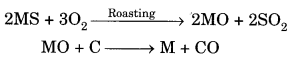
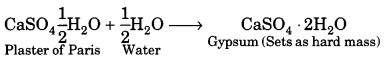
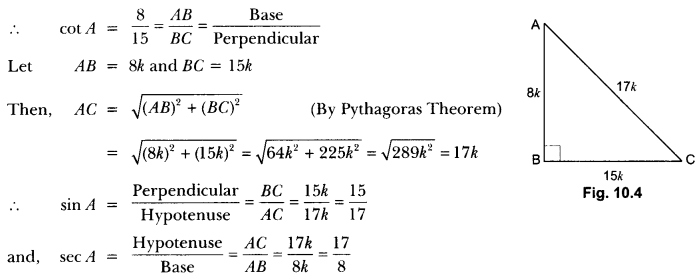
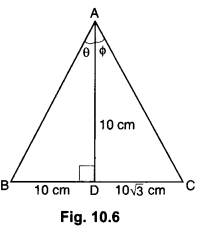
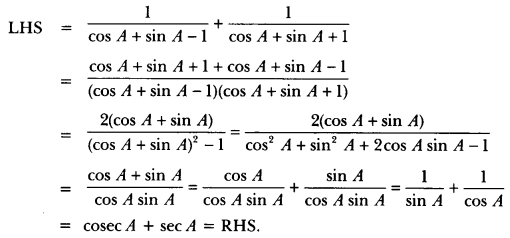
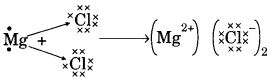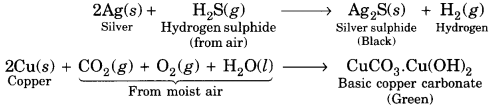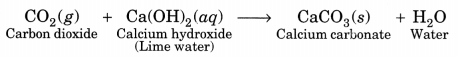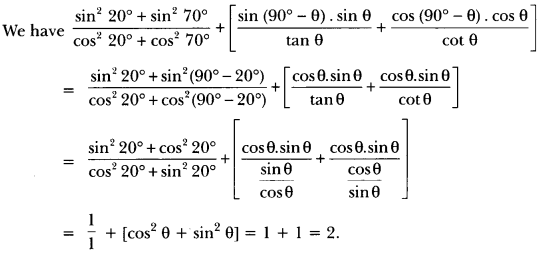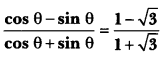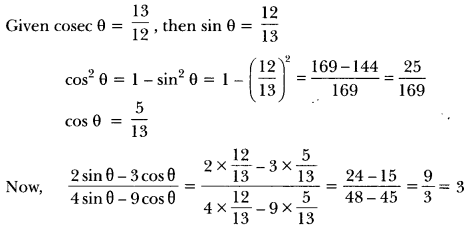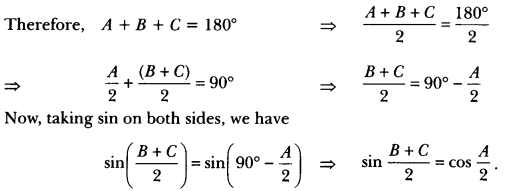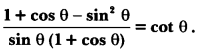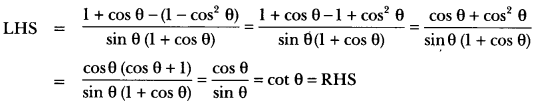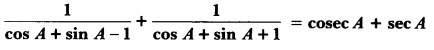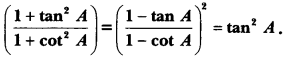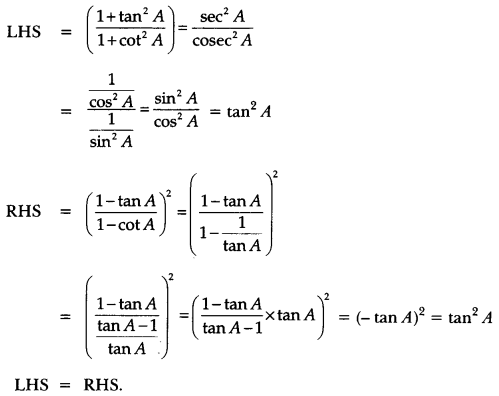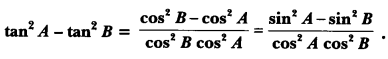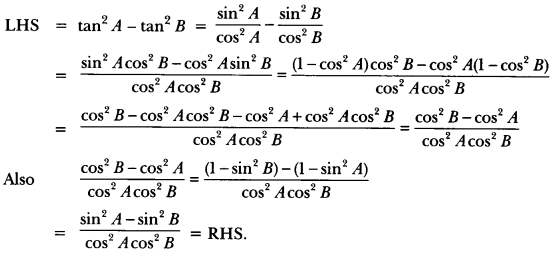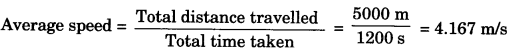Here we are providing A Dog Named Duke Extra Questions and Answers Class 9 English Literature Reader, Extra Questions for Class 9 English was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-9-english/
A Dog Named Duke Extra Questions and Answers Class 9 English Literature
A Dog Named Duke Extra Questions and Answers Short Answer Type
Answer the following questions briefly.
