 10 min. What is the rate of reaction in Ms-1 during this interval ?
(a) 2 × 10-4
(b) 4 × 10-2
(c) 2 × 10-2
(d) 1 × 10-2
Answer
Answer: (a) 2 × 10-4
MCQ On Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Question 4.
The decomposition of dimethyl ether is a fractional order reaction. The rate is given by rate =k(PCH3OCH3)3/2. If the pressure is measured in bar and time in minutes, then what are the units of rate and rate constant?
(a) bar min-1, bar2 min-1
(b) bar min-1, bar1/2 min-1
(c) bar1/2 min-1, bar2 min-1
(d) bar min-1, bar1/2 min-1
Answer
Answer: (b) bar min-1, bar1/2 min-1
Chemical Kinetics Class 12 MCQ Questions Question 5.
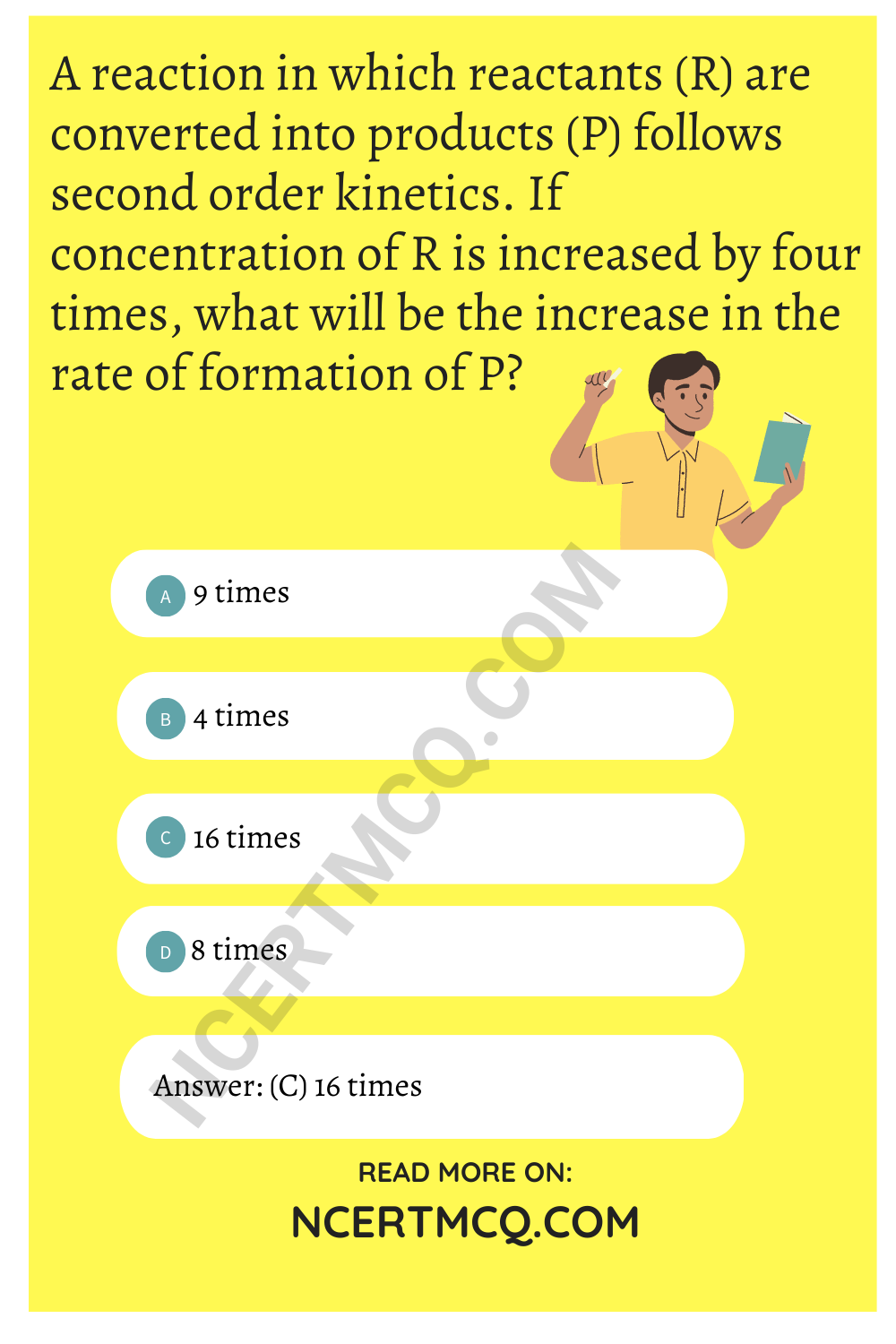
A reaction in which reactants (R) are converted into products (P) follows second order kinetics. If concentration of R is increased by four times, what will be the increase in the rate of formation of P?
(a) 9 times
(b) 4 times
(c) 16 times
(d) 8 times
Answer
Answer: (c) 16 times
MCQ Of Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Question 6.
Which of the following, is an example of a fractional order reaction?
(a) NH4NO2 → N2 + 2H2O
(b) NO + O3 → NO2 + O2
(c) 2NO + Br2 → 2NOBr
(d) CH3CHO → CH4 + CO
Answer
Answer: (d) CH3CHO → CH4 + CO
Chemical Kinetics MCQ Questions And Answers Question 7.
The unit of rate constant for the reaction
2H2 + 2NO → 2H2O + N2
which has rate = K|H2||NO|², is
(a) mol L-1 s-1
(b) s-1
(c) mol-2 L² s-1
(d)mol L-1
Answer
Answer: (c) mol-2 L² s-1
MCQ On Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Pdf Question 8.
