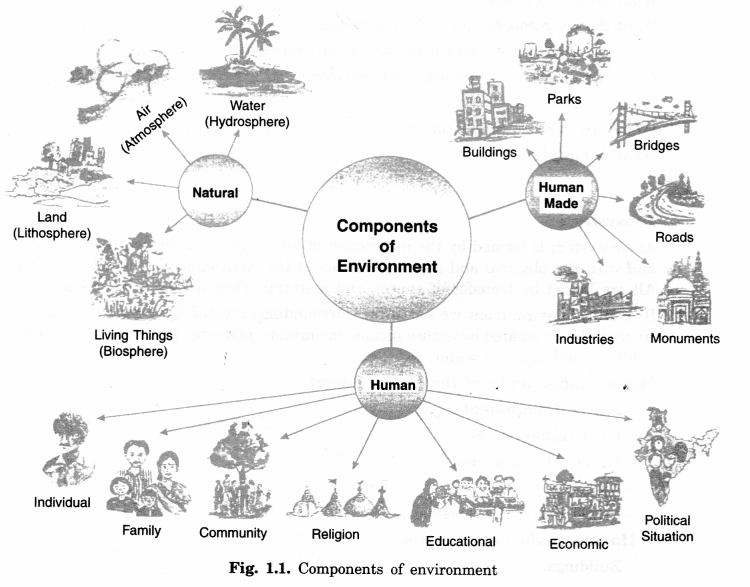
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Human Environment: Settlement, Transport and Communication are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Human Environment: Settlement, Transport and Communication.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Social Science Geography |
| Chapter | Chapter 7 |
| Chapter Name | Human Environment: Settlement, Transport and Communication |
| Number of Questions Solved | 8 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Human Environment: Settlement, Transport and Communication
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
- What are the four means of transport?
- What do you understand by the term ‘settlement’?
- Which are the activities practiced by the rural people?
- Mention any two merits of railways.
- What do you understand by communication?
- What is the mass media?
Answer.
1. The four means of transport are:
- Roadways
- Railways
- Waterways
- Airways
2. Settlements are places where people build their homes.
3. The activities practiced by rural people are farming, fishing, forestry, trading, and craftwork, etc.
4. Two merits of railways are:
- They carry people over long distances quickly and cheaply.
- They carry heavy goods in bulk.
5. Communication is the process of conveying messages to others.
6. The modes of communication through which we can communicate with a large number of people, like newspapers, radio, and television, are called mass media.
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which is NOT a means of communication?
(a) telephone
(b) books
(c) table
Answer.
(c) Table
(ii) Which type of road is constructed under the ground?
(a) flyover
(b) expressways
(c) subways
Answer.
(c) Subways
(iii) Which mode of transport is most suitable to reach an island?
(a) ship
(b) train
(c) car
Answer.
(a) Ship
(iv) Which vehicle does not pollute the environment?
(a) cycle
(b) bus
(c) aeroplane
Answer.
(a) Cycle
Question 3.
Match the following.
(i) Internet (a) areas where people are engaged in manufacturing, trade, and services
(ii) Canal route (b) closely built area of houses
(iii) Urban areas (c) houses on stilts
(iv) Compact settlement (d) inland waterway
(e) a means of communication
Answer.
(i) Internet (e) a means of communication
(ii) Canal’route (d) inland waterway
(iii) Urban areas (a) areas where people are engaged in manufacturing, trade, and services
(iv) Compact settlement (b) closely built area of houses
Question 4.
Give reasons.
Today’s world is shrinking.
Answer.
Modern technology has traped the whole world in its fist. With the advancement of communication and information technology, the world has contracted. We can get the news of a far-off land just with a blink of our eyes. England or America or even Moon or Mars are not now far from us. Newspapers, radio, and television have brought a revolution in communication. The satellites have made them even faster. Wireless telephonic communications through cellular phones have become more popular today. The use of the internet has made everything available on our plates. So, it is not exaggerating to say that today’s world is shrinking.
Question 5.
For fun.
(i) Conduct a survey in your locality and find out how people commute to their respective workplaces using
(a) more than two modes of transport
(b) more than three modes of transport
(c) stay within walking distance.
Answer.
Hints:
- First of all, prepare a schedule consisting of the families living in your locality like the following.
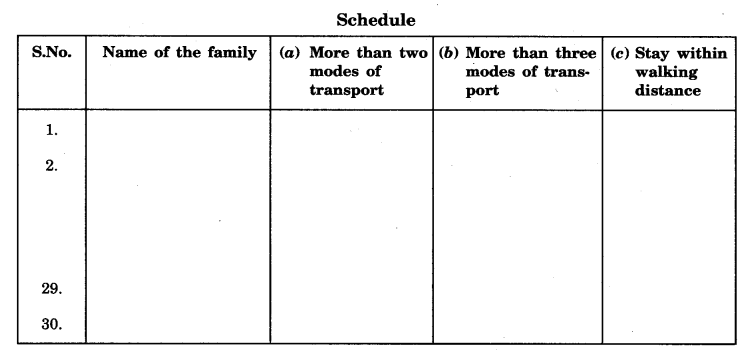
- Now ask each family and tick out the column against them regarding which modes of transport they use.
- After filling the schedule, now do calculations by counting numbers of each category of the mode of transport.
- A sample report
Out of 30 families, 15 families use two or more modes of transport. Out of which 5 families use more than three modes of transport. - families live within walking distance, it means they do not use any mode of transport.
(ii) Mention which mode of communication you will prefer most in the following situations:
- Your grandfather has suddenly fallen ill. How will you inform the doctor?
- Your mother wants to sell the old house. How will she spread this news?
- You are going to attend the marriage of your cousin for which you will be absent from school for the next two days. How will you inform the teacher?
- Your friend has moved out with his/her family to New York. How will you keep in touch on a daily basis?
Answer.
- I will inform the doctor by telephone.
- She will spread this news through newspapers.
- I will send a leave application to the teacher.
- I will keep in touch through the telephone or the internet.
INTEXT QUESTIONS WITH THEIR ANSWERS
Question 1.
Where do you find dwellings made of ice?
Who makes them and what are they called? (NCERT Page 49)
Answer.
- In Tundra Region.
- Eskimoes make them.
- They are called Igloos.

Question 2.
List the different modes of transport used by the students of your class while coming to school. (NCERT Page 49)
Answer.
- On foot
- Bicycles
- School buses
- Cars
- Public transport
- Private contract vehicles.
Question 3.
Find out the names of some newspapers and TV news channels in English, Hindi, and a regional language. (NCERT Page 52)
Answer.
Names of Newspapers:
- Hindustan Times (Eng.)
- Dainik Jagaran (Hindi)
- Nav Bharat Times (Hindi)
- Dinathanthi (Tamil)
- Maryam Manorma (Malayalam)
- Loksatta (Marathi)
T.V. News Channels:
- D.D. News
- Aaj Tak
- Z News
- NDTV
- Sun TV (Tamil)
- Asianet (Malayalam)
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Human Environment: Settlement, Transport and Communication help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 7 Human Environment: Settlement, Transport and Communication, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.