Question 1.
Why was Duke put in a kennel?
Answer:
Duke was put in a kennel because Chuck had an accident which meant he would not be returning home for a long time. Marcy also would not be home much and there would have been no one to take care of Duke.
Question 2.
Why did Chuck not show much improvement in the hospital?
Answer:
Chuck was probably not being able to come to terms with the fact that he would never regain his health but would remain a cripple all his life. This thought depressed him and slowed down his rate of recovery.
Question 3.
How did Duke behave when he saw Chuck after he came back from the hospital?
Answer:
Duke was so excited to see his master that he launched himself on his master causing him to almost fall down.
Question 4.
Did Duke’s return have any effect on Hooper?
Answer:
After the first day when Duke threw himself on him and Chuck had stood up to welcome him, Chuck did not show any more enthusiasm. He would spend his days in silence, staring at the ceiling for hours.
Question 5.
“The dog knew instantly”—What did he know? How did he behave thereafter?
Answer:
He instantly realised that his master was not well and after that he never jumped on Chuck again but stayed by his bedside around the clock, staring at him in silence.
Question 6.
“Duke finally couldn’t take it.” What does the narrator mean by this? What change did Duke bring about?
Answer:
Duke could not take the long hours of silence from Hooper and his apathy and listlessness. He started poking and nudging Chuck till at last Chuck was forced to respond.
Question 7.
“It was like lighting a fuse. Duke shimmied himself U-shaped in anticipation.” Explain.
Answer:
This line refers to the effect Chuck had on the dog when his good hand idly hooked the leash onto the dog’s collar. The dog jumped up in anticipation that his master would take him for a walk. It made the dog all excited.
Question 8.
“The pair set daily goals.” Who were the pair? What were their daily goals?
Answer:
The “pair” refers to Chuck and his dog Duke. Their goal refers to their determination to get Chuck walking and resuming his normal life. Every day they increased the distance and walked till Chuck was able to walk long distances without help from Duke.
Question 9.
What did Duke do when his master fell in his attempt to walk?
Answer:
Duke would stand very still while his master struggled to get up. It seemed as if he felt it was his job to get his master back on his feet.
Question 10.
Did Chuck give up after Duke’s death? Give reasons for your answer.
Encourage the students to think creatively and formulate their own answer.
Answer:
No, Chuck continued to walk and work as he had done with Duke by his side. He had realised the deep love, dedication, and patience that the dog had shown in getting him back on his feet and he could not let all that effort go in vain.
A Dog Named Duke Extra Questions and Answers Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Describe the first attempts made by Hooper to walk.
Answer:
Hooper’s good hand held onto the leash attached to the dog’s collar and he asked Marcy to help him to his feet. With Marcy supporting him by the elbow, he moved his right leg out in the front, causing the left foot to drag forward alongside the right leg. Duke felt the sudden slackness in his leash and he pulled it tight. Chuck swayed forward, broke the fall with his right leg, and then straightened.
Thrice he repeated the same before collapsing into his wheelchair, thus taking his first step since his accident. Everyday thereafter the dog and his master would set targets for the day, slightly further from the day before and not rest till the target for the day was accomplished. In this way from one step they took several steps to reach the door and finally covered the neighbourhood and beyond.
Question 2.
