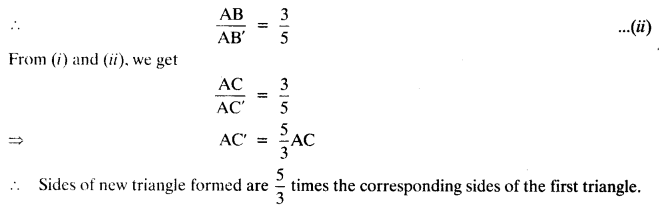CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies Paper 2 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies Paper 2.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies Paper 2
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Business Studies |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 2 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 2 of Solved CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
(i) Answer to questions carrying 1 mark may be from one word to one sentence.
(ii) Answer to questions carrying 3 marks may have about 50 to 75 words.
(iii) Answer to questions carrying 4 – 5 marks may have about 150 words.
(iv) Answer to questions carrying 6 marks may have about 200 words.
(v) Attempt all the parts of a question together.
Question 1:
Aircel started an earnest awareness campaign ‘Save our Tigers’. The campaign’s main agenda was to conserve tigers. This campaign highlights which objective of management?
Question 2:
Some products have certain unique features. They attract significant groups of buyers. Identify the kind of product.
Question 3:
Sunrise Ltd intends to achieve a return of 20% on investment. What type of plan is it?
Question 4:
The employees of Murfi Wear Ltd take part in hockey matches on Sunday. Name the type of organisation formed.
Question 5:
Priyanka wants to buy a gold ring. As an aware customer, how can she be sure about the quality of gold ring, which she is going to buy?
Question 6:
However qualified, experienced and learned a teacher may be, he/she is required to give a demo and teach a class before being selected. What kind of test is it?
Question 7:
XYZ Services was looking to hire 100 new employees in the month of February, 2018. The human resource department is asked to achieve this target with the help of operations department. By the end of February, 2018, the target could not be achieved. For this HR department is blaming operations department and vice-versa. Which concept is missing in the above paragraph?
Question 8:
Give the meaning of capital market.
Question 9:
Differentiate between management principles and values on the basis of mode of formation and nature.
Question 10:
Nature of money market can be well explained with the help of its features. State any three such features of money market.
Question 11:
In a manufacturing unit which is located in the remote town area, a labourer gets ₹ 400 after completing 100 units of product in a day. Another gets ₹ 500 after completing 80 units in a day.
(i) Which principle is violated in the given case?
(ii) State some of its adverse effects.
Question 12:
“Packaging has acquired great significance in the marketing of goods.” In the light of this statement, explain any three functions of packaging.
Question 13:
If planning involves working out details for the future, why does it not ensure success?
Question 14:
XYZ Co produces leather purses and they are using animal’s skin as a raw material.
- Which values do you find disturbing in the above para?
- Find out the component of business environment which is being overlooked?
Question 15:
(i) Name the organisation which has the benefit of easy to fix responsibility.
(ii) Name the type of organisation which does not have pre-determined objectives.
(iii) Differentiate between formal and informal organisation
Question 16:
“Management is skillful and personal application of existing knowledge to achieve desired results.” Explain.
Question 17:
Khushi purchased some household goods from a general store. After reaching home she found a face cream in her merchandise, for which she has not been billed. After checking the date of expiry and other details, she started using it. Her face burnt due to the use of cream.
- Can Khushi file a complaint? Justify your answer.
- Under Consumer Protection Act, 1986, who can file a complaint?
Question 18:
You are a management guru. In your opinion, is controlling the last function or the beginning of the process of management?
Question 19:
A company X Ltd is setting-up a new plant in India for manufacturing auto components. India has a highly competitive and cost effective production base in the sector. Many reputed car manufacturers source their auto components from here. X Ltd is planning to capture about 40% of the market share in India and also export to the tune of atleast $5 million in about 2 years of its planned operations. To achieve these targets, it requires a high trained and motivated work force. You have been asked by the company to advise it in this matter, which function of management helps in obtaining right people and putting them on the right place/jobs? Explain any three benefits of this function.
Question 20:
What do you mean by strategy? Explain its features.
