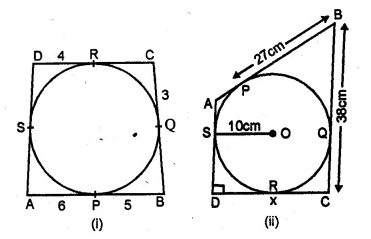
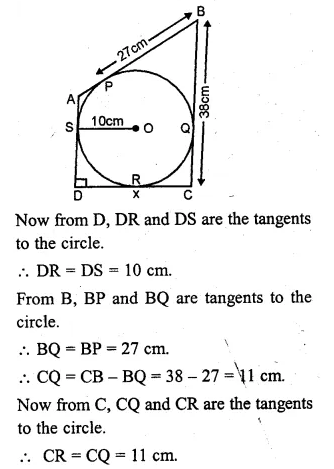
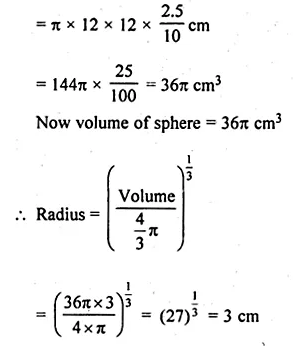
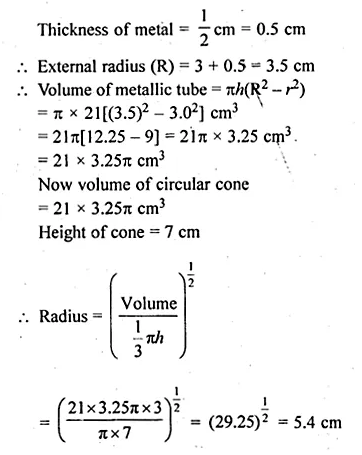
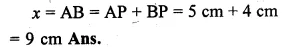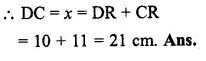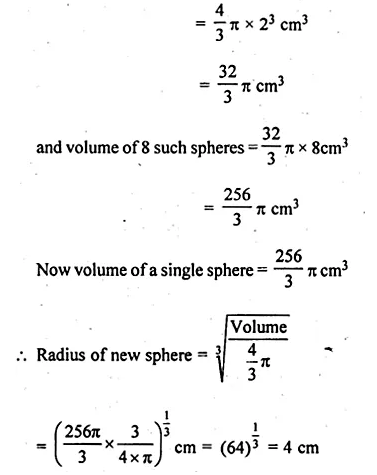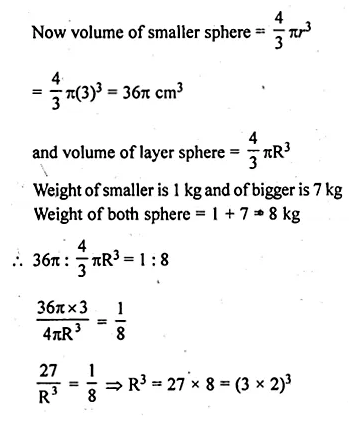NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi Sparsh Chapter 15 अब कहाँ दूसरे के दुख से दुखी होने वाले
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi Sparsh Chapter 15 अब कहाँ दूसरे के दुख से दुखी होने वाले.
पाठ्य पुस्तक प्रश्न
मौखिक
(क) निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक-दो पंक्तियों में दीजिए-
प्रश्न 1.
बड़े-बड़े बिल्डर समुद्र को पीछे क्यों धकेल रहे थे?
उत्तर:
बिल्डर निर्माण कार्य हेतु उसे धीरे-धीरे पीछे धकेलते जा रहे थे।
प्रश्न 2.
लेखक का घर किस शहर में था?
उत्तर:
लेखक का घर वर्सावा शहर में था।
प्रश्न 3.
जीवन कैसे घरों में सिमटने लगा है?
उत्तर:
जीवन छोटे-छोटे डिब्बे जैसे घरों में सिमटने लगा है।
प्रश्न 4.
कबूतर परेशानी में इधर-उधर क्यों फड़फड़ा रहे थे?
