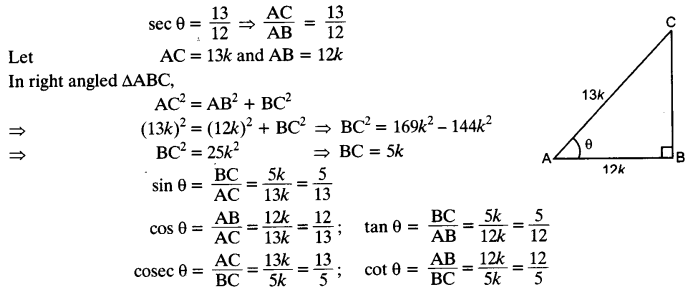
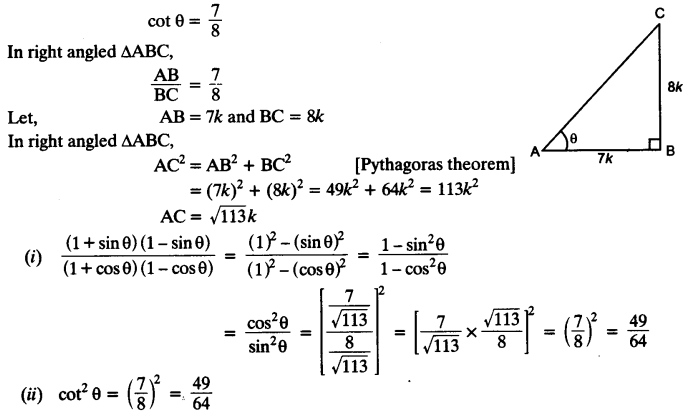
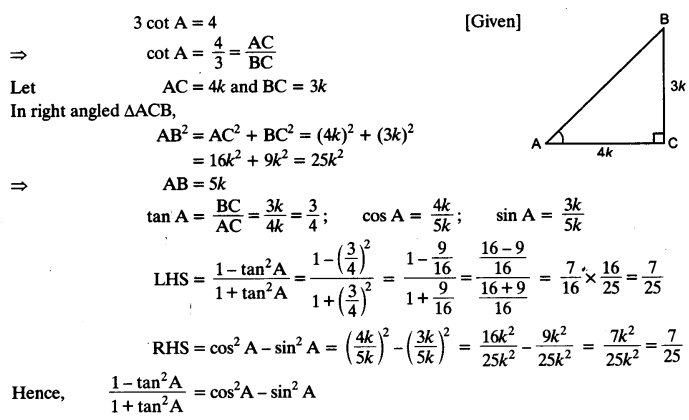
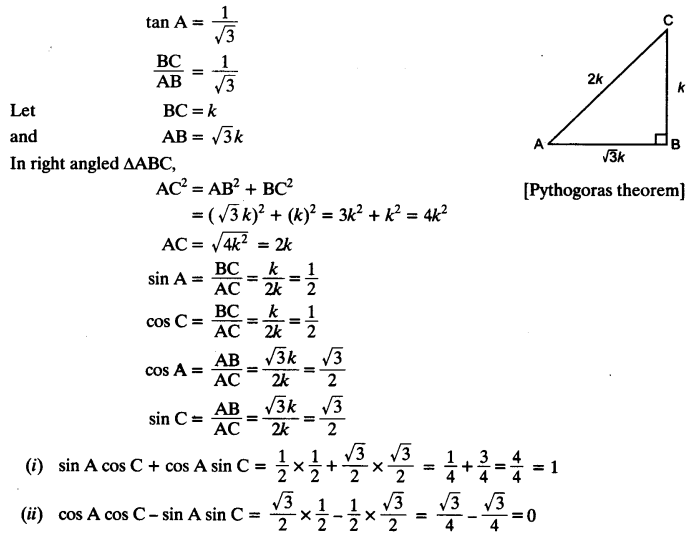
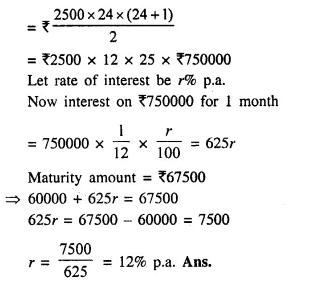
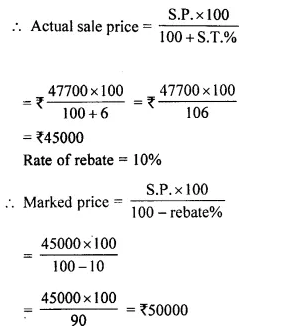
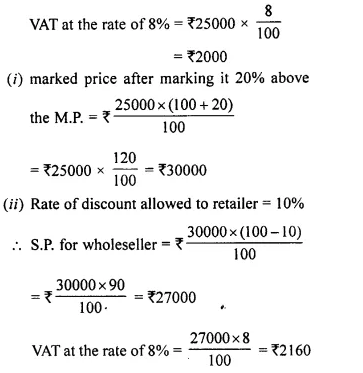
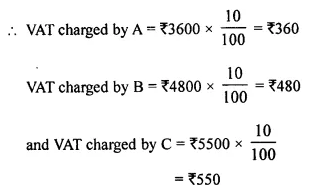
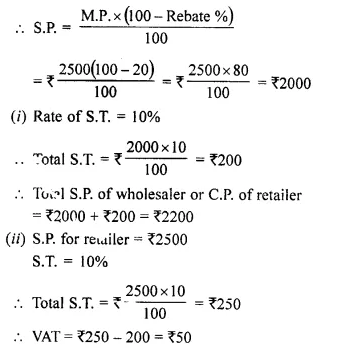
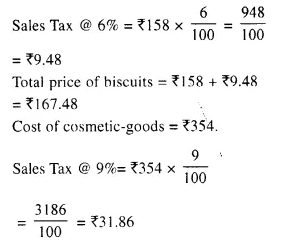
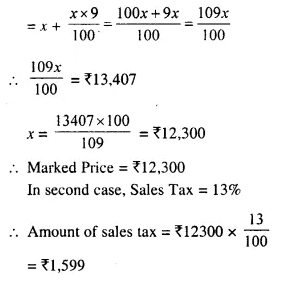
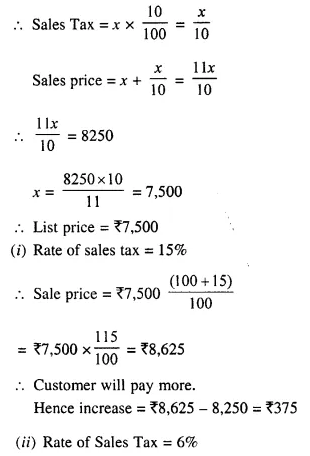
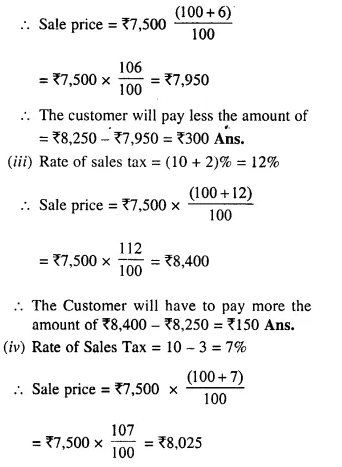
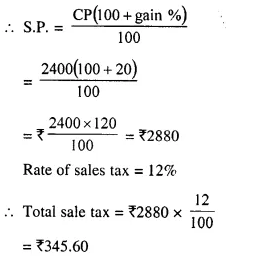
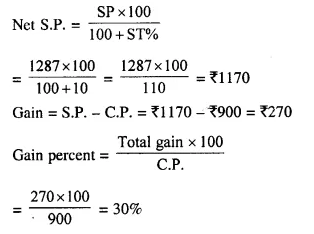
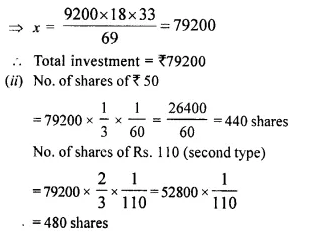
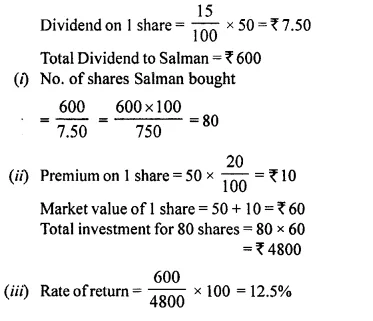
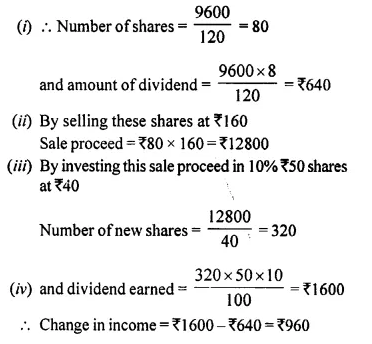
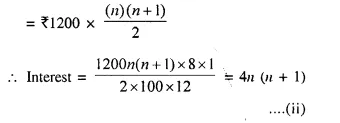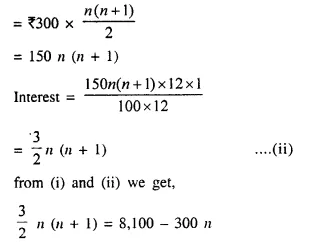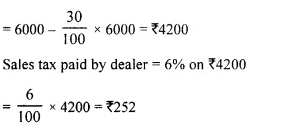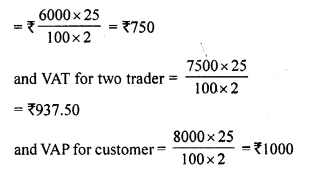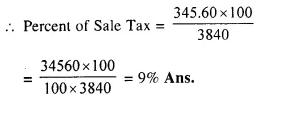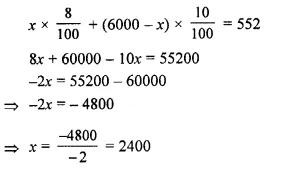Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Computer Applications with Solutions and marking scheme Set 1 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Computer Applications Set 1 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 50
General Instructions
- This question paper contains two parts A and B. Each part is compulsory.
- Part A carries 20 marks while Part B carries 30 marks.