Write a character sketch of Chuck Hooper. What kind of a man do’you think he was?
Answer:
Before the accident Chuck appears to be a happy-go-lucky m$n who has everything going for him. He has a job, a loving wife, a comfortable home with a dog he loves, and the opportunity to play in the football team. But the accident brings out the real depth of his character. After he shakes off his initial despair and gloom, he appears to be a determined, persevering young man who is not afraid to stretch his limits. He shows tremendous courage in facing his handicap and finding a way to live life on his terms in spite of it. He also has the sensitivity to appreciate the dog’s efforts to help him. His hard working nature and independence is apparent in the way he comes back to work and is promoted due to the excellent work that he puts in.
Question 3.
Charles Hooper writes a diary entry after Duke dies, detailing the impact the dog has had on his life. Write the entry.
Answer:
12 April 20xx
Duke died today. A part of me has been buried with him. There is much that I have to thank Duke for. After my accident I saw no reason to live. I lay in my bed for months staring at the ceiling. Marcy, my wife was so upset to see me so morose and depressed. That is when she decided to bring Duke back home from the kennel where she had put him while I was in hospital. The day he returned I tried to stand up to welcome
him. With a giant leap he launched himself on me. He was so excited and happy to see me! But he was so sensitive; he immediately sensed that all was not fine with me. After that he never jumped on me but sat by my bedside quietly staring at me. For some weeks he sat patiently but one day he decided to take me outside and started prodding and nudging me till I had to give in and try to stand.
I can never forget the care and effort he put in to help me walk. I would hold on to his leash while he would walk forward holding it tight waiting for me to drag my legs till I reached him, then he would run ahead and wait for me. In this way I started walking—first a few steps then some more and finally around the neighbourhood. I owe Duke so much. It is really hard to let him go. May you rest in peace!
Question 4.
Marcy writes a letter to her mother in another city informing her about the change in Chuck’s attitude since the return of Duke, mentioning the effort Duke has been putting in goading Chuck out of the bed. Write the letter.
Answer:
15 August 20xx XYZ
Dear Mother,
I never thought there would be a day when I would be grateful to Duke! But it is true, that dog is a wonder! He has managed to get Chuck out of his bed today! I could hardly imagine this was possible.
When I returned from work I saw Chuck standing holding on to Duke’s leash. Then Duke moved ahead and waited with his leash tight while Chuck slowly shuffled his legs to move forward till he was just behind Duke and the leash was loose. Then Duke again moved forward and stood with his leash straining tight. Once again • Chuck moved forward but was so tired out by the effort that he collapsed into his wheelchair!
I am so happy, Duke is such a godsend. He is so sensitive in spite of his huge size. He understands Chuck’s needs and adjusts his movements to suit Chuck’s. He is better than any physiotherapist! He has got my Chuck once again interested in life. Now I am hopeful that Chuck will resume as normal a life as possible under the circumstances.
Your daughter,
Marcy
A Dog Named Duke Extra Questions and Answers Reference to Context
Read the extracts given below and answer the questions that follow.
Question 1.
In 1953, Hooper was a favoured young man. A big genuine grin civilized his highly competitive nature. Standing six-foot-one, he’d played on the university football team. He was already a hard-charging zone sales manager for a chemical company. Everything was going for him.
(a) With reference to Hooper, the author says, “Everything was going for him.” What does it imply?
Answer:
The author implies that Hooper had everything that a man aspires for.
(b) What was Hooper’s occupation and what made him well suited for the job?
Answer:
Hooper was a hard-charging zone sales manager for a chemical company. He was well suited because of his pleasant personality and competitive nature.
(c) In your own words can you define what hard-charging means?
Answer:
Hard-charging means ambitious or working or performing with a lot of energy and skill
Question 2.
“Hooper was taken to the hospital with a subdural haemorrhage. ”
(a) How did Hooper get hurt?
Answer:
Hooper got hurt in a car accident.
(b) What does subdural haemorrhage mean?
Answer:
The medical term subdural haemorrhage means bleeding in the brain.
(c) For how long did Hooper have to stay in the hospital?
Answer:
Hooper stayed in the hospital for many months.
Question 3.
“But Chuck did not make much headway. ”
(a) What was wrong with Chuck?
Answer:
Chuck was paralyzed after an accident.