उत्तर:
कबूतर परेशानी में इधर-उधर इसलिए फड़फड़ा रहे थे, क्योंकि उनका एक अंडा बिल्ली ने तोड़ दिया और दूसरा अंडा लेखक की माँ की असावधानी के कारण टूट गया। इस तरह दोनों अंडों के टूट जाने पर अर्थात् अपने बच्चों का विनाश देखकर कबूतर परेशानी में इधर-उधर फड़फड़ा रहे थे।
लिखित
(क) निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर (25-30 शब्दों में) लिखिए-
प्रश्न 1.
अरब में लशकर को ‘नूह’ के नाम से क्यों याद करते हैं?
उत्तर:
अरब में लशकर को ‘नूह’ के नाम से लोग इसलिए याद करते हैं, क्योंकि ‘नूह’ नामक पैगंबर का असली नाम ‘लशकर’ ही था।
प्रश्न 2.
लेखक की माँ किस समय पेड़ों के पत्ते तोड़ने के लिए मना करती थीं और क्यों?
उत्तर:
लेखक की माँ सूरज ढलने के समय आँगन के पेड़ों से पत्ते तोड़ने के लिए मना करती थीं, क्योंकि उनकी कहना था कि इस समय पत्ते तोड़ने से वे रोते हैं और किसी को भी दुख पहुँचाना ठीक नहीं है।
प्रश्न 3.
प्रकृति में आए असंतुलन का क्या परिणाम हुआ है?
उत्तर:
प्रकृति में आए असंतुलन का भयंकर परिणाम हुआ है। जैसे-अब गरमी के मौसम में गरमी की अति, बेवक्त की बरसातें, ज़लज़ले, सैलाब, तूफ़ान और नित नए रोगों का उत्पन्न होना आदि अर्थात् अतिवृष्टि, अल्पवृष्टि तथा अनावृष्टि का होना इसी का परिणाम है।
प्रश्न 4.
लेखक की माँ ने पूरे दिन का रोज़ा क्यों रखा?
उत्तर:
लेखक की माँ ने पूरे दिन का दोज़ा पश्चाताप हेतु रखा। दरअसल उनके मकान के दालान में दो रोशनदान थे, जिसमें कबूतर के जोड़े ने घोंसला बना लिया था। घोंसले में दिए दो अंडों में से एक को बिल्ली ने उचक कर एक तोड़ दिया। यह देखकर माँ बहुत दुखी हुईं। उन्होंने दूसरे अंडे को बचाने के लिए प्रयास किया, लेकिन ऐसा करने से दूसरा अंडा भी टूट गया। इस गुनाह के लिए ही उन्होंने एक दिन का रोज़ा रखा।
प्रश्न 5.
लेखक ने ग्वालियर से बंबई तक किन बदलावों को महसूस किया? पाठ के आधार पर स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
लेखक ने ग्वालियर से बंबई तक कई बदलावों को महसूस किया। जैसे–लेखक का वर्सावा में आज जो घर है, वहाँ पहले दूर तक जंगल था। पेड़ थे, परिंदे थे तथा दूसरे जानवर थे और अब यहाँ समंदर के किनारे लंबी-चौड़ी बस्ती बन गई है।
प्रश्न 6.
“डेरा डालने से आप क्या समझते हैं? स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
‘डेरा डालने से आशय है कि अपने रहने के लिए अस्थायी घर बनाना। पाठ में बताया गया है कि समुद्र के किनारे बस्तियाँ बन जाने से कई पेड़ कटे, कई पक्षी पलायन कर गए और जो न जा सके, उन्होंने जहाँ-तहाँ डेरी डाल लिया।
प्रश्न 7.
शेख अयाज़ के पिता अपनी बाजू पर काला च्योंटा रेंगता देखे भोजन छोड़कर क्यों उठ खड़े हुए?