- Part A consists very short answer and case based MCQ Questions and Part B is Descriptive Paper.
- Both Part A and Part B have choices.
Part-A
- It consists two sections-1 and II.
- Section I has 13 questions of Very Short Answer Type. An examinee is to attempt any 10 out of 13 questions.
- Section II has two Case Studies. Each Case Study has 7 case-based sub-parts. An examinee is to attempt any
5 out of 7 sub-parts.
Part-B
- Question numbers 16 to 20 are Short Answer Type (SA-I) Questions of 2 marks each, Question numbers
21 to 25 are Short Answer Type (SA-II) questions of 3 marks each and Question numbers 26 is Long Answer \ Type Question of 5 marks. - Internal choice is provided in 1 question of 2 marks, 1 question of 3 marks and 1 question of 5 marks.
Part-A
Section 1
This section consists of 13 questions of very short answer type. Question numbers 4 to 8 are of “fill in the blank’ type. Fill the blank with the most appropriate answer. Attempt any 10 questions from Question numbers 1 to 13.
Question 1.
Expand the term SMTP.
Answer:
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Question 2.
What do you understand by blog?
Answer:
A blog is a website or web page, in which an individual records opinion links to other sites on regular basis.
You are advised to attempt this sample paper without referring the answers given here. However, cross check your answers once you complete the paper.
Question 3.
Nisha wrote the following HTML statement:
<IMG src=”school.jpg”>
She did not use closing tag of IMG and told her friend that IMG is empty element. What is an empty element?
Answer:
Empty elements are standalone tags, i.e. empty tags do not have to be wrapped around text or graphics and do not require a closing tag.
Question 4.
______ and ______ tags break the line flow.
Answer:
<BR>, <HR>
Question 5.
______ is used to change the color of a visited link.
Answer:
vlink
Question 6.
______ are used to connect web pages. They are created with <A> tag.
Answer:
Hyperlinks
Question 7.
<TH> tag is used to specify the column ______ in a table.
Answer:
heading
Question 8.
______ attribute of <AUDIO> tag specifies the audio file standard type.
Answer:
type
Question 9.
Neha wants to transfer multimedia documents through Internet. Her friend told her that some type of protocol is used to transfer documents through Internet. But she is confused about its name. Which protocol help her to transfer the documents through Internet?
Answer:
The name of this protocol is HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol).
Question 10.
How does gender contribute to the digital divide?
Answer:
Gender is stated that in some countries and organisations, females have less access to the Internet than males.
