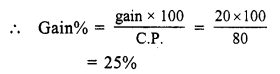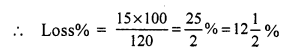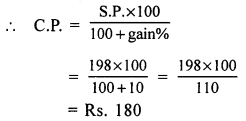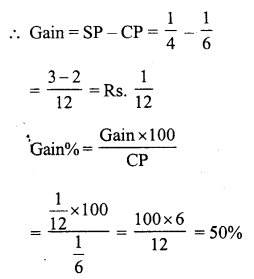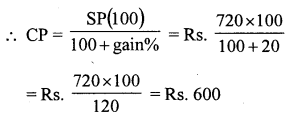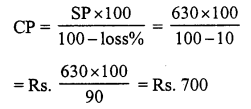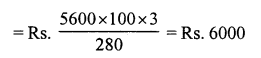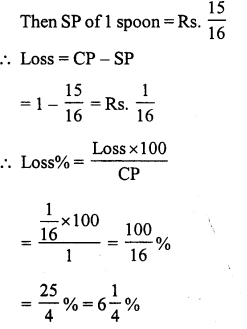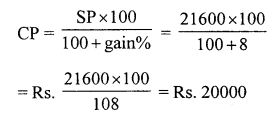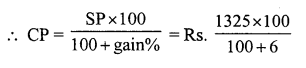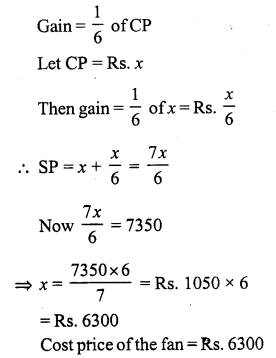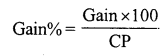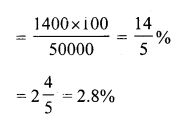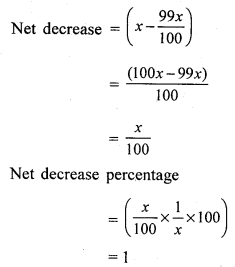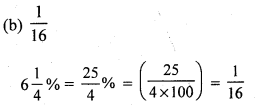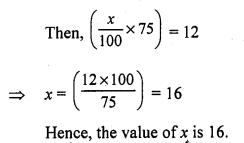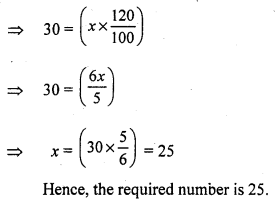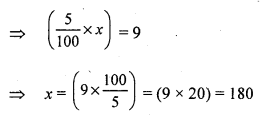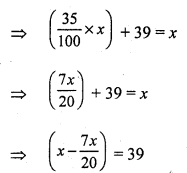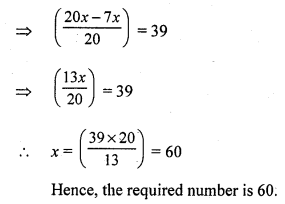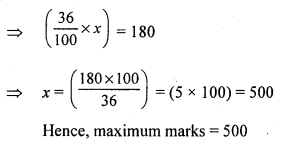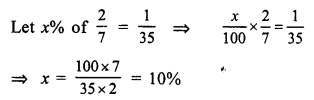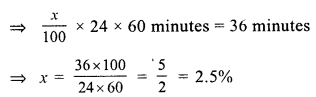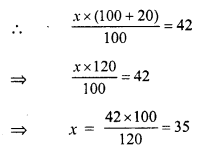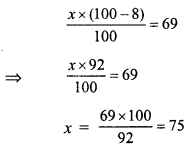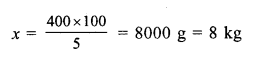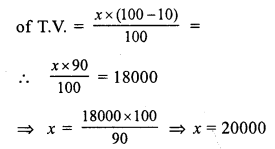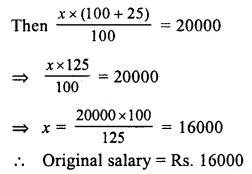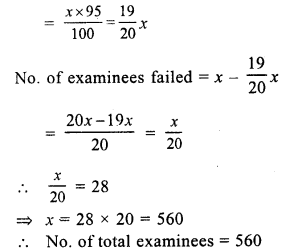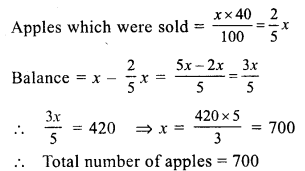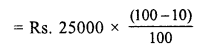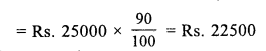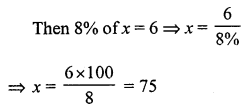