उत्तर:
शेख आयाज़ के पिता अपनी बाजू पर च्योंटा रेंगता देख, भोजन छोड़कर इसलिए उठ खड़े हुए, क्योंकि उन्हें लगा कि उन्होंने एक च्योंटे को बेघर कर दिया है। वह च्योंटा कुएँ पर रहता था। इसलिए वे उसे छोड़ने कुएँ पर गए।
(ख) निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर (50-60 शब्दों में) लिखिए-
प्रश्न 1.
बढ़ती हुई आबादी का पर्यावरण पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ा है?
उत्तर:
बढ़ती हुई आबादी का पर्यावरण पर गहरा प्रभाव पड़ा है। बढ़ती हुई आबादी के कारण समुद्र ने पीछे सरकना शुरू कर दिया है, पेड़ों को काट-काटकर उन्हें रास्तों से हटाया जा रहा है तथा फैलते हुए प्रदूषण ने पंछियों को बस्तियों से भगाना शुरू कर दिया है। बारूद की विनाशलीला ने वातावरण को प्रदूषित करना शुरू कर दिया है। गर्मी की अति, सर्दी की अति, बरसात की अति, ज़लज़ले, सैलाब, तूफ़ान और नित नए-नए रोगों का उत्पन्न होना आदि का बढ़ती हुई आबादी के कारण ही तो सामना करना पड़ रहा है।
प्रश्न 2.
लेखक की पत्नी को खिड़की में जाली क्यों लगवानी पड़ी?
उत्तर:
लेखक की पत्नी को खिड़की में जाली इसलिए लगवानी पड़ी, क्योंकि लेखक के घर में कबूतरों के एक जोड़े ने अपना घोंसला बना लिया था, जिससे उन कबूतरों का आना-जाना शुरू हो गया। जब वे कबूतर अपने बच्चों को दाना खिलाने आते, तो घर की किसी-न-किसी चीज़ से टकराकर उसे गिरा देते तथा कभी पुस्तकालय में घुसकर किताबें खराब कर देते थे।
प्रश्न 3.
समुद्र के गुस्से की क्या वजह थी? उसने अपना गुस्सा कैसे निकाला?
उत्तर:
समुद्र के गुस्से की वज़ह थी कि उसे निरंतर सिमटते जाना पड़ रहा था। बिल्डर निर्माण कार्य हेतु उसे धीरे-धीरे पीछे धकेलते जा रहे थे। उसने स्वयं को काफी सिकोड़ा, पर जब उसकी सहन-शक्ति समाप्त हो गई, तो उसे गुस्सा आ गया। उसने अपना गुस्सा प्रकट करने के लिए अपनी लहरों पर दौड़ते हुए तीन जहाज़ों को उठाकर बच्चों की गेंद की तरह तीनों दिशाओं में फेंक दिया। एक जहाज़ वर्ली के समुद्र के किनारे पर जा गिरा, तो दूसरा जहाज़ बांद्रा में कार्टर के सामने औंधे मुँह गिरा और तीसरा गेट-वे ऑफ इंडिया पर टूटकर सैलानियों का नज़ारा बना। ये तीनों जहाज़ कोशिश करने के बावजूद भी दुबारा चलने-फिरने योग्य न रहे।
प्रश्न 4.
‘मट्टी से मटूटी मिले, खो के सभी निशान। किसमें कितना कौन है, कैसे हो पहचान – इन पंक्तियों के माध्यम से लेखक क्या कहना चाहता है? स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
लेखक इन पंक्तियों के माध्यम से दो बातें कहना चाहता है। पहली-मृत्यु होने पर सभी प्राणियों के शरीर मिट्टी में मिलकर मिट्टी ही बन जाते हैं। अर्थात् फिर कोई पहचान नहीं रहती कि किस मिट्टी में किसका शरीर मिला है। दूसरी-आध्यात्मिकता की दृष्टि से जिस प्रकार समुद्र में बूंद के मिलने पर उसकी पहचान खो जाती है, उसी प्रकार सभी आत्माएँ मृत्यु के बाद कहाँ जाती हैं, मुक्त होती हैं अथवा परमात्मा में मिल जाती हैं; यह पहचानना भी अति दुष्कर है। संसार का रचयिता अपने अनुसार सबको रचता है, इसमें किसी की चाहत या इच्छा कार्य नहीं करती। जीवन के अंत में सभी इस मिट्टी में मिल जाते हैं। सबकी एक ही गति होती है।
(ग) निम्नलिखित के आशय स्पष्ट कीजिए-
प्रश्न 1.
