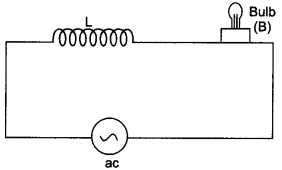
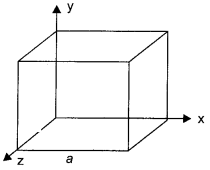
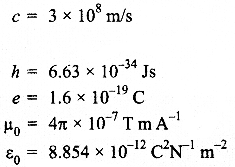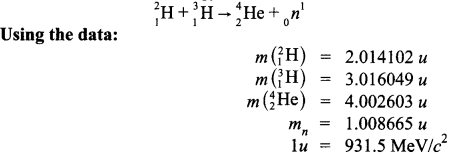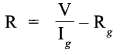CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Paper 2 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Paper 2.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Paper 2
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Political Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 2 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 2 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Political Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- All questions are compulsory.
- Questions nos. 1 to 5 are of 1 mark each. The answer to these questions should not exceed 20 words
- Questions nos. 6 to 10 are of 2 marks each. The answer to these questions should not exceed 40 words
- Questions nos. 11 to 16 are of 4 marks each. The answer to these questions should not exceed 100 words
- Questions nos. 17 to 21 are of 5 marks each. The answer to these questions should not exceed 150 words
- Questions no. 21 is map based question
- Questions nos. 22 to 27 are of 6 marks each. The answer to these questions should not i exceed 150 words
Question 1.
What is meant by seven sisters?
Question 2.
When was Soviet System introduced?
Question 3.
Define globalisation.
Question 4.
What is foreign policy?
Question 5.
Mention the historic decision given by the court in famous Kesavananda Bharati Case.
Question 6.
Mention the major challenges faced in Europe after the Second World War.
Question 7.
Mention the features of SAFTA.
Question 8.
How many member countries have got veto power in the UN Security Council and why?
Question 9.
What do you mean by Grand Alliance?
Question 10.
Who wrote the poem on Dalit? What does the poem signify?
Question 11.
What are the various positions on the issue of regional autonomy for Kashmir? Which of these do you think are justifiable? Give reasons for your answer.
Question 12.
Trace the emergence of BJP as a significant force in post-Emergency politics.
Question 13.
How did Europe become main arena of conflict between the superpowers?
Question 14.
Describe any four consequences of the disintegration of Soviet Union.
Question 15.
Describe the hegemony of the United States of America as a structural power.
Question 16.
The emerging economies of China and India have great potential to challenge the unipolar world. Do you agree with the statement? Substantiate your arguments.
Question 17.
Read the following passage carefully and answer the following questions:
During the Cold War years, India found itself on the opposite side of the divide from the US. India’s closest friendship during those years was with the Soviet Union. After the collapse of Soviet Union, India suddenly found itself friendless in an increasingly hostile international environment. However, these were also the years when India decided to liberalise its economy and integrate it with the global economy. This policy and India’s impressive economic growth rate made the country an attractive economic partner for a number of countries including the US.
(i) Name the country which was India’s closest friend during Cold War years.
(ii) What was India’s policy during post Cold War years?
(iii) What made India an attractive economic partner for the countries like the US?
Question 18.
Why is the EU considered a highly influential regional organisation in the economic, political and military fields?
Question 19.