Question 21:
KAY Ltd is a company manufacturing textiles. It has a share capital of ₹ 60 lakh. In the previous year its earning per share was ₹ 0.50. For diversification, the company requires additional capital of ₹ 40 lakh. The company raised funds by issuing 10% debentures for the same. During the year, the company earned profit of ₹8 lakh on capital employed. It paid tax @ 40%.
- State whether the shareholders gained or lost, in respect of earning per share on diversification. Show your calculations clearly.
- Also, state any three factors that favour the issue of debentures by the company as part of its capital structure.
Question 22:
Timely Ltd is a manufacturer of premium wall clocks. The company has been doing extremely well and has been able to carve a niche in the market. The company recently decided to go global. To achieve the above objective, the company decided to increase its production to 30,000 units per month. But, after two months, the management observed that only 45,000 units were manufactured. Company is * opting for a good control system in order to achieve the targets on time.
- In context to this, give some of the advantages of controlling.
- State the values that will be served by an effective control system.
Question 23:
Motivation refers to the way in which urges, desires, aspirations, strivings or needs direct, control and explain the behaviour of human beings. It is something which moves the person to action and continues him in the course of action already initiated. With reference to this, explain the process of motivation.
Question 24:
Dev Ltd is a company engaged in the production and distribution of films. The company is an established name in Bollywood. Now the company wants to enter in the regional cinemas also and for this, they are now targeting the South Indian Film Industry. They have launched three films in South with leading actors and actresses and even managed to sign Rajnikanth. To fund its projects, the management takes a decision to raise money for long-term capital needs of business from certain sources.
- State the different sources of long-term capital.
- Decision to raise money for long-term capital needs is affected by several factors. Discuss any five such factors.
Question 25:
“Generally, consumers prefer to buy goods directly from the producers but it is not always possible.” Explain four different factors responsible for this.
Answers
Answer 1:
This campaign highlights social objective of management.
Answer 2:
These products are known as speciality products.
Answer 3:
It is an objective plan.
Answer 4:
Informal organisation is formed by the employees of Murfi Wear Ltd.
Answer 5:
She should check the BIS’s (Bureau of Indian Standards) ‘Hallmark’ on the ring.
Answer 6:
Trade test, which is used to evaluate candidate’s professional efficiency.
Answer 7:
In the given paragraph, coordination is missing between the HR department and the operations department. It affects the organisational value of cooperation among different departments.
Answer 8:
Capital market refers to facilities and institutional arrangements through which long-term funds, both debt and equity are raised and invested.
Answer 9:
Difference between management principles and values are:
| Basis | Management Principles | Values |
| Mode of formation | They are formed after research and experimentation in real life work situations. | They are formed through common practice. |
| Nature | They are technical in nature. | They are ethical in nature. |
Answer 10:
Features of money market are as follows :
- It deals in short-term monetary assets, whose period of maturity is upto one year.
- It is a market where low risk, unsecured and short-term debt instruments are issued and actively traded everyday.
- Liquidity is provided by the Discount and Finance House of India, specially formed for this purpose.
Answer 11:
- Principle of equity is violated.
- Adverse effects are:
- It creates dissatisfaction among the employees.
- Skilled workers lose confidence in the organisation.
- It emerges poor relations between workers and managers
Answer 12:
Packaging refers to the act of designing and producing the container or wrapper of a product.
Three functions of packaging are as follows:
- Product Identification Packaging helps a product to be identified by the customer, e.g. Maggi Noodles in yellow colour, Lays in blue, green and red colour can be identified easily.
- Product Protection Packaging protects the contents of a product from spoilage, breakage, leakage, damage, etc. e.g. Air tight containers and packets are used for biscuits, tea, etc.
- Product Promotion Packaging promotes the sales of the product. Package is the buyer’s first encounter with the product and is capable of attracting or repulsing the buyer. The colourful attractive packing of the product may induce the customer to buy it. e.g. Ferrero Rocher Chocolates, Calcium Sandoz, etc
Answer 13:
The success of an enterprise is possible only when plans are properly made and then implemented. In order to achieve goals, plans need to be translated into action or else, they become meaningless. Managers usually rely on previously tried and tested successful plans and like to use them in every similar condition/situation. It is not necessary that just because the plan has worked before, it will work again. There are so many unknown factors to be considered. The kind of complacency and false sense of security that plans provide, may actually lead to failure instead of success.