नेचर की सहनशक्ति की एक सीमा होती है। नेचर के गुस्से का एक नमूना कुछ साल पहले बंबई में देखने को मिला था।
उत्तर:
इसका आशय है कि जैसे प्रत्येक मनुष्य की सहन-शक्ति की एक सीमा होती है, ठीक उसी तरह नेचर (प्रकृति) की सहन-शक्ति की भी सीमा होती है। जब हम प्रकृति के साथ छेड़खानी करते हैं, खिलवाड़ करते हैं, तो कुछ समय बाद उसकी सहन-शक्ति समाप्त हो जाती है। और तब वह बदला लेती है, आंदोलन करती है। ऐसा ही एक नमूना कुछ समय पहले बंबईवासियों को झेलना पड़ा था। उस समय भूकंप ने बंबईवासियों को इतना डरा दिया था कि उन्हें पूजा-स्थलों की शरण में जाना पड़ा था।
प्रश्न 2.
जो जितना बड़ा होता है, उसे उतना ही कम गुस्सा आता है।
उत्तर:
इसका आशय है कि जिस प्रकार धीर पुरुष छोटी-मोटी बातों से तथा दुख व अपमान आदि से नहीं घबराते, लेकिन अत्याचारों की अति होने पर वे अत्यधिक गंभीर परिणाम भुगतने के लिए अत्याचारी को बाध्य कर देते हैं उसी प्रकार समुद्र पर बिल्डरों और मछुआरों का कोप, धरती पर शिकारियों तथा भूमाफियों का अतिक्रमण तथा वायु में कल-कारखानों से निकलती ज़हरीली गैसों के कारण प्रकृति सभी को गंभीर परिणाम भुगतने के लिए बाध्य कर रही है, क्योंकि प्रकृति सबसे अधिक शक्तिशाली है।
प्रश्न 3.
इस बस्ती ने न जाने कितने परिंदों-चरिंदों से उनका घर छीन लिया है। इनमें से कुछ शहर छोड़कर चले गए हैं। जो नहीं जा सके हैं, उन्होंने यहाँ-वहाँ डेरा डाल लिया है।
उत्तर:
इसका आशय है कि मानव की बढ़ती महत्त्वाकांक्षाएँ, कभी न समाप्त होने वाली इच्छाएँ, बढ़ती हुई आबादी की लोलुपता की पूर्ति हेतु पेड़ों की कटाई, जंगलों का सफ़ाया, जंगली-जानवरों का शिकार तथा प्रकृति के साथ अनावश्यक छेड़खानी इत्यादि हरकतें पशु-पक्षियों को बेघर कर देती हैं, जिससे मनुष्य अपने दुर्भाग्य को ही निमंत्रण देता है। अतः मानव इस प्रकार के प्रकृति को असंतुलित करने वाले कुकृत्यों से बाज आना चाहिए।
प्रश्न 4.
शेख अयाज़ के पिता बोले ‘नहीं, यह बात नहीं है। मैंने एक घरवाले को बेघर कर दिया है। उस बेघर को कुएँ पर उसके घर छोड़ने जा रहा हूँ।’ इन पंक्तियों में छिपी हुई उनकी भावना को स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
इन पंक्तियों में शेख अयाज़ के पिता की परोपकार की भावना प्रकट हो रही है। वे एक परोपकारी व्यक्ति थे। समस्त जीवों के प्रति इन पंक्तियों के माध्यम से उनकी प्रेम-भावना उजागर हो रही है। दरअसल वे एक सरल हृदय, निष्कपट, दयालु और नेक इंसान थे। वे पशु-पक्षियों तथा कीड़े-मकोड़ों के दर्द और दुख-तकलीफ़ को भी समझते थे। उनकी भावनाएँ सभी के लिए समान थीं।
भाषा अध्ययन
प्रश्न 1.
