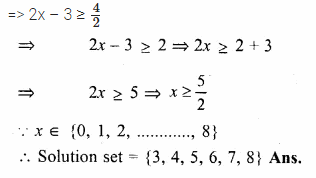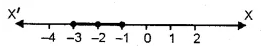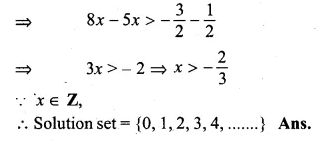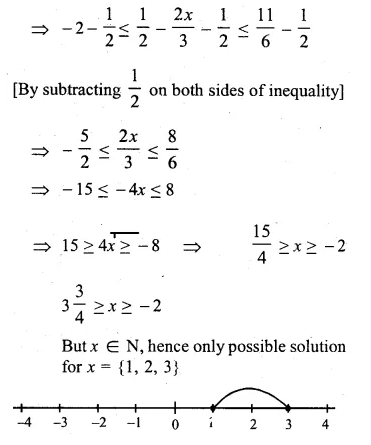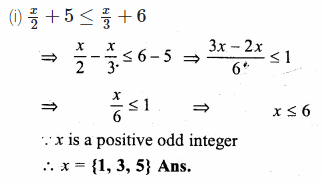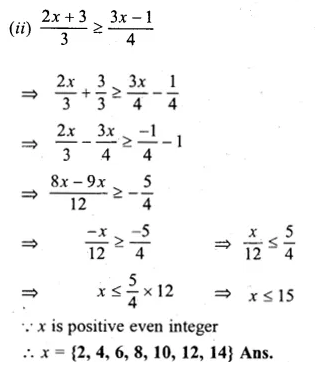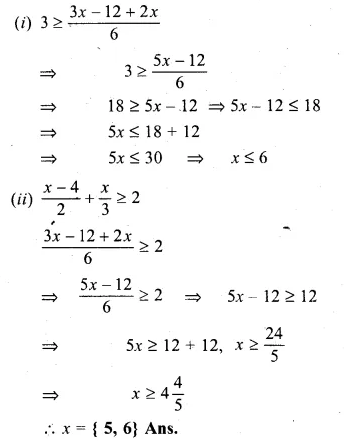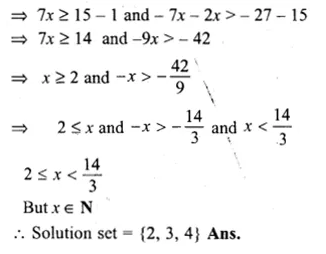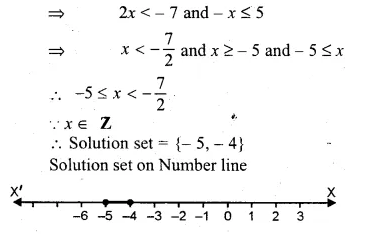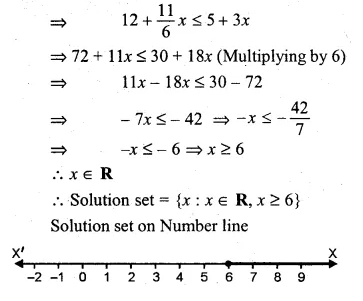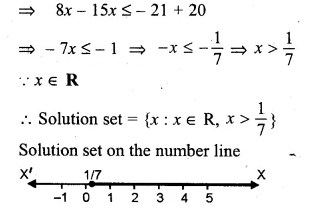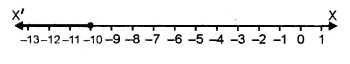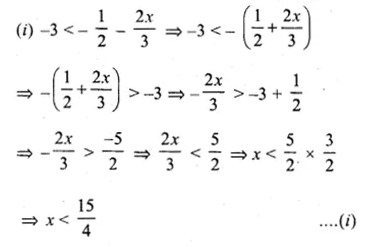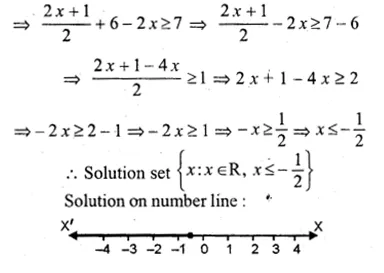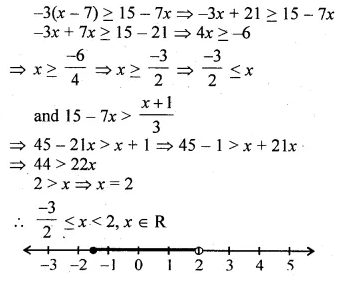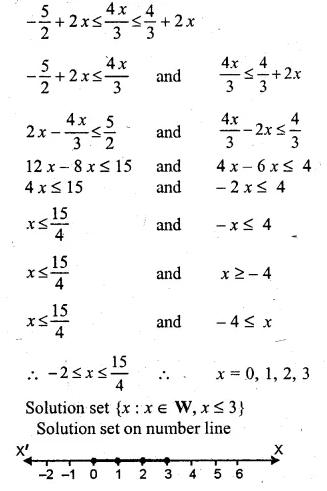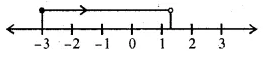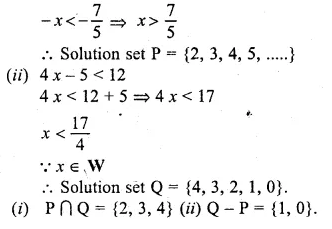ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 4 Linear Inequations MCQS
These Solutions are part of ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths. Here we have given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 4 Linear Inequations MCQS
More Exercises
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 4 Linear Inequations Ex 4
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 4 Linear Inequations MCQS
- ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 4 Linear Inequations Chapter Test
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (1 to 5) :
Question 1.