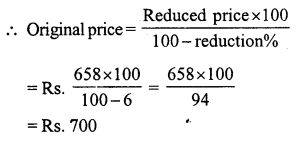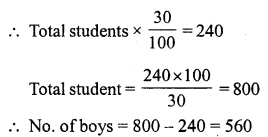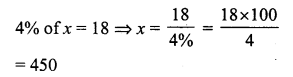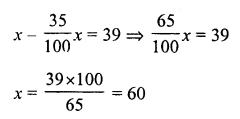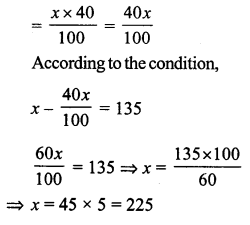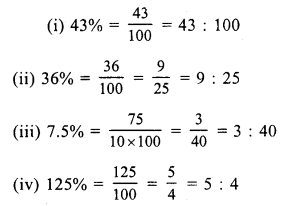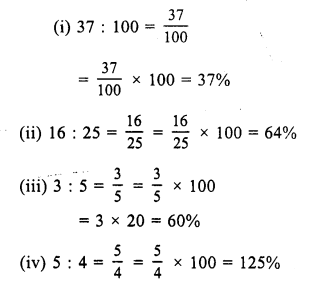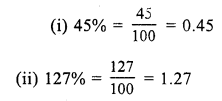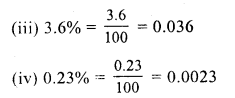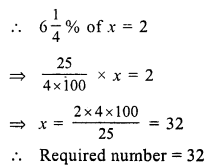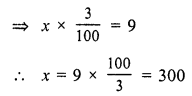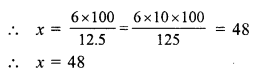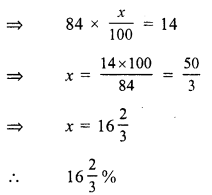RS Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions Chapter 11 Profit and Loss CCE Test Paper
These Solutions are part of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7. Here we have given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 11 Profit and Loss CCE Test Paper.
Other Exercises
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 11 Profit and Loss Ex 11A
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 11 Profit and Loss Ex 11B
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 11 Profit and Loss CCE Test Paper
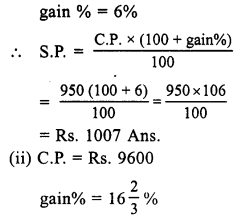
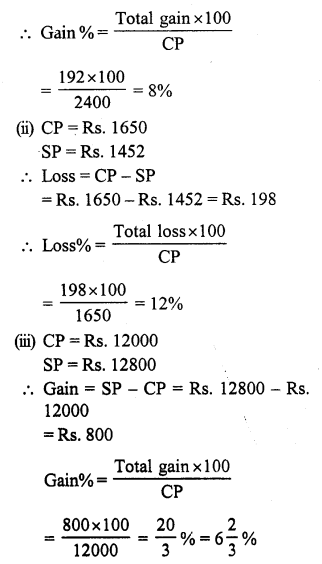
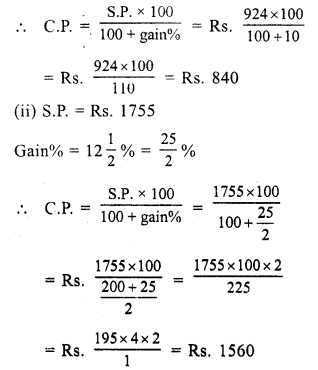
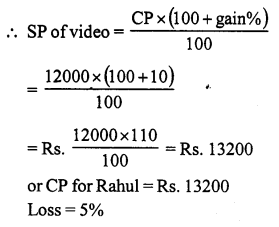
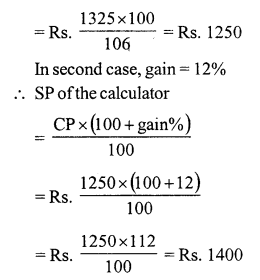
Question 1.