Question 11.
Which services are provided by CPA WebTrust in E-commerce?
Answer:
In E-commerce, CPA WebTrust provides services titled WebTrust and SysTrust.
Question 12.
Which attribute of <BODY> tag specifies the color of visited links in a document?
Answer:
vlink attribute
Question 13.
Write the syntax of <INPUT> tag.
Answer:
<INPUT type = “fieldtype” name = “fieldname” value = ”fieldtext”>
Section II
Both the case study based questions are compulsory. Attempt any 5 questions (out of 7 questions) from each case study. Each question carries 1 mark.
Question 14.
URL
Web is a collection of documents (web pages) stored on computers around the world. Each web page has an address describing where it can be found. This address is known as web address or URL. A web address identifies the location of a specific web page on the Internet, such as
http://www.leamyoga.com
Every computer connected to the Internet has its unique web address, without which it cannot be reached by other computers.
(i) Which of the following is used by the browser to connect to the location of the Internet resources?
(a) Linkers
(b) Protocol
(c) Cable
(d) URL
Answer:
(d) URL
(ii) An absolute contains the complete address of a file on the Internet.
(a) JavaScript
(b) URL
(c) SQL
(d) String
Answer:
(b) URL
(iii) The full form of URL is
(a) Uniform Resource Locator
(b) Universal Resource Locator
(c) Universally Resource Locator
(d) Uniform Reference Locator
Answer:
(a) Uniform Resource Locator
(iv) Which of the following must be contained in a URL?
(a) A protocol identifier
(b) The letters, www
(c) The unique registered domain name
(d) A protocol identifier, www and the unique registered domain name
Answer:
A protocol identifier, www and the unique registered domain name
(v) What is URL?
(a) A computer software program
(b) A type of programming object
(c) The address of a document or page on the www
(d) A piece of hardware
Answer:
(c) The address of a document or page on the www
(vi) The types of URL is
(a) absolute
(b) relative
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) mixed
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(vii) It points to a file/directory in relation to the present file/directory.
(a) Absolute URL
(b) Relative URL
(c) Either (a) or (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
Relative URL
Question 15.
Embed Audio Element
The HTML <AUDIO> element is used to embed sound content in documents. It may contain one or more audio sources, represented using the src attribute. The <AUDIO > element defines an in-browser audio player. The audio player can provide a single piece of audio content. To specify the source file of the audio content, use one or more <SOURCE> elements inside the <AUDIO> element. All <SOURCE> files should contain the same audio content, but in different file formats. The browser will select the first file format that it is able to play. If you are not going to provide multiple source file formats, you may indicate the source file in the src attribute, instead of in a separate <SOURCE> element.
(i) <AUDIO> tag is used in (1)
(a) < HTML > tag
(b) <BODY> tag
(c) < HEAD > tag
(d) <TITLE> tag
Answer:
<BODY> tag
(ii) Which of the following attributes of <AUDIO> tag?
(a) autoplay
(b) src
(c) type
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
(iii) What is the attribute of <SOURCE> tag?
(a) src
(b) type
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) height
Answer:
Both (a) and (b)
(iv) This attribute specifies the location of the audio file.
(a) loop
(b) src
(c) type
(d) controls
Answer:
(b) src
(v) Most commonly used audio format(s) is/are (1)
(a) ogg
(b) mp3
(c) wav
(d) All of these
Answer:
All of these
(vi) What is the full form of src? (1)
(a) Source
(b) Service
(c) Support Cast
(d) Specify Resource
Answer:
(a) Source
(vii) Which attribute of < AUDIO > tag allows audio automatically see back to the start after reaching at the end?
(a) src
(b) autobuffer
(c) loop
(d) autoplay
Answer:
(c) loop
Part-B
All questions are compulsory. In case of internal choices, attempt any one.
Question 16.
Below are given names of some websites : (2)
(i) www.google.co.in
(ii) www.microsoft.com
Identify the components of all the web addresses given above.
Answer:
(i) www.google.co.in
Host name – www
Domain name – google.co.in
Domain type – co.in
(ii) www.miqrosoft.com
Host name – www
Domain name – microsoft.com
Domain type – com
Question 17.