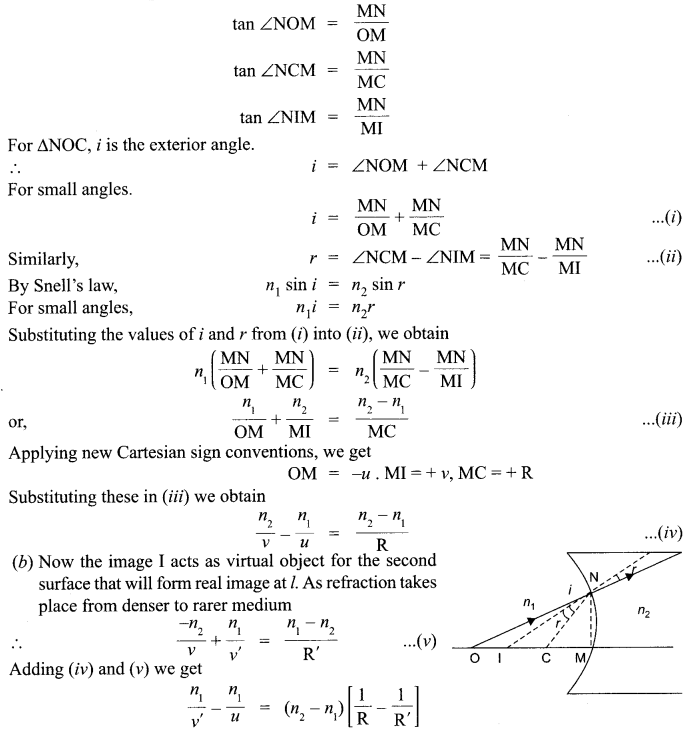
Study the picture and answer the following questions.

(i) What is being shown by these cartoons?
(ii) What is being depicted in the first cartoon?
(iii) What is the subject matter of the second cartoon?
Question 20.
Read the passage and answer the following questions:
“Broadly, non-alignment means not tying yourself off with military blocs… It means trying to view things, as far as possible, not from the military point of view, though that has to come in sometimes, but independently, and trying to maintain friendly relations with all countries”. —Jawaharlal Nehru
(a) Why does Nehru want to keep off military blocs?
(b) Do you think that the Indo-Soviet friendship treaty violated the principle of non-alignment? Give reasons for your answer,
(c) If there were no military blocs, do you think non-alignment would have been unnecessary?
Question 21.
On a political outline-map of India, locate and label the following and symbolise them as indicated:

(i) Name and mark any two of the Princely States.
(ii) Name and mark the original state from which the Gujarat was carved out.
(iii) Name and mark thexountry reorganised on religious grounds.
(iv) Demarcated boundary of this countries by country zones.
Question 22.
How far is it correct to say the international alliances during the Cold War Era were determined by the requirements of the superpowers and the calculations of the smaller states? Explain. (Delhi 2016)
OR
Analyse the three different views within India about the type of relationship India should have with the United States of America. (Delhi 2016)
Question 23.
How did the European countries resolve their post-Second World War problem? Briefly outline the attempts that led to the formation of the European Union. 6
OR
What are some of the commonalities and differences between Bangladesh and Pakistan in their democratic experiences?
Question 24.
Like India why could democracy not take roots in Pakistan despite the fact that both the countries share a common part?
OR
Describe briefly any four problems faced in the process of partition of India.
Question 25.
Did the prevalence of a ‘one-party dominant system’ affect adversely the democratic nature of Indian politics?
OR
What were the major differences in the approach towards development at the time of Independence? Has the debate been resolved?
Question 26.
“The conduct of foreign affairs is an outcome of a two-way interaction between domestic compulsions and prevailing international climate. Take one example from India’s external relations in the 1960s to substantiate your answer.
Question 27.
Analyse the circumstances that favoured Indira Gandhi to become Prime Minister after the death of Lai Bahadur Shastri. Mention any four achievements of Indira Gandhi that made her popular as a Prime Minister. (Delhi 2016) 6
OR
What was Mandal Commission? Did it try to solve the problems of other Backward classes? State any two arguments in support of your answer?
Answers
Answer 1.
The north-east region which consists of seven states is known as seven sisters. This has approx 4 percent of country’s population.
Answer 2.
It was introduced after Russian Revolution in 1917 based on the principles of egalitarian society and planned economy controlled by the state.
Answer 3.
Globalisation refers to integration of an economy with the other country based on interdependence.
Answer 4.
Foreign policy of a nation reflects systematic statements of national interests along with the interplay of domestic and external factors.
Answer 5.
There are some basic features of Constitution not to be amended by the Parliament at all. It led to a crisis between the government and judiciary.
Answer 6.
- Shattered many assumptions and structures on which European states maintained their relations.
- The European states confronted the ruin of economies and the destruction on which Europe had been founded.
