Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 12 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics Term 2 Set 12 for Practice
Time allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- This is a Subjective Question Paper containing 13 questions.
- This paper contains 5 questions of 2 marks each, 5 questions of 3 marks each and 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- 2 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 30-50 words.
- 3 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 50-80 words.
- 5 marks questions are Long Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 80-120 words.
- This question paper contains Case/Source Based Questions.
![]()
Question 1.
“Induced consumption expenditure is income elastic in nature.” Defend or refute the statement with valid argument.
OR
Consumption curve always starts from a positive incept on Y-axis.” Justify the statement with valid reason. (2)
Question 2.
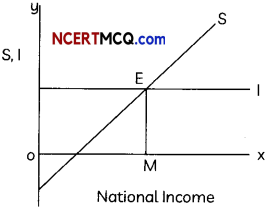
In an economy, the consumption function is C = 400 + 0.75Y, where C is consumption and Y is national income and investment expenditure is 2,000. What will be the equilibrium level of national income?
OR
Calculate change in final income, if Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) is 0.8 and change in initial investment is ₹1,000 crore. (2)
Question 3.
“In the normal course of development, countries first shift their employment and output from agriculture to Industry and then to services. This is what happened in Pakistan.”
Defend or refute the statement with valid reason. (2)
Question 4.
“In Pakistan, Green revolution changed the agrarian structure dramatically.” Justify the statement. (2)
Question 5.
What is the important implication of the ‘one child norm’ in China?
OR
Analyze and compare all three economies on the basis of given information.
Select Demographic Indicators, 2017-18
| Country | Estimated Population (in million) | Annual Growth of Population |
| India | 1352 | 1.03 |
| China | 1393 | 0.46 |
| Pakistan | 212 | 2.05 |
Source: World Development Indicators, 2018.
www.worldbank.org (2)
![]()
Question 6.
Giving reasons, state how the following are treated in the estimation of national income:
(A) Payment of interest by banks to its depositors.
(B) Expenditure on old age pensions by government.
(C) Expenditure on engine oil by car service station. (3)
OR
Firm A spent ₹200 on non-factor inputs and produced goods worth 1900. It sold goods worth 1450 and 1350 to Firm B and consumer households respectively. Find out Gross value added by Firm A. (3)
Question 7.
Analyse the following information on the basis of ‘Place of Residence’.
Distribution of Workforce by Industry, 2017-2018
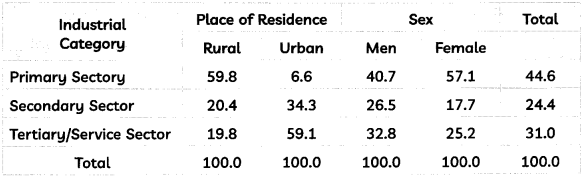
Read the following case carefully and answer questions number 8 and 9 given below:
Triple Wins for Sustainable Development Sustainable development is the synonymous in the minds of many with the colour green and for good reasons. Twenty years ago, at the First Earth Summit at Rio de Janeiro, in Brazil, world leaders set out what today is conventional wisdom: SOCIAL AND ECONOMIC HUMAN PROGRESS – cannot be divorced from environmental protection unless both are advanced together, both will flounder together. Sustainable development is as much about health, education and jobs, as it is about the ecosystems. It is about ever-widening inclusion and movement away from decisions that erode democratic space and do not address social inequality, intolerance, and violence.
Sustainable Development is about changes that transform impoverished people, communities, and countries into informed, educated healthy and productive societies. It is about wealth creation that generates equality and opportunity. Sustainable Development is about consumption and production patterns that respect planetary boundaries; it is also about increasing tolerance and respect for human rights at all levels.
Building on human development legacy that oriented with Economists like Amartya Sen and MahbubUlHaq and was captured by the first Human Development Report in 1990. United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has long promoted alternative approaches to measure human progress, along with the Human Development Index (HDI).
Today, we are building on this legacy by exploring how to adjust the index to reflect environmental sustainability, so that governments and citizens might better track real progress towards truly sustainable development. This must be our collective objective.
www.undp.org
![]()
Question 8.
“Sustainable development is all about ecosystem only.” Defend or refute the statement with valid argument. (3)
Question 9.
As per the above text, which must be our collective objective? (3)
Question 10.
Which of the following source of energy is extremely useful for remote areas and free from pollution? (3)
Question 11.
(A) Government incurs expenditure to popularize yoga among the masses. Analyse its impact on gross domestic product and welfare of the people.
(B) “Net factor income from abroad can never be negative.” Defend or refute the given statement with valid argument. 5
Question 12.
(A) State any two limitations of GDP as an index of economic welfare.
(B) Calculate Net Value added at Factor Cost (NVAFC) from the following data:
| Particulars | Amount (in ₹ crores) |
| Value of output | 800 |
| Intermediate Consumption | 200 |
| Indirect Taxes | 30 |
| Depreciation | 20 |
| Subsidies | 50 |
| Purchase of machinery | 50 |
OR
![]()
(A) State any two approaches to correct the problem of double counting.
(B) Calculate Net Domestic Product at factor cost. (5)
| Particulars | Amount (in ₹ crores) |
| Intrest | 700 |
| Compensation of Employees | 3,000 |
| Net Indirect Taxes | 500 |
| Rent and Profit | 700 |
| Transfer Payments by Government | 10 |