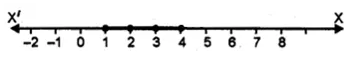
If x ∈ { – 3, – 1, 0, 1, 3, 5}, then the solution set of the inequation 3x – 2 ≤ 8 is
(a) { – 3, – 1, 1, 3}
(b) { – 3, – 1, 0, 1, 3}
(c) { – 3, – 2, – 1, 0, 1, 2, 3}
(d) { – 3, – 2, – 1, 0, 1, 2}
Solution:
x ∈ { -3, -1, 0, 1, 3, 5}
3x – 2 ≤ 8
⇒ 3x ≤ 8 + 2
⇒ 3x ≤ 10
⇒ x ≤ \(\\ \frac { 10 }{ 3 } \)
⇒ x < \(3 \frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)
Solution set = { -3, -1, 0, 1, 3} (b)
Question 2.
If x ∈ W, then the solution set of the inequation 3x + 11 ≥ x + 8 is
(a) { – 2, – 1, 0, 1, 2, …}
(b) { – 1, 0, 1, 2, …}
(c) {0, 1, 2, 3, …}
(d) {x : x∈R,x≥\(– \frac { 3 }{ 2 } \)}
Solution:
x ∈ W
3x + 11 ≥ x + 8
⇒ 3x – x ≥ 8 – 11
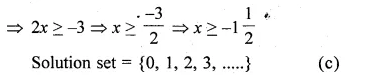
Question 3.
If x ∈ W, then the solution set of the inequation 5 – 4x ≤ 2 – 3x is
(a) {…, – 2, – 1, 0, 1, 2, 3}
(b) {1, 2, 3}
(c) {0, 1, 2, 3}
(d) {x : x ∈ R, x ≤ 3}
Solution:
x ∈ W
5 – 4x < 2 – 3x
⇒ 5 – 2 ≤ 3x + 4x
⇒ 3 ≤ x
Solution set = {0, 1, 2, 3,} (c)
Question 4.
If x ∈ I, then the solution set of the inequation 1 < 3x + 5 ≤ 11 is
(a) { – 1, 0, 1, 2}
(b) { – 2, – 1, 0, 1}
(c) { – 1, 0, 1}
(d) {x : x ∈ R, \(– \frac { 4 }{ 3 } \) < x ≤ 2}
Solution:
x ∈ I
1 < 3x + 5 ≤ 11
⇒ 1 < 3x + 5
⇒ 1 – 5 < 3x
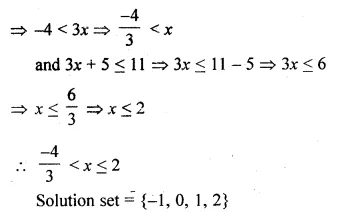
Question 5.
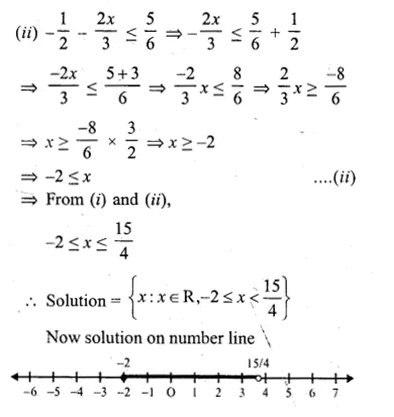
If x ∈ R, the solution set of 6 ≤ – 3 (2x – 4) < 12 is
(a) {x : x ∈ R, 0 < x ≤ 1}
(b) {x : x ∈ R, 0 ≤ x < 1}
(c) {0, 1}
(d) none of these
Solution:
x ∈ R
6 ≤ – 3(2x – 4) < 12
⇒ 6 ≤ – 3(2x – 4)
⇒ 6 ≤ – 6x + 12
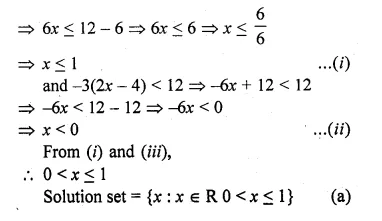
Hope given ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 4 Linear Inequations MCQS are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.