Answer 14:
(i) The values overlooked by the company are :
(a) Conservation of wildlife and natural heritage of fauna.
(b) Religious sentiments of the people/society.
(ii) Social component of business environment is being overlooked in this case. Social environment of business includes the social forces like customs and traditions, values, social trends, society’s expectations from business, etc.
Answer 15:
(i) Formal organisation has the benefit of easy to fix responsibility.
(ii) Informal organisation does not have pre-determined objectives.
(iii) Difference between formal and informal organisation are:
| Basis | Formal Organisation | Informal Organisation |
| Meaning | It is a structure of authority relationship created by the management. | It is network of social relationship arising out . |
| Origin | Arises as a result of company’s rules and policies. | Arises as a result of social interaction. |
| Authority | Arises by virtue of position in management. | Arises out of personal qualities |
| Flow of communication | Communication takes place through the scalar chain. | Flow of communication is not through a planned route. It can take place in any direction. |
Answer 16:
The above statement highlights the nature of management as an art, which is clarified by the following points:
- There is a lot of literature available in various areas of management like marketing, finance, etc which the manager needs to specialise in.
- A manager applies scientific methods and body of knowledge to a given situation, issue or problem in his own unique manner.
- A successful manager practices the art of management in the day-to-day activities of managing an enterprise based on studies, observation and experience.
Thus, we can conclude that management is an art.
Answer 17:
(i) No, Khushi cannot file a complaint, as she is not a consumer under the Consumer Protection Act, 1986 because she has not paid any consideration for the face cream.
(ii) Under Consumer Protection Act, 1986, a complaint can be filed by:
(a) Any consumer.
(b) Any registered Consumer Association.
(c) Central or State Government.
(d) One or more consumers on behalf of numerous consumers.
(e) Legal heir or representative of deceased consumer.
Answer 18:
Controlling should not be misunderstood as the last function of management. It is a function that brings the management cycle back to the planning function.
In general, the process of management begins with planning and ends at controlling, but when a manager performs the function or steps of controlling, it is observed that the first step of controlling is setting standards. The controlling function finds out how far actual performance deviates from standards and analyses the corrective actions to be taken.
This process helps in formulation of future plans, thus becomes the premise of setting plans. Therefore, we can say it is the beginning of management process. Thus, it can be stated that, controlling function is both the beginning as well as the end of the management process.
Answer 19:
Staffing is that function of management which helps in obtaining right people and putting them on the right jobs.
Proper staffing ensures the following three benefits to the organisation:
- Obtaining Competent Personnel It helps in discovering and obtaining competent personnel for various job positions in an organisation.
- Higher Performance Staffing ensures high performance by putting right person on the right job.
- Continuous Survival and Growth Proper staffing ensures continuous survival and growth of the enterprise through succession planning of managers.
Answer 20:
Strategies are general programmes of action towards the attainment of comprehensive objectives.
According to Allen, “Strategy is a unified, comprehensive and integrated plan designed to assure that the objectives are achieved.”
Features of strategy are as follows:
- Strategy is flexible in nature. Changes can be incorporated, whenever required.
- Strategy is formulated by top level management and its implementation is done by middle and lower management.
- Strategy is formulated for allocation of resources necessary for achieving objectives.
- Strategy is relative combination of actions. The combination is to meet a particular condition, to solve certain problems or to attain a desirable objective.
Answer 21:

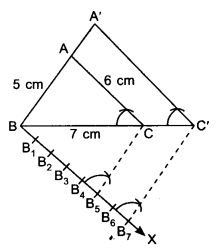
Since, earning per share has fallen from 0.50 to 0.40, therefore the shareholders stand to lose on diversification.
Note In the absence of any information, shares are assumed to be of ₹ 10 each.
![]()
(ii) Three factors that favour issue of debentures by the company as part of its capital structure are :
(a) Debenture interest payable is a charge to the profits. Hence, a company stands to gain in terms of tax benefits.
(b) Issue of debentures help the shareholders of the company to gain through Trading on Equity’.