Explain the two elements which with search engine works. (2)
Answer:
Search engine works with two elements, which are as follows:
(i) Web Crawler It is a software that browses the Internet in a systematic manner. It retrieves the information, which follows every link on the site that are stored by Web search engines. It is also known as spider, ant, automatic indexer or Web scutter.
(ii) Indexing Software It is a software that receives the list of Web documents and addresses collected by Web crawler. Some search engines provide proximity search which allows users to define the distance keywords.
Question 18.
Explain the open source software movement. (2)
Answer:
The open source software movement is a movement that supports the use of open source licenses for some softwares. It was started to spread the concept of open source software. Thus, open source software is a software whose source code is available for modification or enhancement by anyone. Programmers develop the open source movement contribute to the open source community by writing and exchanging programming code for software development.
Question 19.
Give any six reasons behind plagiarism. (2)
Answer:
The reason behind plagiarism are
- Fear of failure (ii) Not having enough knowledge
- Being lazy (iv) Lack of enforcement (v) Competition (vi) Lack of management skills
Question 20.
6CO2 +6H2O → C6H12O2 +6O2 (2)
To display above given chemical expression on a web page, following HTML code was written:
6CO<SUP>2</SUP> + 6H<SUP>2</SUP>0 —> C<SUP> 6</SUP> H<SUP>
12 </SUP > O < SUP > 6 </SUP >+ 60 < SUP > 2 </SUP >
But it is not displaying the expression in desired format. Identify the fault(s) and suggest the required correction(s).
Or
Write a simple HTML code to show an example of internal linking.(2)
Answer:
<SUP>tag will not be use in the given expression because it is a superscript tag. In this
expression, subscript tag, i.e. <SUB> tag will be use. ‘
Or
<HTML>
<HEAD><TITLE>Internal Li nki ng</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<H1> It is <A name =”top”>top</A> of the page </H1>
<BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR>
<BR>
<BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR>
<BR>
<BR><BR><BR>
<H1><A href =”#top”>Top</A></H1>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Question 21.
Write the HTML code to create the exact table which is given below : (3)
| Roll_No | Name | Class | Subject |
| 1 | Neha | Vth | Maths |
| 2 | Amit | 10th | English |
| 3 | Sneha | IIIrd | G.K. |
Answer:
<HTML>
<BODY>
<TABLE border = “2”>
<TR align = “center” valign = “middle”>
<TH> Roll_N0 </TH>
<TH> Name </TH>
<TH> Class </TH>
<TH> Subject </TH>
</TR>
<TR align = “center” valign = “middle”>
<TD> 1 </TD>
<TD> Neha </TD>
<TD> Vth </TD>
<TD> Maths </TD>
</TR>
<TR align = “center” valign = “middle”>
<TD> 2 </TD>
<TD> Amit </TD>
<TD> 10th </TD>
<TD> English </TD>
</TR>
<TR align = “center” valign = “middle”>
<TD> 3 </TD>
<TD> Sneha </TD>
<TD> IIIrd </TD>
<TD> G.K. </TD>
</TR>
</TABLE>
< / BODY >
</HTML>
Question 22.
Define the cascading style sheet.
Answer:
Cascading Style Sheet (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language. CSS is designed primarily to enable the separation of document content from document presentation, including aspects such as the layout, colors and fonts.
This separation can improve content accessibility, provide more flexibility and control in the specification of presentation characteristics, enable multiple HTML pages to share formatting by specifying the relevant CSS in a separate .css file, and reduce complexity and repetition in the structural content such as semantically insignificance tables that were widely used to format pages before consistent CSS rendering was available in all major browsers.
CSS makes it possible to separate presentation instructions from the HTML content in a separate file or style section of the HTML file. For each matching HTML element, it provides a list of formatting instructions.
Question 23.
Write about the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA). (3)
Answer:
FOIA (Freedom of Information Act) is a federal law that generally provides that any person has a right to obtain access to federal agency records. It is intended to increase transparency. It does not provide access to all government documents.The FOI Act provides that every person has the following legal rights:
- The right to access official records held by government departments as defined by the act.
- The right to be given reasons for decisions taken by government that affect them.
Question 24.
Give advantages and disadvantages of secure electronic transaction. (3)
Answer:
Advantages of SET (Secure Electronic Transaction) are as follows:
- SET prevents merchants from seeing the customer payment information.
- To ensure merchant privacy, SET prevents the payment gateway from seeing the order information.
