On this page, you will find Acids, Bases and Salts Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 5 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Notes Acids, Bases and Salts
Acids, Bases and Salts Class 7 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. Any of the various water-soluble compounds having sour taste and capable of turning litmus red and reacting with a base to form a salt and water are called acids; e. g. curd, lemon juice, orange juice, vinegar, etc. The chemical nature of these substances are said to be acidic. The acids in these substances are natural acids.
2. Any of various water-soluble compounds having bitter taste and capable of turning litmus blue and reacting with an acid to form a salt and water are called bases. They feel soapy when touched. Bases include oxides and hydroxides of metals and ammonia. The nature of such substances is said to be basic; g., calcium hydroxide, ammonium hydroxide, magnesium oxide, etc.
3. Some special type of substances are used to test the acidic or basic nature of a substance. These substances are known as indicators.
4. Indicators change their colour when added to a solution containing an acidic or a basic substance. There are some naturally occurring indicators such as turmeric, litmus, china rose petals (Gudhal), etc.
5. The most commonly used natural indicator is litmus which is extracted from lichens.
6. It has a mauve (purple) colour in distilled water. It turns red when added to an acidic solution and blue when added to a basic solution. It is available in the form of a solution, or in the form of strips of paper, i.e., red and blue litmus paper.
7. Turmeric is natural indicator which turns from yellow to red in alkaline (basic) solution.
8. China rose petal solution turns dark pink in acidic solution and green in basic solution. It is also a natural indicator.
9. There are also some substances which are neither basic nor acidic. The solutions (substances) which do not change the colour of either red or blue litmus are called neutral substances or solutions, e. g., distilled water, common salt solution, sugar solution, etc.
10. The reaction between an acid and base is known as neutralisation. Salt and water are produced in this process with the evolution of heat.
Acid + Base ➝ Salt + Water (Heat is evolved)
The following reaction shows neutralization:
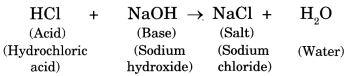
11. In neutralisation reaction salt is formed which may be acidic, basic or neutral in nature.
12. Neutralisation reaction is helpful in everyday life. It is used in case of indigestion, ant bite, soil treatment, etc.
Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Notes Important Terms
Acid: Substance that tastes sour and turns litmus red in colour is called acid.
Acidic: The chemical nature of acid substance is said to be acidic.
Base: Substance which is bitter im taste, feel soapy on touching and turns litmus blue is called base.
Basic: The chemical nature of base substance is said to be basic.