(c) Debenture is a cheaper source of finance as compared to equity.
Answer 22:
(i) Some advantages of good control system are as follows:
(a) Attainment of Organisational Objectives Budgeting as a system of control, focuses on specific and time bound targets. Thus, it helps in attainment of organisational objectives.
(b) Motivation to the Employees It is a source of motivation to the employees, who knows the standards against which their performance will be evaluated.
(c) Optimum Utilisation of Resources By allocating the resources according to the requirements of the different departments, it helps in optimum utilisation of resources.
(d) Budgeting Process It helps the management to learn from past experience. The management can
critically look at the success or failure of the past budgets and isolate errors, analyse their cause and establish steps to be taken to avoid repetition of such errors.
(ii) Values that can be served by good control system are as follows:
(a) Discipline (b) Orderliness (c) Efficiency/Increase in productivity
Answer 23:
Motivation process is based on unsatisfied human needs. It is as follows:
(i) An unsatisfied need of an individual creates tension which stimulates his or her drives.
(ii) These drives generate a search behaviour to satisfy such need.
(iii) When such need is satisfied, the individual is relieved from tension.
e.g. An employee has a need for promotion to a higher position. If this need is strong, it creates tension for the employee which stimulates his or her drives. Finally, he/she will fix it as his/her goal and search behaviour to reach the goal. If he/she succeeds in getting promotion (goal achievement), his/her need for promotion would be satisfied. This reduces his/her tension.
This process is explained with the help of a flow chart given below :

Answer 24:
(i) Sources of long-term capital are as follows:
(a) Equity shares
(b) Preference shares
(c) Debentures
(d) Long-term loans and advances
(e) Retained earnings
(ii) The following factors affect the financing decision :
- Cost The cost of all the sources of finance is different. The rate of interest on debt, fixed rate of dividend to be paid on preference share capital and the expectations of the shareholders on the equity share capital are in the form of costs. If the situations happen to be favourable, the benefit of cheap finance can be availed of by choosing debt capital.
- Risk Debt capital is most risky and from the point of view of risk, it should not be used.
- Flotation Cost From the point of view of floating costs, retained profit is the most appropriate source. Therefore, its use should be made.
- Cash Flow Position If the cash flow position of the company is good, the payment of interest on the debt and the refund of capital can be easily made. Therefore, in order to take advantage of cheap finance, debt can be given priority.
- Level of Fixed Operating Costs
In business, there are mainly two types of costs which are as follows:- Fixed Operating Cost e.g. Rent of the building, payment of salary, insurance premium, etc.
- Fixed Financial Cost e.g. Interest on debt, etc.
If the level of fixed operating costs is in excess, it is better to keep the fixed financial costs at the minimum. Therefore, debt capital should not be used. On the contrary, if the level of fixed operating cost is low, the use of debt capital is more profitable.
Answer 25:
Generally, consumers prefer to buy directly from the producers but it is not always possible. Instead, consumers are supposed to take the help of channels of distribution, i.e. middlemen. In this channel, mainly agents, wholesalers and retailers are included.
Following four reasons are responsible for this are:
(i) Geographical Difference There are limited number of producers of any product while consumers are unlimited and scattered over a wide geographical areas. Hence, it is not possible to buy goods directly from the producers.
(ii) More Risk At the time of transportation of goods from one place to another, element of risk is always there. By using channel of distribution, such type of risk can be avoided.
(iii) Heavy Buying Costs It is a costly and difficult task to contact the producers directly.
(iv) Unavailability of Credit Facility Generally, it is not possible to have credit facility while purchasing directly from the producers.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies Paper 2 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Business Studies Paper 2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.

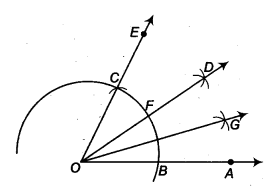
 The above figure illustrates the scalar chain. If D and G wants to communicate, the message should usually move up through C, B, A, E, F and then G whereas, the manager is communicating with all levels and all departments, without following the scalar chain.
The above figure illustrates the scalar chain. If D and G wants to communicate, the message should usually move up through C, B, A, E, F and then G whereas, the manager is communicating with all levels and all departments, without following the scalar chain.