Solution:
SP of the chair = ₹ 1375
Gain% = 10
CP of the chair
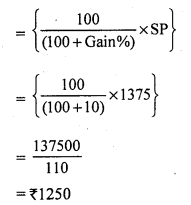
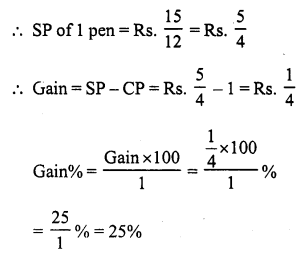
Question 2.
Solution:
Let the cost of each pen be ₹ 1
CP of 10 pens = ₹ 10
SP of 10 pens = CP of 14 pens = ₹ 14
Gain = SP – CP = 14 – 10 = ₹ 4
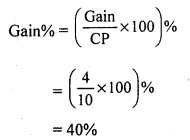
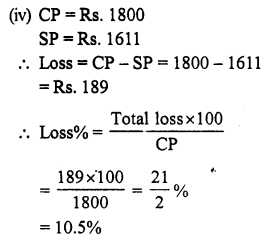
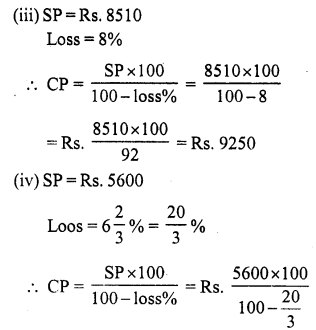
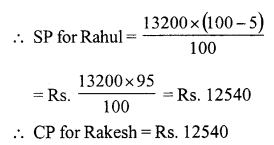
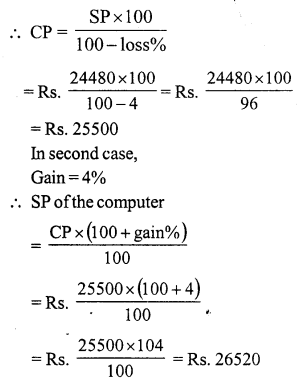
Question 3.
Solution:
Let the cost price of the fan be ₹ x
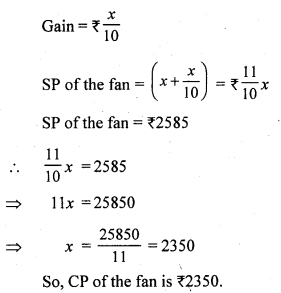
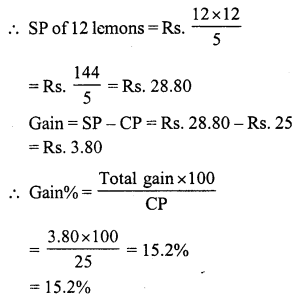
Question 4.
Solution:
Cost price of six lemons = ₹ 10

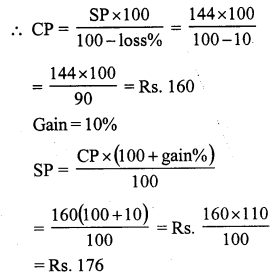
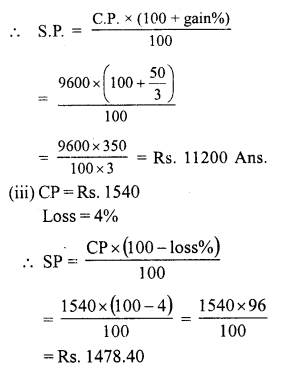
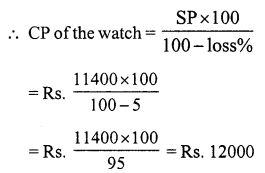
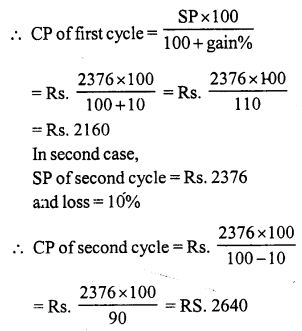
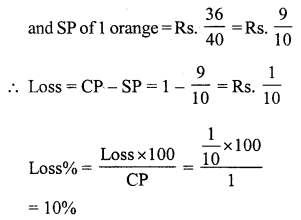
Question 5.