Answer 7.
South Asian Free Trade Agreement (SAFTA) was signed by SAARC members in 2004 with the following features:
- Formation of Free Trade Zone for whole South Asia.
- To sustain mutual trade and cooperation among SAARC members.
Answer 8.
Five Permanent Member countries i.e. France, Russia, UK, the US and China got veto power because they have been emerged as industrialised developed countries to stall any decision.
Answer 9.
Grand Alliance was an electoral alliance of all the major non-communist, non-Congress and opposition parties. The SSP, PSP, Bharatiya Jana Sangh, Swatantra Party and the Bharatiya Kranti Dal came together under this umbrella.
Answer 10.
The Marathi poet Namdeo Dhasal wrote poem on Dalit during the decade of seventies which expresses the anguish that the Dalit masses continued to face even after twenty years of Independence.
Answer 11.
On the issue of regional autonomy for Kashmir, the following positions are states as:
- Kashmiris were promised to make accession on reference of people after situation created by tribal invasion, becomes normal. But it has not been fulfilled, hence, it generated the demand for “Plebiscite”.
- Sometimes, it was felt that special federal status guaranteed by Article 370 has been eroded practically which led the demand for restoration of autonomy or “Greater State Autonomy”.
- It is felt that democracy, which is practised in rest of India has not been similarly institutionalised in Jammu and Kashmir.
We prefer the first position because ‘Plebiscite’ provides better opportunity to people of J & K to protect and sustain their regional autonomy in a very democratic manner.
Answer 12.
The major trends in the electoral performance of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) since 1989 can be traced as follows:
- In the elections of 1989, the National front under V.P. Singh came to power supported by left front and BJP from outside because they wanted to keep the Congress out of power. Due to Mandal Commission Report and implementation of its recommendations forced BJP to reconsider its support and finally withdrew it. Thus, in November 1990, the rule of National Front came to an end.
- In 1996, BJP minority government was formed for a short period. In June 1996 BJP failed to get majority support in the vote of confidence and thus collapsed.
- From March 1998 to October 1999, BJP and others formed alliances NDA (National Democratic Alliance) under the leadership of Atal Bihari Vajpayee. The regional parties demanded more share in the government to extend their support. dv) The political competition during nineties and divided between the coalition led by BJP and coalition led by Congress.
Answer 13.
- Superpowers used their military power to bring countries into their respective alliances.
- Soviet Union used its influence in Eastern Europe so that the eastern half of Europe remained within its sphere of influence.
- In East and Southeast Asia and in West Asia, the US built an alliance called South East Asian Treaty Organisation (SEATO) and the Central Treaty Organisation (CENTO).
- The Soviet Union responded by having close relations with regional countries such as North Vietnam, North Korea and Iraq.
Answer 14.
- The disintegration of Soviet Union meant the end of Cold War confrontations which demanded the end of armed race and restoration of possible peace.
- This disintegration created the possibility to bring in a ‘multipolar system’ where no power could dominate.
- The US became the sole superpower and the ‘capitalist economy’ was now dominant economic system at international level.
- This disintegration emerged in many new countries dividing Soviet Union into 15 independent countries alongwith their own aspirations and choices.
Answer 15.
Hegemony as a structural power implies economic perspective of world economy. It can be summed up in the following ways :
- An open world economy requires a dominant power to support its creation and existence.
- The hegemon must possess both the ability and the desire to establish certain norms for order and must sustain global structure i.e. Bretton Woods system set up by the US after Second World War.
- The US reflects this hegemony by providing the global public goods, those can be consumed by one person without reducing the amount of goods available for someone else.
- A classical example of structural power of the US is the academic degree Master’s in Business Administration (MBA) to sharpen business skills in a University.
Answer 16.
The Indo-China relations experience strategically organised as rising economic powers in global politics and to play a major role in Asian economy after the end of the Cold War. It can be proved on the following grounds:
- The new economic policies of India and China have broken their economy from stagnancy.
- The creation of special economic zones led to a phenomenal rise in foreign trade.