Disadvantages of SET are as follows:
- The customer must install additional software, which can handle SET transactions.
- Implementing SET is more costly than SSL for merchants as well.
- Users must have credit card.
Question 25.
What is web server? Explain any one web server. (3)
Or
What do you mean by hypertext markup language.
Answer:
Web server is a computer program that serves requested HTML pages or files from the Web client. Every Web server that is connected to the Internet is associated with a unique address, i.e. IP address. Web server software generally requires a fairly robust operating system like Unix, Windows NT. Every Website need to be stored on a computer called the Web server from which it can be accessed.
Currently, there are five major Web servers commonly used for hosting Websites as follows:
(i) Apache HTTP Server
(ii) Internet Information Server
(iii) Lighttpd
(iv) Sun Java System Web Server
(v) Jigsaw Server
Apache HTTP Server was developed by Apache Software Foundation. It is the most popular Web hosting server in the world. This software can be installed virtually on all operating systems including Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, UNIX etc. At present, 60% of server machines run on the Apache Web server.
Or
HyperText Markup Language (HTML) is a markup language used for designing Web pages. A markup language is a set of markup (angular bracket, < >) tags, which tell the Web browser, how to display a Web page’s words and images for the user. Each individual markup code is referred to as an element or a tag. The text placed between a pair of angular brackets (< >) defines an HTML element.
HTML elements have two basic properties, i.e. attributes and content. Attributes are used to apply the desired style on the text and content refers to the text that you want to display on the browser. When a Web page is opened in a Web browser, then the formatted content is displayed.
Question 26.
Write the code to generate the following web page: (5)

Note The following points while generating the web page:
(i) Title of the page is “Indian Food”.
(ii) Link color is blue, vlink color is brown and alink color is pink.
(iii) Font face of heading is “arial”.
(iv) The color of the heading of the page is green.
(v) Image used as foodl.jpg.
(vi) Table border is 4px and border color is maroon.
(vii) Use link as:
For Available Food as Fl.html
For Dishes Price as F2.html
For Get Recipes as F3.html
(viii) E-mail id for bottom message “To get order click here” as inquiry@abc.com.
Or
Answer the following:
(i) Write the HTML code to create a link for school.jpg located at C:\.
(ii) Name the attribute used for setting cell width.
(iii) Name the attribute used for changing the cell span.
(iv) What is the use of dir attribute of <HTML> tag?
(v) Name any two attributes you can use with <TABLE> tag but not with <TR> tag.
Answer:
<HTML>
<HEAD><TITLE> Indian Food </TITLE></HEAD>
<BODY link=”blue” vlink=”brown” alink=”pink” bgcolor=”orange”>
<FONT face=”arial” color=”green”>
<H1 align=”center”><U> Indian Food </U></H1>
</FONT>
The traditional food of India has been widely appreciated for its fabulous use of herbs and spices. Indian cuisine is known for its large assortment of dishes. The cooking style varies from region to region and is largely divided into South Indian & North Indian cuisine. India is quite famous for its diverse multi cuisine available in a large number of restaurants and hotel resorts, which is reminiscent of unity in diversity. <BR>
<P align=”right”><A href=”Fl.html ”> Available Food </A><BR>
<A href=”F2.html “> Dishes Price </A><BR>
<A href=”F3.html “> Get Receipes </A></P>
<IMG src=”foodl.jpg” align=”right” width =”180” height=”150”>
<TABLE border=”4” borderedor=”maroon” cel 1padding=”6″ align=”center”>
<CAPTION> Select Dishes </CAPTION>
<TR>
<TH> STATE </TH>
<TD> Gujrat </TD>
<TD> Punjab </TD>
<TD> Tamil Nadu </TD>
</TR>
<TR>
<TH> DISHES </TH>
<TD> Khandvi <BR> Dhokla <BR> Dal Vada </TD>
<TD> Falooda <BR> Nan <BR> Lassi </TD>
<TD> Masala Dosa <BR> Sambhar Idli <BR> Upma </TD>
</TR>
</TABLE>
<BR>
<A href=”inquiry@abc.com”> To get order click here </A>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Or
(i) <A href = “C: \school . jpg”> IMAGE</A>
(ii) width
(iii) rowspan and colspan
(iv) dir attribute tells the browser, the direction in which the displayed text is to be read.
(v) summary, rules