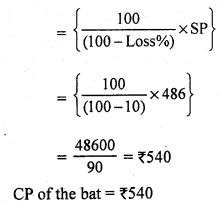
Solution:
SP of the bat = ₹ 486
Loss = 10%
CP of the bat
Mark (✓) against the correct answer in each of the following :
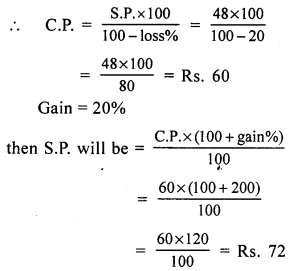
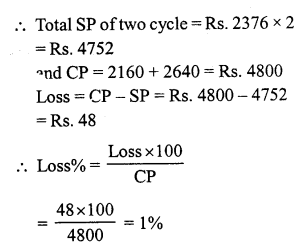
Question 6.
Solution:
(b) ₹ 85
SP of a football = ₹ 100
Gain = ₹ 15
Gain = SP – CP
⇒ 15 = 100 – CP
⇒ CP = ₹ (100 – 15)
⇒ CP = ₹ 85
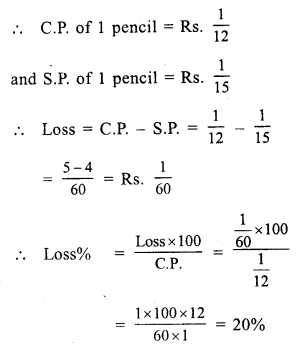
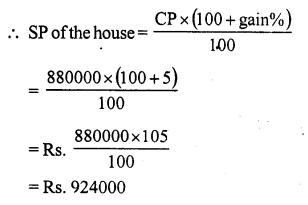
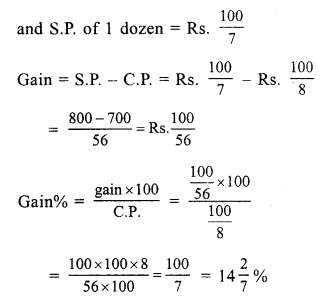
Question 7.
Solution:
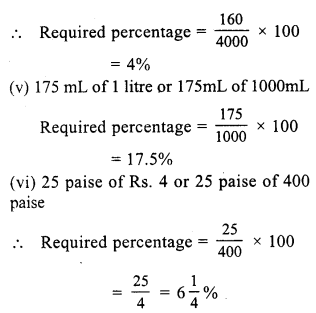
(c) 15.2%
Cost price of 12 bananas = ₹ 25
Cost price of one banana = ₹ \(\frac { 25 }{ 12 }\)
Cost price of five bananas = 5 x \(\frac { 25 }{ 12 }\)
= \(\frac { 125 }{ 12 }\) = 10.42
He shells five bananas at the cost (SP) of ₹ 12.
Gain = SP – CP = ₹ (12 – 10.42) = ₹ 1.58

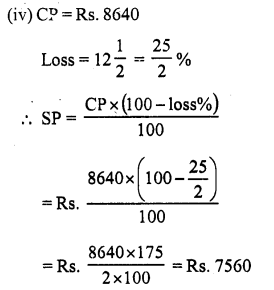
Question 8.
Solution:
(c) ₹ 196
Let the cost price of the jug be ₹ x


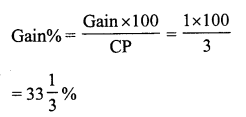
Question 9.
Solution:
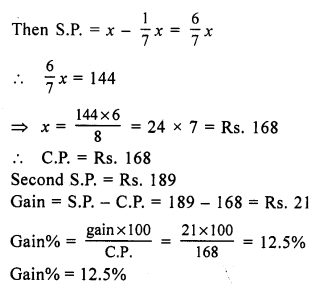
(c) 66\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) %
Let the cost price of each banana be ₹ 1
Cost price of three bananas = ₹ 3
SP of three bananas = CP of five bananas = ₹ 5
Gain = SP – CP = ₹ (5 – 3) = ₹ 2

Question 10.
Solution:
(i) Loss = (CP) – (SP).
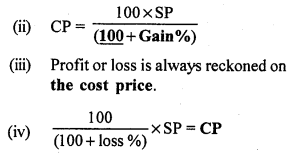
Question 11.
Solution:
(i) False
Gain or loss is always reckoned on the cost price.
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) True
Hope given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 11 Profit and Loss CCE Test Paper are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.