- China has become the most important destination for foreign direct investment anywhere in the world. Hence, it has large reserves for foreign exchange to allow it to make big investment in other countries.
- At the global level also, India and China have adopted similar policies in World Trade Organisation to deepen integration with the world economy to challenge unipolar world.
Answer 17.
- Soviet Union
- India decided to liberalise its economy and integrate it with global economy.
- India’s policy of liberalisation and its impressive economic growth rate.
Answer 18.
Because :
1. Economic Influence:
(a) Three times larger share in World trade than the US.
(b) Its currency Euro can pose a threat to the dominance of US Dollar.
(c) The EU functions as an important bloc in World Trade Organisation (WTO).
2. Political Influence:
(a) Two members of the EU, Britain and France hold permanent seats in Security Council to influence UN policies.
(b) The EU also includes various non-permanent members of UNSC.
(c) The European Union plays an influential role in diplomacy and negotiations except military force i.e.
EU’s dialogue with China on Human Rights and environmental degradation is remarkable.
3. Military Influence:
(a) The EU’s combined armed forces are second largest in world.
(b) Its total military expenditure is second to the US.
(c) Its two important members—Britain and France also experience nuclear arsenals of 550 nuclear warheads.
(d) The EU is world’s second most important source of space and communication technology.
Answer 19.
- These cartoons show Indian view on Cold War.
- The first cartoon was drawn when the US came to a secret understanding with China keeping the USSR in dark. The cartoon also expresses changing the international political scenario as after a long time. China made overtures to the USA.
- The second cartoon shows the American midadventure in Vietnam. It also depicts that the US President Johnson was in more trouble over Vietnam.
Answer 20.
(a) Nehru wanted to keep off military blocs to maintain friendly and peaceful relation with all nations of world as well as to maintain India’s uniqueness at international stage.
(b) No, the Indo-Soviet friendship treaty did not violate non-alignment because it was not to maintain military relations but to maintain diplomatic friendly relations.
(c) NAM emphasises on disarmament, decolonisation and terrorism except staying away from military blocs.
Answer 21.
-
- Junagarh
- Manipur
- Gujarat (from Bombay)
- Pakistan
- Bangladesh
Answer 22.
The superpowers used their military power to bring countries into their fold :
(a) Soviet Union used its influence in Eastern Europe backed by the large armies of countries of its alliance.
(b) The statement is utmost correct about the superpower as well as their alliances.
(c) On the other hand, the United States built alliance called SEATO and CENTO on the question of North Vietnam, North Korea and Iraq, Russia and China came closer.
(cl) Alliances were made for the requirement of vital national resources.
(e) Superpowers needed territories to launch their weapons and troops. In return, they helped them in many ways.
(f) Economic support was another factor.
OR
During the Cold War phase, India was on the opposite side of the divide from the US as it had close relationship with Soviet. India’s decision to pursue a policy of NAM in 1945 was not liked by the US as it sided with Pakistan.
After the collapse of Soviet Union, India decided to liberalise its economy and integrate it with global economy. Hence, the US also found India an attractive economic partner due to technological dimension, and the role of Indian-American diaspora.
India-US relationship have never looked so brighter as it today. Both the countries are coming close to each other and both began to gain by coming closer.
Within India, the debate seems to be around three possible views. .
- India should maintain its aloofness from the USA and forms upon increasing its other comprehensive national power.
- India should take advantage of US hegemony and national understandings to establish best possible options for itself. Opposing the US would be a futile exercise and will only hurt India in long run.
- India should take the lead in establishing a coalition of countries from the developing world.
Answer 23.
After the end of Second World War in 1945, the European States confronted the ruin of their economies and the destruction of assumptions and structures on which Europe had been founded. European countries resolved their post-second
World War problems in the following manner :
- Under the ‘Marshall Plan’ the USA provided financial help to revive European economy.
- The US also created a new collective security structure under NATO.
- Under the ‘Marshall Plan’ the organisation for European Economic Cooperation was established in 1948 to extend cooperation on trade and economic issues among the Western European States.
- European Union was founded in 1992 for a common foreign and security policy, cooperation on justice and home affairs and creation of a single currency. It evolved from an economic union to political one over time.
