This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used.
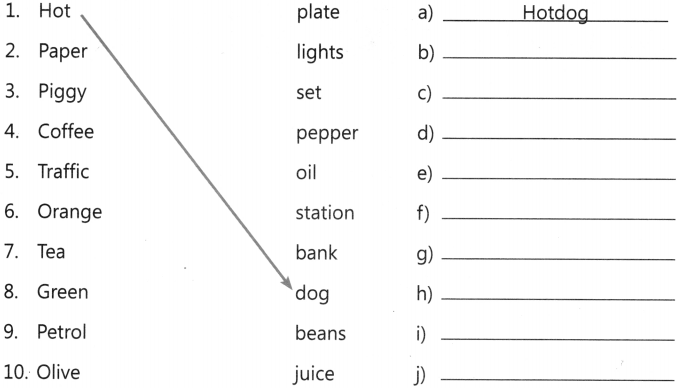
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used.
Pronouns Exercises for Class 4 CBSE with Answers PDF
- Words that are used in place of nouns are called pronouns.
- We use I, he, she, it, we, you, they so that we don’t have to repeat the nouns.
- I, he, she, it, we, you, they are subject pronouns. They are also called personal pronouns.
- We use I, He, She, It in place of the name of one person.
- We use We, You, They in place of names of more than one person.
- Me, us, you, him, her, it, them are also pronouns. They are called object pronouns.
- Me introduces I in a sentence.
- Us introduces We in a sentence.
- Him introduces He in a sentence.
- Her introduces She in a sentence.
- It introduces Object in a sentence.
- Them introduces They in a sentence.
- This, That, These and Those are demonstrative pronouns.
- This is used for objects that are nearby. That is used for objects that are far away, (one object)
- These is used for objects that are nearby. Those is used for objects that are far away, (more than one objects)
- When the object of a sentence is the same as the subject, it is called reflexive
- The singular reflexive pronouns are: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself.
- Plural reflexive pronouns include: ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
A. Write the pronouns that can take the place of the bold nouns in the following sentences.
1. Urmila planned a party for Sunanda. ___________________
2. Is Mom going to take us to the movie? ___________________
3. Sunil is taking a present for Sonia ___________________
4. Rakesh and Harish bought her a CD. ___________________
5. Dad gave the boys their pocket money. ___________________
6. Snighda will like the gift ___________________
7. Snighda saw Rakesh yesterday. ___________________
B. Fill in the blanks with correct pronoun to complete each sentence.
1. Siddarth and (me, I) went camping ___________________

2. (We, Us) went to the baseball game ___________________
3. The teacher took (we, us) to the library. ___________________

4. (Him, He) was a famous Indian ___________________
5. Aunt Sunita gave ten rupees to (them, we). ___________________
6. (Her, You) and Sunil are my best friends ___________________
7. Please take this note to (he, him) ___________________
C. Read the following passage. Write the missing demonstrative pronouns in the blank spaces.
Hari and I went for a walk on the beach. “What’s __________ over there?” I asked. “It looks like broken glass said Hari. He gave me a bag.
said Hari. He gave me a bag.
“Put it in __________,” he said. I put the broken glass into the bag. “We’d better put __________ in the trash,” I said. He took the bag from me. “You have to hold it like __________,” said Hari, “so that you don’t cut your hand.
D. Complete the sentences by choosing the correct pronoun from the brackets.
1. __________ watch on my wrist says it is noon. (These, This)
2. __________ cat across the street has a striped tail. (That, Those)
3. Whose skates  are __________ by the stairs? (this, those)
are __________ by the stairs? (this, those)
4. I don’t know why I’m wearing my hair __________ way. (this, those)
5. Did you eat __________ cookies on the table? (those, that)
6. __________ tests on my desk don’t have names on them. (These, This)
7. Remember __________ movie we watched yesterday? (that, those)
8. __________ trees are going to grow very tall. (These, This)
9. __________  storm we had last night kept me awake. (Those, That)
storm we had last night kept me awake. (Those, That)
10. Did you buy __________ grapes from the market? (that, those)
11. Ask __________ policeman for directions. (that, those)
12. How many of __________ napkins do you need? (these, this)
E. Underline the pronoun in each sentence. Write ‘S’ if it is a subject pronoun or ‘O’ if it is an object pronoun.
1. __________ Mona gave me the letter.
2. __________ You can sit down by the fire.
3. __________ They are going to watch a movie at the new theater.
4. __________ Pawan and Chetan can go with us tomorrow.
5. __________ We have been friends for many years.
6. __________ It is inside the pocket of the black backpack.
7. __________ The librarian gave me the library book.
8. __________ Jyoti’s mother brought her a sandwich for lunch.
9. __________ She played with the new puppy all day.
10. __________ Did you go to the party on Saturday night?
F. Underline the reflexive pronoun in each sentence.
Example
- A: He told himself to never be foolish again.
Answer.
himself
1. Make sure to remind yourself of the things you need to do.
2. She thought to herself while she was in the library.
3. 1 saw myself in the mirror.
4. We blamed ourselves for the mistake.
Directions: Write a sentence using reflexive pronouns gïven below.
5. Yourself – __________________________
6. Myself – __________________________






 This grammar section explains
This grammar section explains 




 This grammar section explains
This grammar section explains