(b) What does “did not make much headway” mean?
Answer:
It means that Chuck did not show any signs of recovering.
(c) How did Chuck regain his enthusiasm for life?
Answer:
He regained his enthusiasm for life because of his dog, Duke
Question 4.
“Finally they decided to bring Duke home. ”
(a) Whom does “they” refer to?
Answer:
In the given extract “they” refers to Hooper and his wife.
(b) Where had Duke been?
Answer:
Duke had been put in a kennel after Hooper met with an accident.
(c) Why did they decide to bring Duke home?
Answer:
Hooper was bed ridden and needed companionship. They decided to bring Duke home as he could help Hooper get out of his listlessness.
Question 5.
Those who saw it said the dog knew instantly. He never jumped on Chuck again. From that moment, he took up a post beside his master’s bed around the clock.
(a) Why did Duke never jump on Chuck again?
Answer:
Duke realised that Chuck was not well and could not balance himself.
(b) The author says that Duke “knew his job”. What was the job?
Answer:
Duke’s job was to look after Chuck.
(c) Explain the phrase ‘around the clock’.
Answer:
The phrase around the clock means all day and all night.
Question 6.
“ Go run around the house Duke. ’ But Duke wouldn’t. He’d lie down with a reproachful eye. ”
(a) Why was Duke unhappy with Hooper?
Answer:
Duke was unhappy with Hooper as Hooper was not showing any interest in getting well.
(b) What do these lines tell us about Duke?
Answer:
These lines tell us that Duke did not wish to leave his master alone. He was determined to make his master get up.
(c) What does the phrase ‘reproachful eye’ mean?
Answer:
The phrase ‘Reproachful eye’ means that Duke was looking at Hooper disapprovingly.
Question 7.
“Duke felt the sudden slack in the leash and pulled it taut. ”
(a) Why did Duke pull his leash?
Answer:
Duke pulled the leash as he was helping Chuck to walk.
(b) What does the word “taut” mean?
Answer:
Taut means very tight.
(c) What was the result of Duke’s help?
Answer:
The result of Duke’s help was that Hooper regained his confidence and started to walk.
Question 8.
“By mid-April, neighbours saw a daily struggle in front of Marcy’s house. ”
(a) What is the “daily struggle” being referred to?
Answer:
Here the “daily struggle” refers to Hooper getting out of the house to practice his walk.
(b) Who were the ones who struggled?
Answer:
Duke and Hooper were the ones who struggled.
(c) What had happened to Hooper?
Answer:
Hooper had become paralyzed after an accident.
Question 9.
“Gordon this isn’t just a visit. Bring me up to date…”
(a) Who is Gordon?
Answer:
‘ Gordon was Hooper’s manager at work.
(b) Who is the speaker?
Answer:
The speaker of the extracted line is Hooper.
(c) What does he mean when he says “this isn’t just a visit?”
Answer:
When Hooper says “this isn’t just a visit”, he means he had come to work.
Question 10.
“Chuck hit the target and after March 1, there was no time for the physiotherapy programme… ”
(a) What target does Chuck hit?
Answer:
The target Chuck had was to work a full day.
(b) What did this prove about Chuck? What was the result of Hooper’s hitting the target?
Answer:
It proved that he was persevering, determined, and painstaking. He was appointed regional sales manager for hitting the target.
(c) What do you mean by physiotherapy?
Answer:
Physiotherapy is the treatment of injuries or disease by exercise or massage.
Question 11.
“They carried the big dog into the house.”
(a) Why did they have to carry the dog into the house?
Answer:
They had to carry the dog into the house because he had been run over by a car.
(b) Who carried the dog in?
Answer:
Marcy carried the dog inside.
(c) How does the person’s present attitude differ from earlier attitude?
Answer:
Marcy did not like the dog earlier but after everything he did for Hooper she loved him now.
Question 12.
“Marcy was not really a dog lover…It took a long time before Marcy was more than polite to the dog. ”
(a) Who was Marcy?
Answer:
Marcy was Hooper’s wife.
(b) Explain “More than polite to the dog”
Answer:
“More than polite to the dog” means Marcy finally accepted the dog in their house.
(c) Why was Marcy wary of the dog at first?
Answer:
Marcy was wary of the dog at first because it was very big and boisterous.