The following attempts led to the formation of European Union:
- The Council of Europe was established in 1949 for political cooperation.
- The process of economic integration of European Capitalist countries led to the formation of European Economic Community in 1957.
- The above mentioned processes acquired a political dimension with the creation of European Parliament.
- The collapse of Soviet bloc put Europe on a fast track and resulted in the establishment of European Union in 1992.
OR
Bangladesh has been the part of Pakistan itself. Both of these countries bear some similarities and differences as follows:
Commonalities :
- Both Bangladesh and Pakistan were under a military rule.
- At both the places, the struggle for democracy took place in their own way.
- Pakistan’s administration began under the command of General Ayub Khan and gave up due to dissatisfaction among people giving way to Yahya’s military rule and continued with the army rule though elections were held by military rulers to give a democratic shape to their own rule.
- In the same way, Bangladesh drafted its own constitution to begin with democracy. Sheikh Mujibur Rahman formed Presidential setup by abolishing all the parties except Awami Legue. But after his assassination the new military ruler Zia-ur-Rahman formed his own party and won elections in 1979. Later on he was also assassinated and another military leader Lt. Gen. H.M. Ershad took over.
Differences :
- In Pakistan, military, clergy and land-owning aristocrats dominated socially to overthrow elected government whereas in Bangladesh the leaders and their party members dominated for the same.
- Pro-military groups have become more powerful due to conflict with India in Pakistan whereas in Bangladesh, pro-military groups are powerful due to friendship and encouragement of India.
Answer 24.
The following factors are responsible for Pakistan’s failure in building a stable democracy :
- The lack of genuine international support for a democratic rule in Pakistan has encouraged to military to continue its dominance. The US and other countries have also supported military rule due to fulfilling their own interests.
- Pakistan’s conflict with India has made paramilitary groups more powerful which have often said that political parties and democracy in Pakistan are flawed, that Pakistan’s security would be harmed by selfish minded parties and chaotic democracy, hence army stay in power is justified.
- The social dominance of military, clergy, and owning aristocracy has led to frequent overthrow of elected governments and the establishing of military governments.
- Global Islamic terrorism and their apprehension that Pakistan’s nuclear arsenal might
fall into hands of these terrorist groups, the military regime in Pakistan was seen as the protector of western interests in West Asia and South Asia.
The two pro-democracy factors present in Pakistan that can pave the way for establishing a lasting democratic set up over there are:
- Pakistan bears a courageous and entirely free press.
- Pakistan enjoys strong human rights movement.
OR
The process of partition had been started in 1940 when Muslim League under the leadership of Muhammad Ali Jinnah propounded Two-Nation Theory. This process involved various problems:
- Areas were supposed to be distributed on the basis of religions majority i.e. Muslim majority areas built Pakistani territory and rest stayed with India. It created communal riots in country.
- No single belt of Muslim majority was the part of British India. They were concentrated in East and West. Hence, it was decided that Pakistan will comprise two territories namely East and West Pakistan separated by long expansion of India territory,
- All Muslim majority areas did not want to be merged with Pakistan i.e. it was opposed in NWFP. But ultimately NWFP was made to merge with Pakistan.
- Another problem belonged to minorities on both sides of border i.e. lakhs of Hindus and Muslims and Sikhs from both the sides were left with no option except to leave f their homes.
Answer 25.
No, the prevalence of one party dominance system did not affect adversely the democratic nature of Indian politics because:
- The key role of the Congress in the freedom struggle gave it a head start over others.
- The Congress accommodated diversified interests, religion, beliefs and aspirations to strengthen democracy.
- Despite being taken place of free and fair elections, Congress won elections in the
same manner again and again. - The Congress Party consisted of various factions inside itself, based on ideological considerations who never taught together or went out of Congress.
- Hence, on the basis of above mentioned criterion, it can be concluded that Congress strengthened ideals of democracy and held unity and integrity of the country.
OR
At the time of Independence, development was about becoming more like the industrialised countries of the West, to be involved with the break down of traditional social structure as well as rise of capitalism and liberalism.
