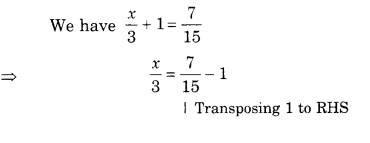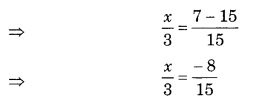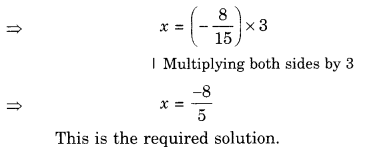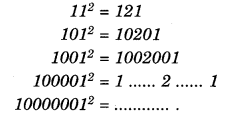NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 11 |
| Chapter Name | Transportation in Animals and Plants |
| Number of Questions Solved | 13 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
Question 1.
Match structures given in Column I with functions given in Column II:
| Column I | Cotumn II |
| (i) Stomata | (a) Absorption of water |
| (ii) Xylem | (b) Transpiration |
| (iii) Root hairs | (c) Transport of food |
| (iv) Phloem | (d) Transport of water |
| (e) Synthesis of carbohydrates |
Answer:
| Column I | Cotumn II |
| (i) Stomata | (b) Transpiration |
| (ii) Xylem | (d) Transport of water |
| (iii) Root hairs | (a) Absorption of water |
| (iv) Phloem | (c) Transport of food |
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The blood from the heart is transported to all parts of the body by the ………..
- Hemoglobin is present in cells.
- Arteries and veins are joined by a network of ……….
- The rhythmic expansion and contraction of the heart is called …………
- The main excretory product in human beings is ………..
- Sweat contains water and ……….
- Kidneys eliminate the waste materials in the liquid form called ………..
- Water reaches great heights in the trees because of suction pull caused by ………..
Answer:
- arteries
- red blood
- capillaries
- heartbeat
- urea
- salts
- urine
- transpiration
Question 3.
Choose the correct option:
(a) In plants, water is transported through
(i) xylem
(ii) phloem
(iii) stomata
(iv) root hair
(b) Water absorption through roots can be increased by keeping the plants
(i) in the shade
(ii) in dim light
(iii) under the fan
(iv) covered with a polythene bag
Answer:
(a) (i) xylem
(b) (iii) under the fan.
Question 4.
Why is the transport of materials necessary in a plant or in an animal? Explain.
Answer:
Transport of materials is essential for plants or animals because nutrients and oxygen are made available to all the parts of the body through transpiration. If the transport of necessary nutrients and oxygen does not take place in the body, the body will not be able to survive.
Question 5.
What will happen if there are no platelets in the blood?
Answer:
Whenever we get injured, blood comes out from the cut. The function of platelets is to make a clot which plugs the cut to stop bleedings. If there are no platelets in the blood, no clot will be formed and as a result, bleeding will not stop and leads to a disease: haemophilia. This may lead to fatal consequences.
Question 6.
What are stomata? Give two functions of stomata.
Answer:
Stomata are the tiny pores present on the surface of the leaves. These are surrounded by two bean shaped cells called guard cells.
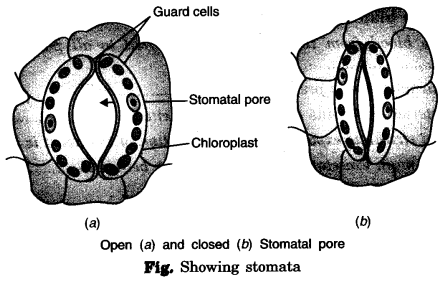
Functions of stomata :
(i) The exchange of gases in plants occurs through stomata.
(ii) The excess water in plants evaporates through stomata by a process called transpiration.
Question 7.
Does transpiration serve any useful function in the plants? Explain.
Answer:
Due to transpiration, a suction pressure develops which helps in the transportation of water.
Question 8.
What are the components of blood?
Answer:
Blood has two components: (a) Plasma and (b) Corpuscles, suspended in the plasma, with three kinds of blood cells.
(а) Plasma: It is the fluid part of blood.
(b) Corpuscles: It is of three types:
(i) Red Blood Cells (RBCs): Contain hemoglobin and impart a red color to the blood. Haemoglobin also carries oxygen from the lungs to all other body parts.
(ii) White Blood Cells (WBCs): Fight against the germs.
(iii) Platelets: Help in the clotting of blood.
Question 9.
Why is blood needed by all the parts of a body?
Answer:
Blood carries digested food and oxygen to all parts of the body. It also carries away the waste products.
Question 10.
What makes the blood look red?
Answer:
Blood contains three kinds of blood cells. Out of which Red Blood Cells contain an iron pigment called haemoglobin. Hemoglobin imparts red colour to the blood.
Question 11.
Describe the function of the heart.
Answer:
The heart collects and distributes purified blood to all parts of the body through arteries.
Question 12.
Why is it necessary to excrete waste products?
Answer:
Waste products are harmful to the body.
Question 13.
Draw a diagram of the human excretory system and label the various parts.
Answer:
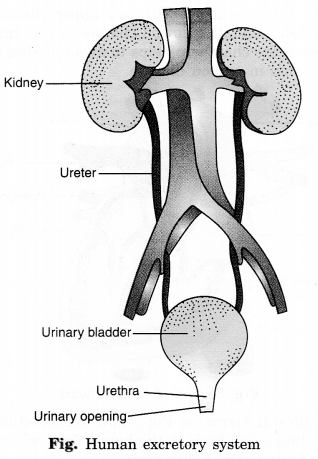
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.