Fora reaction x + y → z, rate ∝ |X|. What is (i) moleculariiy and (ii) order of reaction?
(a) (i)2, (ii) 1
(b) (i)2,(ii) 2
(c) (i) 1, (ii) 1
(d) (i) 1, (ii) 2
Answer
Answer: (a) (i)2, (ii) 1
Chemical Kinetics MCQ Questions Question 9.
For a reaction nx – y → z the rate of reaction becomes twenty seven times when the concentration of X is increased three times. What is the order of the reaction?
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 0
Answer
Answer: (c) 3
MCQ Of Chapter 4 Chemistry Class 12 Question 10.
The rate constant of a reaction depends upon
(a) temperature of the reaction
(b) extent of the reaction
(c) initial concentration of the reactants
(d) the time of completion of reaction
Answer
Answer: (d) the time of completion of reaction
Chemical Kinetics MCQ With Answers Pdf Question 11.
The chemical reaction, 2O3 → 3O2 proceeds as
O3 \(\rightleftharpoons\) O2 + |O| (fast)
|O| + O3 → 2O2 (slow)
The rate law expression will be
(a) Rate = k [O] [O3]
(b) Rate = k [O3]² [O2]-1
(c) Rate = k [O3]²
(d) Rate = k [O2] [O]
Answer
Answer: (b) Rate = k [O3]² [O2]-1
Class 12 Chemical Kinetics MCQ Question 12.
The unit of rate and rate constant are same fora
(a) zero order reaction
(b) first order reaction
(c) second order reaction
(d) third order reaction
Answer
Answer: (a) zero order reaction
Chapter 4 Chemistry Class 12 MCQs Question 13.
The number of molecules of the reactants taking part in a single step of the reaction is indicative of
(a) order of a reaction
(b) molecuiarity of a reaction
(c) fast step of the mechanism of a reaction
(d) half-life of the reaction
Answer
Answer: (b) molecuiarity of a reaction
MCQ Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Question 14.
Fora unimolecular reaction
(a) the order and molecuiarity of the slowest step are equal to one
(b) molecuiarity of the reaction can be zero, one or two
(c) molecuiarity of the reaction can be determined only experimentally
(d) more than one reacting species are involved in one step
Answer
Answer: (a) the order and molecuiarity of the slowest step are equal to one
MCQ Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Question 15.
The overall rate of a reaction is governed by
(a) the rate of fastest intermediate’step
(b) the sum total of the rates of all intermediate steps
(c) the average of the rates of all the intermediate steps
(d) the rate of slowest intermediate step
Answer
Answer: (d) the rate of slowest intermediate step
Question 16.
The order of reaction is decided by
(a) temperature
(b) mechanism of reaction as well as relative concentration of reactants
(c) molecularity
(d) pressure
Answer
Answer: (b) mechanism of reaction as well as relative concentration of reactants
Question 17.
Rate constant in case of first order reaction is
(a) inversely proportional to the concentration units
(b) independent of concentration units
(c) directly proportional to concentration units
(d) inversely proportional to the square of concentration units
Answer
Answer: (b) independent of concentration units
Question 18.
Half life period of a first order reaction is 10 min. What percentage of the reaction will be completed in 100 min?
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 99.9%
(d) 75%
Answer
Answer: (c) 99.9%
Question 19.
In pseudo unimolecular reactions
(a) both the reactants are present in low concentration
(b) both the reactants are present in same concentration
(c) one of the reactant is present in excess
(d) one of the reactant is non-reactive
Answer
Answer: (c) one of the reactant is present in excess
Question 20.
A first order reaction takes 40 min for 30% decomposition. What will be t12?
(a) 77.7 min
(b) 52.5 min
(c) 46.2 min
(d) 22.7 min
Answer
Answer: (a) 77.7 min
Question 21.
A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10-3s-1. How long time will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce to 3 g?
(a) 444 s
(b) 400 s
(c) 528 s
(d) 669 s
Answer
Answer: (a) 444 s
Question 22.
Radioactive disintegration is an example of
(a) zero order reaction
(b) first order reaction
(c) second order reaction
(d) third order reaction
Answer
Answer: (b) first order reaction
Question 23.
A plot of log (a – x) against time t is a straight line. This indicates that the reaction is of
(a) zero order
(b) first order
(c) second order
(d) third order
Answer
Answer: (b) first order
Question 24.
Rate of which reaction increases with temperature?
(a) Exothermic reaction
(b) Endothermic reaction
(c) (a) and (b) both
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) (a) and (b) both

Question 25.
The activation energy in a chemical reaction is defined as
(a) the difference in energies of reactants and products
(b) the sum of energies of reactants and products
(c) the difference in energy of intermediate complex with the average energy of reactants and products
(d) the difference in energy of intermediate complex and the average energy of reactants
Answer
Answer: (d) the difference in energy of intermediate complex and the average energy of reactants
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Chemical Kinetics CBSE Class 12 Chemistry MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 12 Chemistry MCQ:
- The Solid State Class 12 MCQ
- Solutions Class 12 MCQ
- Electrochemistry Class 12 MCQ
- Chemical Kinetics Class 12 MCQ
- Surface Chemistry Class 12 MCQ
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 MCQ
- The p-Block Elements Class 12 MCQ
- The d-and f-Block Elements Class 12 MCQ
- Coordination Compounds Class 12 MCQ
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 MCQ
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 MCQ
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 MCQ
- Amines Class 12 MCQ
- Biomolecules Class 12 MCQ
- Polymers Class 12 MCQ
- Chemistry in Everyday Life Class 12 MCQ