उदाहरण के अनुसार निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में कारक चिह्नों को पहचानकर रेखांकित कीजिए और उनके नाम रिक्त स्थानों में लिखिए-
जैसे-
(क) माँ ने भोजन परोसा। कर्ता
(ख) मैं किसी के लिए मुसीबत नहीं हूँ। ………………..
(ग) मैंने एक घर वाले को बेघर कर दिया। ………………..
(घ) कबूतर परेशानी में इधर-उधर फड़फड़ो रहे थे। ………………..
(ङ) दरिया पर जाओ, तो उसे सलाम किया करो। ………………..
उत्तर:
(ख) मैं किसी के लिए मुसीबत नहीं हूँ। संप्रदान
(ग) मैंने एक घर वाले को बेघर कर दिया। कर्म
(घ) कबूतर परेशानी में इधर-उधर फड़फड़ा रहे थे। अधिकरण
(ङ) दरिया पर जाओ तो उसे सलाम किया करो। अधिकरण
प्रश्न 2.
नीचे दिए गए शब्दों के बहुवचन रूप लिखिए-
- चींटी,
- घोड़ा,
- आवाज़,
- बिल,
- फौज,
- रोटी,
- बिंदु,
- दीवार,
- टुकड़ा।
उत्तर:
एकवचन बहुवचन
- चींटी चींटियाँ
- घोड़ा घोड़े
- आवाज़ आवाजें
- बिल बिलों
- बिंदु बिंदुओं
- फौज फौजें
- रोटी रोटियाँ
- दीवार दीवारें
- टुकड़ा टुकड़े
प्रश्न 3.
ध्यान दीजिए नुक्ता लगाने से शब्द के अर्थ में परिवर्तन हो जाता है। पाठ में ‘दफा’ शब्द का प्रयोग हुआ है, जिसका अर्थ होता है-बार (गणना संबंधी), कानून संबंधी। यदि इस शब्द में नुक्ता लगा दिया जाए, तो शब्द बनेगा ‘दफा जिसका अर्थ होता है-दूर करना, हटाना। यहाँ नीचे कुछ नुक्तायुक्त और नुक्तारहित शब्द दिए जा रहे हैं, उन्हें ध्यान से देखिए और अर्थगत अंतर को समझिए।
- सजा – सज़ा
- नाज – नाज़
- जरा – ज़रा
- तेज – तेज़
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में उचित शब्द भरकर वाक्य पूरे कीजिए-
- आजकल ……………………… बहुत खराब है। (जमाना/ज़माना)
- पूरे कमरे को ……………………… दो। (सजा/सज़ा)
- ……………………… चीनी तो देना। (जरा जरा)
- माँ दही …………………….. भूल गई। (जमाना/ज़माना)
- दोषी को ………………………….: दी गई। (सजा/सज़ा)
- महात्मा के चेहरे पर ………………… था। (तेज/तेज़)
उत्तर:
- ज़माना
- सजा
- ज़रा
- जमाना
- सज़ा
- तेज
योग्यता विस्तार
प्रश्न 1.
पशु-पक्षी एवं वन्य संरक्षण केंद्रों में जाकर पशु-पक्षियों की सेवा-सुश्रूषा के संबंध में जानकारी प्राप्त कीजिए।
उत्तर:
छात्र स्वयं करें।
परियोजना कार्य
प्रश्न 1.
अपने आसपास प्रतिवर्ष एक पौधा लगाइए और उसकी समुचित देखभाल कर पर्यावरण में आए असंतुलन को रोकने में अपना योगदान दीजिए।
उत्तर:
छात्र स्वयं करें।
प्रश्न 2.
किसी ऐसी घटना का वर्णन कीजिए, जब अपने मनोरंजन के लिए मानव द्वारा पशु-पक्षियों का उपयोग किया गया हो।
उत्तर:
छात्र स्वयं करें।
Hope given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Hindi Sparsh Chapter 15 are helpful to complete your homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online tutoring for you.