- Modernisation referred to growth, material progress and scientific rationality.
- India had two models of modern development at the time of independence into considerations to be adopted i.e. the liberal capitalist model like Europe and the US and the socialist model like the USSR.
- A debate had been occurred regarding adoption of model of development as communists, socialists and Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru supported the socialist model to reflect a broad consensus to be developed during national movement.
- Above mentioned intentions cleared that the government made the priority to poverty alleviation alongwith social and economic redistribution.
- At the same time, these leaders differed and debated:
- Industrialisation should be the preferred path or
- Agricultural development should take place, or
- Rural poverty should be alleviated.
Answer 26.
The statement is justified to maximum extent to be proved during ‘Sino-Indian Conflict of 1962’ to dent India’s image at home and international level. India had to approach the Americans and the British for military assistance to tide over the issues.
The Soviet Union remained neutral during the conflict:
- All the occurrings, created a sense of national humiliation but strengthened a spirit of nationalism also on the other hand.
- Pt. Nehru was also criticised for his naive assessment of Chinese intentions and lack of military preparedness.
- Political mood of country began to change, when no-confidence motion against Nehru moved in and debated in the Lok Sabha.
- ‘Sino-Indian Conflict’ splitted the Communist Party of India in 1960s split fraction formed communist party of India (CPI-M).
- Besides, the war with China alerted Indian leadership to volatile situation in the North east region.
- Apart from being isolated and extremely underdeveloped, this region posed the challenge of national integration in front of India.
Answer 27.
Circumstances that favoured Indira Gandhi to become Prime Minister after the death of Lai Bahadur Shastri are as follows:
- On 10 January 1966, Shastri’s Prime Ministership came to an abrupt end when he died suddenly in Taskhent. Now, the Congress had to face the challenge of political succession.
- The senior party leaders decided to support Indira Gandhi, but the decision was not unanimous. There was intense contest between Morarji Desai and Indira Gandhi. The contest jvas resolved through a secret ballot among the MPs of the Congress. Indira Gandhi got the support of more than two-thirds of the Congress party’s MPs.
Achievements of Indira Gandhi that made her popular as a Prime Minister are:
- Indira Gandhi adopted her strategy boldly and diplomatically. When the Congress had lost in 1967 elections, she converted a simple power struggle into an ideological struggle.
- Indira Gandhi did not revive old Congress Party but she re-invented the party by forming an entirely different popular party to accommodate some social groups, the poor, the women, the dalits, adivasis and the minorities. Thus, she restored the Congress system by changing the nat are of Congress system itself.
- Indira Gandhi focussed on the growth of the public sector, imposition of ceiling on rural land holdings and urban poverty, removal of disparities in income and opportunity, and abolition of princely privileges. Her slogan ‘Garibi Hatao’ and the programmes that followed it were part of her political strategy of building an Independent nationwide political support base. As a result, she won 352 seats with about 44 per cent of the popular votes on its own in the Lok Sabha elections of 1971.
- After the 1971 Lok Sabha election, a major political and military crises broke out in East Pakistan (present Bangladesh). The 1971 elections were followed by the crisis in East Pakistan and the Indo-Pak war leading to the formation of Bangladesh.
All these events added to the popularity of Indira Gandhi. Even the opposition party leaders admired her statesmanship.
OR
The Mandal Commission under the chairmanship of Bindeshwari Prasad Mandal set up in 1978 to investigate the extent of educational and social backwardness among various sections of society and recommended way to identify these classes.
The Mandal Commission gave its recommendations in 1980:
- The Commission advised that backward classes should be understood to mean backward castes since many castes other than the SCs were also treated as low in caste hierarchy.
- Reservation 27% seats in educational institutions and government jobs for these groups.
- It recommended land reforms to improve the condition of OBCs.
- Hence, Mandal Commission made recommendations in economic and occupational structures.
The Government of India accepted recommendations in 1990:
- 27% jobs reservation has been made in central and state government.
- Many welfare schemes have also been launched as Swarnima National Backward Classes Finance and Development Corporation.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Paper 2 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Paper 2, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.